Tongue diseases do not develop as often as pathologies of teeth and gums. However, they cause a lot of trouble and pain. As a rule, people are faced with the problem of enlargement of the papillae, changes in their color and texture. Their hypertrophy causes pain and discomfort, signaling an inflammatory process and problems in the body.
The cause of an increase in receptors may be infections of the oral cavity, bacterial microflora, tongue injuries, or hidden ailments. Each specific case is individual, so if you have a similar problem, you should see a dentist. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe effective therapy.
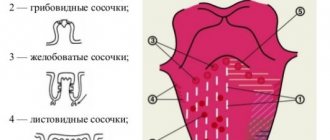
Anatomy of the tongue with photos
The tongue is formed by striated muscle tissue covered with a mucous membrane. It is involved in digestion, speech formation, allows you to express emotions, sense tastes, and regulates salivation. In a healthy person, the tongue has a pale pink color, with an even hollow running along it. Normally, it is covered with a whitish coating, which allows the grooved papillae of the tongue to be clearly visible.
Anatomically, the tongue consists of a root (1/3) and a body (2/3), separated by a terminal groove, as can be seen in the photo. The part facing the sky is called the back. On the lower surface there is a frenulum attached to the floor of the mouth. The tongue moves freely in the oral cavity and is rarely at rest. Thanks to the muscles, it can rise, shorten and thicken.
INTERESTING: photo of the root of a person’s tongue and the reasons for its color change
Diagnostic measures
If you notice the first signs of glossitis, you should definitely consult a dentist, and, if necessary, a therapist and specialists. The following examinations may be needed:
- A smear from the surface of the tongue to identify bacterial flora.
- PCR tests for the presence of bacterial, viral, fungal infections.
- Histological and cytological laboratory analysis (if cell degeneration is suspected).
- Blood tests - general, biochemical, for hormones, for the presence of pathogens of AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis and other infectious diseases.
If a fungal or bacterial infection is detected during the diagnosis, it is necessary to test for the sensitivity of the pathogenic flora to antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
After the examination, the patient may be referred for further observation and treatment by an endocrinologist, immunologist, allergist, or otolaryngologist.
Types of papillae on the tongue, their functions
Papillae are growths of the mucous membrane on the body of the tongue, covered with non-keratinized epithelium. Their main function is to analyze touch and taste. Receptors are located along the edges and on the back of the tongue, the highest concentration is observed in the anterior sections. There are 5 types in total: filamentous, leaf-shaped, groove-shaped, mushroom-shaped and conical. Each has its own characteristics:
- Thread-like stretched along the edges of the tongue. Their number is greatest, their function is to touch and hold food in the mouth, they do not perceive taste.
- Conical ones are located together with filiform ones and are similar to them in structure and functions. They are designed for mechanical processing of food and contain temperature and pain receptors.
- The groove-shaped papillae are located closer to the root. They include the body, ridge and glands, and are responsible for the perception of bitter taste.
- Leaf-shaped are located near the palatine arches. They have an oval shape, like folded leaves. Deep down there are glands that detect bitter taste.
- Mushroom-shaped taste buds resemble white caps covered with epithelium. They are randomly located on the body of the tongue, excluding the center of the back. Responsible for the perception of sweets.
Causes
If we exclude everyday causes associated with mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling is almost always a symptom of other diseases. Therefore, you cannot delay visiting a doctor. The most common reasons are:
- Allergic reaction. Swelling can be caused by taking medications or foods that cause allergies. Typically, patients prone to allergies are aware of their problem. If you suspect allergic edema, you should consult a doctor. A severe allergic reaction can cause angioedema or angioedema. This condition develops rapidly, quickly spreading to the lips, cheeks, and larynx. The patient finds it difficult to breathe. In the most severe cases, angioedema can be fatal.
- Mononucleosis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the throat. Swelling of the tongue with mononucleosis is one of the accompanying symptoms.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Edema develops against the background of colitis, enterocolitis, peptic ulcer, gastritis and other diseases. This reason is one of the most common.
- Hormonal disorders. For many diseases associated with hormonal imbalances, a swollen tongue is one of the symptoms.
Swelling of the tongue is not always a symptom of other diseases. Swelling often appears for everyday reasons:
- Bite.
- Burn.
- Mechanical damage (dentures, braces, poor-quality fillings, piercings, etc.).
Why do the papillae sometimes become inflamed and enlarged?
Hypertrophy of the taste buds of the tongue often occurs in children and unbalanced people. The first ones to put dirty toys and hands into their mouths cause infection. The latter may bite their nails or stationery, from the surface of which pathogenic bacteria enter the mouth.
