From this article you will learn:
- the best types of basal implants,
- reviews on basal implantation in Moscow,
- options for fixed dentures, price 2021,
- forum of patients and implantologists.
Basal dental implantation is a method that involves installing dental implants into the deeper basal layer of the jaw bone tissue, which is particularly dense and not subject to atrophy. Thanks to this (even in the case of a significant lack of bone volume), there is no need for bone grafting. In addition, you can get teeth in one day, because... Fixed prosthetics are performed already on the 2nd day after surgery.
Implantation without bone grafting and such early prosthetics become possible thanks to the special design of the implants and their fixation in a denser basal bone. Basal implants are produced under the brands “ROOTT” (Switzerland), “Ihde Dental” or “Oneway Biomed” (Switzerland). They are distinguished from classic dental implants by the presence of a non-removable abutment, the special nature of the thread, the length of the implant, and the presence of a long polished neck.
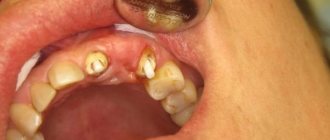
Basal implantation: photo
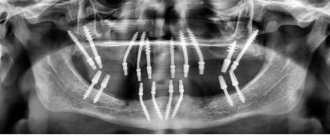
In Fig. 3 you can see the differences between basal dental implantation and the All-on-4 technique, which uses the classic type of implants. The picture clearly shows that with basal implantation, the chewing load is distributed more evenly over a larger number of implants, while a bridge with only 4 implants has overhanging consoles in the area of 6 chewing teeth (which can lead to overload of the lateral implants). In turn, a bridge on basal implants no longer has overhanging consoles.
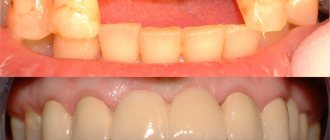
Basal dental implantation: before and after photos
- Clinical case No. 1 - the patient has complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw, and during the surgical stage of implantation, 11 basal implants were installed. Photo after (Fig. 5) - shows the appearance of the teeth after the stage of permanent prosthetics with a fixed bridge made of zirconium dioxide.
- Clinical case No. 2 – the patient also has a complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw. In Fig. 7-8 we see the stage of permanent prosthetics with a fixed metal-ceramic bridge. The patient was very pleased with the aesthetic result obtained.
Important: we specifically cited more complex clinical cases at the beginning of the article, but basal implantation can be used not only in cases of complete absence of teeth. We can successfully use this method in cases of partial absence of teeth, when the patient is missing 3 or more teeth (in a row). But if only 1-2 teeth are missing, you will only be advised to install classic implants.
More before and after photos at the end of the article.
Differences between installing basal and classic implants –
To understand where implants are installed using different implantation methods, look at the anatomy of the bone tissue of the jaws (Fig. 9-10). The bone tissue of the jaw is heterogeneous in its density. The roots of your own teeth are located in the softer spongy bone of the alveolar processes of the jaws. Spongy bone is very porous, and due to its lower density, it is most susceptible to atrophy - especially in areas where teeth have been removed.
Classical implants are installed precisely in the spongy layers of bone, and that is why a sufficient volume of spongy bone tissue of the alveolar process is very important for such implants. But the installation of basal implants occurs in deeper and denser layers of bone. This bone is called basal, and it is practically not subject to atrophy even in the complete absence of teeth.
Some models of basal implants have a very wide diameter of threads, due to which, firstly, they are well fixed in the deep layers of the bone, and secondly, they also receive the so-called bicortical fixation. The latter means that the edges of the threads will be adjacent to the very hard cortical layer of bone from the inside, which covers the jaw from the outside on all sides.
Important: precisely because the working part of these implants simultaneously has both basal and bicortical types of fixation, it provides all the main advantages of basal-type implants, for example, the absence of the need for bone grafting or the possibility of immediate prosthetics.
Why did basal implantation take root in Russia?
While Julier was introducing his implants, the best minds were successfully creating and developing techniques for building bone tissue. it was so fast that very soon there was no longer any need to fix the artificial root into the deep tissues. Juliet's technique turned out to be of no use to anyone and was no longer used.
