Treatment and prevention of gingivitis at home should be of high quality and effective. If a patient neglects hygiene procedures, eats poorly, smokes, and does not treat caries and other dental diseases in a timely manner, the person will constantly experience inflammatory processes in the mouth, and the stages of remission will not last long.
The disease is divided into several types, which are accompanied by certain symptoms. Therapeutic regimens also differ, having their own characteristics depending on the type of disease. If a small child or a pregnant woman gets sick, it is important to adhere to some rules and exceptions in order not to harm the vulnerable body.
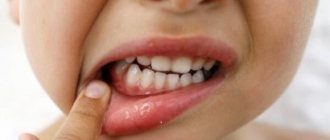
What is gingivitis
This is an acute or chronic inflammation of the gums in areas adjacent to the teeth. It occurs quite often in both adults and young patients. This problem also affects pregnant women in different trimesters. Babies during the teething period, as well as teenagers, are most susceptible to pathology. The disease occurs when the immune system is weakened, poor hygiene, or systemic illnesses.
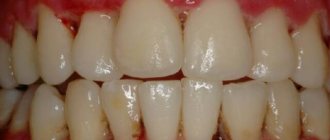
The inflammatory process proceeds quite slowly. However, it is not difficult to detect it by its characteristic symptoms. If you do not consult a dentist in a timely manner, serious complications arise that are rarely treatable.
There are several successive stages of inflammation: mild, moderate, severe. At first, only the interdental spaces are affected, then the lesion spreads further. Then the lesion covers all mucous membranes in the oral cavity.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of gingivitis is carried out in several ways, which are used in combination. At the initial stage, the doctor collects anamnesis:
- The diet and bad habits are revealed;
- The reasons for tooth extraction/loss are clarified;
- Genetic predisposition is determined.
After this, an examination of the oral cavity is carried out, the depth of the dental canals is studied with a special probe. Additional methods of diagnostic testing include x-rays and testing the sensitivity of the pulp.
The following methods can be used to diagnose gingivitis:
- Fedorov-Volodkina index;
- RMA index;
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
Causes of gingivitis
The main factor that contributes to the development of the disease is considered to be non-compliance with basic hygiene rules. When a person neglects daily cleanings and other maintenance procedures, the likelihood of ending up in the dental office with excruciating pain, bleeding, loose incisors, canines and molars, and other problems increases significantly.
Conventionally, all prerequisites for the appearance of pathology can be divided into internal and external. The first group includes:
- Growth of molars. Sometimes during this process soft tissue is injured, resulting in bleeding.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body. The patient's immunity decreases and he is unable to resist pathological agents.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Infections. This usually happens when preschool children have insufficient immune protection.
- Presence of carious lesions. They must be eliminated in time; caries must not be allowed to progress, otherwise complications will arise (periodontitis, loss of units, etc.).
External reasons:
- traumatic impact;
- burns of the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- irradiation;
- entry of heavy metals (lead, bismuth) into the patient’s body.
The problem is often diagnosed in pregnant women. This is due to hormonal and other changes. The same goes for teenage children.
Types and symptoms of gingivitis
The types and symptoms of the pathological process are presented in the table:
| Type of pathology | Characteristic signs |
| Atrophic |
|
| Catarrhal |
|
| Hypertrophic |
|
| Ulcerative-necrotic |
|
How to treat gingivitis depending on the type
Therapeutic tactics depend on the type of disease. However, there are general steps that every dentist follows when developing a treatment regimen.
- Assessing the degree of contamination of hard surfaces. To determine the amount of plaque and calculate hygienic indices, tinting compounds are used. Areas covered with deposits immediately change color, so the doctor can assess the extent of the damage.
- Teaching the patient special rules of care. A brush, paste and other products are selected individually. The person is also told about the role of proper nutrition in oral health. For example, if you refuse solid foods, the interdental spaces and enamel will be poorly cleaned of food debris and accumulated pathogenic microflora.
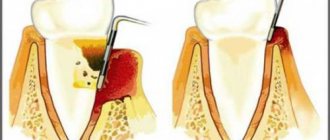
- Professional cleaning in a clinical setting. For this purpose, ultrasound is often used, followed by polishing of the cervical area.
- Treatment of affected tissues with medications. Physiotherapy and surgical methods are used according to indications.
- If there is a history of chronic systemic diseases, the patient is referred for additional studies, including blood and urine tests. Consultations with specialists of a narrow profile are shown.
