Infectious pathologies that are transmitted during coitus are increasingly being registered by dermatovenerologists. Moreover, the patients include men and women of different ages. Why are STDs so common? First of all, due to promiscuity, when unfamiliar partners have sex without using a condom. But many pathologies are asymptomatic, therefore, being a carrier of bacteria or viruses, a person does not know about it and infects his sexual partners.
Many patients use a condom during traditional coitus, but neglect it during oral sex. This also increases the risk of contracting STDs of a bacterial, viral and fungal nature. There are frequent cases of diagnosing sexually transmitted diseases in the oral cavity.
Which STDs most often affect the oral mucosa?
Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and herpes are mainly transmitted orally. There is also a risk of transmission of diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, and condylomas during oral-genital contact. Infection occurs directly by transmission of the pathogen through saliva and natural secretions from the genitals [2]. Sexually transmitted infections and diseases enter the body not only during vaginal or anal contact. Oral sex, that is, that which involves contact using the mouth, lips or tongue, is also a route of transmission. Not all STDs that develop in the mouth cause any symptoms. Sometimes they can occur without any special signs or with non-obvious symptoms [3].
Risk factors for oral lesions due to STDs
There are several conditions in which the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases through the oral route is significantly increased. These include:
- Sexual intercourse during menstruation.
- Oral-genital contact in the presence of dental diseases with damage or inflammation on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, gums, tonsils, and throat.
- Ingestion of infected body fluid.
It is not necessary to have a pathological process in the mouth to become infected with an STD [3].
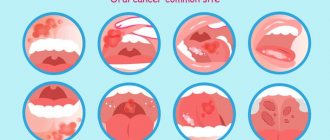
Possible symptoms of oral STDs
These infectious processes do not always have obvious signs. The most studied in this regard are gonorrhea, in which the pharynx is most often affected, and syphilis with its typical course and appearance of symptoms - chancre, enlarged local lymph nodes, rash.
You should pay attention to manifestations that arose some time after unprotected oral contact.
- Mouth ulcers, one or more.
- Manifestations of stomatitis, which can be very painful, or can proceed almost unnoticed.
- Herpes-like rashes on the lips and the inside of the mucous membrane around the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing, especially if it is not associated with other symptoms of a cold.
- Redness of the back of the throat.
- Angina-like symptoms.
- A plaque like a sore throat or diphtheria on the surface of the tonsils.
- The formation of tonsilloliths in large quantities (unpleasant-smelling, dense, yellowish-gray formations that fly out of the mouth when coughing).
- Saliva takes on a different color, such as yellowish or streaky [2, 3].
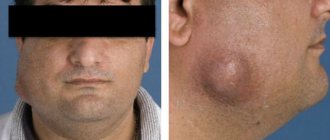
Gonococcal infection
It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and is one of the most common STDs [4]. When infected through the oral route, it occurs as gonococcal pharyngitis with subtle symptoms: a feeling of dryness in the mouth and throat, difficulty and pain when swallowing, slight hoarseness. There may be redness and areas of swelling with whitish films on the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx. Diagnosed by culture (culture), treatment is carried out with specially selected antibiotics. If necessary, symptomatic therapy is prescribed - pain relief for sore throat, rinsing for dry mouth, etc. [5].
Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases in the mouth
Before making a diagnosis, various examinations are prescribed that will help determine the type of pathogen and select the correct therapy. Most often, the list of tests includes PCR, ELISA, microscopy, and bakpasev. To carry out diagnostics, blood and a smear are taken.
After an accurate diagnosis has been made, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment, which may consist of antibiotics, immunomodulators, vitamins, and physiotherapy.
Our multidisciplinary medical center employs doctors of the highest category with extensive practical experience. We guarantee highly accurate diagnostics, effective therapy, and confidentiality. If necessary, you can call a venereologist at home.
Syphilis
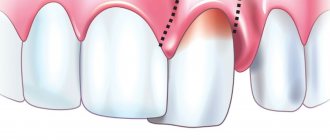
Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum. Despite the certain “familiarity” of the name of this disease, it is not the most common. The pathogen penetrates the skin and mucous membranes, causing a cascade of manifestations. When infected through oral contact, it affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and lips [4]. Symptoms of syphilis develop in stages. In the first stage, one or more ulcers form in the mouth and throat - chancre. They are round, slightly recessed, the edges are smooth, the bottom is shiny, pink, sometimes with a grayish coating and the release of a translucent liquid. As a rule, the lymph nodes become inflamed at the same time, in this case the cervical ones. If the infection is not treated, it progresses to the stage of secondary syphilis, during which a skin rash appears. In this case, the lymph nodes swell strongly and painfully, not only regionally, but also distantly. Sometimes this stage occurs latently, without manifestations, and then, over time, syphilis spreads and affects other organs and systems of the body [6].