Probably, from this moment on, basal implantation would forever remain only on the pages of textbooks for implantologists. But the Iron Curtain and doctors began to popularize this technique among millions of potential patients. They are not in modern dentistry and for the first time they learned that a lost tooth can be restored using implantation. Moreover, Juliet’s method turned out to be easy to advertise.
Thus, residents of Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and Eastern Europe became the main consumers of this service and still remain in favor of advertising basal implantation.
Types of implants for basal implantation –
There are only a few manufacturers of basal implants in the world, and only two of them are represented in Russia. The first company is Trate AG (Switzerland), which produces Roott-basal and Roott-compressive implants. The second main manufacturer is the Swiss company Ihde Dental AG, which produces basal-type implants under the BCS® and KOS® brands (in the Russian market, these implants are sold under the Oneway Biomed brand).
Today there are 2 main types of basal implants. They differ from each other in the features of fixation of the subgingival part of the implant in the bone tissue. Please note that although type 2 implants will be called “compression”, in essence they also belong to basal ones.
- “Classic” basal implants (Fig. 11) –
the working part of these implants has a pronounced thread diameter.
This thread ensures reliable fixation of the implant not only due to the basal bone itself, but also due to the bicortical fixation mechanism. The latter means that after screwing the implant into the bone, the edges of the threads will be almost closely adjacent to the hard cortical layers of the bone. The combination of implant fixation due to both the basal bone and the bicortical type of fixation leads to the fact that the implants receive high primary stability immediately after their installation in the bone. Thanks to these features, Roott-basal and BCS® implants (Fig. 8) can be used without bone grafting, even with significant bone deficiency at the implantation site.
- Compression implants (Fig. 12) –
examples of compression-type basal implants are “Roott-compressive” and KOS®.
If basal-type implants are installed only in the basal bone, then the working part of the compression implants will be fixed simultaneously in both the basal and cancellous layers of the bone. Another feature of these implants is the presence of a compression thread, which, when the implant is screwed in, seals the bone surrounding the implant. The latter quality contributes to obtaining very high primary stability. This type of implant can be used without bone grafting if the patient has moderate bone atrophy. In addition, these implants can be installed in very narrow alveolar ridges of the jaw (minimum values 2.5-3.0 mm).
- Compression implants with Multi-unit abutments –
These include Roott implants of the “Compressive M” and “Compressive MS” series.
Please note that all previous types of basal and compression implants have abutments intended only for cement fixation of fixed dentures. In turn, Roott implants of the Compressive M and MS series have non-removable multi-unit abutments, which are designed for screw fixation of dentures. Multi-unit abutments are the gold standard for prosthetics of edentulous jaws with fixed dentures on implants. Because, in fact, it is very important to be able to carry out periodic professional hygiene of the prosthesis outside the oral cavity. And to do this you just need to unscrew the screws. In addition, in acrylic and composite types of fixed dentures, artificial teeth gradually wear out, which will require replacing artificial teeth every 6-7 years and relining the denture base (artificial pink gum).Multi-unit abutments allow you to remove the prosthesis at any time and reline it (including replacing artificial teeth) and immediately install it back. Therefore, of course, Roott implants of the Compressive M and MS series are the best option for complete absence of teeth. Although more expensive.
Basal implantation: overview video
In the first two videos you can see clinical cases, including the stage of prosthetics and the appearance of the prostheses. In two other videos, we showed exactly how the surgical stage of installing basal implants takes place (without taking much time and with minimal trauma to the bone tissue).
Surgical installation of basal type implants –
Features of the technique
The use of basal implantation is justified when it is necessary to restore missing teeth in the shortest possible time - within 3 days, with a significant lack of jawbone volume, without the use of a bone plate. This method involves the implantation of specially designed implants into the cortical and basal (deep) layers of the jaw bone tissue. These layers are not subject to atrophy due to their special density. This implantation technique is called one-stage, which allows prosthetics to be performed already on the third day after its implementation. To make it clearer what basal implantation is, it is necessary to consider the structure of the maxillary bone tissue and the features of implant installation.
