Definition
· Poisoning occurs when consuming fluoride (F, Latin fluorum) or fluorine-containing substances in toxic concentrations.
· The toxicity of fluorine compounds depends on the degree of solubility of the compound.
· The toxic dose in children under 5 years of age is considered to be greater than 25 mg of fluoride.
· The toxic dose in people over 5 years of age is considered to be more than 5 mg fluoride/kg body weight.
· Consumption of more than 17-22 mg sodium fluoride/kg (8-10 mg fluoride/kg) causes symptoms of severe toxicity in children.
· Sodium fluoride is a commonly used compound F in caries prevention (eg, toothpaste and other dental care products). 1 mg of fluoride corresponds to 2.2 sodium fluoride.
· Swallowing too many fluoride tablets or toothpaste is common in the 1-3 year age group.
· Some insect/pest poisons are also rich in F and their consumption causes poisoning.
· Unlike children, high fluorum intake in adults is often intentional (eg, suicide attempts).
Fluoride in modern toothpastes
As mentioned above, various fluorine compounds are added to modern pastes, namely:
- Sodium monofluorophosphate. This compound disintegrates into ions at a low speed, which is why fluorine is also released very slowly. If a person is used to brushing his teeth for no more than a few minutes per procedure, then toothpastes with such a compound will be ineffective and even useless for him.
- Sodium fluoride has the property of quickly breaking down into ions and releasing fluorine. Provides rapid supply of necessary mineral components to the dental tissues, affecting their rapid strengthening. This effect also applies to children. Pastes with sodium fluoride are recommended specifically for use by children, since they do not have the habit and desire to brush their teeth for a sufficient amount of time.
- Aminofluoride ensures the supply of mineral components at an even higher rate than fluoride. When brushing teeth, the compound creates a film on the enamel that remains for some time after the procedure is completed. This means that fluoride will enter the enamel both during the actual cleaning and after it. Aminofluoride is the most commonly used component in the production of toothpastes recommended for both adults and children.
- The compound of tin and fluorine is a component of pastes, the popularity of which reached its apogee in the 20th century. Despite its good remineralizing ability, the compound has a serious drawback, namely, it stains individual areas of the enamel in a chalky color. These stains gradually darken over time, which negatively affects the aesthetic properties, especially when it comes to teeth that fall into the smile zone. In addition, the compound changes the color of the fillings and can provoke a worsening of periodontitis. However, the component is still actively used in a number of Blend-a-med brands.
Etiology and pathogenesis
· Gastrointestinal genes are often dominant. These genes are caused by the formation of irritant/corrosive and systemic hydrogen fluoride in the acidic environment of the stomach, which in turn causes gastrointestinal irritation and erosion.
· Fluoride tablets contain the filler sorbitol, which causes nausea, vomiting and diarrhea without necessarily consuming toxic doses of fluoride.
· Once F is absorbed, it binds to calcium and causes hypocalcemia. It is this hypocalcemia that is the main cause of the symptoms and consequences of poisoning.
· Fluorine also acts directly cytotoxic, affecting various cellular enzyme systems.
Fluorine and its beneficial properties
- Strengthens enamel. The composition of enamel includes calcium, or, to be more precise, hydroxyapatite. When the latter reacts with fluorine, fluorapatite is formed - a strong compound that is especially resistant to the effects of cariogenic microorganisms. Regular use of toothpastes containing fluoride is a reliable means of caries prevention.
- Has a bactericidal effect. In simpler terms, fluoride kills organisms that cause tooth decay while also acting as a natural disinfectant.
- Prevents the formation of tartar. Since microorganisms do not stick to enamel treated with fluoride, tartar does not appear.
- Enhances the beneficial qualities of saliva. It has been practically established that fluoride, once in the oral cavity, increases the activity of the glands that secrete saliva, which plays an important role in the formation of caries. Saliva, which contains active calcium and phosphorus ions, intensively saturates tooth enamel. Under the influence of fluorine, it is saturated with mineral components that compensate for washed-out substances such as chlorine, magnesium, calcium apatite and many others. Saliva in combination with fluoride paste restores natural calcium loss, while reducing the risk of caries.
- Improves metabolism. It has been found that fluoride improves overall well-being and has a positive effect on metabolism. In the course of a long-term scientific study, it was found that pregnant women who include fluoride-containing products in their daily diet provide the child with stronger enamel without depressions and crevices.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic criteria
· Ingestion of fluoride compounds in doses that cause characteristic symptoms.
· Possible mixed poisoning with another substance.
· Hypocalcemia due to any other cause.
Disease history
Signs of poisoning include nausea and abdominal pain, thirst and central nervous system depression (fatigue/lethargy). If excessive fluoride intake is suspected, the patient should answer the following questions to obtain a complete medical history:
- When did the reception take place? How much time has passed since then?
