July 18, 2011
Fluoride is found in water, foods, and even soil in the form of minerals called fluorite and fluorapatite. However, most often a person encounters industrially produced fluoride compounds, which are added to a variety of products to protect teeth.
However, fluoride doesn't just save teeth. Fluorine compounds are included in some blood substitutes because they are harmless to the body and have a good ability to dissolve oxygen and other gases. Other organofluorine compounds are found in artificial heart valves.
Why is it needed?
The main role of fluoride in maintaining human health is maintaining the health of tooth enamel
and
preventing caries
.
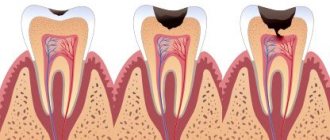
Bacteria that live in the mouth feed on sugars in food and produce acid that erodes enamel. Fluoride prevents this destruction by preserving minerals in the enamel. It is able to accumulate in already damaged areas of enamel and strengthens it - this process is called remineralization
. Together with calcium and phosphorus, fluoride also protects bones from the development of osteoporosis. Fluoride also helps the body absorb iron.
What is fluoride?
Fluorine is a chemical element widespread in nature, compounds of which are found in the earth’s crust, volcanic gases, thermal and artesian waters. It is part of plant tissues and is present in the bones of animals and humans. In terms of oral health, fluoride compounds are effective in protecting teeth from tooth decay.
Tooth enamel is constantly subject to demineralization and remineralization. During demineralization, mineral components are washed out from the structure of the enamel or other hard tissue of the tooth. A significant decrease in their concentration leads to tooth decay. On the contrary, during the remineralization process, fluoride ions penetrate the hard tissues of the tooth, and the balance of minerals in the enamel is restored.
As it turns out?
Fluoride can enter the body through topical use
of toothpastes, rinses and special dental preparations containing it.
They are applied directly to the teeth and are actively absorbed by the enamel. It is especially important to use such drugs in young children – during the period of growth and formation of permanent teeth. They are also needed by adults - with the development of caries, smokers, lovers of sweets and those for whom dentists perform dental restoration, as well as implantation of implants or installation of crowns and bridges. But fluoride can also be obtained through food
- from foods rich in it or through
drinking water
. It is absorbed in the digestive tract, enters the bloodstream and is absorbed by the tissues of teeth and bones. People receive most of their fluoride from water and about 20 percent from food.
Impact on general health
Caries is the most obvious, but by no means the only dental problem. Bacterial plaque that forms on the surface of teeth can also cause gum disease. Unfortunately, many people do not pay enough attention to the health of their gums - and completely in vain, because it significantly affects their overall health. With periodontal diseases, bacteria can spread from the oral cavity through the bloodstream to other organs and tissues, which often causes atherosclerosis, the development of cardiovascular diseases and stroke.
What if it's not enough?
The main signs of fluoride deficiency in the body are the active development caries
.
of periodontal disease
appear - inflammation and destruction of the gum tissue around the tooth.
This disease is caused by the activity of harmful microorganisms living in the oral cavity, which is usually suppressed by fluoride. Also, with a lack of fluoride, bone tissue begins to deteriorate - osteoporosis
.
However, if you consume large amounts of fluoride-containing products and products, over time, a change in the color of the enamel may occur - fluorosis
. And in more serious cases, there is a decrease in mobility and pain in the joints - skeletal fluorosis.
Maximum permissible concentration of fluorine in water
The permissible fluorine content in drinking water (depending on climate) is 0.5-1 mg/l. At higher temperatures, the fluoride concentration should be lower, since the volume of water consumed under these conditions increases. According to Russian SanPin 2.1.4.1074-01, the maximum permissible fluorine content in water should not exceed 1.5 mg/l.
Compared to other countries, this standard is too high and can have a detrimental effect on the human body. Fluoride has no characteristic color, smell or taste, so it is impossible to determine its amount in water yourself. To accurately determine the concentration of fluoride, it is necessary to conduct a water examination in laboratory conditions.
Excess fluoride in water
Review of the characteristics of water with a high fluorine content, determination of impurity standards, harmful effects on humans and household appliances
- Impurity standards
- Types of fluoridated water
- Harm from water with high fluoride content
- Summary
Fluorine is a light yellow gas, distinguished by its toxic properties and extremely pungent odor.
At the same time, fluorine is an important microelement necessary for the formation of bones and teeth.