Prosthetics on basal implants (with complete absence of teeth) –
Thus, during the 1st stage of basal implantation (surgical stage), from 8 to 12 implants will be installed in your jaw. The difference in the number of implants depends on many parameters: the size of the jaw, the bone density, as well as the diameter and length of the implants that we can use in a particular patient. The number of implants does not affect the cost of basal implantation, and you will have exactly as many of them installed as needed.
And the next stage is prosthetics. But you will need to choose the option of prosthetics (a type of fixed denture) before the operation. In most cases, prosthetics are carried out in 2 stages. At the first stage, only a temporary fixed denture will be made for you, which very often can also be called “adaptive”. It will be fixed to your implants already 2-3 days after the operation. You can use this temporary prosthesis for about 2 years, after which it will need to be replaced with a permanent one.
Options for temporary (adaptive) fixed prostheses:
- Metal-plastic prosthesis (with cement fixation) - such a prosthesis will be made of acrylic plastic and have a simple metal frame inside. Such a prosthesis will only be cement-retained, which will mean that it cannot be removed from the implants without damage and the need for complete replacement. Together with the installation of 8-12 basal or compression implants, such a prosthesis will cost only 265,000 rubles.
- A prosthesis on a titanium frame (with cement fixation) - in fact, it will also be metal-plastic, but the metal frame of the prosthesis will be made of titanium.
The titanium frame makes your denture much stronger, which is very important for patients with well-defined masticatory muscles and large jaws, patients with bruxism (hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles), who have an increased risk of breaking dentures on a conventional metal frame. In addition, thanks to the titanium frame, the prosthesis will be much lighter than when the frame is made of ordinary metal, for example, a nickel-chromium alloy. In turn, this will make it much easier for you to get used to the prosthesis. The price for basal dental implantation (including the installation of 8-12 implants and a temporary fixed prosthesis on a titanium frame) will be 295,000 rubles. - A prosthesis on a titanium frame (with screw fixation) is exactly the case when Roott implants of the Compressive M and MS series, having non-removable Multi-unit abutments, will be used. This type of abutment provides screw fixation of a fixed dental prosthesis to the implants, and the prosthesis itself will be made on a durable and lightweight titanium frame. The cost of a prosthesis and installation of 8-12 implants will be 325,000 rubles.
Important: the prices listed include the full cost of the turnkey work, including all necessary x-rays, anesthesia, post-operative examinations, prosthesis correction procedures, as well as a guarantee. The warranty for any type of temporary fixed prosthesis is 1 year, but their service life is usually 2 years (up to a maximum of 3 years).
What is implantation
In the majority, people generalize methods for restoring teeth under the concept of “prosthetics.” This is not entirely correct. Implantation is a stage of reconstruction, which is the installation of an artificial root (implant), onto which a crown or solid prosthesis is subsequently attached.
Implantation is performed with an estimated period of 5 to 30 years. The service life of the product has the main influence on when the next dental implantation will be required, but there are a number of other factors that can shorten not the warranty period, but the actual service life.
In order to extend the period of wearing artificial roots, it is necessary to pay special attention to preparing for the procedure, to choose the right clinic/doctor and the products themselves, before carrying out the mini-operation to install the pins.
Stage of permanent prosthetics –
After 2-3 years of wearing a temporary prosthesis, it will be necessary to replace it with a permanent one. Moreover, if you initially had a cement fixation of a temporary prosthesis, then changing it to a screw one will not be possible at the stage of permanent prosthetics. Screw-fixed prostheses are a priori better, but they are much more labor-intensive to manufacture and therefore are always more expensive.
Options for permanent fixed dentures:
- Metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis - it is very important that the metal frame of such a prosthesis is not cast, but made by milling. This option of prosthetics allows you to achieve quite decent aesthetics if high-quality ceramic mass is used and the clinic has a good dental technician. The price for a bridge prosthesis with cement fixation will be from 230,000 rubles, with screw fixation – 270,000 rubles.
