Modern people have a fast pace of life, everyone has a lot of things to do, meetings, and obligations. Therefore, most of us tend to ignore minor symptoms such as an aching tooth, pain when biting, or reddening of the gums. As a result: tooth inflammation, pain, discomfort, postponed meetings and rescheduled plans.
Symptoms of tooth inflammation
Inflammation is the body's response to bacterial attack. Tissues begin to produce immune cells, signaling the hematopoietic organs that more white blood cells are needed. As a result, the vessels dilate, and the place where the microbes have penetrated swells and turns red. Nerve endings connect the pain syndrome so that we react as quickly as possible.
How to cope with pain?
Toothache is always a good reason to see a doctor; it’s worth taking the time to avoid complications!
If professional dental care is not possible, first aid is to relieve pain and minimize inflammation.
Analgesics of various effects used in dentistry - tempalgin, ketorol, nurofen; standard dosage regimen - 1-2 tablets every 4 hours; The effect of the drugs begins within the first 15 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours.
Main features
- Pain
In each case it can manifest itself differently. Sometimes it is pain when biting, sometimes it is continuous. It may get worse at night and subside with meals. It can radiate to the temple, ear, even nose. Being whiny or harsh.
- Redness
It may or may not be visible. This is a symptom that is more often detected by a doctor.
- Edema
Any inflammation is accompanied by swelling, but we cannot always determine this.
- Temperature increase
This doesn’t always happen, but fever is a sign of inflammation, so in this case you definitely shouldn’t put off going to the dentist.
- Tumor
This is also a dangerous signal; you need to see a doctor urgently.
If a tooth is inflamed and hurts, temporary measures will not help; you need a full diagnosis and treatment in a clinic. The alternative is tooth loss due to an advanced process.
Why might this happen?
The reasons are obvious:
- Dental nerves are sensitive to cold.
- Prolonged exposure to wind on an unprotected face.
- Lack of headwear in cold weather.
- General hypothermia of the body.
Possible provoking factors should also be highlighted
- Development of caries.
- Tooth chips and injuries.
- Tooth infection.
- The use of low-quality fillings in dental treatment.
- Poor quality prosthetics.
Causes
Accurate diagnosis is important for a positive treatment outcome. It is this that allows you to determine why the tooth is inflamed. There are 3 diseases hidden under the general term.
Pulpitis
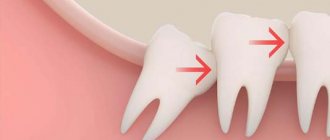
Microbes penetrate through the dentin layer to the neurovascular bundle - the pulp. People call it a nerve. Usually, this happens with deep caries. The pulp is penetrated by nerve endings. The pain is often acute and difficult to endure. But sometimes it is not strong, periodic. We ignore it and the inflammation becomes chronic, destroying the pulp. A small bun makes a huge difference:
- produces secondary dentin, therefore, although the height of the teeth changes throughout life, they do not disappear completely;
- participates in tissue metabolic processes;
- conducts nerve impulses.
When the pulp dies, the tooth is said to become “dead.” Such teeth are quickly destroyed.
To treat pulpitis in dentistry, therapeutic and surgical methods are used. In the first case, medications are placed into the tooth cavity and closed with a temporary filling. After some time, the tampon with the medicine is removed and the tooth is filled. This method does not always help relieve inflammation inside the tooth.
If the process has gone far, the pulp or part of it is removed and then a permanent filling is placed.
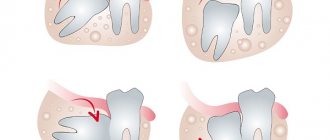
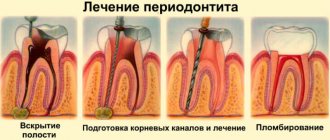
Periodontitis
Under the crown of the tooth there is connective tissue - periodontium. As a result of injury or poor treatment, microbes penetrate there, causing inflammation of the tooth root - periodontitis.
.
There is an apical form, when only the apex is affected, and a marginal form, when all the tissue around the root is infected.
Symptoms of periodontitis:
- pain while eating or when jaws touch;
- feeling that the tooth stands out from the row (has become taller);
- temperature increase;
- tissue redness;
- tooth mobility;
- discharge of pus.
