Enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body and a natural protective barrier for teeth. However, some people are diagnosed with its deficiency. Hypoplasia of dental enamel - as this condition is professionally called - can have different causes, but appropriate treatment methods must be used each time.
The main function of enamel in the oral cavity is to protect teeth from harmful factors: the action of bacteria, thermal and chemical irritants, as well as abrasion during chewing. Although there are proven ways to strengthen enamel, its gradual erosion is associated with various reasons. Some patients, even children, are also diagnosed with underdevelopment of this tissue. Dental hypoplasia can have many causes and each time requires appropriate treatment.
Dental hyperplasia in children: causes and treatment
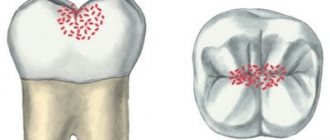
Dental hyperplasia externally looks like small growths on the enamel, formed due to excessive tissue formation.
In children, the defect is detected during examination by a dentist or by radiographic methods. Tubercles measuring 3-5 mm are located in the neck of the tooth, near the roots and are often covered by the gums. There is also localization on the crown. The causes of hyperplasia are not fully understood. Among the possible options for the formation of an enamel defect:
- improper development of the rudiments of mammary and permanent units;
- pathologies of dental tissue growth;
- metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- heredity.
The incidence of hyperplasia in children is less than 1%.
The defect does not bother the patient and therefore does not require special treatment. If there are “enamel drops” on the surface of the chewing teeth, the doctor will recommend fissure sealing to reduce the risk of caries.
If the localization of the anomaly is unsuccessful and the gums are injured, the pediatric dentist will carefully remove the tubercles with special burs, treat the enamel with remineralizing compounds, and return the dental crown to its anatomically correct shape.
Symptoms
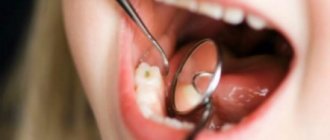
In most cases, enamel hypoplasia is diagnosed by a dentist; clinical symptoms of the disease are difficult for the patient to detect. The disease may appear as white or brown spots on the surface of the enamel, small pits on the teeth, grooves on the crowns or curled edges of the incisors of the teeth.
Only microscopic examination can give a reliable picture of enamel hypoplasia. Then it is discovered that the layer is much thinner than in healthy people. In addition, the disease is sometimes accompanied by disturbances in the dentin structure.
Hypoplasia of primary teeth: what is it and its causes
Hypoplasia is characterized by thinning of the enamel and a pronounced change in relief. On the crown of a baby or permanent tooth there are depressions, dots, pits, and grooves. Affected teeth differ from healthy ones already at the moment of eruption - the enamel is covered with white, yellowish or brown spots.
Hypoplasia of primary and permanent teeth is observed in 40% of patients. And the number of children with this pathology is growing steadily. Scientists associate the development of the anomaly with poor ecology, lack of a balanced diet, and hereditary factors. And all because the development of the defect occurs already at the stage of formation of the tooth germ.
A tooth—deciduous or permanent—is made up of pulp, dentin, enamel, and other tissues. Special cells, ameloblasts, are responsible for the proper development of enamel. In the absence of pathologies, one ameloblast forms one enamel prism. And it is these “prisms” that make up the outer tissue of the erupted tooth. As soon as the ameloblasts complete the task assigned to them, the destruction of the building cells occurs. After this, the tooth enamel of the erupted unit loses its ability to recover.
Ameloblasts are only the first stage in creating strong enamel of a child’s tooth. After eruption, it takes about a year for another stage of formation - final mineralization - to be completed. If all stages of development are successful, the child pleases his parents with strong, snow-white, healthy teeth.
Failure at any stage means potential enamel hypoplasia.
Causes of tooth enamel hypoplasia in children
There are three risk factors for the development of hypoplasia:
- features of fetal development during pregnancy;
- illnesses of the child himself;
- external circumstances.
The health of the expectant mother is the basis for the child’s excellent well-being. The risk of hypoplasia can be provoked by:
- Rh conflict - negative Rh factor of the mother and positive Rh factor of the child;
- severe pregnancy, toxicosis;
- acute viral infections or toxoplasmosis during pregnancy;
- taking tetracycline drugs during pregnancy;
- smoking, drinking alcohol.
Among the diseases of the child himself, the risk of defects in the formation of teeth increases:
- CNS lesions, Down syndrome;
- rickets, vitamin deficiency;
- digestive disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
External factors include poor nutrition of the child and injuries to the jaws, which prevent the normal development of tooth germs.
Intrauterine factors provoke hypoplasia of primary teeth. The rest have an equally negative impact on both temporary and indigenous units.
