Summer has come - a time for active recreation, summer cottages and vegetable gardens. A time of abrasions and wounds, and therefore a high demand for antiseptics. More than 250 trade names of antiseptics in the form of ointments, solutions, sprays and powders are registered in Russia. Let's figure out which drugs are classified as antiseptics in medicine, how they differ from each other, and which of them can be recommended for every home medicine cabinet.
First of all, we note that the pharmacist independently selects the product only for external use, and the choice of antiseptic for the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and urinary tract, as well as for the genital organs remains with the doctor. We also remind you that many antiseptics cannot be applied to injured skin. Here are two main points to consider when selling and talking to a client. The mechanism of action of antiseptics may be different, depending on the main active ingredient.
Where is Chlorhexidine used?
The pharmaceutical product is used for the treatment and prevention of diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to Chlorhexidine.
Depending on the concentration of the substance, the medicine can be used in the treatment of various pathologies.
After operations, in order to prevent infectious pathologies, doctors resort to using a pharmaceutical solution.
Chlorhexidine is often used for dental purposes for the treatment of dentures. In some cases, medication is used to treat periodontitis, stomatitis, and they are used to rinse the gums.
The medicine is used in:
- Urology
- Gynecology
- Surgery
Iodine/povidone-iodine
Used in an alcohol solution (the so-called “tincture of iodine”) or in Lugol’s solution. Only the edges of the wound are treated with iodine so as not to cause soft tissue burns. The great advantage of iodine is its wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity: it kills all major pathogens and, with prolonged exposure, even spores - the most resistant forms of microorganisms. The use of large amounts of iodine is contraindicated in cases of hypersensitivity to it, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, thyroid formations, dermatitis, and kidney diseases. Application to mucous membranes is not advisable, especially in children.
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine is contraindicated:
- In case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug
- People suffering from dermatitis
- Do not use together with other antiseptics, for example, with hydrogen peroxide
- For ophthalmic use, rinsing the eyes with this product is prohibited.
- For disinfection of the surgical field
- After intervention on the auditory canal and central nervous system
It is important to know that the pharmaceutical product should be used with caution when treating children.
Dangers of using chlorhexidine mouthwash
You should not uncontrollably use chlorhexidine solution to rinse your gums and teeth; this can lead to a number of problems.
- Chlorhexidine affects not only pathogens, but also the natural flora of the oral cavity, which can ultimately lead to imbalances in the microflora. Uncontrolled use of an antiseptic has an effect on both good microbes and bad ones, but after stopping use, the bad microbes grow faster than the good ones.
- Constant use of an antiseptic can cause microflora resistance. According to recent studies, chlorhexidine causes resistance to antibiotics when they are really needed.
- Due to regular use of chlorhexidine for rinsing, intense dark plaque may appear on the teeth and tongue. This problem will have to be solved in the dentist's chair. This solution should be used only after consultation with a doctor and only for a limited period. This also applies to various toothpastes and rinses that contain it.
Book an appointment with a periodontist now by clicking the “Plus” button on the right side of your screen.
To the list of posts
Brief instructions for use
To prevent sexually transmitted diseases, after unprotected sexual intercourse, after a maximum of 2 hours, 2-3 ml of a 0.5% solution should be administered into the urinary canal of a man, 1 ml into the canal for women and 5-10 ml into the vagina. You can treat skin areas near the genitals with the product. After administering the drug, try to postpone urination for 2 hours.
Your doctor should tell you about douching for gynecological diseases.
For sore throat, rinse the mouth with 0.5% or 0.2% Chlorohexidine solution.
For inflammatory pathologies of the urinary tract, it is necessary to inject 2-3 ml of 0.05% of the product into the urinary canal.
Before using the drug, you should consult your doctor.
Fukortsin
Coloring antiseptic. A combination of fuchsin, boric acid, phenol, acetone, resorcinol and ethanol. Indications for the use of fucorcin are fungal and pustular skin diseases, abrasions, cracks, etc. Apply to the edges of wounds. Has less drying effect than brilliant green and iodine. It is used much less frequently in wound treatment. It is undesirable to use in children due to the boric acid and phenol contained in it, which have a large number of side effects. When applied to the skin, boric acid easily penetrates the blood (especially in children) and enters the internal organs and tissues, accumulating there. Therefore, long-term use can cause intoxication. This property forced us to sharply limit the use of boric acid, especially in childhood. Phenol also has the ability to easily penetrate the skin and lead to intoxication of internal organs.
Where to put candles
Depending on the type of disease, the method of administering Chlorhexidine suppositories can be different: rectal or vaginal.