This substance cannot be detected organoleptically (by taste and appearance) - fluorine does not affect the taste and smell in any way, and also does not change the appearance of water.
Level of fluoride impurities in water
Fluoride-containing substances are almost always added to tap water. But there are cases when the natural concentration in water exceeds permissible standards. In this situation, the amount of this microelement is artificially reduced.
The maximum permissible concentration of fluoride in water was established in 1994 by decision of an expert committee of the World Health Organization.
This rate is now 0.5-1 milligrams per liter and depends on the climate.
In equatorial countries with the hottest climates, where people need to drink more water, this figure is 0.5 milligrams per liter. As you move towards colder areas, the maximum permissible concentration in water increases.
In the coldest countries, where drinking water consumption is low, the concentration of fluoride should be the highest - 1 milligram per liter. In the United States, the fluoride standard in water ranges from 0.7 to 1.5 milligrams per liter.
The maximum permissible concentration in the world is set at 1.5 milligrams per liter.
Types of fluoridated water
Water containing fluoride is classified according to the method of fluoridation.
There are three such methods in total.
- Sodium fluoride (chemical formula – NaF). This substance was the first to be used to enrich water with fluorine.
It is this that is now considered the basis on which calculations are made regarding the content standards in water. Sodium fluoride is used in white crystals or powder form. It is the most expensive of all fluorine-containing substances, but very convenient to use. Sodium fluoride is most often used in small public utilities.
- Fluorosilicic acid (chemical formula H2SiF6).
This is an inexpensive liquid substance that is formed during the production of phosphate fertilizers. It is used in concentrations approximately equal to 23-25 percent. The only drawback is the expensive transportation of this substance, which is complicated by a large amount of water.
- Sodium fluorosilicate (Na2SiF6). Inexpensive powder or small, barely visible crystals. When used in mass quantities, it is the most popular substance, since it is much easier to transport than acid.
All three substances are highly soluble, safe to use and relatively inexpensive.
For comparison, natural concentrations of this substance are very high.
In groundwater the amount of fluoride can reach 67 milligrams per liter, in sea waters - 1.2 - 1.4 milligrams per liter. In surface waters this number is very small - only 0.1 milligrams per liter. Fluoride is also found in food products, such as fish and tea.
Causes of deficiency
Several factors or a combination of them can trigger the development of fluoride deficiency:
- drinking water with insufficient fluoride content;
- nutritional supplements containing magnesium and calcium;
- metabolic disease;
- poor nutrition.
Element characteristics
Fluorine is a chemical with a pungent odor and a strong oxidizing agent, like all halogens. Under normal conditions it has the appearance of a light yellow gas. Translated from Greek, its name means “harm,” which reflects the toxic properties of the element. Fluorine is even more harmful than lead.
It accumulates in the ground as a result of volcanic activity. A large amount of fluorine is contained in one of the most popular ornamental minerals - sparkling fluorite, which is also used in metallurgy, optics, the chemical industry and in the manufacture of glazes for ceramic products.
Fluoride is present in many foods, such as onions, fish, lentils, wine, and (in greatest quantities) regular water.
Fluoride in water: benefits and harms
The effect of fluoride on the body
Fluorine is an element that is found everywhere: in air, water, soil, and also in the bones of a living organism. Back in 1931, it was discovered that excess fluoride in water contributes to dental disease. Then it was decided to purify the water from fluoride, but another problem arose - the lack of fluoride began to cause dental caries. Scientists have looked into this issue and found that the fluoride content in drinking water is less than 0.5 mg per liter, which is too low, which contributes to the development of caries, especially in those areas where fluoride is insignificant.
A sufficient amount is a fluorine content of 1 to 1.5 mg/l. But there are areas where there is a lot of this fluorine both in water and in the air, especially in places where aluminum is mined.
Aluminum smelters release fluoride into the air, polluting the environment.
The difference between the benefits and harms of fluoride is so small that most researchers oppose water fluoridation.
On the other hand, fluoride supporters argue that it is thanks to fluoride that adults and children get rid of tooth decay. In fact, both are true, so it would be wise to stick to the middle ground.
Scientists came to the conclusion that 10 years ago, water fluoridation made sense, since there was little fluoride and only drinking water contained this element, so people really needed it.
Today the picture has changed. A developed network of industrial enterprises has greatly increased the content of this element in both air, water, and soil.
There are areas where literally everything is poisoned with fluoride, however, there are places where there is not enough of it.