In the presence of erosions or ulcers, repeated studies should be carried out in a dark field of view of a microscope to separate them for treponema pallidum.
Its detection is decisive in the diagnosis of primary syphilis, since specific serologies become positive only 2–3 weeks after the onset of primary syphiloma. Dyadkin Yu. V., Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Dermatovenereology KSMU [6]
To detect syphilis, various laboratory diagnostic methods are used: PCR, RPGA, ELISA, RIF, RMP and others. Blood or scrapings from the chancre may be used for testing. Antibiotics are selected for treatment depending on the stage and location of the process and manifestations. During treatment, complications may develop, including the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction - a sharp and severe exacerbation of the disease due to the rapid disintegration of treponemes and severe intoxication [6].
How is an STD diagnosed?
To identify a sexually transmitted disease transmitted through genital-oral intercourse, the doctor may prescribe a scraping test from the oral mucosa. It can be carried out:
- by bacteriological culture (an accurate method that allows you to find out not only the pathogen, but also its sensitivity to antibiotics) - costs 2100 rubles;
- using PCR (the method is 100% reliable) - costs from 300 to 1700 rubles, depending on the type of infectious agent;
- via ELISA.
To diagnose syphilis, specific serological reactions are used, and to detect hepatitis, antigens in the patient’s blood are determined. The cost of tests ranges from 600 to 1500 rubles (depending on the pathogen).
Herpes simplex virus, HSV-1
Herpes simplex virus type 1 causes the disease popularly known as the “cold.” Its causative agent is the herpes virus HSV-1 (herpes simplex). It is similar to HSV-2, or genital herpes, but they are different forms of the disease.
A “cold” on the lips (although herpes can develop on the gums, and on the mucous membranes of the cheeks, etc.) during sexual intercourse infects the mucous membrane and causes a typical herpes rash. It may appear as a spot, vesicle, or focal erosion. Depending on the course of such elements, there may be one or several; they can form in one place, or they can disperse throughout the mucous membranes of the mouth and oropharynx. The temperature often rises and regional lymph nodes become enlarged. Various methods are used for diagnosis (virological, cytological, serological), but more often the PCR method is used to detect HSV.
The causative agent of herpes remains in the cells of the body forever, and so far there is no way to completely cure this infection. But there are methods that can be used to reduce or prevent the appearance of herpetic rashes. In the acute period, local treatment is prescribed - treatment with antiviral drugs, drying of crusts, anesthesia of ulcers on the mucous membranes. Special antiviral antiherpetic drugs are prescribed internally, which inhibit the development of the virus in the cells, preventing it from “getting out” and causing an acute process [7].
STDs localized in the oral cavity can occur almost unnoticed and masquerade as other diseases. Because of this, diagnosis can be delayed and the impact on health can be devastating. Therefore, during oral-genital contacts, prevention plays a huge role. The only method that can reduce the risk of developing an oral form of STDs is a condom and a latex napkin.