Periodontitis is an insidious enemy. Often the disease occurs without symptoms. It can only be suspected when the signs of the disease become pronounced: roots are exposed, gums bleed, pus is released, bone tissue decreases.
Treatment depends on the type of periodontitis and severity:
- Therapeutic method
The doctor opens access to the root canals, removes part or all of the pulp, and installs drainage to drain the pus. After a few days, the drainage is removed, the canals and tooth are processed and filled. It is recommended to place a crown on such a tooth.
- Surgical method
They resort to it if fibrosis has developed or there are granulomas.
Dentist:
- Cuts off the root tip
- Removes 1 root in multi-rooted teeth
- Amputates the root but leaves the crown intact
- Removes a tooth
- Performs separation (cuts the tooth in half, cleans it and puts it back together)
A course of antimicrobial tablets helps relieve inflammation inside the tooth.
Periodontitis
Periodontium is the fibers that hold the tooth in its socket. Plaque allows bacteria from it to penetrate into the periodontium and begin to rapidly multiply, forming a periodontal pocket. From the pocket, it is easy for them to get under the crown of the tooth and cause an inflammatory process there.
Before treating tooth inflammation under the crown, periodontal pockets are curetted, freeing the surface from tartar and plaque. Then they begin other manipulations: getting rid of caries, splinting teeth. Often, for periodontitis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The inflammation must be stopped so that the tooth does not have to be removed.
The best treatment is prevention
Many patients are interested in whether it is possible to get a cold in their teeth if nothing bad has happened before under the same circumstances? It is possible if you have caries, but you did not cure it in time, and as a result, due to hypothermia, inflammation begins and the nerve hurts greatly. From this it becomes clear that it was caries that served as the root cause of subsequent inflammation, and if it had been cured, then a walk in the cold would not have brought any unpleasant surprises.
Pay closer attention to the health of your teeth, brush them thoroughly twice a day and do not forget to use dental floss and mouthwash. All these measures will help you avoid caries and visit the dentist less often, limiting yourself only to routine examinations.
It is important to take care of your health and choose the right clothes based on weather conditions. Severe hypothermia can cause serious illness.
Here are some simple tips to prevent colds in your teeth or facial nerve:
- Dress according to the weather; if it’s winter, don’t forget about warm clothes. Take care of gloves, a scarf and a warm hat, even if you leave the car for a short time. Sometimes a short stay in the cold wind is enough and a visit to the dentist becomes inevitable;
- Do not ignore even small manifestations of caries; a few unpleasant minutes in the dental chair are better than excruciating, incessant pain from a cold nerve. Do not skip preventive examinations with your doctor;
- A responsible attitude to oral hygiene can save you from many possible dental problems and save a lot of money on dental services;
- You can also get inflammation of the dental nerve in the summer when you are in a strong draft, near a working air conditioner or in a cold wind.
Do not forget that sometimes you need to have your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque and tartar, which can cause caries.
What is dangerous about severe inflammation of tooth tissue?
If measures are not taken in time, the inflammatory process can lead to:
- to the formation of granulomas, cysts, abscesses;
- pulp death;
- loosening of teeth;
- removal or loss of teeth;
- spread of infection to the jaw bone (flux);
- development of general diseases, including myocardial infarction.
It is very important to start treating tooth inflammation on time, and even better, to prevent it. Many clinics provide services for the treatment of dental inflammation. It is worth choosing one that has gained a lot of experience, has its own diagnostic base, and provides guarantees for the doctor’s work.
Possible complications and diagnosis
If the disease is not treated properly, very serious complications soon develop: osteomyelitis (purulent inflammation of bone tissue, provoking its necrosis), phlegmon (a diffuse purulent process that affects nearby tissues and requires immediate surgical intervention), sepsis (a general infection of the body, often ending in the death of the patient ). Each of these conditions requires emergency medical care and long, painstaking treatment. Therefore, it is better not to let the situation lead to complications and contact a dentist at the first signs of an inflammatory process.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will need to conduct a differential diagnosis using instrumental diagnostic methods (radiography, CT). This disease is similar in symptoms to acute periodontitis, acute inflammation of the salivary glands, lymphadenitis, and osteomyelitis. Therefore, in order to prescribe adequate treatment, it will be necessary to exclude these conditions and accurately determine the cause of the patient’s poor health.