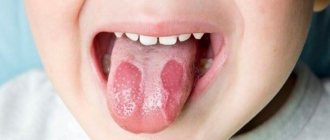
Inflammation of the white fungiform papillae of the tongue is provoked by viruses, bacteria, fungal infections, and systemic diseases. In this case, quite unpleasant symptoms are felt: burning and loss of taste, sensation of a foreign body on the tongue, pain when eating, talking, brushing teeth. READ ALSO: for what reasons can inflammation on the side of the tongue occur and how to eliminate it?
The cause of red spots is often irritation of the circumvallate papillae. They can become inflamed due to chemical and thermal burns of the oral cavity, gastroesophageal reflux disease. People with dentures and lovers of hard sweets and lollipops also complain about this problem. Inflammation cannot be avoided in the presence of chipped teeth that injure the mucous membrane of the tongue.
READ ALSO: tongue diseases with descriptions and photos
Symptoms
The main symptoms of tongue swelling are its increase in size and swelling. In difficult cases, the patient has difficulty breathing, and there is a sensation of a foreign object in the mouth. The mucous membrane becomes loose, with prominent papillae, and tooth marks become noticeable on the lateral surfaces. Blood vessels become clearly visible on the lower part of the tongue.
Swelling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Change in taste sensations.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane.
- The appearance of heaviness when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swelling of lips.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Paleness of the skin.
If the problem is not detected in a timely manner, the tongue continues to swell, does not fit in the oral cavity, and falls out. The help of a doctor cannot be neglected. If the tongue is swollen and this process persists for several days, it is dangerous to self-medicate or wait until the problem goes away on its own.
Diagnosis of tongue diseases
The dentist diagnoses tongue diseases by its appearance, size, thickness, and state of the receptors. Almost always there is an abnormal shade of its surface, uncontrolled copious secretion of saliva, and immobility of the organ. It increases in size, making it difficult to swallow, and an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. When examining the oral cavity, the specialist pays attention to the condition of the teeth and gums, the presence of pustules, pimples and rashes.
READ ALSO: what does it mean if pimples appear on the tongue, located closer to the larynx?
In addition to visual inspection, the following tests are carried out:
- smear to determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process,
- biochemical and general blood tests to assess the condition of the body,
- blood tests for viral, bacterial infections, AIDS,
- tissue histology (in the presence of an abscess),
- if necessary, a referral is given to an immunologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist and other specialists.
Glossitis
Glossitis is caused by bacteria and viruses (most often herpes and Candida fungus). The spread of infection occurs through injuries and microcracks of the mucous membrane, consumption of hot foods, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. Sometimes it is a symptom of iron deficiency anemia, HIV, lichen planus, and oncology.
A characteristic sign of glossitis is red dots on the tip and in the area of the root of the tongue (vallate papillae enlarge), its inflammation and swelling (we recommend reading: bright red tongue: causes and methods of treatment). The surface of the organ becomes smooth, it hurts when swallowing and talking. Additionally, the patient complains of a constant burning sensation in the mouth and that the tongue has become very enlarged (more details in the article: why does the tongue sometimes swell a lot?). If you consult a dentist in time, treatment for glossitis will be quite simple and quick. In advanced cases, respiratory dysfunction and swelling of the tongue are possible (we recommend reading: tumor under the tongue: causes, photos and treatment).
Black tongue
Fungus
Gastritis
Colitis
22293 September 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Black tongue: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Black tongue is a condition in which a person's tongue is completely or partially dark or black in color. This symptom is more common among older people, although it occurs in all age groups, and is more common in men than women.
Varieties of black tongue
Normally, the tongue has a pale pink color, it is moist, with a smooth surface and clearly visible papillae.
Plaque on the tongue is formed by food debris and exfoliated dead cells of the mucous membrane of the tongue, which can become saturated with food dyes. The appearance of a thin, white, easily cleaned plaque that does not have an unpleasant odor is considered acceptable, and the formation of a dense plaque with a non-physiological color is regarded as a pathology.
On the surface of the tongue there may be individual black dots, one large spot, the tongue may be colored on the sides or completely.
Most often, a black tongue is caused by staining from plaque, such as food or medications, but it can also result from excess melanin deposits or lead poisoning.