Sexually transmitted diseases
- HIV and AIDS
- Gonorrhea, or clap
- Chlamydia
- Syphilis
- Condylomas or bleeding warts
- Herpes
- Candidiasis
- Hepatitis
- Pubic lice
- Scabies
- Trichomoniasis (or trichomoniasis)
HIV and AIDS
HIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that destroys the human immune system. This virus penetrates the cell and has the ability to change its structure in such a way that upon further division, each new cell carries HIV. Over the years, the virus destroys so many lymphocytes that the resistance of the human body decreases, and the infected person is exposed to various diseases. Because HIV can mutate, it is difficult to kill with drugs. AIDS - Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (English: AIDS - Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) - is the final stage of HIV infection, which a person becomes ill with several years after infection. Infection. HIV is transmitted through seminal fluid (sperm), vaginal secretions during unprotected sexual intercourse, or through blood. Sharing needles and syringes when injecting drugs poses a high risk of infection. There is also a risk of infection during organ transplants or blood transfusions. Viral infection can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. In Western countries, 10-20% of children from mothers exposed to viral infection became infected. HIV is most easily transmitted to another person during the initial period of infection, as well as during the stage of AIDS. HIV is not transmitted through everyday interactions. It is not transmitted by kissing, shaking hands, or visiting the toilet or bathhouse. They do not transmit the infection. Symptoms and course of the disease. In some people (about 1/3 of those infected), the first symptoms appear 1-8 weeks after becoming infected. Signs of the disease may include fever, sore throat, headache, joint pain, eczema and swollen lymph glands. The first symptoms disappear on their own after a few weeks. After an initial period of early symptoms or even no symptoms, the virus continues to spread in the body, but the person may feel healthy. As the disease progresses, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, collarbones and under the arms becomes noticeable. The general condition is deteriorating. Fever, diarrhea and night sweats are common. The time at which these symptoms appear is very individual. 10 years after infection, symptoms of the disease appear in approximately 50% of those infected. During the AIDS stage, a person’s immune defense is weakened, so he is affected by various inflammatory diseases (for example, tuberculosis) and tumors develop (for example, Kaposi’s sarcoma). The patient's condition depends on what diseases he becomes susceptible to and how they can be treated. Examination. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the symptoms, since many other diseases have the same symptoms and almost no one infected shows early symptoms. The only way to detect a possible infection is to get tested. HIV infection is determined by a blood test. Since the process of antibody formation is examined, the presence of infection does not appear immediately, but only after 2-4 months. A completely reliable analysis result can be obtained 6 months from the moment of possible infection. The results of the analysis are confidential information, and they are reported only to the person being studied. It takes 1-2 weeks to receive analysis results. You can get tested anonymously in many medical institutions. Treatment. According to the law on infection, examination of AIDS patients, their treatment and medicines are free.
It is not yet possible to cure AIDS. However, recently more and more effective drugs for AIDS patients have been developed. Life expectancy after the disease has increased, and a normal lifestyle can be maintained for a longer period of time. Thus, we can say that at present AIDS is a long-term chronic disease. There is no need to stop sexual activity even if you are infected with HIV. The most important thing is to remember responsibility in all situations and, of course, engage in only safe sex. The law obliges to ensure that both the HIV carrier and his partner adhere to the requirements of safe sex. back to contents
Gonorrhea, or clap
Pathogen: Gonococcus bacterium Gonorrhea is infected through sexual intercourse through the vagina, anus or mouth. From the hands the disease can spread to the eyes. Infection of the rectum also occurs. A newly born child can become infected through the reproductive organs. Symptoms usually appear within a day or a couple of weeks after infection. Symptoms in women. Leucorrhoea (vaginal discharge) that may appear normal but is heavier than usual. There may be a burning sensation when urinating. Pain in the lower abdomen and fever may be a sign of inflammation that has spread to the ovaries. If gonorrhea infection occurs through the mouth, the throat may feel painful, like a sore throat, or there may be no symptoms. Very often, in women, the symptoms of the disease appear very weakly or not at all. Symptoms in men. Burning sensation when urinating and frequent urge to urinate. Yellowish-greenish discharge from the urethra. Painful erection. When infected through the mouth, a sore throat occurs. In men, gonorrhea can also occur without symptoms. Examination. Samples for analysis are taken with a cotton swab from the urethra, cervix, pharynx and rectum. Treatment. Gonorrhea is treated with antibiotics. According to the law on contagious diseases, tests, treatment and medicines are free in health centers and city venereal clinics. In women, gonorrhea, if left untreated, can lead to inflammation of the oviducts. This leads to childlessness. In men, advanced disease can cause inflammation of the testes, which can also cause childlessness.
back to contents
Chlamydia
Causative agent: Chlamydia bacterium Currently, chlamydia is the most common sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia is transmitted sexually. A newborn child can become infected through the reproductive organs. Symptoms appear approximately 10-14 days after infection. Symptoms in women.
75% of women infected with chlamydia do not show symptoms.
Unusual vaginal discharge may be a sign of infection. Minor bleeding after sexual intercourse or between periods. Itching and burning when urinating. Pain in the lower abdomen and sacral area. In case of inflammation of the rectum, slight bleeding or mucus discharge. Symptoms in men.
Among men, approximately 25% have no symptoms.
The most common symptom may be a grayish, curd-like discharge from the urethra in the morning. Mild burning sensation when urinating. When the rectum becomes inflamed, slight bleeding or mucus may appear. Examination.
