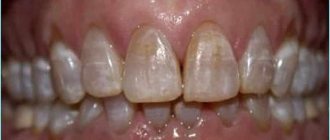
“You urgently need to remove the 48th tooth!” - such a statement from the dentist can seriously puzzle the patient, because even from a school biology course everyone knows that there are only thirty-two teeth in the mouth. Where did this mysterious 48th come from, and what is with the strange numbering of teeth among dentists? Cunning doctors have invented a diagram of a person’s teeth with numbers that only they understand, and patients get confused in these numbers, trying to understand what they are talking about and where they suddenly got “extra” dental units from.
In fact, the teeth numbering scheme in dentistry is quite simple, clear and accessible - it was created in order to facilitate the “accounting” of dental units in patients and bring it to some uniform standards. After all, if every dentist starts counting dental units as he pleases, nothing good will definitely come of it. Especially if the patient subsequently gets an appointment with another doctor and he simply does not understand what tooth numbers are indicated in the medical record and what kind of treatment was ultimately carried out earlier.
How dentists count teeth: arrangement and numbering principles
Each dental unit has its own functions, depending on its structure and location on the jaw. Thus, incisors are designed for biting off pieces of food, canines help to hold hard food and “tear off” stubborn pieces, premolars are needed for primary processing, and dense “plump” molars are designed for thoroughly chewing and grinding food. The order of the teeth in the mouth, accordingly, will be as follows: on each jaw there are four incisors, two canines, four premolars (two on each side) and six molars (three on each side).
In dentistry, tooth numbers are assigned according to their location on the jaw and function. Since the incisors and molars are located symmetrically on the right and left, the count starts from the middle of the row, that is, from the central incisors and further to the right and left. If we divide this row into two halves and start counting on one of them, we get: two incisors (teeth numbers 1 and 2), a canine (3rd number), two premolars (4th and 5th), three molar (6th, 7th and 8th, the last one being the wisdom tooth). These are the names and numbers of teeth that are universally accepted in dentistry.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
But if you simply say “sixth tooth,” then how can you understand whether it is upper or lower, and on which side of the jaw – left or right – it is located? To eliminate confusion in this matter, it is customary to designate a person’s teeth by numbers, indicating the segment of the jaw on which they are located. The segments are considered as follows: the upper right is the first and is indicated by a ten in front of the number of a particular tooth (for example, the 11th is the central right upper incisor, the 16th is the upper right molar, next immediately after the premolars, etc.), the upper left - twenty. Accordingly, the lower left is designated by thirty, and the lower right by the number 40. That is, the segments of the jaws are numbered clockwise, this makes it much easier to remember the order and, if necessary, count.
Thus, the notorious 48th number indicates the location of the wisdom teeth in the lower right segment of the jaw. And insisting on removing the 48th dental unit, the dentist simply indicates what number the wisdom tooth has in the lower right, and does not inform the patient about the supernumerary teeth that came from nowhere in the mouth.
A similar sign
Since ancient times, fangs and teeth, along with claws, have been considered a symbol of power and courage - they were carried with them as amulets, attributing unprecedented magical power. Until now, signs and superstitions haunt many. Let's consider what the situation portends if a person's tooth breaks or chips? Does this cause concern for his future fate?
Content
How to neutralize negativity
Even if a sign directly indicates trouble, these negative consequences can always be reduced. The main thing is to look at things positively, maintaining a good mood and not allowing circumstances to break you. But if the injury causes a feeling of heaviness in the soul, anxiety, fear, then important plans should be postponed until later.
If there is a noticeable deterioration in your health, you should immediately run to the doctor.
After trouble with a tooth, you need to pay special attention to relationships with relatives and friends. The same principle applies at work when interacting with colleagues. For those who believe, it’s a good idea to turn to the church and light a candle for the repose of close relatives.
Signs and superstitions
Each specific case means different things. All the moments at which the split occurred are important.
If a molar has not previously caused any inconvenience and suddenly breaks off, this means trouble in love. In relationships with your significant other, conflicts will become more frequent, and swearing will arise “out of the blue” for any reason. If there is no partner at all, then you shouldn’t even try to look for one in the near future - nothing will work.
If your tooth hurts, then you expect problems in your relationship with your closest friend. Gatherings will become rare, and interest in each other will noticeably decrease.
