Many parents are still confident that baby teeth do not need the same thorough treatment as permanent teeth - after all, they will still break down and fall out. Unfortunately, this point of view is erroneous and often leads to serious health problems in children. Children, like adults, can also develop various diseases of the teeth and gums, and they must be treated in a timely manner. If you do not treat children's teeth, over time problems with the bite and dental system will arise, and in some cases the general health of the body may be at risk. This is especially true if infants are teething.
Content:
- After caries closure
- After root canal treatment
- After extraction
- After implantation
- After sinus lift
The problems that dentists have to solve can be serious or not so serious.
But any medical intervention must be carried out in accordance with established norms and rules. Only then will the likelihood of complications develop to a minimum. One of the most common unpleasant symptoms after dental treatment is fever. Many patients are confused and do not know what to do when it increases. After all, it is not always clear whether a fever is related to a recent dental course.
Dentists insist that if the temperature rises after dental treatment, patients immediately consult a doctor. Timely receipt of qualified medical care is the most reasonable decision in such situations.
Features of dental treatment in children
Since baby teeth are somewhat different in structure from permanent teeth (they have thinner enamel and dentine layers, a larger pulp chamber, enamel wears out faster, etc.), and also have a relatively short lifespan, dental treatment in children has a number of features. Since the enamel wears off quickly, the filling material is not too hard so that over time the filling does not destroy the walls of the teeth and does not protrude beyond the edges of the tooth, interfering with normal chewing. Typically, glass ionomer cements are used, which are not as hard as photopolymer composites. They contain fluoride ions and therefore have a strengthening effect on dental tissue.
In addition, you need to take into account that caries in children can develop very quickly and spread to other teeth - parents do not always have time to notice the beginning of the process in time, so they have to treat several teeth at once. At the same time, timely detection of the disease guarantees painless dental treatment for children without the use of a drill: if the infection has affected only the enamel, it is possible to carry out remineralization therapy or treat caries using Icon technology, which involves the use of a special composite material that reliably closes and seals the carious cavity. However, it must be taken into account that this technology is not recommended for use in children under 3 years of age and cannot be used for cervical caries.
In cases where the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones is still far away, and the dental tissues are already thoroughly destroyed or the tooth needs to be removed, special children's prosthetics are used using crowns without grinding.
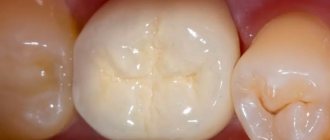
After caries closure
Sooner or later, everyone faces the need to close carious cavities. With caries, the pathological process does not extend beyond the hard tissues. If your health condition worsens after filling, you can assume:
- development of a viral, infectious or bacterial infection not related to a recent medical intervention;
- the addition of complications such as pulpitis, abscess, phlegmon.
Determining the root cause of the problem is actually not difficult. If the sealed molar looks healthy and does not hurt, the gums are not swollen or swollen, and the mucous membranes are not ulcerated, it means that with a 90-95% probability the temperature has not increased due to treatment at the dental center. It’s just that at the time of therapy the patient was already sick, but the symptoms of the disease had not yet manifested themselves or were barely noticeable.
The stress experienced during the operation of the drilling machine can create conditions for the rapid spread of infection. Then, upon coming home, a person will see frightening numbers on the thermometer.
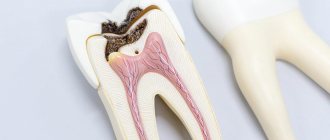
Caries
3673 16 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Caries: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Caries is an infectious lesion of the teeth in which demineralization and softening of the hard tissues of the tooth occurs with the formation of a defect in the form of a cavity. This is the most common disease of the dental system. Caries occurs among all age groups, but more often among adults over 35 years of age, where it accounts for 98-99%.
Causes of caries
In the oral cavity of any person there live a large number of microorganisms that are in balance and actively interact with the human body and with each other. This balance may change briefly under the influence of various factors, for example, after a teeth whitening procedure, but then the balance is restored again. If the body's defenses are reduced, the changes can be more significant and lasting.
Various bacteria, fungi and protozoa live on the oral mucosa, in the ducts of the salivary glands and in saliva, in gingival fluid and oral fluid, but most of them live in dental plaque - up to 90% of all microflora.