What to do if a tooth becomes inflamed?
It is clear that it is better to consult a dentist. What if the doctor is far away, you are at the dacha, it’s night and there is no one to leave the children with? You can try to relieve the pain yourself, using what you have at hand. The World Wide Web is full of tips on how to relieve tooth inflammation at home.
Folk remedies recommend:
- Gargling with herbal decoctions. Sage, chamomile, calendula are suitable. It is important that the broth is not too hot or cold. The optimal temperature is 50-60 degrees.
- Applications from clove oil, eucalyptus, propolis tincture. Be careful with tinctures, alcohol can burn the mucous membranes.
- Solutions of salt and soda help wash away food debris and relieve irritation. A drop of iodine in the solution will perform a disinfecting function.
If there are no herbs and it is unclear what to rinse with, there is a modern life hack. Mouthwashes contain antimicrobial agents and herbal extracts. They will cope no worse than infusions and decoctions.
Important! A sick tooth should not be heated. Avoid heating pads, bags of hot sand, and salt.
But a cold compress can relieve swelling and reduce discomfort.
If you have painkillers in your medicine cabinet, don’t delay taking them. The pain is exhausting and makes it difficult to concentrate. It’s better to relieve the pain and think about the next steps.
Remember, taking a pill does not fix the problem. Knowing how to relieve pain is useful, but only a qualified dentist can find the cause and eliminate it.
Medicines
Ledocaine, Ketanov, Indomethacin - first aid against pain from an inflamed tooth nerve.
You can name several of the most popular medications that are used as an anesthetic for inflammation of the dental nerve:
- Ledocaine is a very well-known local anesthetic used in various fields of medicine. To anesthetize the inflamed nerve, apply the drug (gel) to a cotton swab and apply to the affected area for fifteen minutes. If you bought the drug in the form of a spray, then spray about 20 mg on the aching tooth, repeat the procedure every hour and a half, the maximum dose per day is 20 procedures. Before starting treatment with Ledocaine, read the instructions, especially the “Contraindications” section.
- Ketanov , usually widely used in tablet form. Do not exceed the daily dose of 5 pcs. and do not take the drug for more than one week. The greatest effect is when taken before meals. Much superior to the usual Analgin and Indomethacin. The action lasts up to eight hours. There are a number of contraindications.
- Indomethacin is a good pain reliever, taken three times a day; if the effect is not sufficiently pronounced, the dose can be increased to 50 mg. It is better to use after meals and wash down with milk. With prolonged use, exacerbations of chronic diseases are possible. It is advisable to read the instructions carefully before use.
All these drugs will help relieve attacks of severe pain, but do not forget that only a visit to the dental office can relieve you of the disease itself and help avoid possible complications.
Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Stages of the procedure
Simple extirpation is carried out using forceps, consisting of cheeks, a handle, and a lock. It is performed if the coronal part is well preserved and there are no various complications. Incisors and canines on the upper jaw are removed with straight forceps, on the lower jaw - curved at an angle of 90 degrees. S-shaped instruments are used to extract premolars and molars.
Removing an upper wisdom tooth is easier than on the lower jaw, since it has an even, small root, so a simple operation is performed if there are no complications. The lower jaw bone is denser and more massive, and the root part of the figure eight is complex.
A simple extraction consists of several steps:
- local anesthesia;
- antiseptic treatment;
- application of forceps followed by advancement of the cheeks under the gums and fixation;
- rocking, dislocation and extraction of a dental unit from the socket.
Complex extirpation requires the use of several different instruments, takes a longer time, injures nearby tissues, is dangerous for complications, and the rehabilitation process lasts longer. Pain relief during tooth extraction, especially eights, can be general. The surgeon uses a scalpel or laser, drill, elevator, excavator, and other instruments.
Step-by-step complex removal:
- local or general anesthesia;
- antiseptic treatment;
- dissection of the gums, separation of the flap from dental and bone tissues;
- if necessary, drilling or cutting off part of the bone, dividing the root into several fragments;
- extraction of a dental unit in whole or in parts;
- bleeding stop;
- application of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- suturing the gum.
To stitch soft tissues, self-absorbing or non-absorbable threads are used, which are removed after 7-10 days.