Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
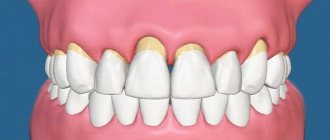
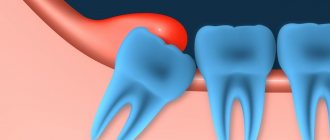
Inflammation of the gums, or periodontitis, is one of the most common dental diseases. This pathology of the oral cavity can occur due to both chronic diseases and local traumatic injuries.
The main symptom of periodontitis is an acute inflammatory process of gum tissue. Lack of treatment can lead to the development of severe forms of the disease, characterized by tooth loss and displacement.
Prevention and treatment of periodontitis at home
The most effective method of treating almost any disease, including periodontitis, is its prevention. There are simple prevention methods that can be used at home. Their use will prevent the occurrence of periodontitis symptoms and avoid the need for drug and surgical treatment.
The main thing that needs to be done to prevent any pathologies of the oral cavity is to strictly follow the principles of dental hygiene:
- brush your teeth twice a day with therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste using a medium-hard brush;
- After a meal, remove leftover food using dental floss.
- a rinse with an antibacterial effect, for example, Asepta based on lemon balm, calendula or St. John's wort extract, has a soothing effect on the gums;
- it is necessary to regularly consume solid and plant foods, ensuring sufficient chewing load on the teeth;
- one of the reasons for the development of periodontitis is a lack of vitamins A, C and B vitamins in the diet. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to take a vitamin complex containing a sufficient amount of these vitamins;
- You should visit your dentist twice a year for preventive teeth cleaning. Timely removal of plaque and tartar will help avoid gum inflammation and further development of pathology.
Ingestion
A peroxide solution is used for oral administration. To prepare it, mix 1 drop of the product with 50 ml of warm water. During the course of treatment, the dosage is increased by adding one drop every day, bringing their number to 10.
The solution should be taken 30 minutes before meals, or 2 hours after. The course of treatment involves taking the drug 3 times a day for 10 days. After this time, take a break for 3 days, and then repeat it all over again.
When treated with hydrogen peroxide, side effects may occur, such as skin reactions, indigestion, nausea. If the listed symptoms do not go away after a few days, further treatment should be abandoned.
Important! Under no circumstances should hydrogen peroxide be taken undiluted, nor should the dosage be exceeded.
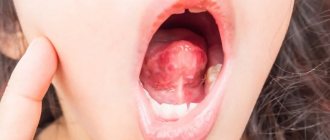
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
Rules for gargling with peroxide
To make the procedure comfortable and safe, you must follow simple rules:
- Treatment should be carried out after meals.
- Before the session, you should rinse your mouth with plain water to remove any remaining food.
- For better rinsing, you should take a sip of the solution into your mouth, throw back your head and, for 10 seconds, treat the back wall of the pharynx and tonsils. Then spit out the solution completely.
- When the solution is finished, rinse your mouth with water with salt and soda, a decoction of chamomile or sage, or regular boiled water will also do.
- After finishing the procedure, do not eat or drink for 30 minutes.
Gargling with peroxide can be hazardous to health if the dilution is incorrect. A “stronger” solution damages the mucous membrane and can do more harm than good, while a weaker one does not have a pronounced therapeutic effect.
Up to contents
Acute and chronic periodontitis: symptoms and treatment
As mentioned, the treatment plan will depend on the severity of the inflammation and how widely it has spread. Periodontitis affecting a few teeth is localized; periodontitis affecting most (or all) teeth is generalized.
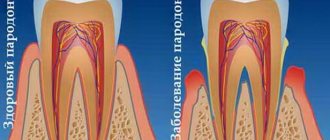
Acute periodontitis, which has pronounced symptoms, occurs less frequently than chronic periodontitis and usually affects one or two teeth. It is often caused by trauma to the tooth or periodontal tissue, or improper installation of a crown or filling. This type of disease often occurs aggressively, causing rapid destruction of bone and muscle tissue.
If the pathology is chronic, then phases of exacerbation are replaced by phases of remission. At the same time, chronic periodontitis slowly and steadily progresses from the initial stage to the severe one. This form of pathology can be caused by both local factors (for example, trauma to the oral cavity) and general ones.
How does acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid manifest?
Patients with acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid complain of a protrusion, “bump” (neoplasm) and/or pain of varying intensity in the anus. The size of the “bump” can range from several millimeters to several centimeters and is often accompanied by swelling of the surrounding tissues (up to the entire circumference of the anal canal). In some patients, the disease proceeds without pain, but most assess the pain as significant or unbearable.