Dental plaque is a soft sticky deposit on the surface of teeth containing a large number of microorganisms, their metabolic products, epithelial cells, leukocytes, proteins and lipids of saliva. The formation of dental plaque is a natural process, and in the absence of timely and thorough dental care, it forms within 1-2 days. As a result of structural changes in plaque, dental plaques form quite quickly. Bacteria present in dental plaque and plaques actively “exchange information”, build a large number of connections, and then stick together, forming a microbial biofilm. In a biofilm, microorganisms exchange genetic material, nutrients, and remove metabolic products. The creation of such a biofilm protects bacteria from the body's defense cells and from the action of antibiotics. As a result of the vital activity of microbial biofilm, a large amount of organic acids is formed, under the influence of which demineralization of tooth enamel begins. Small defects form, microorganisms penetrate there, destroying the enamel further, resulting in the formation of a cavity in the tooth - caries.
Carbohydrates serve as food for microorganisms, so eating sweet foods contributes to the development of caries.
In addition, predisposing factors are a decrease in the body's defenses, smoking, poor oral hygiene, and taking antibiotics - all this leads to an imbalance in the oral microflora, resulting in the proliferation of streptococci and lactobacilli, which are responsible for the production of organic acids and the development of caries.
Classification of caries
Doctors classify caries depending on the stage and location of the lesion. The stage of initial caries, in which the process does not extend beyond the enamel-dentin boundary, is called the white or chalky spot stage. This is followed by the stage of dentin caries, in which the disease crosses the enamel-dentin boundary without affecting the pulp, and the stage of cement caries with damage to the exposed surface of the tooth root in the cervical region.
Focal demineralization of enamel is characterized by the appearance of a dark pigmented spot within the enamel and is called the stage of suspended caries.
Based on the location of the cavities, there are 6 classes of the disease:
Class I - cavities localized in the area of grooves on the chewing surface of the teeth (fissures) and natural recesses of the incisors, canines, molars and premolars.
Class II - cavities located on the contact surface of molars and premolars.
Class III - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines without breaking the cutting edge.
Class IV - cavities located on the contact surface of the incisors and canines with a violation of the angle of the crown of the tooth and its cutting edge.
Class V - cavities located in the cervical region of all groups of teeth.
Class VI - cavities located on the cusps of molars and premolars and the cutting edges of incisors and canines.
Symptoms of caries
Symptoms of the disease depend on its stage. A sign of initial caries is a change in the color of the tooth enamel in a limited area and the appearance of a chalky or gray stain, lacking shine - a focus of demineralization. Then an enamel defect develops, and then a cavity. Patients with caries at the stage of cavity formation note increased sensitivity of the tooth to chemical, temperature and mechanical irritants, while the painful sensations disappear immediately after the irritant is eliminated. A defect can be seen on the visible surface of the teeth.
Further, tooth damage spreads to the underlying tissues - to the upper layers of dentin, after which, in the absence of treatment, the process captures the deep layers of dentin and approaches the pulp - soft connective tissue penetrated by blood vessels and nerve plexuses. At this stage, patients also note increased sensitivity to irritants and pain during chewing.
When the dental pulp becomes inflamed – pulpitis – severe toothache begins. If the disease is not treated, the pathological process can spread beyond the tooth into the bone tissue and periodontitis will develop.
Diagnosis of caries
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the oral cavity, examining the mucous membrane, establishes the presence of fillings and the degree of their adherence, the presence of defects in the hard tissues of the teeth, and notes the number of teeth removed. The dentist carefully evaluates the condition of all teeth, determines the density of hard tissues, texture and degree of surface uniformity, checks pain sensitivity, and probes the identified carious cavity. If indicated, radiography is performed.
Which doctors should I contact?
Dentists treat caries.
Treatment of caries
The main goals of caries treatment are to stop the pathological process, restore the shape and function of the affected tooth, prevent the development of complications and restore the aesthetics of the dentition. If the carious lesion is limited to the enamel, then patients may be prescribed deep fluoridation of the hard tissues of the tooth to prevent further development of the process.
If a defect occurs in the hard tissues of the tooth, conservative remineralizing treatment does not have an effect; in this case, the altered tissues are removed and the tooth crown is restored using a filling.