In addition, there is such a thing as “black hairy tongue” - a benign and temporary phenomenon in which the filiform papillae of the tongue lengthen, and the keratinized cells of the epithelium of the tongue do not exfoliate and become black or brown due to the activity of certain bacteria and fungi. The length of the papillae can reach 1-3 cm, and the diameter is 2-3 mm. Hyperplastic filiform papillae are located mainly on the posterior and middle third of the dorsum of the tongue. The tongue takes on a “hairy” or “furry” appearance. The disease occurs in both children and adults, but is much more common in older people. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation on the tongue, itching of the palate, burning of the tongue, dry mouth, impaired taste sensitivity, and bad breath. If enlarged taste buds touch the palate, a gag reflex occurs, especially during conversation.
Possible reasons for the appearance of a black tongue
A black tongue is often associated with poor oral hygiene. In addition, people who abuse tea and coffee, smoke, suffer from alcoholism, and use intravenous drugs are at risk. Dry mouth contributes to the tongue turning black when, due to insufficient salivation, more bacteria accumulate on the tongue, the activity of which leads to the plaque becoming pathologically colored. Severe dehydration of the body is accompanied by the formation of a dark, sometimes almost black coating, which is difficult to remove from the tongue.
Some medications give the tongue a black color, for example, activated carbon, iron, bismuth, or antibiotics that disrupt the balance of microflora in the mouth.
A black tongue can also be observed in harmless situations, for example, after eating blueberries, red wine, and foods that contain dyes (sweets, chewing gum, lollipops).
Diseases that can cause the tongue to turn black
A black tongue is often observed with severe advanced candidiasis of the oral cavity, with sore throat, with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (diseases of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas), adrenal insufficiency, acid-base imbalance and with the development of increased acidity (acidosis). If a chromogenic fungus has settled in the mouth, then the gums, teeth and tongue become covered with a black coating with a greenish tint. In adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease), one of the signs of the disease is hyperpigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes due to increased levels of melanin. Pigmentation of the oral mucosa occurs, spots and stripes of brown or grayish-black color appear on the red border of the lips, in the corners of the mouth, on the gums and on the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
Predisposing factors to hypertrophy (enlargement) of the papillae with a black hairy tongue can be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (anacidic gastritis, hypoacid gastritis, colitis, infectious diseases). In some cases, the formation of a black hairy tongue occurs against the background of a deficiency in the body of riboflavin (vitamin B2). In addition, black hairy tongue occurs with pulmonary tuberculosis, papillary pigmentary dystrophy, and after the use of certain medications (for example, antibiotics).
Which doctors should I contact if a black tongue appears?
If you have an oral disease that has caused the formation of a black coating on the tongue, you should consult a dentist.
If plaque is associated with an infectious disease, for example, sore throat or candidiasis, then treatment is carried out.
For diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you should contact.
If the cause of the black tongue is Addison's disease (adrenal insufficiency), then consultation is required.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of a black tongue
Some tests may be needed to determine the cause of tongue discoloration:
- general blood analysis;
Inflammation of the papillae in children
The most common cause of inflammation of the papillae on the tongue of children is desquamative, allergic, traumatic or fungal glossitis. In children, inflammation of the papillae on the root of the tongue occurs in a more acute form than in adults. Therefore, if the baby’s oral mucosa begins to become inflamed, it is necessary to immediately seek advice from a specialist. Treatment of inflammation and enlargement of the papillae on the child’s tongue should be carried out in strict accordance with the pediatrician’s recommendations.
Prevention of papillitis
To avoid inflammation of the anal papillae, it is recommended:
- Observe hygiene procedures: rinse the anus after each act of bowel movement;
- If gastrointestinal diseases are detected, undergo timely treatment;
- Move more to eliminate congestion in the pelvic area;
- Get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- Avoid “heavy” foods;
- In case of constipation, use laxatives.
General treatment recommendations and consequences
The formation of small blisters or ulcers, the appearance of white or pink papillae on the tongue, the proliferation of villi are the first symptoms of the inflammatory process, which can subsequently lead to hypertrophy of the grooved, mushroom-shaped and other types of papillae.
The dangerous consequences of glossitis are suppuration and the spread of infection to the respiratory and digestive organs. The pain that accompanies the enlargement of receptor structures interferes with talking and eating, and in children it causes severe anxiety and even weight loss. Therefore, any symptoms of glossitis require immediate treatment. The treatment tactics for inflammation of the tongue papillae depend on the cause of its development.
Treatment of tongue papillae inflamed due to injuries and burns
Burns and traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane of the tongue lead to the development of papillitis. In the absence of other alarming symptoms - fever, severe swelling and suppuration of tissues - papillitis can be dealt with at home. Carrying out at home:
- Rinsing the mouth with disinfectants. It is better to take decoctions of medicinal herbs, for example, calendula.
