Enlarged tonsils in a child are not a disease, but a symptom that signals pathological changes occurring in the young body. As practice shows, parents go to the doctor only if the baby’s body temperature increases, since it is believed that temperature is the only significant signal indicating that the child is sick. And this is a big mistake. The condition when one tonsil is larger than the other, or both are enlarged at once, can occur without fever or sore throat. And it also requires increased attention from parents.
Why do tonsils get enlarged? Tonsils are special organs of the immune system in the human nasopharynx. They consist of lymphoid tissue, protect the body from pathogens and prevent their further spread. The leading role in the body belongs to the palatine tonsils, or tonsils. The tonsils are located on the sides of the pharynx and meet infection that has entered through inhaled air or food. As soon as viruses and bacteria come into contact with the surface of the tonsils, the child's tonsils enlarge. At this time, there is an increased production of leukocytes - cells that attack and destroy the infection. When an enemy is defeated, the tonsils return to their original size. In other words, the large size of the palatine tonsils indicates that they are fighting pathogenic microflora.
But even when the tonsils are in a healthy state, it is important not to lose vigilance: normally, every person has bacteria on their mucous membranes that do not manifest themselves in any way, but under the influence of favorable conditions, they begin to multiply, provoking hypertrophy of the tonsils. These reasons for enlarged tonsils in children include:
- hypothermia;
- allergic reactions;
- deviated nasal septum;
- chronic diseases of the ENT organs;
- too dry air;
- living in a place with an unfavorable environment.
The degree of enlargement of the tonsils.
There are four stages of enlargement of the tonsils. At the first stage, the tonsils occupy a third of the space between the pharynx and the palate. In this case they are said to be slightly enlarged. Symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way.
At the second stage, the tonsils already occupy half of the free space. There is discomfort when swallowing liquids, food and breathing. Tissue hypertrophy is average.
In the third stage, swallowing becomes very difficult as the lymphoid tissue increases to an impressive size.
The fourth stage is characterized by severe hypertrophy, when the tonsils completely block the pharynx. This condition interferes with proper breathing and nutrition.
If inflammation of the tonsils begins, without timely treatment, the stages quickly replace each other.
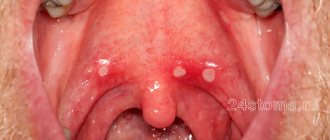
The concept of “loose tonsils”
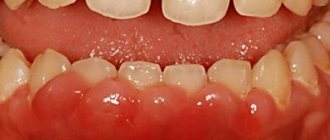
The tonsils or tonsils are located behind the palatine arches and create a protective barrier against bacteria and germs. In normal condition they are almost invisible. If the inflammatory process develops, they begin to increase in size and become swollen and convex.
This occurs due to inflammation of the lymphoid tissue, which is the first to encounter the harmful effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
Loose tonsils can occur in the following cases:
- the beginning of the acute phase of the disease (ARVI, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and other diseases);
- chronic form of throat diseases;
- as a residual phenomenon after severe infectious diseases (angina, scarlet fever and others).
Loose tonsils require some care, as food debris gets stuck in them, which is an excellent flora for the proliferation of bacteria and the development of inflammatory processes.
When should you see a doctor?
If parents notice that their child’s tonsils have become enlarged, this is a good reason to take the child to an ENT doctor. The sooner the problem is identified and the throat is treated, the more favorable the prognosis will be.
And of course, there is no need to postpone a visit to the otolaryngologist if, in addition to the hypertrophied tonsil, the following signs are noticeable:
- constant sore throat;
- large lymph nodes, which also hurt a lot;
- red throat;
- white palate;
- plaque on the surface of the tonsils;
- dryness and sore throat;
- difficulty swallowing.
All these symptoms may not be accompanied by an increase in temperature, but regardless of this, they require examination by an ENT doctor.
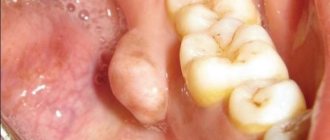
If a child has an enlarged tonsil on one side, this is an alarming sign. In addition to classic inflammation, this condition may indicate the formation of a peritonsillar abscess or phlegmon. These are purulent inflammations of the pharynx. Both conditions require surgical treatment. Otherwise, pus may enter the body and lead to sepsis.
Main causes
If you notice loose tonsils in a child, which clearly stand out with their rounded shapes, you should not panic and buy all the pharmaceutical drugs intended for the treatment of throat diseases. This condition indicates the onset of the development of the inflammatory process.