- Ceramic composite prosthesis (option 1) - the prosthesis will be made on an individually milled titanium frame, but the frame will be simplified (there will be no stump for each artificial tooth). Artificial teeth and artificial gums will be made from a mixture of acrylic plastic and ceramic microparticles. This is a good option for a prosthesis, which will cost about 250,000 rubles if it is cemented, and 320,000 rubles if it is screwed.
- Ceramic composite prosthesis (option 2) - it will be made on an individually milled premium titanium frame (where the titanium beam will have a stump for each artificial tooth). The frame will be lined with ceramic composite on the outside, and the artificial teeth will also be made of ceramic composite. This is an excellent option for a prosthesis, which, subject to cement fixation, costs about 400,000 rubles, and subject to screw fixation – 420,000 rubles. We draw your attention to the fact that if the difference in cost is not critical for you, then when choosing a ceramic-composite prosthesis, it is better to choose a manufacturing option where the titanium beam will have a stump for each artificial tooth. This ensures high strength of fixation of artificial teeth and reduces the risk of their breakage, which is quite possible in the absence of stumps.
- Zirconium dioxide bridge – such a prosthesis will have an individually milled zirconium frame inside, coated on the outside with denture ceramics. Artificial teeth will also be made of zirconium dioxide. This is a very aesthetic version of the prosthesis, which will look especially advantageous on the upper jaw. Its cost, subject to cement fixation, will be about 320,000 rubles, subject to screw fixation - about 370,000 rubles.
Important features of zirconia bridges:
If it is planned to make artificial crowns also from zirconium dioxide in a bridge made of zirconium dioxide, then it is not recommended to make them in the form of single crowns. It is better to make them in three blocks, similar to bridges (a block of 6 front teeth + two blocks for the chewing groups of teeth). Thanks to this, there will be only 3 seams between the artificial teeth, which will protect the prosthesis from darkening and odor.
But there are also zirconia bridges where single E-max ceramic crowns are used as artificial teeth. Such prostheses look impressively beautiful, but only for the first time. In the future, such dentures quickly darken in the area between the teeth (where the seams between the artificial crowns are located), and also begin to smell not very pleasant. But it will not be possible to solve this problem by making blocks of several crowns, because Emax crowns can only be single.
Well, the last recommendation is that if you are planning basal implantation on two jaws at once, then a zirconium dioxide bridge can be made only on 1 jaw (preferably on the upper one), and on the second - only a ceramic composite prosthesis. If you make zirconium dioxide on two jaws at once, then after 2-3 years it will end with the breakage of one of the dentures.
Option for permanent prosthetics IMMEDIATELY after surgery –
Patient reviews of basal implantation are often positive for only one reason - this type of implantation allows us to avoid the stage of temporary prosthetics and makes it possible to immediately install a permanent fixed denture. With other methods of implantation and prosthetics in the complete absence of teeth (for example, All-on-4 or All-on-6), we have the opportunity to first make only a temporary fixed prosthesis.
In this case, the prosthesis is made from a ceramic composite (a combination of acrylic plastic and ceramic microparticles), from which both artificial teeth and pink artificial gums will be made. Inside, such a prosthesis will have an individually milled titanium frame (CAD/CAM technology). In addition, such a prosthesis will require screw fixation on Multi-unit abutments. The cost of this prosthetic option will be 580,000 rubles.
Those. in this case, we save approximately 65,000 rubles on the cost of a temporary fixed prosthesis, and immediately receive a permanent screw-fixed prosthesis. Moreover, this also turns out to be much cheaper than the All-on-4 technique, where the cost of installing implants (taking into account a similar type of permanent fixed prosthesis) will cost no less than 700,000 rubles.
Basal dental implantation: patient reviews
How effective is basal dental implantation? Patient reviews most often mention the following 3 points.