- Treating the tongue with agents that accelerate healing and restoration of soft tissues. Solcoseryl ointment, Lugol's solution, Chlorophyllipt, and sea buckthorn oil can be used.
- Use of analgesics: Lidocaine, Anestezin. It is better to consult your doctor about the dosage and regimen of taking painkillers.
During the treatment of inflammation of the taste buds of the tongue, you need to adhere to a special regime that allows you to create gentle conditions for soft tissues damaged by papillitis:
- It is undesirable to smoke and drink alcohol.
- You should not eat food with a strong salty or spicy taste.
- Temporary removal of removable dentures may be necessary.
If the cause of inflammation of the tongue papillae is a prosthesis, you should definitely consult a dentist to correct the shape or completely replace the uncomfortable design.
Treatment of infectious inflammation
In case of inflammation of the oral mucosa, glossitis and papillitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- If the papillae on the root and edges of the tongue are enlarged, you should not drink alcohol-containing drinks, and it is not advisable to smoke.
- Food should be moderately salty, without hot spices, not hot and not very cold.
- If the cause of the appearance of red papillae on the tongue is an infection or disease of an internal organ, or the patient’s temperature rises, you should definitely go to the doctor to find out why the inflammation has developed. Such inflammatory processes pose the greatest danger to children, so you should contact a pediatrician immediately.
Papillitis and glossitis are serious diseases that not only cause discomfort, but also entail other dangerous consequences. If a person notices that his papillae on the tip or back of his tongue have enlarged, he should immediately consult a doctor in order to identify and treat the disease at an early stage. Mild forms of glossitis can lead to the development of more severe ones, accompanied by complete death of enlarged papillae and the risk of poisoning the body with microorganism toxins .
Hypertrophied anal papillae. Treatment of inflammation of the anal papillae
Inflamed anal papillae, papillitis, fibroanal polyps are an acute or chronic proctological disease characterized by pain, intense itching in the anus, sensation of a foreign object, discomfort and difficulty during defecation, sphincter spasm. The cause of inflammation is hypertrophied anal papillae (papillae) - anatomical nodular intraluminal formations at the level of the anorectal line, normally not exceeding 1 cm and having a pale pink color. Under normal conditions, a proctologist can detect them next to the Morganian crypts during palpation of the anorectal area.
Papillae are classified into two types based on their shape:
- cone-shaped with a wide base;
- spherical on a narrow stalk.
Cause and symptoms of papillitis
Problems begin when the formations become inflamed, multiply in size, and acquire a red-purple hue. At the initial stage of the disease, discomfort occurs only during bowel movements. When the disease progresses for a long time, the inflamed anal papillae may even protrude from the rectum, which significantly aggravates the problem. Also, when they grow up to 3 cm, they may be pinched by the sphincter muscles, which is accompanied by acute pain spreading to the coccyx area.
The initiation of the inflammatory process occurs at the time of frequent mechanical injury to the papillae from feces and penetration of infection into the tissue, which is typical for chronic constipation. Another way is possible, when the papillae are irritated under the influence of toxins eliminated by the body after poisoning.
Patients report the following symptoms:
- “foreign body” in the anus;
- pain that gets worse with bowel movements;
- burning and swelling at the base of the anus;
- formation of erosions;
- traces of blood;
- the appearance of mucus from the anus due to weakening of the sphincter function.
Provoking factors for inflammation of the anal papilla include:
- inactive lifestyle and poor circulation in the pelvis, including obesity and pregnancy;
- regular constipation and trauma to the rectal mucosa;
- food poisoning;
- abuse of cleansing enemas;
- allergies to the composition of linen, personal hygiene products;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- proctological diseases (cryptitis, hemorrhoids, proctitis).
Diagnostic features
Hypertrophy of the anal papillae and the development of the inflammatory process are easily detected by a proctologist when examining the rectal area. The nature of the patient’s complaints is of great importance, since papillitis can manifest itself against the background of other problems. The peculiarity of the diagnosis is that enlarged anal papillae are similar in shape to tumor-like growths in rectal polyposis. They can also be confused with the so-called sentinel tubercle (a sign of chronic anal fissure) or hemorrhoidal node. In this regard, to make an accurate diagnosis, a detailed examination with mirrors can be performed, and anoscopy can also be prescribed.
Differences between hypertrophied anal papillae (papillitis) and polyposis:
- the papillae are externally pale, covered with multilayered squamous epithelial tissue;
- polyps in one layer are covered with columnar epithelium to match the color of the mucous membrane;
- papillae are located approximately at the level of the anorectal line;
- Rectal polyps are always localized above the anorectal level.