The tonsils began to form local protection so that the pathogenic microbes that got on them did not penetrate further into the body.
Interesting: in young children, the tonsils produce special enzymes that help break down food in the mouth.
The main culprit of looseness is a change in the functioning of the gland on the tonsils. In certain cases, the tonsils cannot cope with the effects of external infections. To fight microbes, a large number of lymphocytes are produced, but they are not always enough. As a result, painful processes begin to develop in the throat and nasopharynx.
There are several main reasons for the appearance of loose tonsils.
Entry of pathogenic viruses or bacteria into the oral cavity and nasopharynx. The production of plasmacides, microphages and lymphocytes begins in the follicles and lacunae. If the immune defense fails, the development of diseases such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis and others begins.
A decrease in the child’s immunity after suffering from infectious diseases as a result of the glands on the tonsils does not work correctly and the tonsils remain voluminous and loose.
Severe hypothermia or cold.
A residual phenomenon after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections.
The presence of chronic diseases in the oral cavity (carious tooth decay, periodontitis, long-lasting wounds, etc.). The lymphatic system has to regularly suppress pathogenic microflora, which results in swelling of the tonsils.
In the case of frequent severe throat diseases, especially sore throats, damage to the lymphoid tissue begins as a result of which the mucous surface of the tonsils remains deformed forever.
Treatment.
An effective treatment tactic will be chosen by an ENT doctor only after the cause of tonsil hypertrophy has been established.
Depending on the cause of inflammation, the patient is prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs if the causative agent of the disease is bacteria. Moreover, the medicine must be taken “from start to finish” - a strictly defined number of days, even if the child feels better. Continuous treatment is the key to a quick recovery without complications;
- antiviral drugs, if the causative agent of the disease is a viral infection;
- antifungal agents, if the cause of inflammation is fungi;
- gargling and irrigating the throat with antiseptics - constantly gargling is necessary to wash away pathogenic flora from the mucous membranes;
- antihistamines to relieve tissue swelling, and if the cause of throat discomfort is an allergic reaction;
- washing the lacunae of the palatine tonsils from pathogenic flora (it is optimal to start washing from 6-7 years of age);
- physiotherapeutic procedures (laser, ultrasound, photodynamic therapy, ultraviolet exposure, etc.)
Some parents believe that it is easier to remove the tonsils and get rid of the problems associated with them. But this is not a solution! Removal requires strict indications: more than four sore throats during the year, bad rheumatic tests, peritonsillar abscess and complications in the heart, kidneys and joints. If there are no indications, you need to be observed by an ENT doctor and, if necessary, carry out timely treatment.
How to treat chronic tonsillitis?
In this case, treatment should only take place under the supervision of a doctor. Its necessity is due to the fact that tonsillitis depletes the child’s immunity, and if treatment is not completed, it can worsen and lead to various kinds of complications: kidney disease, heart pathology, bronchitis, psoriasis, and diseases of other ENT organs.
Several ENT treatment options are possible; the doctor will determine the appropriate one after examining the child. In some cases, you will need to take a general analysis of ESR - erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which will allow you to identify the infection even in a latent form and begin treatment immediately.
To cure chronic tonsillitis, one of 2 treatment options is used: conservative or surgical.
The first involves taking antibacterial, antiviral, and antihistamine drugs. Local antiseptics and homeopathy and physiotherapeutic procedures (UVR, electrophoresis) are also prescribed.
Indications for surgery are frequent sore throats, purulent inflammations, lesions of other organs that arise against the background of tonsillitis. If based on all the symptoms you believe that your child has this disease, contact a specialist. The medical office is attended by an experienced doctor who diagnoses the disease and prescribes effective treatment, and gives recommendations for the prevention of chronic tonsillitis. The clinic also offers tests for children and adults and receives quick results by email. To make an appointment, use the convenient form on the website or the hotline number
What are adenoids?
Adenoids are three of the six lymphoid formations (tonsils) of the so-called lymphoid “Pirogov’s ring”: two tubal tonsils (located around the mouths of the auditory tubes) and the nasopharyngeal tonsil (located in the center of the nasopharynx vault. In addition to these three tonsils, the “Pirogov’s ring” includes two palatine tonsils tonsils (tonsillar) and one lingual (located at the root of the tongue in front of the epiglottis). The function of the “Pirogov ring” is very important. This is the main “guard” of the body at the “entrance gate” from possible infection. Everything that enters our body from the outside: air for breathing, food and water, everything undergoes careful control by the lymphatic formations of the nasopharynx and oropharynx (“Pirogov’s rings”). And inflammation is nothing more than the body’s response to an infectious agent (virus, bacteria or fungi), with the aim block the infection, prevent it from entering the body, destroy and remove it.
