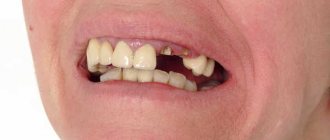
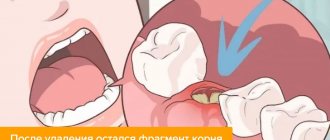
Modern dental clinics provide their patients with such a service as hemisection of the tooth. We are talking about an extremely responsible and technically complex operation. Its result is the removal of the root of a tooth damaged by a cyst or granuloma. Moreover, only one root is amputated. The pathological neoplasm is excised along with it. The remaining roots are kept intact.
Indications
The operation is performed in case of a complicated course of advanced carious process, which has already affected the root of the tooth. The procedure is prescribed in the following clinical cases:
- deep periodontal pockets have formed at the root level;
- pathological changes are observed in the structure of the root of the damaged tooth;
- perforation of the tooth roots occurs during poorly performed endodontic treatment.
The amputation method is most often used to remove the roots of teeth located in the upper jaw.
Hemisection of tooth root
Dentistry Apex-D / Surgical dentistry / Hemisection
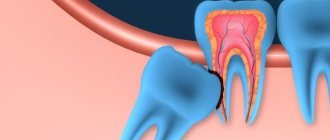
Root hemisection is performed on the teeth of the molar group of the lower jaw, if one of their roots has significant destructive lesions.
This surgical procedure refers to tooth-preserving operations, the essence of which is to remove one of the roots of a multi-rooted tooth along with the adjacent coronal part and inflamed periapical tissues.
The remaining part, not affected by the pathological process and capable of withstanding the functional load, is preserved.
Hemisection of the tooth root allows you to save a living unit in advanced (chronic) forms of the disease, which arose, for example, due to poor-quality endodontic treatment, as a result of which the remaining pathogenic microorganisms continue to multiply, localizing the source of inflammation in the area of the tooth root, while the inflammatory process spreads further, destroying the crown and infecting tissue in the periapical region.
In such cases, traditional methods of treatment do not allow access to the source of infection for proper treatment, so a surgical approach to eliminating the outbreak is considered effective.
In this case, technically the operation can be performed in the following ways:
The first method involves accessing the root through the crown. To do this, the doctor cuts the coronal part to the bifurcation zone (i.e., to the place where the roots begin to diverge). After this, the damaged root is extracted.
The second method is to make an incision from the gum to the bone and peel off the mucoperiosteal flap. Next, a bone fragment is drilled into the root projection to form an operative approach. Through the formed hole, the root is cut off and removed. This technique is also used in case of detection of a cystic formation in the periapical area.
The perihilar cyst is excised through a perforated window, the cavity is thoroughly cleaned of remnants of pathogenic tissue, treated with antiseptic drugs and, depending on the size of the cyst, filled with osteo-replacing material. The flap is then returned to its place and the wound is sutured.
This patchwork technique is also used for tooth root amputation. This procedure also applies to tooth-preserving techniques and differs from hemisection in that only the part of the root affected by the inflammatory process is removed, and the crown is preserved.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Preliminary treatment and filling of healthy root canals is carried out.
Indications for hemisection and root amputation include the following reasons:
- Obstruction of one of the root canals of a molar due to its atypical anatomy, which makes it impossible to treat it with conservative methods
- Diagnosis of cystic formation in the apical region
- Single root fracture
- If the infectious disease is accompanied by a purulent-inflammatory process
- Caries of one of the roots
- Late stage chronic periodontitis
- Deep periodontal pocket in the projection of one of the roots
- Perforation of the root canal wall
Contraindications include:
- Old age of the patient
- Merged roots
- Diabetes
- Diseases of the cardiovascular, circulatory and nervous systems
- Malignant neoplasms
Hemisection of the infected root allows you to preserve the functionality of the tooth for some time and prevent the destructive effects of pathogenic microorganisms on the tissue of the mandibular bone. This helps prevent bone tissue atrophy and maintain favorable conditions for further implantation.