Firstly, the surgical stage of implantation is quite easy, because the installation of basal implants, as a rule, does not require detachment of mucoperiosteal flaps from the bone. Even older patients tolerate the operation quite easily, and in the postoperative period, as a rule, there is no significant pain, swelling or bruising. The second point is that patients with experience wearing removable dentures especially pay attention to the fact that a completely fixed denture is fixed on implants already in the first 2-3 days after surgery. Moreover, they can immediately start chewing (at first only soft food). Thirdly, basal implantation in the complete absence of teeth is the only technique that allows you to immediately install a permanent fixed prosthesis. It will be made of ceramic composite on a milled titanium beam.
All other alternative methods (for example, All-on-4) initially involve only the stage of temporary prosthetics. If, when installing basal implants, you choose the option of immediate prosthetics with a permanent prosthesis, you save approximately 150,000 rubles (when compared with a similar type of permanent All-on-4 prosthesis). The savings are achieved due to the fact that we save on a temporary fixed prosthesis, which in itself is not cheap. Below we will talk about the disadvantages.
Clinical case No. 3 – complete absence of teeth in the lower jaw. Basal implants with multi-unit abutments were installed. In Fig. In Fig. 18 you can see a fitting of the titanium frame of the future prosthesis, and in Fig. 19 you can see the finished fixed bridge prosthesis (with screw fixation).
Clinical case No. 4 - prosthetics of missing 5-6-7 teeth on the lower jaw with a metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis on three compression implants.
Reliability and durability –
Clinical studies show that in patients who have undergone installation of basal implants, the “survival” rate of implants for 8-10 years is about 98% success in the lower jaw and approximately 95% in the upper jaw. These are quite high figures. It should be clarified that a lower success rate in the lower jaw is natural (including for other implantation techniques).
A higher success rate in the mandible is associated with greater bone density (bone types D1 and D2). The upper jaw consists of softer bone (types D3 and the softest - D4), which is generally not very good for implantation, because The primary stability of implants in soft bone is much worse, which also affects their survival rate.
As for the durability of prostheses, the highest quality options are - 1) a ceramic composite prosthesis, in which the frame is made in the form of an individually milled titanium beam (the beam must have “ledges” for each artificial tooth), 2) a bridge prosthesis made of zirconium dioxide. And of course, prostheses should only have screw fixation to implants, which will allow for better servicing of the prosthesis in the clinic, and also reduce the risk of inflammation around the implants.
Less risk of peri-implantitis and rejection –
The design of basal implants assumes that the implant and abutment are a monolithic unit. This assumes that there is no connection between them (and, accordingly, a microgap), which reduces the risk of bacterial colonization of the microgap and the development of peri-implant. The second important point is that basal implants have a long polished neck, which can additionally be anodized (Fig. 23).
Due to the long neck, the osseointegration zone of the implants (i.e., the zone of fusion of the root part of the implants with the bone) is located deep in the bone. For example, the osseointegration zone of classical implants begins immediately under the mucous membrane. It turns out that anodizing complicates the adhesion of bacteria to the neck of the implant, and the long neck prevents their migration to the osseointegration zone, i.e. where their carving begins (24stoma.ru).
The best implantation option for smokers is
Firstly, when smoking, nicotine affects the blood vessels in the mucous membrane of the gums and the surface layers of the bone, leading to a narrowing of the lumen of these vessels. The consequence of this is a decrease in blood flow, impaired saturation of tissues with oxygen and nutrients, which greatly affects the healing process after surgery. Secondly, smoking leads to the development of dry oral mucosa, which promotes increased growth of pathogenic bacteria.
These two factors greatly increase the risk of developing peri-implantitis in smokers, as well as the risk of implant rejection. According to statistics, the percentage of implant rejection in smokers is 2 times higher than in non-smoking patients. However, the osseointegration zone of basal implants is located in deeper parts of the bone (compared to classical implants), and therefore vasoconstriction in the mucosa and superficial layers of the bone during smoking is no longer so important.
Indications/contraindications
Implantation is carried out exclusively according to indications. The need to install artificial roots is determined by the dentist who examines the patient at the first appointment.