But it is important to understand that the use of suppositories is only permissible as prescribed by a doctor.
Before using the suppository, you need to wash and dry your hands well, then you need to remove it from the package and insert it into the vagina in a lying position.
To avoid leakage of the drug, do not rush to get out of bed.
Chlorhexidine suppositories help well with thrush and cystitis.
When is chlorhexidine needed? Indications
- After tooth extraction . The doctor may prescribe oral baths with chlorhexidine if the tooth was removed due to severe inflammation and not planned. During normal extractions, there is no need to make baths or rinse, so as not to damage the blood clot in the socket of the extracted tooth.
- For stomatitis . This is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the cheeks and lips, which manifests itself in small wounds. Inflammation can be caused by various reasons: hormonal, taking medications, allergic reactions and household ones, for example, when eating crackers or seeds.
- For inflammation of the gums . In this case, you can use an antiseptic at home for pain and discomfort, but you should definitely see a doctor. Most often, the gums become inflamed due to supra- and subgingival plaque that needs to be removed. The procedure is called periodontal oral hygiene and after it the doctor will no longer prescribe chlorhexidine.
This is due to the peculiarity of the product to create a film on the surface of the teeth, to which new plaque and coloring pigments will “stick”. Therefore, after a course of chlorhexidine, a dark plaque forms on the teeth. Residues of food “stick” to this roughness, which are already difficult to remove on your own, they begin to provoke inflammation and the problem appears all over again. Thus, all the benefits of treatment are negated.
Why is Chlorhexidine better than peroxide?
- Hydrogen peroxide and Chlorhexidine are antiseptics. Medicines differ in their spectrum of effects and medicinal properties.
- Hydrogen peroxide, unlike Chlorhexidine, is available in only one dosage form, which is not very convenient.
Chlorkesidine suppositories are used for the treatment of gynecological and urological pathologies.
Both products disinfect wounds and abrasions well.
Chlorhexidine has a wider range of therapeutic effects; it is used to treat the hands of the surgeon and nurse before surgery, and it is also used in gynecology.
Classification of antiseptics
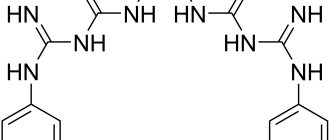
Halides (halogens and halogen-containing compounds) Chlorine or iodine compounds (antiformin, iodoform, iodinol, Lugol's solution, chloramine B, chlorhexidine).
The bactericidal effect is based on the fact that upon contact with organic substrates, these products release active halogens - chlorine and iodine, which destroy the proteins of microorganisms. Due to their high bactericidal activity, they are widely used both in medical institutions and at home. Oxidizing agents (hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, hydroperite). In contact with tissues, they release active oxygen, which creates unfavorable conditions for the development of anaerobic and putrefactive microbes. They are used to a limited extent due to their moderate bactericidal activity and short shelf life. Acids (salicylic, boric). A shift in pH to the acidic side leads to denaturation of the protoplasmic protein of the bacterial cell. Salicylic acid has a weak antiseptic effect, and boric acid has a large number of side effects associated with toxicity. Currently, antiseptics for treating skin are practically not used as antiseptics. Alkalies (ammonia, sodium tetraborate). Currently, drugs are practically not used as antiseptics due to their low antiseptic activity. Aldehydes (formalin, lysoform). Penetrating inside the microbial cell, they come into contact with the amino groups of proteins, which leads to cell death. The same effect explains the strong irritant effect on human mucous membranes and skin. Currently, they are used more for disinfecting surfaces in medical institutions. Alcohols (ethyl). They dehydrate tissues and irreversibly coagulate the proteins of microorganisms. They are used quite widely and have a pronounced antiseptic effect. In 2006, the WHO declared alcohol-based hand sanitizers to be the gold standard for hand sanitizers. Cationic antiseptics (benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium). The active substance acts on the membranes of microorganisms, leading to their death. It has a very wide spectrum of antimicrobial action, stimulates the immune system, and accelerates the healing process of wounds. Widely used in surgery, obstetrics, gynecology, traumatology, burn therapy, otorhinolaryngology and other fields of medicine. Salts of heavy metals (preparations of mercury, silver, copper, zinc, lead). The antimicrobial effect is associated with blocking the sulfhydryl groups of microbial enzymes. Use is limited due to toxicity. Dyes (methylene blue, brilliant green, fucorcin). They are active against gram-positive bacteria and cocci. Methylene blue has a very weak antiseptic effect and is practically not used. Herbal antibacterial drugs (urzaline, calendula tincture, imanin and others). Weak antiseptic properties. Rarely used. All these substances have different degrees of activity, antimicrobial spectrum and toxicity. To understand how to choose the right antiseptic, you need to be guided by all these characteristics in accordance with the intended purpose: primary wound treatment, treatment of festering wounds, or treatment of damaged mucous membranes or intact skin/mucous membranes. When choosing which antiseptic to treat a particular wound, you must also follow the instructions in order to avoid side effects, as well as determine the dosage required in a particular case. Let's take a closer look at the most popular antiseptics.