To assess the degree of pain, a special visual analogue scale is used, in which you can independently determine the severity of pain. After all, this is the key point when choosing a treatment method. Surgical treatment will be most effective when the severity of pain is 7 or more points, while for pain up to 4 points, a conservative method of treatment can be considered optimal.
Rice. Visual analogue scale for pain assessment.
Pain usually worsens during bowel movements and/or sitting. The pain and swelling can be severe, even unbearable for several days. The intensity of pain depends on the size of the blood clot and its location in relation to the anal sphincter muscles. In general, manifestations of the disease can persist for several weeks, in exceptional cases longer. Sometimes spontaneous evacuation of a blood clot from a hemorrhoid occurs. This is preceded by necrosis (destruction) of the skin over the thrombus, and the thrombus seems to “fall out” of the node. Externally, this is accompanied by the sensation of a “bursting” ball and the release of a small amount of blood. Usually, after evacuation of the blood clot, the pain and discomfort in the anus gradually decrease. However, necrosis of the mucous membrane above the thrombus does not always end only with the evacuation of the thrombus; necrosis can continue to spread to the hemorrhoid itself and surrounding tissues, which is why this condition requires consultation with a specialist. After acute thrombosis subsides, the patient is most often left with so-called “skin fringes” - excess skin where the thrombosis was. They do not require medical treatment, but may cause cosmetic discomfort.
Professional hygiene for effective treatment of periodontitis
In the vast majority of cases, the development of this disease is associated with insufficient oral hygiene. The periodontal tissues become inflamed due to extensive dental plaque, so the first thing to do to treat periodontitis is a professional cleaning.
This procedure includes the following steps:
- removal of dental plaque
- polishing the tooth surface
- treating the tooth with protective varnish.
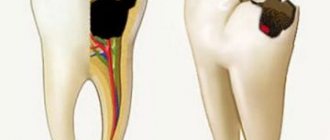
Modern cleaning methods are gentle on the enamel and cause minimal discomfort. Also, at the stage of removing tartar and plaque, preparations should begin for the treatment of caries and the removal of hopelessly affected teeth.
Gargling for children
Small children under 3 years of age are not recommended to use rinsing solutions as a treatment method. At this age, the child will not be able to correctly perform what is required of him, there is a risk of choking or drinking the solution. Until the age of three, it is better to use other dosage forms. In older children, lavage of the oropharynx is used as an element of complex therapy for tonsillitis.
Children are more likely than adults to experience drug intolerance and allergic reactions due to the fact that the immune system is still developing. When rinsing a child, there is always a risk of swallowing the drug. If ingested, peroxide is toxic to the body, and the effectiveness of a solution with a lower concentration is controversial, so peroxide for gargling in children is not recommended. In all cases of tonsillitis in children, consultation and examination by a doctor is necessary. The health of our children is the most important thing!
Up to contents
Drug treatment of periodontitis
The next stage of treatment is to relieve inflammation and eliminate bleeding gums to prevent further development of the disease. This goal is achieved through drug therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of periodontitis are divided into local and general:
- local remedies are used to treat the affected areas. This includes rinses, antiseptic solutions, anti-inflammatory gels and balms. Local treatments also include therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes, which can be used as an addition to the main therapy;
- general drugs, which are combinations of antibiotics in the form of tablets or intramuscular injections.
Non-invasive treatment for periodontitis may also include physical therapy. Auxiliary procedures using laser or electrophoresis will help eliminate inflammation faster.
Is it possible to gargle with peroxide?
Only a doctor can correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment. To effectively get rid of tonsillitis, consult a specialist.
According to the instructions for use, peroxide is used as a treatment for the pharynx in acute tonsillitis, gingivitis, stomatitis and other pathologies. For treating mucous membranes, a 0.25% solution of hydrogen peroxide is acceptable1. When rinsing, microbial contamination in the throat decreases and inflammation decreases. Lubricating the mucous membrane of the tonsils with a cotton swab dipped in a solution is also used, which helps to avoid unwanted effects on the rest of the epithelium. On the other hand, peroxide does not act selectively on tissues, that is, it damages, along with bacteria, unchanged tissues of the body, which can delay recovery. With long-term treatment with peroxide, adverse reactions are possible: burns of the mucous membrane; in case of allergic reactions, bronchospasm and laryngospasm may develop; if accidentally swallowed, it has a toxic effect on the gastrointestinal tract; if it enters the bloodstream, it causes hemolysis of red blood cells. As science moves forward, this method of treatment fades into the background. Safer and more effective drugs are appearing.