The need for implantation is confirmed in the following indications:
- missing one tooth;
- absence of 2 or more dental organs, with adjacent location;
- absence of the last teeth without the possibility of restoration by other methods;
- complete edentia (congenital pathology characterized by the absence of teeth);
- the presence of reasons preventing the wearing of a removable denture (for example, a gag reflex);
- pain caused by functional occlusion;
- absence of alveolar processes in the upper jaw with concomitant complete absence of teeth;
- anatomical defects that arise as a result of diseases, mechanical effects, as well as as a result of disturbances during intrauterine development or genetic predisposition.
In professional dentistry, the patient is additionally sent for diagnostics to determine contraindications:
- severe diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- malignant oncological diseases;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- blood pathologies (especially poor clotting);
- severe connective tissue diseases;
- open tuberculosis;
- liver/renal failure during exacerbation;
- increased tone of the masticatory muscles in combination with bruxism;
- diabetes mellitus;
- immunodeficiency diseases;
- allergic reaction to painkillers;
- age up to 18 - 22 years (depending on indications);
- addiction to drugs or alcohol.
If a patient undergoes implantation with contraindications, the shelf life of dental implants will be reduced to 1 - 2 months, or even several days. In case of contraindications, 90% of patients experience rejection of the structure with the development of associated complications.
Disadvantages of basal implantation –
Negative reviews of basal dental implantation are also found, and most often these are patients with a large degree of jaw atrophy (loss of bone height). Techniques such as All-on-4 or basal implantation are positioned as “implantation without bone grafting.” This is true, but in this case we are simply obliged to compensate for the lost height of the jaws, and if we do not do this with bone grafting, then the only option left for us is to do this with the artificial gum of a denture.
Thus, with jaw atrophy, a fixed denture will always have an artificial pink gum, the size of which will correspond to the lost bone volume. Some patients remain disappointed by this. Therefore, patients who want to get an ideal aesthetic result are recommended to undergo bone grafting for aesthetic reasons (so that the prosthesis then has as little artificial gum as possible).
Also, sometimes you come across reviews that after basal implantation in the upper jaw, sinusitis may occur. Yes it is possible. But to exactly the same extent as after any other implantation technique, where implants are installed near the maxillary sinuses. In this case, sinusitis is not associated with the basal implantation technique, but with the skills of a particular implant surgeon and his mistake when installing implants.
Other disadvantages are related to patients’ attempts to save money. Choosing cement rather than screw fixation increases the risk of developing inflammation around the implants and the appearance of odor from under the crowns. Choosing cheaper denture options also has its consequences. For example, metal ceramics often chip. And when choosing the option of a ceramic-composite prosthesis, where the titanium bar will not have special stumps for each artificial tooth, it increases the risk of breaking the front teeth in the prosthesis.
I personally had a patient with a ceramic composite denture who complained that his front teeth in the denture were broken. And he was extremely outraged by this. But we showed the patient his card, in which, along with the patient’s signature, there was a note that in addition to mandatory visits to the implantologist (once every 6 months), once every 6-7 years it is necessary to reline the prosthesis and install new artificial teeth. The fact is that artificial teeth made of plastic and ceramic composite tend to gradually wear out.
This happens mainly in the chewing areas, which leads to a gradual increase in the load on the front teeth, and as a result they can simply dislocate from the prosthesis. The patient saw his signature under the recommendations and the conflict was settled, and within a few days the prosthesis was as good as new. Therefore, patient reviews that you can sometimes read about are not always objective.
Medical marketing
You can right now type in the search bar “basal implantation in Moscow” and you will see that in nine out of ten articles it is described as a new progressive European method of effective dental restoration. Search engines can even return the address of the Institute of Basal Dental Implantation in Moscow.
The Julier method is often positioned as inexpensive and giving quick results. This is not stated in scientific articles, but on the websites of dental clinics that offer basal implantation services.
However, you and I know that this technique has existed for more than 30 years and has not been used in European countries for a long time. In addition, the price for basal dental implantation in Moscow remains almost at the same level as the cost of implantation using the traditional method. Patients think that they are saving money, since the Julier method does not require restoring the volume of bone tissue. But this procedure will become inevitable after the basal implant.