If it was rotten or had been destroyed for a long time, then friendship with a comrade will come to an end. Suddenly, points of contact will disappear, meetings will become formal and begin to become burdensome. It will become clear that no one needs such a relationship anymore.
Attention! If the loss of a tooth was due to a person’s fault (for example, he himself got into a fight or got into trouble due to his carelessness) - this is clearly a bad sign. Trouble can strike in any area - health, career, matters of the heart.
A fang that is not completely broken off predicts financial losses. These could be lost court cases, ill-conceived investments, and unfortunate losses. A through hole in the molar is a sign of magical influence. Most likely, one of those who like to envy or ill-wishers is trying to ruin life. If an organ bleeds heavily after an injury, then this means the death of someone close.
A separate sign concerns cracks and chips on the wisdom tooth. They talk about the old and secret sins of the victim's parents. If it falls out after chipping, then it should not be thrown away. It is better to string it on a thread and keep it with you as a talisman. Such a thing will attract wealth and good luck. There is also an ancient belief that if you dig the root, you can protect your family from the most powerful witchcraft for the rest of your life.
Tooth location
Ancient healers knew how to make diagnoses and choose treatment tactics based on a fallen or cracked tooth. The main thing is where it is. Their experience was adopted by modern doctors, but, of course, not everyone believes in omens and superstitions.
- A chipped front tooth is always a harbinger of difficulties on the personal front. If the injury occurred due to the fault of third parties, then fate will compensate for the loss in the form of a financial gift - a win, a bonus, a lucky find.
- If a piece of the fang breaks off, it’s fortunate that the most incredible desires are guaranteed to come true. This seems not entirely logical, because the loss of a fang, for example, has always been considered a terrible disaster, leading to inevitable death.
- A chip in the lower incisors means a break in a relationship with a loved one or a quarrel with an old friend. This is especially offensive when you considered these people to be the closest, but they ultimately let you down.
- If one of the upper incisors breaks off, this is a sign of upcoming hard work that will require maximum investment. Its outcome will depend only on the person himself. But having passed these tests, the bonus will be the recognition and approval of everyone around.
What does the diagram of a child’s teeth look like with the numbers of each unit?
The pattern of baby teeth in children differs from the pattern with numbers in adults. Doctors specially designate milk teeth with different numbers so as not to confuse themselves and their patients: after all, a child who was treated for a milk bite in childhood will soon grow up and begin to go to the dentist for treatment of already permanent dental units. And if the same numbering is used in both cases, then there will be incredible confusion in the treatment history - but such a history in the dental record is often extremely important for the further competent and effective elimination of problems of the dental system.
Therefore, the numbering order for baby teeth in children is as follows: the serial number remains the same as in adults (1st, 2nd – incisors, 3rd – canine, etc.), but the segments of the jaws are designated by numbers 50 and 60 for the upper right and left segments and numbers 70 and 80 for the lower left and right, respectively. And when the dentist informs parents that their child has caries on the 82nd tooth, you don’t need to immediately imagine a baby shark with several rows of sharp baby teeth, we are only talking about the second lower right incisor. According to the counting scheme, permanent teeth in children are no different from the scheme of adult molars.
What is the danger of losing chewing teeth?
If there is an end defect on at least one side (not to mention two at once), it will immediately become noticeable. When a person chews food on only one side for a long time, the load on it instantly increases, and the temporomandibular joint is overloaded. Ultimately this leads to:
- problems with chewing food;
- problems with the digestive tract arising from the previous paragraph;
- displacement of teeth in the oral cavity and their falling out of their sockets - there are no “antagonist” teeth that would distribute the load;
- reduction in bone tissue volume;
- facial asymmetry (sunken cheeks, deep nasolabial folds, malocclusion);
- frequent headaches;
- rapid wear of teeth adjacent to the chewing teeth, or chewing teeth on the opposite side.
International Viola system: a convenient diagram of the arrangement of a person’s teeth by numbers
The described method is very convenient and most common in dentistry. It has received international recognition and has been generally accepted among dentists since 1971, called the two-digit Viola system. The convenience of such a system lies primarily in the fact that there is no need to create a special map of a person’s teeth, the numbering is easily calculated in the mind and information about the condition of certain dental units of the patient can be easily conveyed in an oral conversation, by telephone or by e-mail.
However, many people, having read this far, may say: but our teeth were counted completely differently, and the map contains completely different designations! That’s right, because in addition to the Viola system, there are several other systems that can be used by dentists.