Up to contents
Surgical methods
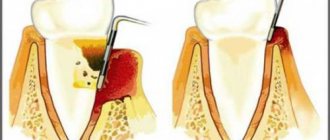
Treating periodontitis surgically is the most radical method. But in the later stages of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate periodontal pockets and remove non-viable teeth. This can only be done surgically.
The degree of intervention depends on the severity of the pathology. In some cases, a positive result can be achieved by simply depulping the tooth to remove pathogenic bacteria. The procedure for splinting teeth (connecting mobile teeth with adjacent teeth to ensure immobility) and other methods is also used.
A separate stage of surgical treatment is prosthetics. This is done to restore the functionality of the dentition, distribute the chewing load evenly, and prevent displacement and further loss of teeth. In some cases, a temporary prosthesis can be used to quickly unload the chewing surfaces and eliminate mobility during the recovery phase.
Scientific confirmation
Scientists are constantly studying this issue, and there is already evidence that people who regularly consume fresh fruits, vegetables and whole grain products reduce the risk and rate of development of cataracts. Omega-3 fatty acids contained in fish have a positive effect on the condition of the organ of vision.
A number of scientific studies in this area form a small evidence base:
In 2014, scientists from Sweden published results linking an antioxidant-rich diet and age-related cataracts. More than 30,000 women over 49 years of age provided dietary data and underwent eye examinations for lens opacities. According to the data obtained, people who ate large amounts of greens reduced the risk of cataract formation and the need for its radical treatment.
Information published in the journal Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science confirms that a diet rich in carbohydrates increases the risk of the disease. The eating habits of 1,600 Australian residents were studied.
There are studies that refute the connection between the disease and daily diet. The inconsistency of information is due to the individual characteristics of patients and difficulties in objectifying the information received. Other predisposing factors include excessive sun exposure, diabetes mellitus, smoking and chronic use of hormonal steroid drugs.
Treatment and prevention of periodontitis at home
After successful treatment of periodontitis, it is necessary to pay increased attention to oral hygiene. To do this you should:
- Visit your dentist regularly to remove plaque and tartar;
- eliminate caries and fill dental canals at the slightest manifestation of pathological processes;
- use hygiene products designed to prevent gum disease;
- After each meal, use dental floss and mouthwash with an antiseptic;
- follow other rules for the prevention of periodontitis.
What are external hemorrhoids? A little anatomy
External hemorrhoids (plexuses) are formations located under the skin on the border of the anal canal and perianal (around the anus) skin. They are venous plexuses (Fig. 3). Usually they do not manifest themselves in any way, are not visible and cannot be detected by touch. As the condition worsens chronically
changes occur in internal hemorrhoids and in external hemorrhoids, leading to their enlargement and loss of connection with the muscular ring of the anal canal. However, the most significant changes in the external nodes occur when a blood clot occurs in them.
Rice. 3. Diagram of the anal canal, at the exit of which the external hemorrhoids are located (number 7 in the diagram).
Asepta Parodontal - specialized products for the treatment of periodontitis
has developed a whole range of drugs for the treatment and prevention of gum disease. It includes:
- Asepta therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste, which helps eliminate inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Contains a unique complex of medicinal extracts and active ingredients;
- Asepta Sensitive toothpaste for sensitive teeth. Provides gentle care for sensitive enamel and gums prone to inflammatory processes. Thermal mud in the paste helps heal damaged tissue and relieve irritation;
- Asepta mouthwash is intended to relieve symptoms of gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and toothache caused by infection. The antimicrobial components of the drug help relieve inflammation and pain, and also have an antiseptic effect;
- Asepta Fresh mouthwash eliminates inflammation and bleeding of gums, prevents the formation of dental plaque, and also gets rid of pathogenic bacteria that cause bad breath;
- Asepta gel with propolis has an intense anti-inflammatory effect, reducing the sensitivity of enamel and promoting the healing of trophic ulcers. Effectively strengthens periodontal tissues and is suitable for patients of all ages.
- The adhesive balm in this series eliminates the causes and symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the mouth. The sticky base ensures a longer and more effective effect of the drug, allowing it to remain on the gums for a long time;
- Asepta vitamin and mineral complex contains all the necessary substances and active components for healthy teeth and gums.
Take care of your health with professional hygiene products!
Positive properties of the composition
Hydrogen peroxide is an active substance, H2O2, which, after application to the skin, mucous membranes, enamel, and also when interacting with blood and saliva, begins to foam strongly, produces oxygen molecules and has an oxidizing effect. It penetrates deep into tissues and various pathological foci, effectively removes contaminants from there and thereby reduces the number of harmful bacteria.