Atrophic
Diagnosis and treatment of gingivitis in adults (photos of symptoms are presented below) in this case should be comprehensive and individual. If the problem is caused by a general systemic disease, all actions are aimed at combating it.
Measures are also being taken to restore and strengthen the immune system. All factors leading to soft tissue trauma are excluded. The doctor performs professional cleaning and prescribes products that accelerate regeneration. If necessary, existing dentures and orthodontic structures are adjusted.
The infection is cleared with antibiotics. The gums are treated with antiseptic solutions. Physiotherapy and massage are provided. In severe cases, surgical intervention (gingivoplasty) cannot be avoided.
Catarrhal
First of all, it is important to exclude local exposure, as a result of which the disease developed. Under anesthesia, tartar and other deposits are removed, caries is eliminated, and dental units are filled. According to indications, prosthetics and frenuloplasty are performed.
Therapy can be either local or general medication. Applications are applied, rinsing and treatment of damaged mucous membranes is carried out.
Effective methods for treating this type of dental gingivitis include folk recipes. For example, you can rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions and apply medicinal bandages. If there is no effect or the patient’s condition worsens, other medications are prescribed and additional procedures are prescribed.
Hypertrophic
The pathological process is treated according to the standard regimen. First, the plaque is cleaned off, then antiseptic treatment is performed, baths are made, and physiotherapeutic methods are applied.
If your health does not improve, you cannot do without sclerotherapy, when special solutions are injected into the gingival papillae and additionally hormone-containing ointments and creams are prescribed. Restorative measures, installation of prostheses and orthodontic devices may be required.
Ulcerative-necrotic
First of all, it is important to take measures to restore and strengthen the immune system. It is also necessary to get rid of the external manifestations of the disease. To do this, the doctor performs professional cleaning, removes dead tissue, and treats the resulting ulcers with antiseptics to prevent infection.
The patient should pay special attention to the hygiene of mucous membranes, constantly rinse the mouth, treat with gels, ointments and other local compounds.
A diet containing foods containing large amounts of protein and vitamins is indicated. Drinking should be plentiful.
Why is it important to see a doctor?
When the first signs of gingivitis appear, you should immediately contact a qualified dentist or periodontist. This is necessary in order to confirm the diagnosis. In terms of external signs, gingivitis resembles periodontal disease or periodontitis, however, there are significant differences between these ailments.
Treatment of gingivitis is carried out according to a single scheme, regardless of the cause of the disease. Treatment usually takes place in two stages: oral hygiene (performed by a dentist) and local rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
In particular, gingivitis affects only the gums, without affecting the bone tissue. With periodontal disease, the picture is the opposite: the teeth begin to loosen, while practically no inflammation is observed in the gums. However, only an experienced doctor can determine this difference. After confirmation of the diagnosis, a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Important! The doctor must be truly experienced. In case of periodontal disease, potentially dangerous teeth are removed. With proper treatment of gingivitis, teeth are usually preserved.
How to cure gum gingivitis at home
It is worth treating at home only if the dentist has already examined the oral cavity, conducted the necessary diagnostic tests, studied the medical history and made recommendations that will help get rid of the unpleasant illness. Along with medications, the patient can use folk recipes that have been proven over the years. However, such drugs, despite their relative safety, can cause adverse reactions due to intolerance to the components and for other reasons. Therefore, the dentist must calculate the dosage himself and advise which herbal decoctions and solutions will not cause harm and are highly effective.
It is important to adhere to a special diet and include fruits and vegetables such as:
- citrus fruits (contain a lot of vitamin C, which helps strengthen vascular walls and prevent bleeding);
- apples, pears (include pectin, which accelerates the restoration of soft tissues);
- currants, raspberries and other berries (increase human immunity);
- zucchini, cabbage, carrots and other vegetables (accelerate metabolic and regeneration processes due to the fiber and antioxidants they contain).
You should exclude fast carbohydrates, baked goods, sweets, and potato dishes from the menu. They lead to the formation of thick plaque on the teeth, and subsequently - tartar.
Anti-gingivitis medications
In some cases, antibiotics cannot be avoided. However, all prescriptions should be made exclusively by the attending physician based on the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history, his well-being and other manifestations. Most often Amoxicillin, Metronidazole, and Erythromycin are used for these purposes.
Local agents
Gel and cream medications significantly alleviate the manifestations of the disease. These are anti-inflammatory compounds for external use such as Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Metrogyl Denta, Asepta and others.