Treatment of wounds in children
Children of different ages very often receive all kinds of injuries and wounds. Kids are very actively exploring a new world for them, and in the process of getting to know it, they do not do without abrasions.
Children learn to rollerblade and bicycle, play outdoor games, climb trees, swing on swings, play various sports, communicate with animals, and quite often they get various injuries that require antibacterial treatment in order to prevent the penetration of harmful microorganisms and spread infections.
Since Chlorhexidine does not have a toxic effect on the body, does not cause adverse reactions or allergic manifestations, it can also be used to treat wounds, abrasions and other skin lesions even in very young children.
What is hydrogen peroxide
The chemical hydrogen peroxide is considered one of the most effective disinfectants. The effectiveness of peroxide is even greater when used in concentrated form. Available in the pharmaceutical network in a concentration of 3-10%.
The starting substance is very powerful, and the chemical composition is quite simple - a water molecule made of hydrogen and oxygen with an additional oxygen atom. The substance is colorless and odorless. Due to the intermediate formation of atomic oxygen, it is a very good oxidizing agent, which is used in the laboratory in the form of aqueous solutions in various concentrations.
It is used not only in medicine, but also for household and cosmetic purposes, decomposing after a reaction into simple substances - water and oxygen.
Application area
The main area of application of chlorhexidine bigluconate is medicine. In various forms it is used to treat runny nose, pharyngitis, laryngitis, stomatitis. This is an effective drug for the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases.
Chlorhexidine can be used both for the treatment and prevention of numerous diseases. But here it is important to choose the right concentration. For example, solutions containing a substance of 0.05─0.5% are used for applications and rinses. Gels with a concentration of 0.5% are used for external and local use. To rinse the mouth, use an aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.2% or an alcohol solution with a concentration of 0.1%.
The use of the drug for hand disinfection is popular; it is an excellent antiseptic: at the height of the coronavirus epidemic, its use has increased significantly.
The substance is used in surgery to treat the hands of medical personnel; it is also used to sterilize instruments; for this purpose, a half-percent alcohol solution or one-percent aqueous solution is used. The injection sites are treated with the product.
Due to its effective disinfecting effect, the places where bigluconate-based antiseptics are used are:
- Children's institutions: kindergartens, schools, colleges, etc.
- Communal facilities: baths, swimming pools, public toilets, etc.
- Sports facilities: gyms, fitness centers, etc.
- Beauty salons: hairdressers, beauty salons.
- Places of recreation and entertainment: nightclubs, cinemas, museums, theaters.
- Catering: canteens, bars, restaurants.
In addition, antiseptics are actively used in resorts, sanatoriums, cultural and health complexes, social security institutions and in everyday life.
Antiseptic Chlorhexidine: composition, release form and its effect on the body
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic, successfully used in the therapy and treatment of many gynecological diseases. It has bactericidal and bacteriostatic properties that are harmful to pathogens.
In the field of gynecology, the following forms of the drug are used:
- aqueous solution - can have different concentrations, from 0.02% to 20% of the active substance.
- vaginal suppositories.
- gel.
The composition of the presented drug includes:
- the active ingredient is chlorgestidine in varying concentrations.
- in the form of excipients it is purified water or an alcohol base.
The solution is effective in combating many microorganisms and suppressing their growth and development. However, it should be remembered that the drug is active only against those viruses that have a cytoplasmic membrane; against bacteria that do not have it, the drug is powerless.
Use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy, as well as breastfeeding a baby, is not a contraindication to the use of the drug.
Using the product to treat wounds is acceptable, but with caution. The drug has no toxicity and does not have a systemic effect. When treating damaged areas of skin, only a small part of the product can penetrate the bloodstream without creating a threat to the developing baby.
The drug does not cause any adverse reactions, so theoretically its use for external treatment of skin lesions cannot cause any harm to the unborn baby. Rather, on the contrary, an infection that penetrates a wound can enter the bloodstream through damaged blood vessels, and through it to other organs. The development of an infection anywhere inside the body will lead to an inflammatory process and the occurrence of diseases that will affect the development of the baby.
Therefore, the use of the drug for treating wounds during the period of bearing and feeding a baby is more than justified, but caution in use will not hurt.