Complications of caries
In almost half of patients aged 35-44 years, there is a need for filling and prosthetics of the affected tooth, and doctors have to resort to tooth extraction in almost a quarter of cases. With late treatment of caries, the pathological process can spread deeper into the dental pulp, and from the infected pulp, inflammation through the tooth canal penetrates further into the bone and under the periosteum of the jaw with the development of inflammation of the periosteum - periostitis or gumboil. Tooth extraction as a result of untimely treatment, which leads to complications, causes deformation of the dentition and can even lead to pathology of the temporomandibular joint.
Dental caries can cause problems with chewing function.
Prevention of caries
To effectively prevent the development of caries, it is necessary, firstly, to prevent the creation in the oral cavity of conditions conducive to the emergence of microbial films and the carious process, and secondly, to increase the caries resistance of dental tissues. The main methods of prevention are regular oral care with proper brushing technology, the use of dental floss, the use of fluoride toothpastes, mouth rinses, reducing sugar consumption and regular dental examinations (once every 6 months).
Sources:
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of “Dental caries” Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014, updated on August 2, 2021.
- A.I. Khavkin, Yu.A. Ippolitov, E.O. Aleshina, O.N. Komarova. Oral microbiota: protective or pathogenic factor? // Issues of practical pediatrics. – 2015. – T. 10. – No. 4. – P. 49-54.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
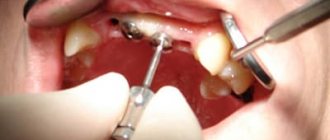
After root canal treatment
Endodontic therapy involves complex manipulations. After it, your health may actually worsen. How long the painful condition will last depends on the degree of damage to the tissues of the oral cavity and the extent of the abnormal process.
Pulpitis itself rarely provokes fever, but its complications - periodontitis, cysts, periostitis, any purulent processes - quite often. Hyperthermia occurs in response to an inflammatory response. In parallel, the following may be observed:
- swollen lymph nodes;
- strong pain;
- swelling of the cheek;
- gum “bump”;
- discharge of purulent masses.
If after endodontic intervention the elevated temperature lasts longer than two to three days, you should definitely consult a doctor. This must be done immediately if the tooth hurts or pus flows.
After extraction
Extracting the root unit is a surgical procedure. It is associated with a violation of the integrity of oral tissues. It is not surprising that the human body reacts so sharply to the treatment.
Normally, after removal, the thermometer can show up to 38.5°C for no longer than three days. It is not advisable to take antipyretics - such tactics can change the course of recovery reactions. However, in some cases, doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to speed up regeneration processes. Some of them not only stop inflammation, but also normalize body temperature. If the doctor told you to use pills, you should do so. Any amateur activity is prohibited here.
In difficult clinical situations, antibiotics are prescribed after extraction. There are patients who are critical of such prescriptions. It seems to them that antibacterial drugs lower the immune system and their use after an ordinary removal of a unit is unjustified.
This attitude towards antibiotics is wrong. They help damaged tissues heal faster and eliminate the development of postoperative complications. Dentists never prescribe them just like that. Therefore, if a specialist issues a prescription after extraction, you need to take its prescription seriously.
Most often, an elevated temperature is recorded after removal:
- "eight";
- incisors, fangs, molars, if the operation was preceded by an advanced purulent process;
- several units at once.
After implantation
Implantation is an operation to implant an artificial titanium root into the bone tissue of the jaw , on top of which, after regeneration is completed, an abutment and crown are fixed. Such treatment is always difficult and traumatic. It is performed under local anesthesia and requires long-term rehabilitation.
Meanwhile, it is implants that make it possible to restore the integrity of the dentition without damaging healthy units. Their installation is not associated with grinding down the “neighbors” or root canal treatment. Implantation is indicated if the tooth is completely destroyed, and even its roots are unsuitable for prosthetics.
Dentists always warn that after installing a titanium base, an elevated temperature may persist for three to five days, and this is normal. Fever indicates the active occurrence of regenerative processes. To avoid possible complications, the patient must take medications prescribed by the implantologist strictly according to schedule.
It is important to understand that the line between normality and pathology is very thin. Fever after implantation can also be a dangerous signal. So, sometimes it indicates rejection of an artificial structure. Then the person feels severe pain in the area of the surgical intervention, observes swollen gums from which pus is released, and constantly feels an unpleasant taste in the mouth. Soon the implant becomes mobile, which indicates its active rejection.