Impacted supernumerary teeth
Often, supernumerary teeth stop growing and remain impacted, that is, unerupted. Such teeth may not appear for a long time; they are discovered by chance during an X-ray examination of the oral cavity. The presence of an impacted supernumerary tooth may be indicated by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of mobility of complete teeth;
- periodic aching pain in the area where the tooth is located;
- tissue compaction if the tooth is located close to the edge of the jaw.
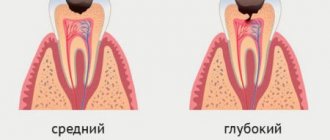
Cysts sometimes develop on the root of the tooth, which may not cause pain for some time; they are also detected during x-ray examination.
What other options exist for naming a person’s teeth by numbers?
There are three other systems common among dentists that can be used to designate and record dental units:
- A universal alphanumeric system developed by the American Dental Association.
- Zsigmondy-Palmer system. One of the oldest counting systems (it was created back in 1876), it is often used in their practice by maxillofacial surgeons and orthodontists.
- Haderup system.
All of them are convenient and easy to use in their own way, and in all such systems the arrangement of teeth by numbers in adults and children is indicated differently.
Alphanumeric system
It provides an indication of not only the number of the dental unit, but also its functional purpose. Thus, incisors are designated by the letter I, canines by the letter C, premolars by the letter P and molars by the letter M. As for the numbers, they indicate the serial number of a specific functional unit in the segment (whereas in other systems the functions of the dental unit are not taken into account, only its position is taken into account in a row). For example, if according to the Viola system the wisdom tooth is numbered 8, then according to the alphanumeric system it is also designated as M3, that is, the third molar in the segment. Additionally, digital segment designations are also used, which is why the serial number becomes two-digit. The same 48th tooth mentioned more than once with such a scheme will be designated as M43.
For milk teeth, lowercase (small) Latin letters are used in the recording, and instead of numbers, sometimes letter values from A to K are also indicated, counting dental units clockwise from the upper right incisor.
Zsigmondy-Palmer system
In old, and sometimes in new dental outpatient records, you can see a special plate for recording the condition of dental units, based on the Zsigmondy-Palmer square-numeric system. The order of growth of an adult’s teeth is indicated here by the familiar Arabic numerals from 1 to 8; for children, they use Roman numerals from I to V. The numbers of the jaw segments are not indicated here, the data is simply entered into the corresponding parts of the table diagram. The system is quite convenient and visual, but in an oral conversation it can cause difficulties when indicating a specific dental unit.
Teeth - how many do children and adults have?
When asked how many teeth a person has, everyone answers 32. Everyone knows about this. This is what we were taught in school, and numerous advertisements in the media speak about this. But if you start counting them in your mouth, many adults will count fewer, which is surprising. So how many teeth does an adult have and what is considered normal?
Structure of permanent teeth
How many teeth does an adult have?
If a person, when counting, finds only 28, and not 32 teeth, then he immediately wonders where the other four went. Every dentist will explain this situation to you.
An adult has exactly 32 teeth. If there are fewer than 28 or 30, this means that the third molars have not yet grown. These are eights. Their development begins much later. All permanent teeth occupy the jaw rows from 6 to 12 years of age. At the age of 16, dentists consider a number of children to be formed. Although the third molars have not yet grown during this period, their rudiments are already there and they have taken their place. But for most people, they may never appear or appear only on the upper jaw. How they develop depends on a dozen circumstances:
- genetic predisposition;
- the influence of evolution on the development of the jaw system;
- food consumed and much more.
Genetics and dentists have noted that in the process of evolution, human teeth have also changed. Initially there were 44 of them. Our distant ancestors consumed solid foods. Therefore, their jaw system was different, and all teeth took part in chewing. Today, soft food predominates in the diet. The human lower jaw has become smaller and there is not enough space for the third molars to develop. This is the reason why they remain in their infancy and sometimes erupt incorrectly.
Eights begin to grow by the age of 17. This process is considered complete by 25. Therefore, if by this time a person does not see the required amount in his mouth, it is recommended to consult a dentist. It will exclude an anomaly in the development of third molars, when they grow to the side and displace the molar located nearby.
Therefore, if we answer the question posed above, there is no clear answer. A person has 32 teeth. But the numbers 28 and 30 are also considered normal, subject to normal development.