The long-term success of the operation depends on how well the remaining molar roots can withstand mechanical stress as a support for the denture. Such factors include: periodontal condition, root anatomy, possible endodontic problems, and the likelihood of fracture of the preserved root.
The successful prognosis of the operation is facilitated by the maximum possible preservation of the structure of the unit, as well as the replenishment of the required amount of bone tissue at the site of root removal to preserve the original relief of the gingival margin.
Due to the violation of the integrity of the root system, the operated tooth will no longer have its former stability and in order for it to last longer, excessive chewing loads should be avoided.
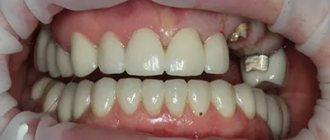
The main advantage of hemisection is that the preserved healthy roots of the tooth can be used as a natural support for the crown and preserve the functionality of the resected molar without compromising the integrity of the dentition.
You can make an appointment at Apex-D Dentistry by calling the administrator at +7 and +7, or filling out an electronic form (the administrator will contact you at the specified phone number and agree on the date and time of the appointment).
How does the procedure work?
Tooth root amputation is a rather complex dental operation, which can only be performed in a dental clinic.
At the first stage, the dentist interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. Since the procedure is carried out under an anesthetic drug, a preliminary test is done to determine the tolerance of the selected anesthetic.
Additionally, to assess the condition of the root, an x-ray of the tooth to be treated is prescribed. If the patient has inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, they are first treated with antiseptic treatment and removal of inflamed or infected tissue.
The root removal procedure consists of several stages:
- Introduction of an anesthetic drug.
- An incision into the gum tissue.
- Detachment of gum tissue to provide access to the root system of the tooth.
- Cutting off the root at the junction with the crown and removing it from the soft tissue.
- Treating the hole with an antiseptic and filling it with a special osteoplastic material (imitation bone tissue).
If the hole is not filled with osteoplastic materials after surgery, then the cavity may become overgrown with gum tissue, which entails the development of infectious and bacterial complications. Sutures are placed on the cut gum.
After the operation, the tooth retains its functionality for many years; in most cases, it is possible to preserve it without the need to install an artificial crown.
Contraindications
This list looks like this:
- serious somatic diseases (diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, etc.);
- the need to preserve root canals;
- obstruction of root canals;
- root fusion;
- bone resorption;
- elderly age.
Along with this, performing root hemisection should not cause damage to adjacent teeth. Another important point is the possibility of allergic reactions in the body. We are talking about the rejection of the artificial material with which the root canal is filled. Such situations are very rare, but they cannot be discounted categorically. Otherwise, the postoperative period will be significantly delayed and will bring serious complications.
Rehabilitation period
After the procedure, the patient may feel pain. Painkillers prescribed by your doctor will help reduce it. It is also necessary to strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations to make the healing process faster, take prescribed medications, and carefully observe oral hygiene. For three days after surgery, it is strictly forbidden to rinse your mouth.
For the first time after surgery, you can eat only soft foods, trying not to injure the damaged area. It will be important to stop smoking tobacco and drinking alcoholic beverages.
It is recommended to exclude baths, saunas, and not take hot baths for several days. If you heat the procedure site, bleeding may begin. If this does happen, it is necessary to apply a cold, wet cloth or ice, which will constrict the blood vessels and quickly stop the bleeding.
Preparation
Formation of a complete clinical picture requires a comprehensive clinical examination. The list of diagnostic procedures prescribed to the patient includes not only a visual examination and oral questioning, but also radiography, orthopantomography, and intraoral imaging. A prerequisite for the preliminary stage is sanitation of the oral cavity, eliminating the possibility of infections getting into the surgical wound.
Upon completion of the sanitation, the selection of instruments used for the operation, antiseptic treatment, and removal of stone deposits from the surface of the operated tooth are carried out. Surgical intervention involves the use of local anesthesia, after which the root part begins to take effect.