In this case, there is no point in hoping that the situation will normalize on its own. You need to go to the doctor immediately. The sooner the patient visits the doctor who implanted the implant, the higher the chances of stopping further progression of inflammation. If time is lost, the titanium base will most likely have to be removed.
When is fever considered a complication?
The main sign of pathological fever after installation of a dental implant is an increase in temperature above 37.5–38.0 degrees. Lower values are also abnormal if they last longer than three to five days after surgery and are accompanied by such phenomena as:
- persistent swelling of the mucous membranes, which can spread to facial tissues;
- Increasing pain, difficult to relieve with analgesics or unresponsive to drugs;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth, which can be caused by wound suppuration;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes is a sign of a developing infection.
The listed symptoms may indicate the onset of a complication, which is usually associated with the development of an acute inflammatory process in the tissues surrounding the artificial root. This pathology is called “peri-implantitis” and requires the fastest possible intervention by a dentist.
After sinus lift
Speaking about the reasons for the increase in temperature after dental therapy, it is necessary to mention bone grafting. Such an operation sometimes precedes procedures to restore the integrity of the row. The need for it arises if the patient has been walking for a long time with a toothless smile. Then the gums in the areas of damaged teeth begin to “sag.”
This effect is due to atrophy of bone tissue and is due to the fact that certain areas of the jaw do not take part in the process of chewing food. Then, before installing the implant, the doctor performs bone grafting. During this procedure, the gum level is raised by placing a special collagen membrane under the soft tissue. After this, they wait about three to four months until the introduced artificial material takes root. Only after this they proceed to implantation.
The human body does not always react calmly to an established bone sample. In the first days after plastic surgery, ailments often appear. There's nothing wrong with that. The main thing is that the patient takes the medications prescribed by the doctor.
Summarize. If you experience a high fever after dental treatment, do not worry. This is usually a normal reaction to complex interventions. But be careful. The fever should not persist for a long time. You shouldn't guess what's going on in your mouth. If you have the slightest doubt, visit your doctor again. He will tell you how to normalize the situation.
Complications after surgery
Sinus lifting, like other dental surgeries, can be accompanied by a number of complications. The main danger of any adverse outcomes lies in problems with the osteoplastic material and an increase in the duration of treatment. In rare cases, the result of the operation is canceled, and the possibility of repeat bone grafting disappears.
There are the following complications of bone grafting and sinus lifting:
- Bleeding. It occurs in the first hours (sometimes within 24 hours) and indicates the presence of problems with blood clotting. As a rule, a complication appears in the dentist’s office, so it is treated professionally and as quickly as possible. But if the problem has already started at home, then there is no need to try to solve it yourself, because bleeding from the arteries quickly leads to significant blood loss and disruption of life.
- Perforation of the sinus mucosa. Perforation of the protective membrane of the maxillary sinus is a complication specific to sinus lifting, from which no one is immune. The outcome of perforation depends on its size. In some situations, it is necessary to stop the process of bone grafting and completely focus on restoring the integrity of the cavity of the maxillary sinus.
- Infection. This problem occurs on days 2-3 of the rehabilitation period or later. The risk exists until the wound surface heals. The clinical picture of the infectious process includes an increase in temperature, progression of pain and swelling, and the appearance of purulent discharge. If the maxillary sinus becomes infected, then pain in the frontal region of the head is added.
- Displacement of osteoplastic material. Such a complication may be a consequence of the above-mentioned adverse outcomes or occur independently if general recommendations are not followed during the rehabilitation period. In the first weeks after a sinus lift, the patient should not overexert himself physically, fly on airplanes, dive, sneeze and cough with his mouth closed, blow his nose, or drink drinks through a straw.
- Loosening and retraction of the implant (if it was installed). This complication is typical only for those types of bone grafting where one-stage fixation of an artificial root is possible, for example, with a closed sinus lift. Poor implant fixation is rarely the cause of an unfavorable outcome. In most cases, the cause is incorrect placement or filling with osteoplastic material, its displacement or excessive load on the implant during the rehabilitation period.
Complications of bone grafting occur very rarely, since modern technologies can minimize the risk of an unfavorable outcome. Patients are fully examined before surgery, and the dentist carefully plans every step. The occurrence of one or another complication indicates a violation of the technique of performing the operation, the patient’s refusal to follow the doctor’s recommendations, and in rare cases, unforeseen accidents.