- What was accepted? In what form, and in what doses (amount of substance and concentration)?
- Consumption intention?
- Is there a danger of others using this substance by mistake?
It is worth considering that sodium fluoride is available as a medicinal product in the form of dentifrice (4 or 10 g plus solvent), dental suspension (22.6 mg/ml), toothpaste (5 mg/g) and chewing gum (0 .55 mg).
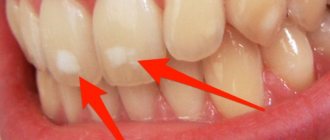
Symptoms, forms and degrees of fluorosis
Dental damage due to excess fluoride is popularly called “strong enamel”, “spotted enamel”. Based on the characteristics of the localization of stains and the degree of fluoride exposure to tooth enamel, several forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Streaked : inconspicuous spots in the form of light stripes, most often on incisors and canines, without destruction of dental tissue.
- Spotted : yellow spots in the center of the crowns of teeth, similar to caries.
- Chalky-mottled : dotted rough spots with specks of yellow, brown color that can be on all teeth.
- Erosive : visually noticeable spots with enamel defects, leading to hypersensitivity and tooth decay.
- Destructive : highly visible areas of tooth decay, corresponding to the last stage of the disease.
Degrees of the disease:
- Easy . Rare milky white streaks or spots are found on only a few teeth. No more than 25% of the enamel is affected.
- Moderate . Spots, specks and streaks are clearly visible on the teeth. The enamel is affected by 50%.
- Average . Brown and yellow inclusions are added to the milky spots. The enamel is significantly thinned, dentin is exposed.
- Heavy . Up to 70% of tooth crowns are affected. The spots are cinnamon and yellow, there are erosive defects, the enamel is chipped, and the teeth are deformed.
Research
If serious poisoning is suspected, the patient is hospitalized. The following blood tests are performed in the hospital:
· Blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
· Electrolyte balance is especially important to monitor.
· Hypocalcemia is usually the most serious and pathogenic variable.
· Hypomagnesemia and hyperkalemia are also observed in poisoning.
· Fluoride poisoning can cause liver and kidney damage. ALT and creatinine should be measured.
Other studies:
· ECG and cardiac monitoring in severe cases. There may be a widened QRS complex, arrhythmia, shock, and cardiac arrest.
Are toothpastes dangerous to health?
Excess fluoride in toothpaste more often than other compounds leads to poisoning in children. Pay attention to the composition, it may contain harmful sodium sulfates. Such chemical bonds are even added to washing powders. When choosing these products, read the labels and look for the “eco” or “fluoride-free” label. Teeth naturally clean themselves and a number of factors influence the processes of demineralization and remineralization of teeth. Reflux, hidden gluten intolerance and/or microperforation of the intestinal walls, deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K). The above and other factors can lead to the development of caries. In any case, it is necessary to understand the cause for treatment to be effective.
Fluoride is a temporary band aid. For teeth, it is important to use exactly those minerals that are part of the natural composition of dental tissue. Remember in the article “8 myths about the thyroid gland” we talked about the drug thyroxine, which is harmless because it is identical to the hormone in our body? A similar principle works here. Use a probiotic paste to optimize your oral flora, and more alkaline rinses and reduced intake of acidic foods may help balance your mouth's pH levels. However, even these recommendations are just an addition to the basic care regimen. Tooth decay is an external symptom through which the body speaks to us and tells us that there is a problem. Your task is to find and treat the sore point in a timely manner.
Treatment
Treatment goals: avoid the harmful effects of fluoride and eliminate existing negative symptoms. It is recommended to drink plenty of milk or calcium-rich drinks. Calcium reacts with fluoride to form poorly soluble calcium fluoride, which is not easily absorbed.
Additional recommendations and treatment regimen depending on age and fluoride dosage.
Age
|
Why is water fluoridated?
A reasonable question arose in my head after reading it. However, the answer is more than banal: those responsible for the situation either do not have information about the real danger of the substance, or deliberately turn a blind eye to the circumstances. Experts consider adding fluoride to water supplies a dangerous way to purify water. Everyone knows the expression “the less you know, the better you sleep,” but while many are silent, people are acquiring extra pounds of harmful fluoride. In the USA, the population filed lawsuits, and the government made a brilliant decision - to recognize fluoride not only as harmless to the body, but also beneficial for teeth. This is why we are so convinced that the more fluoride in the toothpaste, the whiter the teeth.
Progress, complications and prognosis
Make sure fluoride medications are not available to young children.
Gradient
Typically, symptoms of fluoride poisoning occur in less than 1 hour. However, in some cases, symptoms do not appear until several hours after ingestion.
Complications
· The cause of death is usually circulatory or respiratory failure.
· Damage to the liver and kidneys occurs.