All these disadvantages of basal implantation can be learned from the reviews of patients who had to undergo long-term restorative treatment after rejection of the basal implant. As a rule, dental clinics are silent about the disadvantages of basal implantation.
Frequently asked questions about basal implantation –
Above we talked about patient reviews of basal dental implantation, and now we will focus on the most common questions that patients ask.
Timing of prosthetics and diet –
A temporary fixed denture will be fixed on the basal implants already 2-3 days after prosthetics. If we are talking about the option when the patient is immediately fitted with a permanent fixed denture, this option requires more complex manufacturing, and therefore is fixed on the implants only 3-4 days after the operation. Immediately after fixing the denture, you can start chewing with it, but only soft food. Let’s say: you won’t be able to immediately pick up and bite into an apple.
Is it always possible to do without bone grafting?
The basal implantation technique in more than 90% of cases avoids bone grafting, as well as sinus lifting (this is a variant of bone grafting when there is insufficient bone volume in the lateral parts of the upper jaw). Bone grafting may be needed mainly only in cases where patients themselves request it for aesthetic reasons in order to reduce the height of the artificial gum in a fixed denture.
The choice between cement and screw fixation of the prosthesis –
Cement fixation has only 2 advantages. Firstly, it requires less experience and knowledge from doctors, and also makes the production of a prosthesis simpler and less expensive. Secondly – because a fixed denture is fixed on cement, the latter (due to the presence of a certain elasticity coefficient) allows to somewhat compensate for the excessive chewing load.
Disadvantages of cement fixation –
- there may be a violation of the integrity of the cement, the appearance of cracks in it, which will lead to bacterial colonization (this can cause peri-implantitis, the appearance of odor from under the crowns),
- in the process of fixing a fixed denture with cement, the latter can get under the gum (it is not always possible to remove it, and this leads to the development of peri-implantitis),
- It will be impossible to remove the prosthesis from the implants without damaging it (this creates gigantic problems in terms of regular maintenance of the prosthesis).
Advantages of screw fixation - screw fixation using Multi-unit abutments implies a tight connection of the prosthesis to the implants without gaps or cracks, which guarantees the absence of bacterial colonization and reduces the risk of developing peri-implantitis. And most importantly, this makes it possible to easily remove the prosthesis from the implants without damaging it, and just as easily put it in place. The ability to remove the denture is very important for periodic professional cleaning of the denture, as well as when it is necessary to reline acrylic or ceramic composite dentures.
What kind of dental prosthesis care will be needed?
The most vulnerable area of any fixed dentures on implants is their lower surface, which is adjacent to the gum. This is where food debris and bacteria accumulate, and if you don’t take good care of your dentures, tartar can accumulate. You will need to regularly use an oral irrigator (for rinsing) every day, and also use special superfloss to clean the underside of the denture.
However, the denture will require periodic professional cleaning at the dental clinic. This is usually necessary once every 6 months (in patients with poor hygiene - once every 3 months). Of course, such processing can be carried out efficiently only if we have the opportunity to remove the prosthesis from the implants and clean and polish it outside the oral cavity. After which the denture is again fixed to the implants using screws.
In addition, if your denture is made of acrylic or ceramic composite, then these materials tend to gradually wear out. Therefore, once every 7 years or so, we will need to remove the denture and replace worn-out artificial teeth with new ones (and, if necessary, reline the pink artificial gum with plastic).
How difficult is it for a patient to install basal implants?
When we install classic implants, during the operation the implant surgeon is usually forced to make wide incisions, as well as completely or partially detach the gum from the bone. After this, a bone bed is drilled into the bone for each implant, and after screwing in all the implants, sutures are applied. In turn, basal implants are almost always installed without gum detachment (only through a “puncture”) and, accordingly, this does not require sutures.
Transgingival installation of implants (without gum detachment) –
Therefore, basal implantation is often called the terms transgingival implantation, bloodless implantation or sutureless implantation. The severity of the operation is also reduced by the fact that approximately 60% less bone volume is drilled under the basal implants when preparing the bone bed (than when installing classic implants using the All-on-4 technique). Thanks to all this, this type of implantation is well tolerated even by elderly patients.
