Tooth removal – represents the removal of the pulp (popularly the removal of a nerve). Pulp is a bundle of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings and loose connective tissue that fill the tooth cavity and nourish it from the inside. Thanks to the pulp, the process of blood supply and mineralization of the tooth occurs. When the pulp is removed, these processes will not occur.
On average, a tooth with a nerve “lives” longer than a pulpless one. The dentist’s task is to save the pulp, if possible, because removing the nerve is a necessary measure of dental treatment. As an option, the patient is offered a more loyal solution - to preserve the nerve in the tooth and seal it, and in case of pain, depulpate it. Depulping a tooth allows you to save the tooth, but has some negative consequences:
- removal of the pulp deprives the tooth of mineralization and proper blood supply, which shortens its “life”;
- Tooth enamel becomes more fragile and fades, and the strength of the tooth decreases.
Depending on the damage to the pulp, the dentist decides on its complete or partial amputation. There are cases when you have to deal with advanced inflammatory processes that lead to severe destruction, when the nerve cannot be saved - the nerve must be removed.
Some patients try to avoid the depulpation procedure, preferring to endure the pain and/or take painkillers. This should not be done! In such cases, pulpitis can become chronic without any special manifestations - asymptomatic. And due to provoking factors, a purulent abscess may occur, which threatens the development of periodontitis.
Why is pulp needed?
Pulp is a soft connective tissue that fills the internal cavity of the tooth. It ensures the supply of essential nutrients. The pulp contains many nerve endings, as well as blood and lymphatic vessels. This is where the perception of various sensations occurs. And pain too.
The pulp performs a plastic function, participating in the formation of dentin. And also protective, which consists in the disposal of dead cells, the formation of tertiary dentin and the synthesis of immunoglobulins. We are interested in its sensory function, which can be carried out thanks to a fairly large number of nerve fibers.
Removing the nerves of the front teeth: what to pay attention to
A beautiful snow-white smile always attracts attention and encourages communication. That is why during preventive examinations you should pay special attention to the health of the front teeth, which are located on the so-called. "smile lines"
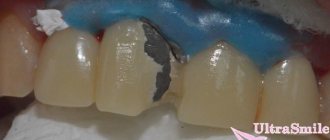
Removing the nerves of the front teeth is not a technically difficult procedure; it is comparable in complexity to similar operations on other teeth. In this case, it should be taken into account that a pulpless tooth becomes a “dead” tooth - without receiving the necessary elements, it darkens and becomes fragile over time. Naturally, in this case it will be necessary to restore the beauty of the dentition over time.
Aesthetic dentistry at the Eurodent clinic offers several options for restoring the appearance of teeth:
- Teeth whitening (including pulpless teeth)
- Installation of veneers (lumineers, ultra-veneers);
- Artistic restoration of teeth;
- Installation of crowns (metal-ceramics, zirconium oxide).
In order to avoid the unpleasant consequences of removing the nerves of the front teeth, you should undergo regular preventive examinations by the dentist. The specialist will be able to notice “problems” before the appearance of alarming symptoms and eliminate them without any problems.
In order to find out how much it costs to remove a nerve in a tooth , you can come for a free consultation at the Eurodent clinic.
With us you can undergo high-quality diagnostics and receive qualified dental care. Based on: 19 votes
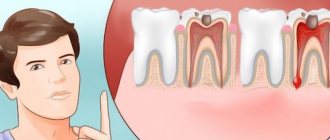
Pulpitis and causes of pain
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the internal soft tissues of the tooth, namely the pulp. The cause of inflammation is usually infection. It is expressed, in most cases, by acute throbbing pain and increased sensitivity.
The tooth cavity is initially closed and sterile. If its integrity is violated, penetration and spread of infection occurs.
Causes of pulpitis:
- Caries;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth, trauma. Violation of integrity may lead to infection;
- Low level dental care. Insufficient experience of the attending physician or poor-quality materials can cause inflammation in the soft tissues of the tooth;
- Unprofessional prosthetics, in particular incorrect grinding of the tooth;
- Retrograde infection in the case of osteomyelitis, sinusitis and other diseases;
- Inflammation of the gums;
- Blood poisoning.