· Repeated and long-term abuse of fluoride can lead to dental or skeletal fluorosis.
Forecast
Most exposures resolve without any symptoms. Fluoride poisoning is common in young children, but the condition can be prevented by keeping tablets and the like out of the child's reach.
Ingestion of toothpaste containing F is also common in children. Poisoning is rarely life-threatening and usually does not cause complications.
How can you avoid contact with Fluoride?
Tap water
One source of Fluoride is drinking tap water. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the water you drink.
Toothpaste
Another big source of this toxic element. Almost all toothpaste contains fluoride, so buy toothpaste without it or make your own tooth powder at home. And think about the fact that caries is mainly a reflection of our diet, and not the need for fluoride.
Dishes
What you cook with directly affects our health. Cookware with Teflon non-stick coating saturates the food cooked in it with Fluoride. Therefore, cook food in environmentally friendly, harmless containers.
Forms
Dentists distinguish the following forms of fluorosis:
- dashed;
- spotted;
- chalky speckled;
- erosive;
- destructive.
Let's take a closer look at each of the forms:
- Stroke is the mildest form of the disease. It is manifested by the formation of small chalky stripes on the enamel of the front teeth, which are almost invisible and can only be examined by an experienced dentist.
- Spotted is heavier than streaked. It is manifested by the formation of chalky stains on the surface of the enamel of the front teeth, which can be located on any part of the tooth enamel. The spots may be whitish or light yellowish.
- With chalky mottled disease, not only the front teeth, but almost all of the patient’s teeth are affected. The disease is manifested by the formation of pigmented spots ranging from whitish to dark brown in color.
- Erosive is one of the most difficult. With this form of the disease, small defects - erosions - form on the surface of the tooth enamel. If the patient has at least one erosion, it means that the disease is progressing and developing quite rapidly.
- Destructive is the most difficult. In this form of the disease, tooth enamel is gradually destroyed and worn away.
Degrees of development
Dental fluorosis develops gradually, it does not occur day by day, it is a complex disease. Doctors distinguish three stages of development, in which tooth enamel suffers differently:
- I degree is characterized by the appearance of small spots on the surface of the tooth enamel or a milky white color on the floor, while not all teeth are affected, but only some;
- Stage II is characterized by the appearance of not only chalky spots, but also pronounced pigmented spots of brown or yellow color;
- The third degree is characterized by damage to most of the enamel on the surface of the tooth, while the crown is deformed, and the tooth enamel becomes soft and easily erased, practically not protecting the tooth from damage.
Fluoride deficiency
If fluoride is supplied with food or water in insufficient quantities, a microelement deficiency develops, which is dangerous for the body; this is one of the main risk factors for the development of caries [4].
Sources of fluoride for a child's teeth are critical. The fact is that in children under 6 years of age, this microelement is involved in the formation of the enamel of permanent teeth, making them more resistant to the action of bacteria and acids in food [2]. A lack of fluoride at an early age can lead to future [5]:
- late teething;
- darkening of the enamel;
- caries.
According to some data, 2 out of 3 Russians suffer from insufficient fluoride intake from water or food [6].
“In many regions of Russia, due to the insufficient content of microelements necessary for health (fluorine) in water, dental caries in children reaches 90-100%” “Fluorides: their importance for human health in modern conditions and prospects for use”, Dr. n. Iordanishvili A.K.
Why is excess fluoride harmful?
However, an excess of this element is no less harmful. It usually occurs in regions where the population uses unfiltered fluoride-rich groundwater for drinking [7]. Another possible source is vegetables and fruits that are watered with such water.
The harm of fluoride accumulation in the body is manifested in the fact that when there is an excess of it, a person gradually develops fluorosis - a disease that affects both teeth and bones. Its main symptom is stains on tooth enamel, usually white [8]. Water quality control is of great importance for the prevention of fluorosis [9].
How and what kind of water to drink then?
Water can become both a dangerous weapon, as we have already found out, and a medicine. Today, research has established that not only water with high mineralization, but also drinking water is active water. It is important to find good bottled water, only then will it be beneficial. The question legitimately arises: “when, how much and what kind of water to drink?” We want to know how a transparent substance will help us be healthy.
Treatment and prevention of diseases must begin with cleansing the intestines. If you notice excessive consumption of fluoride, start taking mineral waters “Stelmas Mg” and “Svetla mineral”, “Izhevskaya”, “Batalinskaya”, they allow you to simultaneously cleanse the intestines, liver, kidneys, blood vessels, cells and MP; lower blood pressure, sugar, cholesterol; lose weight; strengthen the immune system and much more, i.e. normalize metabolism.
And most importantly, according to WHO, our health depends 20% on the environment, 12% on the help of doctors and 48% on yourself. Take preventive measures, help your body, analyze your habits. Your health depends on you.