Softens tissues, promotes easier and faster separation of dead cells, removal of pus from wounds, cleansing, and has an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and even hemostatic effect. It is also believed that peroxide strengthens sore gums and helps stop bleeding from small capillaries
Important ! Peroxide suppresses the activity of gram-positive bacteria well, but it does not fight other pathogens (fungi, gram-negative bacteria, viruses, anaerobes), which is what other products successfully do - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Due to its oxidizing ability and the ability to release active oxygen, it removes not only impurities, but also destroys color pigment, due to which it is actively used in aesthetic dentistry for enamel whitening procedures. True, dentists use formulations with a high concentration of peroxide - from 15%. If we talk about the hydrogen peroxide solution, which can be found in pharmacies and used at home, then it has a low concentration of the active substance - 3%. And this, of course, will not allow achieving a significant change in the tone of the enamel. But it will be useful in other cases, and it is quite inexpensive, which is an undeniable advantage.
Some also find that gargling with hydrogen peroxide has a soothing effect if you have a toothache or sore throat. But this is not entirely true. The product reduces the number of bacteria and pathogens, but for a short period of time, but it cannot relieve pain.
Clinical researches
According to the results of the clinical use of the Asepta line of products: the examined patients, already at the first follow-up examination (after 1-2 days) of using the Asepta line of products, showed a decrease in complaints of discomfort in the gums. On examination, hyperemia and bleeding of the gingival papillae are noted. On the 7th day, complaints of gum bleeding persisted in a minority of patients.
Upon examination, a decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted, but bleeding persisted upon probing. On day 14, 2 patients continued to complain of bleeding gums when brushing their teeth; upon examination, a significant decrease in hyperemia and swelling of the gums was noted. After the final application of the gel with propolis, normalization of clinical manifestations was revealed, which is manifested by the absence of bleeding during brushing and probing.
Improved dynamics of indicators allows us to recommend the Asepta line of products for the local treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. CHPP**, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY*, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV*, dentist A.A. DOMORAD**, O.M. YAKOVLEV** SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, **Department of Microbiology
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Article “Treatment and hygiene features for mild and moderate periodontitis” by S.B. Ulitovsky head Department of PFS, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, A.A. Leontyev Associate Professor of the Department of PFS, Ph.D. PSPbSMU named after. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, aspirant, dentist, Department of Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
Prices for cataract removal:
| № | Service name | Price in rubles | Make an appointment |
| 2009003 | Optical-reconstructive intervention in the anterior segment of the eye for cataracts and post-traumatic and post-traumatic changes | 90000 | Sign up |
| 2008047 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 3 of complexity | 86880 | Sign up |
| 2008046 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 2 of complexity | 79650 | Sign up |
| 2008045 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 1 of complexity | 77400 | Sign up |
| 2008044 | Phacoemulsification for initial and immature cataracts, category 3 of complexity | 71220 | Sign up |
| 2008043 | Phacoemulsification for initial and immature cataracts, category 2 of complexity | 67080 | Sign up |
| 2014001 | Penetrating keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation (complexity category 2) | 96000 | Sign up |
| 2014003 | Penetrating keratoplasty + reconstruction of the anterior chamber with iris plastic surgery, phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation | 120000 | Sign up |
| 2014005 | Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation (complexity category 2) | 108000 | Sign up |
| 2014007 | Posterior layered endothelial keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation | 84000 | Sign up |
| 2008041 | Discision of secondary cataract | 9000 | Sign up |
| 2008053 | A set of consumables and an imported intraocular lens for phacoemulsification of cataracts with cataract removal. | 42000 | Sign up |
| 2008005 | Ultrasound phacoemulsification with IOL implantation for initial and immature age-related cataracts | 79650 | Sign up |
| 2008007 | Ultrasound phacoemulsification with IOL implantation for complicated, mature and overmature age-related cataracts | 84440 | Sign up |
| 2008012 | Cataract removal without phacoemulsification + IOL | 40200 | Sign up |
| 2008021 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the first category of complexity | 40500 | Sign up |
| 2008022 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the second category of complexity | 45600 | Sign up |
| 2008023 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the third category of complexity | 50400 | Sign up |
Making an appointment Today registered: 21
What causes acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid?
The occurrence of thrombosis is often caused by overflow of the veins of the external hemorrhoidal plexus with blood, followed by a slowdown in blood flow in these vessels and the occurrence of blood clots. Thrombosis against the background of venous congestion most often develops after sudden or prolonged stress. Classic examples of such overexertion are heavy lifting, straining during constipation or diarrhea, and childbirth. Chronic stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs (which includes the anal canal) occurs with prolonged sitting, excess body weight, and insufficient physical activity.