In what cases are the nerve and pulp removed?
- Pulpitis and spread of carious destruction;
- Periodontitis;
- Several carious cavities at once or one, but large carious cavity;
- Mechanical trauma to the tooth (impact, chipped tooth, bleeding from the roots).
Of course, if there is an opportunity to keep the tooth “alive” and leave the nerves and pulp, the doctor will certainly take advantage of it. However, with pulpitis or severe damage, there is one difficulty: there are no 100% methods that would cure pulp inflammation. That is, if once it becomes inflamed, then with a high probability it will be an irreversible process. Of course, if you looked into a tooth with a microscope, you could accurately determine whether the pulp can be cured, or whether it is easier to remove it - but the problem is that you cannot look at a living patient under a microscope, and dentists are not pathologists after all. Therefore, to avoid risk, the pulp is almost always removed.
Also, in some cases, the pulp is removed before prosthetics.
- especially if the original, natural tooth has been severely damaged. In addition, when using metal-ceramic prosthetics, most of the tooth is still filed down, and during this process, the nerve can be damaged - so it is also easier and more reliable to remove.
How does pulpitis manifest?
As a rule, this is a sharp, throbbing pain, quite intense at night. Intensifies when exposed to high or low temperatures. As well as sour, salty or sweet foods. Pressure on the tooth also causes pain. There may be bad breath caused by actively reproducing bacteria. The pain usually spreads to neighboring teeth and even to the other jaw.
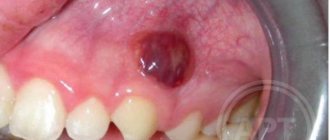
Sometimes soft tissue swelling occurs and the cheek swells. This is how flux manifests itself, which signals the occurrence of purulent processes.
Do not neglect visiting a doctor. After all, pulpitis is not just toothache. It can lead to many serious complications, ranging from tooth loss to blood poisoning.
Signs of tooth pulpitis
It is divided into acute and chronic phases.
The acute stage of pulpitis is characterized by:
- throbbing, sharp pain;
- External irritants can cause pain: temperature changes, cold or hot food, poor quality dental procedures, touching a sore tooth;
The chronic stage is characterized by:
moderate pain that occurs only with temperature changes, cold, or biting on a sore tooth. Increased tooth sensitivity occurs. Often a fistula also forms, with purulent contents that will periodically come out of the formed hole in the gum.
Other symptoms of the disease: headache, sleep disturbances, fever, loss of appetite.
It happens that the cause of tooth pain can be inflammation of the trigeminal nerve or facial nerve.
Surgical
Sometimes inflammation of the dental nerve requires depulpation. In this case, the inflamed pulp is removed, cleaned and then filled with special preparations. The result of the filling is checked using an x-ray. A temporary filling is installed. And after a few days, if no complications arise, a permanent filling is installed.
Modern medicine has various options for anesthesia. Therefore, this procedure will be comfortable and painless.
In some cases, when significant tooth decay has occurred, it will be necessary to remove it.
Why does a dead tooth hurt?
It is logical that a dead tooth, that is, one from which the nerve has been removed, should not feel anything, much less hurt. However, patients often complain of toothache after tooth depulpation. With proper removal, a pulpless tooth cannot hurt; after removal of the nerve, pain can occur in the border structures: jaw bones, soft tissues, neighboring teeth, because the nerves remain there, and it is they that sometimes ache for several days, as they are “concerned” with the surgical intervention. However, if the pain does not stop, you need to consult a dentist; perhaps the nerve was not completely removed, or the pain is caused by some other reason - only a specialist can determine this.
A tooth is a very complex structure, and in this case the saying “Measure twice, cut once” fully reflects the essence of dental treatment!
Help at home
Acute toothache requires immediate contact with a dental clinic. And home treatments are in no way a substitute for visiting a doctor. They should be used only if the patient is outside the city and there are no medical facilities nearby. Or at night, when you need to wait several hours before seeing a doctor.
First of all, the patient should be offered anti-inflammatory drugs. They also have analgesic and antipyretic effects. Among them are Solpadeine, Nimesulide, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and their analogues.
Traditional methods of treatment include rinsing with soda solution or chamomile infusion. They have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect and will help slightly relieve pain.