Pros and cons of basal implantation
There are a number of indications and contraindications for this procedure.
Indications
This type of denture can be recommended taking into account the following indications:
- Pathology of the upper layers of bone tissue.
- A nicotine addiction that is impossible to quit.
- Urgent restoration due to objective needs.
- Severe periodontitis, affecting the stability of certain elements of the jaw row.
- Loss of integrity of supporting organs located under the implants.
- Individual intolerance to materials used in the manufacture of classical bases for securing jaw prostheses.
- Medical contraindications for increasing the volume of the spongy layer of the jaw.
- The absence of more than two teeth in the jaw row or their complete loss.
Contraindications
Factors that prevent basal implantation can be divided into the main ones, as a result of which this type of dentures is completely excluded when:
- Oncology.
- Open tuberculosis, HIV infections.
- Heart failure, complex nervous disorders, immune pathologies.
- Some stages of diabetes.
- Missing one tooth
And minor ones, after elimination of which such prosthetics are possible:
- Pregnancy.
- Temporary mental disorders.
- Progressive arthritis.
In any case, you should inform the dentist about all previous and existing diseases and allergic reactions of the body.
Summary:
For the following groups of patients, basal implantation will be one of the most preferred techniques...
- if you smoke,
- there is a lack of bone volume at the implantation site (and you do not want to undergo bone grafting and especially sinus lift surgery),
- elderly age,
- for women during menopause,
- for osteoporosis,
- if you have hypertension,
- compensated diabetes mellitus.
We have identified patients in a special group who, due to various diseases of the nose, mouth and throat, will have an increased number of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity, which sharply increases the risk of inflammation around the installed implants and their rejection. For these groups of patients, the basal implantation technique is also more suitable -
- for chronic gum inflammation,
- for chronic tonsillitis,
- with irregular oral hygiene,
- dryness of the oral mucosa,
- mouth breathing (chronic nasal congestion).
Recommendations on how to extend the life of an implant
The dental guarantee is not an indicator of the longevity of the implants. If the manufacturer indicates a service life of 20 years or more, then you should rely on this data. The implanted structure can last until the end of your life if you follow the recommendations for its use.
Expert recommendations on how to extend the life of dental implants:
- strict adherence to oral hygiene (brushing teeth twice a day, using mouthwash and special dental floss);
- prevention and treatment of dental diseases at the first signs;
- giving up bad habits (use of narcotic drugs is a categorical contraindication);
- undergoing professional teeth cleaning in dentistry;
- reducing the load on the structure when eating food (it is not advisable to gnaw, constantly chew, eat hard foods, etc.);
- Periodic visits to the dentist for preventive purposes.
The service life of the crowns can also be affected, since when the structure is changed, all its elements are replaced.
A-Medic Dental Clinic provides a guarantee for the installation of implants in accordance with the quality of the products. The specialists of our center have extensive experience in implantation, so we are confident in the work of our implantologists. We offer our patients a choice of implants from the most famous manufacturers at an affordable price.
Basal implantation in Moscow: clinics
It must be said that basal implants are produced in the world by only a few manufacturers. One of them is (Switzerland), which produces the “Roott” line of implants. In addition, there is an implant whose implants are also known under the brand “Oneway Biomed”. In Moscow, only a small number of clinics install basal-type implants, for example:
- Moscow,
- Smile-at-Once Clinic.
The minimum cost for implantation of 1 toothless jaw with 8-12 basal implants ROOTT (including a fixed adaptive prosthesis) will be from 265,000 rubles, and the same with the use of Oneway Biomed implants – from 285,000 rubles. We hope that our article was informative for you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Personal experience as an implant surgeon, 3. American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID), 4. National Library of Medicine (USA), 5. “Dental prosthetics on implants” (Surov O.N. .), 6. https://ihde.com/ and https://trate.com/, 7. https://www.realself.com/.