Plaksina Margarita
My patients really like dental remineralization. Pastes rich in minerals have a pleasant taste and smell, and the procedure itself is painless and even pleasant.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptoms of the pathology include a change in the color of the enamel: white spots appear on the outer surface. Such changes do not cause unpleasant feelings. In addition, the surface of the teeth in the affected areas is smooth and non-pigmented.
More severe forms of hypoplasia are characterized by the presence of pronounced depressions. At the initial stages, the lesions have a natural shade, but over time they become pigmented. Sometimes on such teeth you can notice deep grooves located horizontally or vertically. Despite the hyperpigmentation of certain areas, the integrity of the enamel is not compromised.
Aplasia (complete absence of enamel) is characterized by pain upon contact with any irritant. In addition, aplasia is associated with underdevelopment of dentin. This leads to the fact that the teeth gradually begin to change shape.
Hypoplasia of primary teeth: treatment
Since one of the reasons for the abnormal development of enamel is low tissue mineralization, doctors have found an opportunity to help young patients. During treatment, two goals are set - to stop pathological changes, reduce or eliminate the severity of existing defects.
The following methods are used in pediatric dentistry in Moscow:
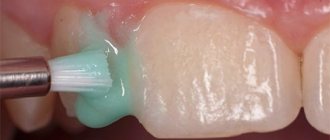
Enamel remineralization
The procedure allows you to replenish the deficiency of missing minerals and strengthen the child’s teeth. At the appointment, the doctor sequentially treats healthy and damaged teeth with a special gel. Treatment is continued at subsequent appointments or even at home. For home procedures, the doctor prescribes the child the optimal paste composition.
Fluoridation of teeth
Treatment of hypoplasia differs in the choice of drug. When fluoridating, the dentist uses a gel with a high fluoride content - up to 65-70%.
The method of restoring baby teeth with hypoplasia is chosen by the dentist after assessing the condition of the enamel and the indications.
Damage to primary occlusion
Diagram
Pathology is formed during the prenatal period. The main factor here is the serious illness of the pregnant woman. Baby teeth suffer much less often than permanent teeth. However, nowadays such cases have become more frequent. This is associated with a significant reduction in perinatal mortality.
Even in the first weeks of life, the occurrence of systemic diseases in a child can provoke the occurrence of hypoplasia. Abnormalities are more common in the incisors and canines of the upper jaw. This is why such anomalies as Hutchinson, Fournier and Turner teeth are so common.
Deciduous incisors undergo changes most often if a pregnant woman has suffered from diseases such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, or suffered from toxicosis. Hypoplasia is also observed in premature babies who have a history of birth trauma, congenital allergies or hemolytic jaundice.
Anomalies develop in utero at approximately 25-30 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes this process occurs within 1 month of life.
Hypoplasia of permanent teeth in children: treatment
Sometimes the process of hypoplasia cannot be stopped by applying mineral and fluorine-containing compounds. In such cases, pediatric dentists offer options for reconstructing tooth enamel or even the crowns of permanent teeth themselves.
Restoration is carried out using one of the following methods:
Filling children's teeth
Using grinding, dentists clean the affected area and then restore the surface using high-quality, reflective filling compounds. Installing fillings makes teeth straight, white and neat, and also reduces the rate of spread of the lesion and reduces the risk of complications.
Prosthetics
Installation of full crowns on affected permanent teeth or production of veneers. For children, prosthetic options are selected by the doctor according to the indications and the current clinical situation.
Plaksina Margarita
Unfortunately, children with hypoplasia are sometimes brought to the appointment too late. It is not always possible to save a tooth; it has to be removed. In the case of a primary malocclusion, the child is given an orthodontic ring to maintain space for the permanent unit. This is necessary so that neighboring teeth do not take up free space and spoil the bite.
Damage to permanent dentition
The higher the incidence rate in childhood, the greater the possibility of dental anomalies. Half of the children who had chronic diseases, especially of the endocrine system, subsequently experienced anatomical changes in the crowns.
In addition, a special role is played by:
- gastrointestinal problems;
- toxic dyspepsia;
- congenital syphilis;
- acute infectious diseases;
- rickets;
- brain disorders.
It is noted that 40-60% of hypoplastic changes occur already in the first 9-10 months of life. During this period, the protective properties of the body are still weakly expressed. The child’s adaptive and compensatory capabilities are not able to withstand aggressive factors of the internal and external environment.
Hypoplasia in permanent dentition
In permanent teeth, the first molars are the first to suffer. The lesion is observed primarily on tubercles and convex surfaces. By 8-9 months, canines and incisors are formed.
If before this period the child suffered from some serious illnesses, then the risk of hypoplasia in the form of Hutchinson’s and Fournier’s teeth is quite high.