Traditional methods
Some people, when the first symptoms of pathology appear, try to find information on the Internet and old books at home on how to treat gum gingivitis at home without pharmaceutical drugs. It should be remembered once and for all - no “grandmother’s” recipes, even if they show high effectiveness, should not be used without the approval of a doctor.
In combination with medications and other means, herbal medicine will help to significantly speed up recovery. Let's look at methods for preparing medicinal decoctions and solutions, often recommended by doctors.
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. sage with a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour. When the composition has cooled to room temperature, it is necessary to strain it through cheesecloth or a sieve. Rinse every time after eating.
- Prepare an aqueous solution from 1 tsp. baking soda per glass of warm liquid. You need to rinse your mouth with this mixture to remove leftover food.
- Mix 2 tablespoons of crushed oak bark and dried celandine, pour boiling water (about 400 ml). It is necessary to rinse the mouth well 4 times a day until the unpleasant manifestations of the pathology completely disappear.
Vitamins
Taking vitamin and mineral supplements is an integral part of complex therapy. Doctors usually issue orders for the purchase of pharmaceutical products containing substances of groups C and P (Ascorbic acid, Ascorutin, etc.).
Healing gels and ointments
Gels and ointments used for gingivitis have an anti-inflammatory, healing and trophic effect. In addition, they relieve pain and eliminate bleeding.
Holisal
Cholisal has both analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The gel should be applied to the inflamed areas in a thin, even layer three times a day until any clinical manifestations of the disease disappear.
Solcoseryl
Gel with a pronounced wound-healing effect. The drug increases blood circulation in damaged tissues, improves metabolism and oxygen utilization. To eliminate inflammation, the drug is applied to the gums on both sides twice a day after regular daily brushing of teeth. The course of treatment is at least 10 days.
Asepta gel
Asepta gel, which contains propolis, is the strongest natural remedy against chronic inflammation and for wound healing. The drug also has an antipruritic and analgesic effect. For therapeutic purposes, the gel is applied to the affected areas in the morning and evening. The course of treatment is 14-21 days.
Apident-active
Multicomponent ointment for gums containing bee venom, propolis and herbal extracts. Quickly eliminates the symptoms of gingivitis, relieves pain and inflammation. Apply the drug with massage movements twice a day. Apident-active should be used after eating any food and brushing your teeth. The duration of the course of therapy is 14 days.
Features of treatment of gingivitis
Some categories of patients require special treatment. The body of the child and the expectant mother, due to its characteristics, is more vulnerable than ever to external factors. However, many drugs and procedures that show effectiveness and speed up recovery are contraindicated. However, this does not mean that you need to abandon all intervention options, suffer with unpleasant symptoms and wait for the pathology to go away on its own.
Treatment in children
Therapeutic tactics in this case are practically no different from those in adult patients. However, there are still some features that are important to pay attention to.
- Ultrasound cleaning. The procedure does not cause pain or other unpleasant sensations and lasts no more than 20 minutes.
- Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial treatment. Gel-like compositions (Metrogil Denta, Cholisal) are applied to the mucous membranes; rinsing with Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, etc. is indicated.
- Strengthening the immune system. It is necessary to give vitamins, A and E are especially important, since they have a beneficial effect on the regeneration of soft tissues.
- Orthodontic intervention. Indicated for children with bite defects, which caused the pathological process.
When diagnosing an ulcerative-necrotic form, upon completion of the initial stage of therapy, dead fibers are removed under local anesthesia, and the mucous membranes are cauterized with electric current. Both before and after the procedure, doctors use light pain-relieving gels, for example, Kamistad, Kalgel.
Particular attention should be paid to the patient's hygiene. Without quality care, the pathology will not go away or will return again.
The disease in infants is treated differently. In such a case, regular massage and antimicrobial cleaning with a finger brush made of silicone are sufficient.
Treatment in pregnant women
How and with what to treat gingivitis in an adult at home, if this is a woman carrying a child? It should immediately be noted that the pathological process in expectant mothers occurs due to hormonal changes and a lack of nutrients in the body. For this reason, vitamin therapy is mandatory.
Antibiotics are contraindicated. The dentist removes accumulated dental plaque and recommends antiseptic medications that are safe for the fetus. Vacuum gum massage shows high efficiency.
You can rinse your mouth with a chamomile decoction at room temperature, this will help relieve swelling and get rid of bleeding. Medicines for oral administration should be prescribed exclusively by doctors; self-medication is unacceptable.
It is better to use brushes with soft bristles and avoid consuming hard products.