Possible complications
Amputation of a tooth root can provoke a number of complications, which are expressed in different symptoms:
- Damage to adjacent teeth.
- Violation of the integrity of soft tissues.
- Inflammatory process.
- Swelling of soft tissues.
- Loss of sensitivity in the operated area of the jaw.
- Increased bleeding.
If there is suppuration in the wound at the operation site, you should immediately consult a doctor. In some situations, it is still necessary to remove the diseased tooth, since it is not always possible to stop the destruction of dental tissue from the inside.
Get a consultation
We will answer all your questions before visiting the clinic!
+7
Online registration
Content
1 The difference between atraumatic tooth extraction and conventional
2 Advantages of atraumatic tooth extraction
3 Indications for atraumatic tooth extraction
4 Stages of atraumatic tooth extraction 4.1 Comprehensive diagnostics
4.2 Preparation of membrane from plasma
4.3 Removal with a piezo scalpel and periotome
4.4 Application of blood plasma membrane
5 Disadvantages of piezosurgery for tooth extraction
6 Dental implantation immediately after extraction
7 Prices for atraumatic tooth extraction
The difference between atraumatic tooth extraction and conventional
Atraumatic tooth extraction involves extraction without forceps or burs. The ligaments are cut off from the dental unit, then segmentation is carried out using microsurgical blades. Subsequent extraction of fragments is easy. The procedure is performed safely, painlessly and comfortably.
The main advantage of gentle tooth extraction is that the healing of the bone hole proceeds much faster and the relief of the gum tissue is preserved. In the process of extracting fragments, the doctor does not affect the bone structures, maintaining the volume of the jaw bone around the hole. All necessary conditions are created for subsequent stable and complete implantation, and soon aesthetic prosthetics. This procedure makes it possible to immediately load the area with prosthetic structures immediately after tooth extraction.
Recommendations for patients in the postoperative period
Persons who have undergone hemisection are recommended:
- avoid any physical activity for 3 days;
- protect yourself from stressful situations and factors that provoke psycho-emotional stress;
- refuse to eat for 2 hours after surgery;
- appear for preventive examinations on the second and fifth days after completion of the operation, undergo an x-ray control procedure.
The average recovery period after surgery is 5 days. Complete healing of damaged tissue occurs after 2.5 weeks, and engraftment of bone material occurs after 5 months.
The procedure for hemisection
Tooth root removal surgery is performed using one of two methods:
- through the crown (the dentist cuts down part of the dental crown and removes the diseased root);
- by exfoliation of the gums (the doctor cuts the gum, peels off a flap of mucoperiosteal tissue and cuts out the damaged root).
The hemisection procedure includes a number of stages:
- examination, cleaning and subsequent filling of root canals that cannot be removed (the filling can be installed either on the day of hemisection or in advance);
- performing local anesthesia in the area of the diseased tooth (if there are certain indications, the patient is operated on under general anesthesia);
- removal of the damaged root and the adjacent part of the crown (or peeling off a flap of mucoperiosteal tissue and cutting down the root);
- filling the formed cavity with osteoplastic material;
- suturing the resulting wound.
The average duration of the procedure is 1.5 hours.
Dental implantation immediately after extraction
The single-stage implantation operation involves installing an artificial root directly into the socket of the extracted tooth. All manipulations can be performed in one visit. This procedure is most in demand when prosthetics are needed in the smile area. The primary goal is to achieve high aesthetics of restorations.
With the help of one-stage implantation, it is possible to significantly reduce the rehabilitation period. It is also possible to fix a temporary prosthesis, allowing the patient to immediately begin the process of chewing food.
Our highly qualified specialists use Straumann and Osstem implants. Healing of Straumann implants occurs within a month, and even a small level of bone will not interfere with installation.
Disadvantages of piezosurgery for tooth extraction
1. The cost of atraumatic tooth extraction can be considered a disadvantage. It is slightly higher than with classical extraction. The cost is made up of professional training, training of a dental surgeon and the use of innovative, expensive equipment. In practice, the safety and reliability of the procedure compensate for the price component.