Hypoplasia of dental enamel in children without treatment
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia in primary teeth is required, since in the absence of timely intervention, the root units will suffer. Among the likely consequences:
- development of caries, pulpitis;
- violation of permanent occlusion due to tooth displacement;
- increased abrasion of tooth enamel;
- painful reaction to cold, heat, sour, sweet;
- tendency to form fistulas;
- absence of rudiments of permanent units;
- loosening, destruction and loss of teeth.
Treatment tactics
Hypoplasia of the enamel of primary or permanent teeth is irreversible. Therefore, all therapeutic measures are aimed at protecting the altered areas of the dentition and restoring the enamel coating. Mild pathology does not require special treatment, but only requires constant monitoring. In most cases, a person does not experience pain: non-carious changes in dental tissues do not interfere with everyday life.
For severe forms of hypoplasia, for example, deep lesions of the enamel or extensive spots, special therapy is carried out. Without timely treatment, there is a risk of developing various complications:
- pulpitis, periodontitis;
- malocclusion;
- pathological abrasion;
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
Hypoplasia can also lead to dentin destruction and complete tooth loss. There are several methods for eliminating the manifestations of hypoplasia. Therapeutic tactics are selected by the dentist depending on the severity of the pathology. The doctor takes into account the condition of the patient’s dental tissues.
Remineralization
Remineralizing therapy involves saturating tooth enamel with fluoride and calcium. Artificial mineralization is carried out using dental gels, pastes, varnishes and other means. Treatment can be done in a clinic or at home.
Remineralization in a clinical setting consists of several stages:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Application of restorative gel.
- Coating with a fluorine-containing compound using a tray or brush.
The dentist selects the frequency of procedures and the type of drug individually. In addition, your doctor will often prescribe oral vitamins and minerals as additional support for your body.
Whitening
Bleaching is carried out after professional hygiene and remineralizing therapy. This method is effective if the defects are located in the surface layers of the enamel or slight clouding of the enamel layer is observed. Chemical bleaching gives the most pronounced results.
In cases of severe damage to the enamel layer and numerous foci of hypoplasia, chemical bleaching with solutions of carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide is contraindicated.
Filling and prosthetics
Filling is used for pronounced erosive depressions, as well as mixed forms of hypoplasia, when the integrity of the dental units is compromised. Composite materials are used to restore teeth. In some cases, the vestibular surface is covered with veneers. This technique helps to give teeth an aesthetic appearance and prevent their destruction.
Prosthetics are used for severe damage to the enamel of primary or permanent teeth. Crowns help maintain the health and aesthetics of your teeth. Installing crowns for hypoplasia in childhood contributes to the formation of a correct bite and the development of normal diction.
Depending on the extent of the damage, the condition of the soft and hard tissues, it may be necessary to remove the affected tooth followed by implantation.
Elimination of hypoplasia, reliable methods and immediate measures
It is advisable to preserve the teeth of Hutchinson, Pfluger, and Fournier with the placement of an artificial crown. Minor changes can be corrected by using modern filling agents. Moreover, tissue preparation should be minimal. Help with hypoplasia has not only physiological significance, but also psychological significance. This is especially true for children and adolescents.
If there are stains on the enamel, remineralizing therapy is indicated. So if the size of pigmentation is 4-5 mm, then the procedures must be carried out within 1 year on average. In this regard, it is necessary to prepare the child for a long period of treatment.
In fact, complex remotherapy gives positive results for everyone. In addition, it is shown even in the absence of color change.
To strengthen hard tissues, the following drugs are prescribed:
- calcium gluconate solution for applications;
- sodium fluoride in the form of varnish;
- vitamins;
- antioxidants;
- natural biologically active substances.
The doctor prescribes all medications in courses every 3 months. Applications can be carried out both at home and in the clinic. Treatment is prescribed for the whole year. Systematic monitoring and conscientious implementation of all therapeutic recommendations are necessary.
Great importance is paid to personal oral hygiene. The use of fluoride toothpastes is required.
Dentists often recommend the following brands:
- President Classic;
- Silka;
- SPLAT Arktikum;
- Elmex - protection against caries;
- New pearls;
- Arbat;
- Children's pearls.
Toothpastes can be used as an application. They can be applied for 15 minutes. 2 times a day.
In case of severe changes in Pflueger’s teeth, it is possible to eliminate the anomaly by preparing and applying composite filling materials. They must have not only aesthetic qualities, but also have good adhesion, and also withstand mechanical stress.
Hypoplasia is much less common than carious lesions. However, it requires no less attention, both from the person himself and from dentists. With timely assistance, it is possible to preserve the dentition for a long time. When there is no treatment, this leads to complete destruction of the crown part and eventual loss of the dental unit.