Samples for analysis are taken from the urethra, cervix and rectum. The presence of infection is not detected immediately; tests must be postponed for approximately 10 days after possible infection. Results can be found out in about a week. If chlamydia spreads into the fallopian tubes, it can cause a blockage (obstruction). The consequence may be childlessness or an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy. Adhesions that appear as a result of the inflammatory process cause pain in the lower abdomen. Men can develop very painful inflammation of the testis, which, in turn, leads to obstruction of the vas deferens and weakened fertility. Both men and women may experience joint pain as a complication after chlamydia. Chlamydia that is not developed during pregnancy can cause inflammation of the baby's eyes and respiratory tract.
back to contents
Syphilis
Syphilis is a slowly developing common infection, the initial symptoms of which often go unnoticed. If left untreated, syphilis can lead to death. Syphilis is transmitted during sexual intercourse, oral sex, or during pregnancy from mother to child. Symptoms
The incubation period for the development of the disease after infection lasts 3-6 weeks.
Upon its completion, so-called so-called sore throats appear at the site of infection on the genitals, rectum or mouth. primary ulcers. They are small, purulent and non-painful and heal slowly over several weeks. About a week after their appearance, the lymph nodes in the groin enlarge and become hard, but no pain is felt. In women, the labia of the vulva may also become swollen. Bacteria spread throughout the body through lymphatic and blood vessels. Approximately 2-4 months after infection, symptoms of the second period appear. Common symptoms may include headache, fever, and sore throat. Small rashes appear on the skin, as well as pimples, especially on the palms and soles of the feet. Hair loss may occur. Pimples may appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs and around the anus. The above symptoms disappear without treatment, approximately six months after infection, and the infection develops into the so-called. latent (hidden) period. In patients who have not been treated, symptoms of the second period of disease development on the skin and mucous membranes may, however, appear repeatedly during the first two years after infection. During this two-year period, syphilis is contagious. Among those who had syphilis and did not treat it, 20-30% may experience the so-called syphilis after many years and decades. late syphilis, which affects the central nervous system and circulatory organs. Examination.
Syphilis is usually diagnosed based on symptoms.
A blood test detects syphilis two months after infection, and only after two years does untreated syphilis cease to be infectious. Treatment.
Treatment of syphilis is carried out with penicillin, which is administered by intramuscular injection for two weeks. The earlier the course of treatment begins, the more effective it is.
back to contents
Condylomas or bleeding warts
Iru or condyloma infection affects both men and women. A newborn can become infected during childbirth through the reproductive organs. Condylomas become infected through contact between mucous membranes, during regular or anal intercourse. The transmission of infection is facilitated by the presence of damage to the mucous membrane or an existing infection in the genital area. Infection can also occur during sexual intercourse, but condylomas in the mouth are extremely rare. Symptoms in women.
The incubation period for condyloma lasts from several weeks to a year.
After it, small light pink or white dots appear on the mucous membrane of the genital organs, which can develop into warts similar in shape to a cauliflower shoot. Warts range in size from one millimeter to several centimeters. In women, warts grow in the pubic lips, vagina, cervix, perineum, anus and at the opening of the urethra. Changes in the mucous membrane may simply consist of thickening of the skin or mucous membrane without the appearance of warts. Sometimes the symptom is painful itching. Most often, condyloma occurs without symptoms and is detected during general examinations. Symptoms in men.
The incubation period is the same as for women.
In men, condyloma warts appear either under the foreskin, on the penis, the head of the penis, near the opening of the urethra, or around the anus. In the oral cavity, condyloma-warts are either light or the color of the mucous membrane. Quite often in men, condyloma occurs without symptoms and is invisible to the eye. Examination.
Condyloma in women is detected during a gynecological examination.
Analysis of a sample of exfoliated tissue taken from the cervix is often used, as well as colposcopy (observation of the reproductive organs through a magnifying device). Condyloma in men is diagnosed by external examination, as well as through a magnifying device, as with colposcopy. Treatment.
There are many treatment options, the choice of which is influenced by the size, number and location of warts. They can be lubricated, treated by freezing, removed by laser or electrocoagulation. Both men and women should be monitored in the future, as there is a danger of cell modification and a relatively high risk of relapse of the disease. The condyloma virus can cause cancer on the cervix. A small percentage of untreated cervical condyloma develops into cancer over the years. Therefore, medical supervision after treatment of the disease and annual testing are very important.
back to contents
Herpes
Pathogen:
There are 2 types of herpes simplex virus (HSV, “Herpes simplex”).