2. Limited prevalence of the technique. Not all clinics have the necessary equipment and staff training, especially clinics.
Prices for atraumatic tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is simple:
- X-ray images
- Anesthesia
- Removal of a tooth
- Applying and removing sutures
- Postoperative examinations
Price : from 3,000 ₽ to 7,800 ₽
Tooth extraction is complicated
| from 10,000 to 20,00 ₽ |
Author:
Indications for atraumatic tooth extraction
- Destruction of the tooth crown of more than 3/4, due to injury or carious process.
- It is not possible to carry out high-quality treatment or restoration of the tooth.
- Severe crowding, lack of space in the dentition, incorrect position.
- Complication of pulpitis or periodontitis.
- Purulent inflammation around the tooth root, cysts that cannot be treated without surgery.
- Creation of space for implant installation.
Retrograde root canal filling
Indications for retrograde filling:
1. Poorly sealed root canal with phosphate cement, resorcinol-formalin paste or other materials that make re-treatment impossible.
2. Poorly sealed root canal and the presence of a metal object in it: a) stump insert; b) anchor pin; c) fragments of an endodontic instrument.
3. Obliteration of the root canal.
4. Extremely long and curved root canal when conventional endodontic treatment is impossible or unsuccessful.
5. Canals with apical deltas or funnel-shaped expansion.
6. The presence of metal-ceramic or other crowns or fixed structures in combination with the above conditions.
| A root apex resection operation was performed. A control photograph was taken after 3 months. The inflammatory process has been stopped. The tooth is saved! Leaky sealed canals of 12, 11, 21 and 22 teeth. Radicular cyst, core inlay of tooth 12, metal-ceramic crowns. | 2 years after retrograde filling with Trioxident cement. The cavity is filled with newly formed bone tissue. Teeth saved! In most cases, doctors would recommend such teeth to be removed and then made with a removable denture. |
Restrictions on the use of the procedure
The hemisection procedure is not used in some cases when the benefit of the intervention is not comparable to the risk to the patient. The cause of failure may be problems with blood clotting. In addition, individual intolerance to drugs and local anesthesia can become a significant obstacle to performing the operation. It is undesirable to carry out the intervention during periods of exacerbation of chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and chronic heart failure.
An obstacle to intervention may be the anatomical structure of the affected tooth:
- location of the roots in close proximity to the maxillary sinus. In this case, the operation of hemisection of the tooth is fraught with damage to the bone walls of the sinus and the occurrence of an inflammatory process in it (sinusitis);
- a tooth whose roots cannot be separated due to fusion cannot be subjected to hemisection;
- too much destruction of the crown. In this case, after the operation there will be a small part of the organ that cannot cope with the load;
- an organ with too short roots may fall out after hemisection. In this situation, intervention is not recommended.
- deficiency of soft gum tissue at the site of the proposed intervention. They may not be enough to close the resulting wound after the procedure.
Application of the technique in dentistry
The surgical technique is used by specialists in the following cases:
- if surgical treatment is necessary for adolescents. Tooth extraction can negatively affect the formation of the bite;
- hemisection is used to eliminate a tumor located in close proximity to the root. The use of the technique allows you to excise only the pathological area without affecting healthy tissue;
- removal of only one root will solve the problem of treating its fracture and preserve the healthy part of the organ;
- root amputation using hemisection allows you to eliminate long-term infectious inflammation of surrounding tissues, which cannot be treated by other methods;
- surgery may be required to eliminate the purulent focus. If an accumulation of inflammatory fluid has formed in one of the roots, it is not necessary to remove the entire organ to remove it; it is enough to perform a hemisection;
- in some cases, it is impossible to cure the carious process by cleaning and filling all root canals due to their complex anatomical structure. This circumstance especially concerns narrow root canals. In this case, surgical intervention will help eliminate the pathological process - excision of the root and part of the crown;
- hemisection of a tooth is the most gentle way out of a situation when it is necessary to remove a dental instrument stuck in the root canal.