Location
This is a human bone organ that is incapable of regeneration. They play an important role in the digestion of food and are the first in the digestive system. The first ones, which appear from 6 months to 2 years, are milky. By the age of 10–12 years, they should be replaced by permanent teeth. Their number is 28. Nature is designed in such a way that a person’s teeth fall out once, and then they are replaced. Therefore, it is important to keep them healthy.
Can a person have 33 teeth? This anomaly is extremely rare. Scientists say that this is 3% of the entire population.
Number of dairy
The moment of the appearance of the first incisors is touching, even despite all the capriciousness of the child. All parents are looking forward to it. Milk teeth, like their successors, also have a root system, blood vessels and nerve endings. That's why some children suffer from pain. They are also susceptible to diseases and require normal care.
They are laid in the embryonic period, and begin to grow when the child is 6 months old. This is an approximate time. It is possible that the start of eruption may move in one direction or the other. This is considered the norm. They grow up to two and a half years. They appear in a certain order.
- If the child is from 7 to 9 months old, there are 4 of them. These are two upper and lower incisors.
- About 8 teeth should be present at 1 year. The readings are inaccurate, since for a certain percentage of children this figure reaches 12.
- From 1.5 to 2 years, their number varies from 18 to 20.
- A child aged 2 years has exactly 20 teeth.
The development of baby teeth is individual and depends on dozens of factors. Therefore, if they notice small deviations from established norms, this is not a reason for parents to panic and worry.
Dentists and pediatricians use a formula to determine the number of teeth: subtract four from the number of months of a child’s life. According to it, the number of teeth at 2 years is 20. These are 8 incisors and the same number of molars, 4 canines.
In the period from 2.5 years to 3 years, a period of freezing begins in the development of the child’s jaw system. All 20 teeth of a child are actively involved in chewing. During this period, it is important to follow the rules of hygiene and monitor their health.
The enamel of baby teeth is thin and is more susceptible to caries, so children are not immune from this disease. Don’t be afraid to contact the dentist if your baby’s row has become unusable. Modern equipment helps make the treatment painless for the child. The formation of permanent ones depends on their health. Therefore, it is important to keep an eye on them.
Number of indigenous
The four, five, six and eight in the upper and lower jaws on each side are called molars. There should be 8 primary molars, 4 on each row. An adult has 20 of them, 10 on each jaw, including the four third molars. But since they may not exist, the number of molars in the mouth of an adult varies from 16 to 20.
Dentists distinguish between small molars (premolars or fours and fives). The crown has 2 visible cusps. They have one or two roots. Their function is to grind food. The rest are large molars (first, second, third molar or six, seven and eight). There are 12 such teeth. The crown already has four visible tubercles. The number of roots reaches 4, and sometimes 5 pieces.
Humans have 8 primary primary teeth. The structure differs from permanent ones, but they perform the same function as their successors. If you want your child to have no problems for a long time after the jaw is fully formed, teach him the procedure for oral hygiene, enrich his diet not only with foods rich in calcium, but also with vitamins and minerals. Teach and explain that you need to visit the dentist regularly.
zubychist.ru
Reasons for appearance
Medicine does not give an exact answer why the program fails in the human body and supernumerary teeth appear.
Hypotheses explaining the etiology of the phenomenon:
- Atavism hypothesis . Supernumerary teeth are a return to the original number of dental elements, which was normal for human ancestors (it is believed that they had 6 incisors on the upper and lower jaws).
- Theory of splitting of the tooth germ . Hyperdontia is a consequence of impaired activity of the dental plate during embryonic development, as a result of which a significantly larger number of dental buds are formed from it. The hypothesis is supported by the increase in recent decades in the number of cases of the appearance of extra teeth as a result of the influence of unfavorable environmental conditions, thyroid diseases and other negative factors.
How much does treatment cost?
The cost of treating hyperdontia is determined by the complexity of the case. The price for a simple removal of an additional tooth is, on average, 1,500 rubles . In cases with impacted or dystopic teeth, it will be slightly higher - for its removal you need to pay from 4,000 to 15,000 rubles .
Depending on the clinic, the cost of treatment may include preoperative examination, the operation itself and postoperative management. You can accurately calculate the final price only in the dentist's chair, since it is impossible to know in advance how the operation will go, whether complications will arise, or how the recovery period will go.