The first type (HSV-1) affects mainly the skin and mucous membrane of the lips (causes herpes labialis or rash on the lips), eyes, nose and other organs, and the second (HSV-2) mainly affects the genitals. This is genital herpes. Currently, due to the widespread prevalence of oral-genital contacts, there are increasingly cases where genital herpes is also caused by the HSV-1 virus. After the initial infection, the virus penetrates the lymph nodes, where it remains in a latent form. Often the virus remains in that state without causing further symptoms, but in some infected people it reactivates painfully often, even several times a year. The disease is transmitted during sexual intercourse, as well as through oral sex. Herpes can infect the fetus during pregnancy of an infected woman, or the newborn becomes infected during childbirth. The result can be dangerous brain inflammation. If the mother has herpes blisters at the time of birth, the birth is performed by caesarean section. Symptoms
The incubation period after infection ranges from several days to a week.
The first symptoms are itching and pain at the sites of infection. After a couple of days, bubbles filled with liquid appear at the sites of infection. In women, blisters may appear on the labia, perineum, around the anus, in the vagina, or on the cervix. In men, they appear on the penis, on the head of the penis or in the anus. Very often, primary infections are accompanied by a violent manifestation of the disease - poor health, headache and fever. The glands in the groin are enlarged almost all the time. The blisters burst after a few days, leaving painful sores that then crust over. Symptoms of a primary infection can last up to two weeks. After a primary infection, the disease always remains, but only in a latent form. The frequency of recurrence of symptoms and the degree of their pain are very individual. With repeated herpes, the manifestation of the disease is usually weaker, and general health does not worsen. Local symptoms are the same as with the primary infection, but they heal faster or in about a week. Re-infection is often caused by stress. Relapse of the disease also appears in connection with other infectious diseases, during menstruation or after mechanical irritation (for example, violent sexual intercourse). Examination.
The sample is taken from the vial onto a cotton swab.
The test result can be obtained within a week. Treatment.
Treatment of genital herpes is a difficult task due to its lifelong presence in the body and the lack of drugs that have an effective effect on it. The most commonly used drugs for treatment today are from the group of nucleoside analogues. In addition, during the acute period, specific anti-herpetic immunoglobulin is used. In complex treatment, immunostimulants, vitamins, antihistamines and other drugs are used. When the interval between relapses is at least 2 months, vaccination is carried out with a hermetic vaccine. After 6 months, a repeat course is carried out. The vaccination is repeated 4-6 more times. The use of the vaccine allows you to increase the intervals between relapses and reduce their manifestations.
back to contents
Candidiasis
Pathogen: Yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida.
This disease is popularly called “thrush”.
It is caused by yeast-like fungi. Candidiasis is a common infection. Fungi can be found in the vagina of many women who do not have any complaints. They enter the genital tract mainly from the intestines and through contact with patients. The development of an inflammatory reaction during candidiasis (candidal colpitis) is facilitated by factors that reduce the body’s immunity, such as diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism disorders, and diseases of the digestive system. In pregnant women, candidiasis is detected more often due to the numerous changes occurring in a woman’s body at this time. Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, broad-spectrum antibiotics, corticosteroids and some others also plays a role. “Thrush” is a manifestation of superficial candidiasis of the skin and visible mucous membranes. With severe immunity disorders, lesions of the urinary tract (cystitis, urethritis), lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia), and intestines (dysbacteriosis) can develop. Symptoms in women.
With candidiasis, women usually complain of white, cheesy discharge and itching.
The disease lasts a long time and may be accompanied by periods of exacerbation (during menstruation, hypothermia, etc.) and subsidence of complaints. Symptoms in men.
In men, the fungus causes itching in the genitals, slight redness on the head of the penis and swelling of the foreskin.
Diagnosis, as a rule, does not present any difficulties. Candidiasis is easily detected in routine vaginal smears. In some cases, cultural (seeding secretions on nutrient media) and other methods are used. When the disease persists, sensitivity to various antifungal drugs is determined, which makes it possible to prescribe the most effective agent. Treatment.