It is worth remembering that these methods have a temporary effect. They are not curative and do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Therefore, you should not delay contacting a specialist. This will help avoid serious complications and tooth loss.
How many nerves are there in a tooth?
Different teeth differ from each other not only in their location in the oral cavity, shape and functions (chewing, incisor, canine), but also in their internal structure, number of roots and canals. The deeper a tooth is in the mouth, the more canals and roots it has, and most of them are in the teeth of the upper jaw.
But the number of nerves located inside a tooth may not depend on the number of canals and roots - for example, in the same tooth, different people may have one single nerve, or two, or even three (mostly again, in the far teeth, seven, six and eight). All of them are visible only during the X-ray procedure - that is why, before treating caries or, especially, pulpitis, an X-ray of the tooth
is mandatory. The doctor needs to know how many nerves there are in a particular tooth, and how badly they are damaged; depending on this, a decision will be made about their removal or treatment.
Removing the nerve of a tooth is a procedure that most dentists try to avoid until the last minute. However, it is not always possible to preserve the nerve and pulp, and here’s why.
How are permanent teeth different from molars?
The most obvious difference is the number of teeth. A person has 28-30 molars, but only 20 primary teeth. There is a difference in the size of the crowns and even the roots of the teeth. According to dentists, baby teeth are smaller than molars. This is explained by the fact that children have a much smaller jaw than any adult. Consequently, it is not able to accommodate teeth the size of molars.
The thickness of dentin and enamel also differs significantly. In baby teeth they are much thinner. But if the dentin and enamel of primary teeth are inferior in thickness to molars, then in the case of pulp volume, it is the non-permanent teeth that take precedence. An interesting fact is that it is not necessary to visit a dentist to remove a baby tooth. But if we are talking about removing a molar incisor, you cannot do without the help of a qualified dentist. After all, this process takes much longer and is characterized by pronounced pain, increased body temperature, and slight bleeding from the gums.
Stages of treatment
Diagnostics. Before removing the nerve, the dentist takes x-rays. The image allows you to assess the condition, number and structure of the root canals, decide on the need to remove the nerve, and plan the procedure.
Anesthesia. For pain relief, conduction anesthesia is used (injection is performed). In case of severe inflammation and severe pain, local anesthesia at the injection site can be additionally used.
Preparation of the working field. After opening the hard tissues, the tooth must be protected from saliva containing bacteria getting inside. To do this, the working field is isolated with latex strips (cofferdam). During further treatment, this insulation protects the mucous membranes from heating by polymerization lamps.
Processing of hard tissues. Performed after injuries, carious lesions, destruction, etc. The damaged tissue is removed, and the dentist creates an opening in the tooth to access the pulp. During treatment, the tooth is cooled with an air-water mixture to prevent overheating of its tissues. After removing the affected tissue, the walls of the pulp chamber are treated in such a way as to increase the reliability of subsequent filling.
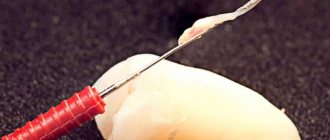
Nerve removal. Performed with a pulp extractor. This is a dental instrument that looks like a needle with small teeth. A pulp extractor is placed in the canal, the nerve is wound around it and removed. This is a disposable tool. In some cases, instruments for cutting pulp tissue can be used instead.
Root canal treatment. Measuring their length, cleaning, treating with an active antiseptic. Needed to remove residual pulp and other particles.
Installation of a temporary filling. Performed as an intermediate stage of treatment. A permanent filling is not placed immediately so that the dentist has the opportunity to check the condition of the root canals during the next visit, before permanent filling or crown installation.
Taking a control shot. It is necessary to make sure that the canals are properly processed and completely sealed.
Contraindications
Doctors at the SDent aesthetic dentistry center collect all data about the patient’s condition before starting treatment. In the health questionnaire, the patient notes the characteristics of his body, and the doctor conducts a survey. Planned nerve removal is not performed if:
- high blood pressure, hypertensive crisis;
- first, third trimester of pregnancy (provided there is no acute pain);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes and facial skin;
- acute respiratory and viral diseases, etc.