Fluoride in drinking water
The fluoride content in drinking water in Russia, depending on the region, can range from 0.01 to 11 mg per liter. Thus, a large amount of it was discovered in the Moscow, Tambov, Tver regions, in western Siberia, in the Urals and in regions where aluminum mining is intensified.
Also, the fluoride content in one region can vary significantly. For example, increased fluoride levels in the Moscow region are observed in the Odintsovo district, Kolomenskoye, Zhukovsky, Ramenskoye and Zelenograd. However, in other areas it may be much less than normal.
It is important to know that there is much more fluorine in groundwater than in surface water. Therefore, if you live in an area where there is little fluoride, but drink water from an artesian well, you risk oversaturating your body with this element.
An excess of fluoride leads to the development of many diseases.
Fluorine is a dangerous element. To avoid many problems, you should treat it with caution. First, check what region you live in and what kind of water you drink. This is especially important for people who like to drink bottled water. It is necessary to carefully study the label of such water, since it may contain much more fluoride than in tap water.
The daily fluoride intake for an adult is no more than 2-3 mg.
Typically, 2/3 of the daily dose of fluoride is supplied with water. Therefore, you need to be very careful when drinking water.
Harm of fluoride
It is impossible to determine the presence of fluoride by sensation, since it has no taste, no smell, no color. Its presence can only be determined in the laboratory. To do this, you need to either do a water test or find out the data from the utility service.
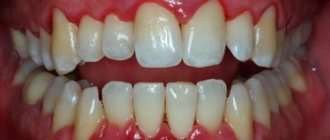
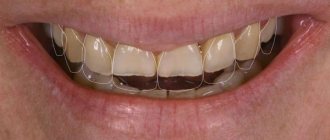
Excess fluoride causes many diseases. First of all, this is the damage of teeth by fluoride, which is called fluorosis.
It causes changes in the color and shape of teeth, the direction of their growth.
Fluorosis has several stages and can appear in the form of pretty streaks and stains on the teeth.
First, individual lesions appear, then brown spots and enamel erosions appear, and the enamel seems to melt. As the disease progresses, a complete absence of enamel can even be observed on the teeth. The last stage is tooth decay. Such dental lesions are often observed in regions with fluoride content in water exceeding 5 mg/l.
Unfortunately, such teeth cannot be restored. As a result, the entire body suffers.
For the first time, the terrible truth about fluoride was revealed to the world by American nutritionist Paul Chappius Bragg. He wrote that “...fluorine is one of the most poisonous substances known to mankind.” He argued that "...selling this poison is big business for the aluminum smelters and nuclear industry."
Fluoride was first added to toothpaste in the 40s in the USA.
The program on mineralization of teeth with fluoride was written in the USSR in the 60s.
Due to the increasing incidence of fluorosis and damage to internal organs, many European countries have abandoned toothpastes containing fluoride. 14 Nobel laureates have become ardent opponents of water fluoridation.
In the United States, 40% of children suffer from fluorosis, but despite this, only 38 out of 50 states have abandoned fluoride.
Excess fluoride salts accumulate over the years in bones and tissues, causing osteochondrosis and sarcoma (cancer), and harming the digestive system. Leads to coarsening of the joints and their immobility. A person has difficulty moving, may experience chronic fatigue, muscle weakness, and cannot regain strength after rest. Fluoride is also a neurotoxin and can cause Alzheimer's disease.
And often people don't even realize that all these problems are related to fluoride.
The human body tries to protect itself by excreting fluoride in the urine, but does not always cope with its excess. Increased doses of fluoride pull magnesium from the body and calcium from the bones.
Therefore, it leads to their calcification, and calcium settles in the muscles, lungs and kidneys.
Fluoride in products
Food contains a lot of fluoride in tea, fish and seafood. Most contain fluoride ranging from 0.2 to 0.3 mg. Fish can contain from 5 to 15 mg. It is also found in whole milk.
Krill meat contains very large and dangerous amounts of fluoride. 1 kg of raw mass contains 2 g of this element, and boiled mass contains approximately 750 mg.
For comparison, the permissible fluoride content in 1 liter of wine is 5 mg. The fluorine content in tea depends on the ability of the tea to absorb fluoride from the soil by the tea bush itself, on fertilizers, and on the time of collection. The more brewed tea is infused, the more its fluoride content increases.