Traditional diagnostic methods (examination by an ENT doctor or pediatrician)
In a regular clinic, to diagnose chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy, an examination of the nose, throat and ears is used using metal instruments for examining ENT organs: nasal and ear mirrors and a spatula illuminated with reflected light, using a conventional head reflector (head mirror) or a head lamp in the form flashlight. In this case, the ENT doctor (or pediatrician) only sees the area of the nasal vestibule and the surrounding parts of the nose. The nasopharynx, the anatomical location of the adenoids, is not visible. The examination is contact (when examining the nose, the wings of the nose in the vestibule area are expanded with a nasal speculum; when examining the ear, an ear speculum is inserted into the ear canal)
In addition, it will be possible to perform a digital examination of the nasopharynx for a subjective assessment of the size of the adenoids (the doctor feels the nasopharynx and the surface of the adenoids through the mouth, trying to determine their size). This method is not reliable, is unpleasant for a small patient and is traumatic for adenoid vegetations.
Types of cleaning loose tonsils
To prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes in loose tonsils, they should be cleaned regularly. Deeper cleansing is performed in a medical facility.
In the case of small children, such manipulation at home is unacceptable. The child undergoes ultrasound treatment. And then, using a special syringe, the entire larynx is irrigated. This allows you to remove food debris, plaque and pathogenic microorganisms from the tonsils. The procedure is carried out at least 10 times both as treatment and prevention of diseases.
For older children, you can use the following methods to clean the tonsils:
- We ask the child to open his mouth wide. Use the convex side of a teaspoon to press on one of the tonsils.
- The exposure is carried out until whitish discharge appears in their lacunae.
- The child should gargle thoroughly with a solution of sea salt.
- We perform the same action with the second amygdala.
Such cleaning can be carried out not only during illness, but also for its prevention.
Therapy and prevention
Young children are more likely to suffer from various throat diseases than adults. If a child has a tendency to develop inflammatory processes in the tonsils, parents can take the following preventive measures:
- Strictly monitor oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day. Rinse your mouth with regular boiled water after each meal.
- Timely treatment of all dental problems. Carious bacteria can cause constant swelling of the tonsils.
- Home or medical rinsing of lacunae. This can be done independently by gargling with a solution of furatsilin or with an antiseptic.
- Gargling the throat with decoctions of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula, sage. It is recommended to alternate herbs.
If treatment and prevention do not produce the desired effect, the doctor may decide to remove the tonsils. This is done in the following cases:
- Severe sore throats 5 or more times a year.
- Therapy, treatment and cleaning do not bring any results.
- Irreversible changes in lymphoid tissue, in which the tonsils cease to perform a protective function.
- Pathological growth of the tonsils, which negatively affects the respiratory tract and hearing organs.
Surgery is indicated only in very severe cases. This is an extreme measure that deprives the child of the initial protective barrier. After removal of the tonsils, the infection will directly enter the upper respiratory tract and provoke diseases.
In order to avoid the need for extreme measures, you need to be attentive to the child’s health. Do not self-medicate, spend more time in the fresh air, playing outdoor games and harden your throat.
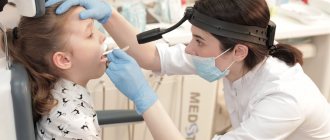
Modern diagnostic methods (endoscopic examination of the ear, nose and throat by an ENT doctor)
The gold standard for diagnosis (and the only correct one) is an endoscopic examination of the nasopharynx by an ENT doctor with good skills and experience working with children from birth. An endoscopic examination is an examination using a video camera, with additional powerful lighting and magnification and display on a television screen, on which both the doctor and the child’s parents will clearly see not only all the structures of the nose, but also the nasopharynx with the mouths of the auditory tubes and adenoid vegetations. In this case, the doctor will evaluate the degree of their increase, inflammation of the mucous membrane, the nature of the discharge, the presence and size of the respiratory lumen. The examination is carried out with a special children's nozzle - a tube less than 3 millimeters in diameter, the examination is non-contact, absolutely painless, does not require special preparation (the ENT doctor only drips vasoconstrictor drops in an age-appropriate dosage before the examination) and has no contraindications and is used in children from birth.