Nystatin, levorin, boric acid and borax (sodium tetraborate) were previously widely used to treat candidiasis. Currently, there are a number of more effective and less toxic agents.
back to contents
Hepatitis
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. The most common types of hepatitis are hepatitis types A, B and C.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A infection occurs when fecal particles containing the virus enter the mouth of another person. Most often, infection occurs through transmission through water and food. If fecal particles enter the oral cavity during alternating anal and oral sex, they can lead to hepatitis infection. Hepatitis A is the least dangerous of all hepatitis. The infection does not lead to chronic inflammation of the liver and cirrhosis, nor does it lead to liver cancer. The disease often begins with fever, muscle pain, general malaise and diarrhea. After about a week, the urine becomes dark and the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow. The disease goes away on its own in approximately 2-4 weeks.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B infection occurs through blood (for example, through drug syringes) or products containing blood through sexual contact (sperm, uterine discharge), or the infection is transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth. Only a small proportion of those infected become infected with symptoms. These symptoms are the same as for hepatitis A. Among those infected, some remain permanent carriers of the virus. A small number of virus carriers develop cirrhosis or chronic liver inflammation within 10-20 years. Some carriers of active chronic hepatitis are cured by taking alpha interferon. If you have hepatitis B, it is possible to use a series of three vaccinations for treatment (first vaccination, second one a month later, third vaccination six months later).
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C infection occurs through the blood. The most common route of infection is the use of syringes and needles when consuming drugs. Half of hepatitis C virus carriers develop an active form of chronic liver inflammation. Chronic hepatitis C increases the risk of liver cancer. Treatment with alpha interferon can cure approximately 20% of patients with chronic hepatitis C.
back to contents
Pubic lice
Pathogen: Flesh-colored flat louse measuring 1-3 mm.
The pubic louse sucks blood and lays eggs on the pubic hair.
Pubic lice infestation occurs through skin-to-skin contact and bedding. Symptoms
Symptoms appear 1-3 weeks after infection.
Skin irritation and itching in the external genital area. Treatment.
At the pharmacy you can buy a hexide solution (Desintan) without a prescription, which is applied to the skin in the pubic area for a day. A week later the procedure is repeated. Underwear and bed linen are changed.
back to contents
Scabies
Pathogen: Scabies mite size 0.3-0.5 mm.
Scabies spreads through skin-to-skin contact.
Symptoms
Itching appears 3-6 weeks after infection.
With scabies acquired as a result of sexual contact, signs of the disease are especially evident in the lower abdomen, groin and thighs. The itching intensifies in the evening. Small reddish pimples appear on the skin. As a result of scratching, the skin may become inflamed and pustules may appear on the fingers, hands and penis. Traces of scabies mite movement may be found. Treatment.
A hexide solution (Desintan) is rubbed over the entire body. After application, the medicine is washed off after 12-14 hours. Underwear and bed linen are changed. The medicine is reused after a week. The partner and family members are treated at the same time, even if they show no signs of illness.
back to contents
Trichomoniasis (or trichomoniasis)
Trichomoniasis (or trichomoniasis) is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. It is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis -
a microscopic pathogen capable of independent movement with the help of flagella and an undulating membrane. Trichomonas very often accompanies other genital tract infections - chlamydia, gonococci, viruses, etc. Infection, as a rule, occurs only through sexual contact. The incubation period is 5-15 days. The development of the disease is facilitated by various diseases of the genital and other organs, accompanied by metabolic disorders, decreased immunity, hormonal disorders, and disruption of the vaginal flora, which reduces its acidity. Trichomonas actively reproduce during menstruation also due to changes in the vaginal environment. The pathogen lives mainly in the vagina and lower cervix. There is no immunity to the disease. There are several forms of the disease: fresh (in turn divided into acute, subacute and torpid, i.e. low-symptomatic), chronic and carriage of Trichomonas, in which there are no symptoms in the presence of the pathogen in the vagina. In acute and subacute forms, patients complain of heavy vaginal discharge, itching and burning in the external genital area. If the urethra is damaged, there is a burning sensation and pain when urinating. The torpid form is not accompanied by complaints of leucorrhoea, itching, or they are only slightly expressed. The chronic form of the disease is characterized by a long course and periodic relapses that occur under the influence of various provoking factors: general and gynecological diseases, hypothermia, violations of the rules of sexual hygiene, etc. The severity of complaints can vary widely. Diagnosis of the disease is based on complaints, examination data and laboratory results of smears from the vagina, cervix and urethra. In some cases, seeding of material is used. Treatment of trichomoniasis. During this period, sexual activity is prohibited. Treatment of the husband or sexual partner, treatment of concomitant diseases is mandatory. Currently, there are a large number of anti-trichomonas drugs.
back to contents