It all depends on where and under what conditions the tea was grown and what fertilizers it was treated with. Very often, tea is treated with fluoride-containing pesticides, which it absorbs. Accordingly, by brewing such tea, we will obtain a fairly high fluoride content.
Fluoride for teeth
The use of fluoride toothpaste, if the paste is not swallowed, can harm or help only the teeth, but not the entire body as a whole.
You only need to use a small pea. It is not advisable to use fluoride-containing pastes for pregnant women and preschool children.
If fluorine in water exceeds one, it is not recommended to use fluoride-containing pastes.
Adults do not need fluoride, nor do adolescents over the age of 16, since they already have formed tooth enamel.
Fluoride should be used with caution in children under 3-4 years of age. Prevention and restoration of enamel can be carried out without fluoride. To do this, you need to brush your teeth properly, use modern products that contain elements that make up tooth enamel - calcium and phosphorus.
List of toothpastes without fluoride
In Russian stores, toothpastes with fluoride and calcium are mostly found on sale.
But if you look hard enough, you can find toothpastes without fluoride. Thus, the domestic toothpaste deserves attention, which has received recognition for the fact that it contains no harmful substances.
Another good toothpaste from the same manufacturer does not contain fluoride - this is “SPLAT-MAXIMUM”, “SPLAT JUICY SET”, children’s toothpaste “SPLAT JUNIOR”.
The line of toothpastes without fluoride is also complemented by toothpastes “ROCS FOR ADULTS”, “ROCS – PRO BABY” for children, “ASEPTA SENSITIVE” from the Nevskaya Cosmetics company.
From the line of imported pastes, one can note such pastes as “PRESIDENT BABY” gel and “PRESIDENT UNIQUE” paste made in Italy, “WELEDA” - calendula gel made in Germany.
But most of these pastes have some disadvantages - the presence of SLS, parabens and other chemicals, which are also not good for the body.
Considering all these pros and cons, I chose for myself organic toothpastes without fluoride, sold in the iHerb online store.
They do not contain harmful substances and are completely natural. To enhance the effect, I also use organic herbal rinses. I especially liked a teeth rinse like PerioBrite from the manufacturer Nature's Answer. It contains coenzyme Q10, chlorophyll, folic acid and 25 plant extracts. It contains no SLS, artificial sweeteners, parabens, preservatives, alcohol or antiseptics that kill beneficial oral microflora.
I tried it with mint and cinnamon. I liked both. Using these organic toothpastes and rinses for two years has significantly improved my oral health, so I decided to buy them on an ongoing basis, and I recommend it to you too!
Did you like the article? Share with friends via social networks. To always keep abreast of new articles on the Women's World website, subscribe to the News Feed. To search for other articles, use the site map.
Methods for purifying water from fluoride
There are several common methods for purifying water from fluoride compounds.
Reverse osmosis method
The principle of the method is to force water through a thin membrane, the pore diameter of which corresponds to the size of the atoms. Thanks to these pores, only water molecules pass through the membrane and other impurities in the form of viruses, bacteria, heavy metals, and organic molecules responsible for the unpleasant taste and smell of water are retained. The output is absolutely pure water, suitable even for the preparation of physiological fluids and injections. This purification technology is also used by bottled water manufacturers.
Filtration using organic bulk material
The method is based on the chemical interaction of organic bulk material with fluorine anion. Such materials are calcium phosphate, magnesium oxide and granular fine aluminum oxide.
Filtration using sorbent materials
The mechanism of this purification method lies in the ability of materials to sorption of fluorinated compounds from water. Such sorbents are ion exchange resins with a certain selectivity towards the fluorine anion. In addition, bone meal, modified zeolites, and activated carbons are used.
Electrocoagulation method
Water purification is carried out as a result of obtaining highly active aluminum hydroxyl in the process of electrolytic dissolution of anodes made of metallic aluminum, as well as its alloys. Due to low productivity, this method is not widely used.
Ultrafiltration
This method involves the separation of fluorine particles and water molecules. Given the larger size of fluoride molecules compared to water molecules, moving through a dense membrane, fluorides accumulate on the surface, and water molecules pass through the filter. This technology allows you to remove about 90% of fluorides.
Method for purifying water from fluoride using ultraviolet light
Water with excess fluoride content is irradiated with ultraviolet rays of a specific wavelength, or bactericidal wavelength. The range of this length is 200-400 nm. The main advantage of ultraviolet disinfection is the ability to disinfect water without changing its physical and chemical properties, as well as its high environmental friendliness.