Of course, with such a diagnosis, digital examination is not required.
It is very important that during an endoscopic examination of the ears, such a significant complication as exudative otitis (accumulation of fluid behind a healthy, non-inflamed eardrum) will not be missed. Thanks to good lighting and magnification, the eardrum is transparent during endoscopic examination, so the liquid and air bubbles behind it are clearly visible. Whereas when examined in the usual way, the eardrum, if it is not inflamed, reflects the light of a flashlight and looks gray and opaque, the liquid behind it cannot be seen.
Comparative characteristics of traditional examination of ENT organs and endoscopic examination of ENT organs
| Criteria | Traditional ENT examination | Endoscopic examination of ENT organs |
| Price | Low inspection costs due to the use of tools and a reflector | High cost due to the use of expensive equipment |
| Painless | The contact method can be unpleasant due to the instrumental expansion of the entrance to the nose for examination; the use of an ear mirror is also contact. Digital examination is traumatic and can be painful | The method is non-contact, painless, as nozzles of less than 3 mm are used. in diameter |
| Diagnostic reliability | The examination is superficial, the structures of the nose are examined only in the anterior sections, the nasopharynx is inaccessible for inspection, the adenoids and the mouths of the auditory tubes are not visible, it is impossible to assess the condition of the middle ear behind a healthy eardrum | The reliability of diagnosis of adenoiditis, adenoid hypertrophy, and complications in ENT organs is 100%. All structures of the nose, nasopharynx, ear and throat are examined on a screen with additional magnification and lighting. A diagnostic error has been ruled out. |
| Accuracy of the diagnosis | The diagnosis is presumptive | Reliable diagnosis with assessment of possible risks and complications |
| Purpose of treatment | Overdiagnosis, high probability of prescribing antibacterial therapy “just in case” | Prescribing adequate therapy |
| Assessment of dynamics during treatment | Assessment of only external signs and symptoms (presence of runny nose, cough, etc.) | Assessment of both the dynamics of symptoms and mucus and size of the adenoids, development or relief of complications. |
| Recommendations for adenoid removal | It is possible to prescribe removal of adenoids if they can be preserved and monitored. | Appointment of adenoid removal only if there are indications for removal and an objective assessment of the lack of effect of treatment. |
| Who can carry out diagnostics | Pediatrician, ENT doctor with any experience and qualifications | ENT doctor with practical skills and experience in endoscopic examination of ENT organs in children from birth. |
Laboratory diagnostic methods (the goal is to clarify the cause of chronic adenoiditis and/or adenoid hypertrophy)
To establish the cause of enlarged adenoids, as a rule, a detailed blood test is prescribed, a nasal smear for cytology (cellular composition of nasal discharge), blood for total immunoglobulin E (to exclude an allergic nature or allergic background), feces for worm eggs and scraping for enterobiasis ( adenoids often enlarge due to helminthic lesions), a PCR test for the Epstein bar virus is possible (if mononucleosis is suspected)
Symptoms of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy
- Frequent lingering runny nose
- Nasal congestion, up to complete absence of nasal breathing
- As a result of the previous symptom, the child often breathes with his mouth open during the day or during sleep
- Cough, including dry cough at night (due to mucus draining down the back of the throat)
- Snoring while sleeping
- Decreased attention and fatigue due to lack of oxygen through nasal breathing
Is it possible to “give up” on these symptoms?
Even the uncomplicated form of chronic adenoiditis cannot be ignored; oxygen starvation, which develops against the background of difficulty in nasal breathing or breathing through the mouth, is manifested by a decrease in memory, perseverance, attention, and learning ability. The child becomes irritable, capricious, and gets tired quickly. The immune system is under constant stress of chronic inflammation, as a result of which a symptom of natural immunodeficiency appears, due to the depletion of the cellular elements of the immune system, and the child becomes weakened and often ill. With a large degree of hypertrophy, the facial skeleton may change, the so-called “adenoid” type of face is formed with an elongated lower part of the skeleton, a change in the bite, and a slightly open mouth.
In addition, we are afraid of the formation of complications
Complications of chronic adenoiditis and adenoid hypertrophy:
- Acute otitis media
- Exudative otitis (so-called “silent” otitis, when in the absence of pain hearing loss occurs due to the accumulation of fluid behind the eardrum)
- Persistent conductive hearing loss
- Frequent sore throats
- Tracheitis, bronchitis
- Sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sinusitis