If during a routine examination the proctologist discovered papillae in you, you should not panic - this is normal if their appearance and location do not go beyond the norm. If they give you anxiety, have signs of inflammation or fall out of the rectum, then the need to remove the hypertrophied anal papillae is obvious. This must be done so that one trouble is not joined by others, more serious and potentially dangerous. In some situations, a histological examination may be required, when a piece of tissue is sent to the laboratory to be analyzed for malignant degeneration.
Treatment of inflammation and hypertrophy of anal papillae
Modern proctology uses two types of treatment: medication and surgery. When choosing a tactic, the attending physician does not rely on the fact of the presence of hypertrophied papillae, but on the cause of their inflammation. So, if the formations are inflamed against the background of hemorrhoids, then it should be treated first, and if they are accompanied by proctitis, then the treatment of proctitis is paramount. As clinical practice shows, when diagnosing a chronic anal fissure (fissure), removal of the anal papillae is considered a strict necessity.
Drug treatment
For isolated inflammation of the anal papillae, treatment with medications is successful. As part of therapy, the following are prescribed:
- special diet;
- warm baths, enemas with antiseptic, astringent, bacteriostatic effects;
- anti-inflammatory suppositories;
- antibacterial therapy.
Surgery to excise hypertrophied anal papillae is indicated in rare cases. Removal is recommended if drug treatment does not bring results, the papillae are large in size, the anal papillae constantly fall out of the anus, their surface is covered with ulcers. Surgery is also necessary when the development of papillitis occurs against the background of another disease of the anorectal mucosa.
Surgical treatment regimen for hypertrophied anal papillae
Two modern methods of surgical intervention are considered the most successful:
- surgery using the Gabriel method - the surgeon excises the anal papilla along with the adjacent crypt;
- cryodestruction of inflamed papillae is a minimally invasive operation using liquid nitrogen to remove the anal papilla.
The surgical intervention is performed on an outpatient basis in a specialized proctology setting, under local or intravenous anesthesia.
Forecast
In the majority of patients, after drug treatment of anal papillae, complete regression of symptoms is recorded, so the prognosis of the disease is favorable. Enlargement and inflammation of papillae in themselves do not threaten human life. But it should be understood that with this diagnosis, neither acute nor chronic inflammation of the anal canal structures occurs independently. With complicated papillitis, the prognosis worsens. To prevent the development of paraproctitis, pectenosis and other serious ailments, you need to be examined, determine the nature of the phenomenon and take the necessary measures.
Prevention of papillitis
To prevent relapses that will lead to a new need for surgical treatment of the anal papillae, the patient should:
- carefully care for the perianal area;
- give up “wrong” nutrition, fight constipation;
- promptly identify and treat gastrointestinal diseases;
- give up bad habits and unconventional sex;
- be moderately active, avoid stagnant processes in the pelvis.
After excision of hypertrophied anal papillae and in the absence of pathological neoplasms in the rectum, the patient should undergo an annual follow-up examination.
How to treat anal papillae if they are inflamed
At the initial stage, the disease is asymptomatic or with minimal symptoms. Therefore, in this case, the appearance of regular discomfort indicates that the disease is in full swing. If you suspect that your anal papillae are inflamed, do not engage in amateur activities. This can be fraught with serious health consequences and interfere with further quality of life. If you experience any discomfort, and even more so with pain in the rectum and anal canal, do not hesitate to make an appointment with a doctor. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the easier it is to restore health!
Many are afraid of surgical intervention for complicated hypertrophied anal papillae, having heard enough horror stories. In fact, high-precision, minimally invasive surgical methods are now used, so the risks are minimal compared to the prospects of refusing treatment. If it is important for you that the operation is performed by a male proctologist surgeon, contact the best private proctology in Rostov on the street. 2nd Five-Year Plan, 29/5. Dr. Tolokhyan has more than 20 years of experience in practical medicine, 16 years of experience in proctology/surgery and hundreds of grateful patients.
Causes
Factors that provoke the development of inflammatory processes include:
- Diarrhea and food poisoning - harmful substances released during bowel movements negatively affect the papillae;
- An inactive lifestyle - this contributes to the appearance of stagnant processes in the pelvis;
- Constipation, in which the papillae are injured during bowel movements;
- Abuse of enemas - with frequent procedures, the mucous membrane of the anal canal is damaged;
- Drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Allergy to personal hygiene products, underwear material;
- Proctological diseases: critpitis, proctitis.