Pain under the tongue can serve as one of the main symptoms of a whole range of problems, from banal mechanical injuries to a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, nervous system or internal organs. Depending on the cause and location of the pain, it can have a different nature and intensity.
If you or your loved one has pain under the tongue, there is no need to panic or self-medicate - this can only lead to aggravation of the situation. Contact a dentist at a dental clinic, he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the exact cause of the discomfort and prescribe an adequate treatment regimen to effectively eliminate the pain.
Reasons for appearance
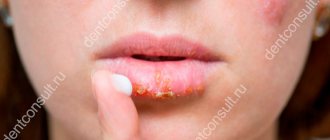
Ulcerations and abscesses are inflammations of an erosive nature, in which the patient constantly feels itching and pain.
Sores under the tongue may indicate dental problems and cancer.
The dentist and specialists will help determine the cause. Treatment includes antibiotics, antiseptics, antiviral and antiherpetic drugs.
Ulcers and ulcers in the mouth can occur sporadically as a result of failure to maintain proper oral hygiene. More often they are a sign of a serious illness.
There are several reasons for the appearance of sores in the sublingual area.
Leukoplakia
This is an inflammatory process on the mucous membrane, leading to its keratinization.
The disease is dangerous because it can develop into cancer. Ulcers under the tongue at the initial stage of the disease do not bother the patient. Over time, they begin to become inflamed, grow, and interfere with talking and eating. Oral leukoplakia is accompanied by a number of specific symptoms:
- white coating on the tongue;
- white-gray formations;
- burning sensation and pain in the affected area.
The causes of the appearance and development of the disease have not been established for certain. Erosive ulcers in the mouth and under the tongue, bleeding, proliferation of affected areas, the appearance of edema and the spread of inflammation to the lips, palate, tongue - a sign of the transition of leukoplakia to the malignant stage.
If the appearance of an ulcer under the tongue is accompanied by abdominal pain, sudden weight loss, or diarrhea, then you need to consult not only a dentist, but also a gastroenterologist.
Such symptoms may be a sign of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, celiac disease.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
Stomatitis
The main cause of stomatitis is failure to comply with hygiene rules, as a result of which pathogenic microbes actively multiply in the mouth. The causes of sublingual stomatitis are previous acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, and decreased immunity.
Stomatitis is often a chronic disease; sores and abscesses under the tongue appear only during the period of exacerbation of the disease. Ulcers under the tongue are a sure sign of aphthous stomatitis, which takes a long time to treat.
Abscesses and sores can occur one by one, and sometimes rashes can be seen. Aphthous ulcers are painful, but with proper treatment you can get rid of the sore in 7-10 days.
With herpetic stomatitis, the lower palate and sublingual area are strewn with small blisters filled with grayish liquid. The inflammatory process lasts 10-14 days.
Stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of 2-3 small ulcers-wounds covered with a white or yellowish film.
Glossitis
The advanced form of glossitis is dangerous due to the occurrence of an abscess and inflammation of the neck and chin. Redness, cracks and ulcers can occur due to a lack of vitamin B.
Concomitant somatic diseases
The appearance of abscesses and sores may be a sign of the presence of somatic diseases in the body: syphilis, tuberculosis, HIV infection, allergies. In this case, treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Oncological diseases
With tongue cancer, ulcers can be located both on the surface of the organ and under it. A non-healing abscess in the oral cavity is the main complaint of patients.
Injuries
Damage to the oral mucosa, tongue biting, malocclusion, trauma due to poor prosthetics, as well as chemical or thermal burns can cause sores.
As a rule, they do not require treatment and do not lead to serious inflammation in the oral cavity. In some cases, wounds and ulcers under the tongue can cause infection to appear and spread.
First aid for angioedema of the tongue
We have already spoken above about first aid - here we will give an example using a specific clinical case with a patient.
Angioedema is considered one of the most dangerous, often leading to death, as it occurs extremely quickly. Not only does a person’s tongue swell, but the neck, inner surface of the mouth, larynx, cheeks, eyelids, lips, and the entire face may also swell. The skin becomes blue, the tongue turns white, and tearing occurs.
What can be done first in case of angioedema of the tongue before the ambulance arrives?
- clear the airways of mucus;
- raise your head a little so that the swollen tongue does not block the airways;
- give an antihistamine, preferably administered intravenously;
- monitor the patient's condition and wait for an ambulance.
Symptoms and signs
The most common cause of sores and ulcers is sublingual stomatitis, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a whitish or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- swelling;
- ulcers and abscesses in the sublingual area.
In especially severe cases, ulcerations heal poorly, fester, and subsequently leave a scar.
With herpetiform stomatitis, the ulcers are located at the bottom of the tongue. In appearance, they resemble herpes - small blisters filled with liquid.
With tuberculosis of the oral cavity, the sores initially look like small tubercles, the ulcers are round, their edges are undermined. Often the formations may bleed. Over time, they become very painful, the patient's condition worsens sharply, and pain occurs when eating and talking.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
With tongue cancer, the patient observes lumps. Mouth ulcers are a sign of metastatic disease. They can reach from 1 to 4 cm. The color of the affected area can vary from dark red to dark gray or yellow.
Tongue cyst is a rare disease. A small, painful white growth forms under the tongue. The patient has difficulty breathing and swallowing.
If inflammation of the salivary gland begins
Our body is designed very thoughtfully. There is practically no process for which only one organ is responsible. Most of them complement and support each other's work. At the same time, a number of organs are responsible for one function at once, forming an entire system. For example, not just the stomach, but the entire digestive tract is responsible for digestion. Digestion of food begins from the moment it enters the mouth.
The salivary glands are responsible for the process of secreting saliva, which is so important for us. There are as many as three pairs of them in our mouth. Saliva is very important for digestion of food, normal swallowing and maintaining the alkaline balance in the mouth. The salivary glands can be susceptible to various diseases. Doctors consider the parotid gland to be the most vulnerable. Inflammation can also affect the sublingual and submandibular glands. Do not underestimate the danger of such inflammation. The inflammatory process in the tissues of the salivary glands is dangerous both due to its symptoms and severe complications. These can result from untimely or incorrect, delayed treatment.
Complications of inflammation of the salivary glands are extremely dangerous. It could be:
- Nephritis.
- Neuritis.
- Myocarditis.
- Meningitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Encephalitis.
This is why it is so important to start treatment as soon as possible. It must be intensive and systematic. Then the disease will pass quickly and without complications.
And it is best not to bring the salivary gland to a state of inflammation at all. Follow simple rules of prevention.
Often, inflammation of the salivary glands begins due to the closure of the excretory duct. There is simply a colossal amount of bacteria in our mouth. If the duct is closed and saliva is not excreted. Then these bacteria quickly penetrate inside the ducts themselves and infect them. A focus of the inflammatory process develops.
If you have undergone surgery in the oral cavity or have had severe flu, encephalitis, typhoid, or pneumonia, your risk of inflammation of the salivary glands increases. Be as attentive as possible to your health and consult a doctor at the first warning signs. In these diseases, the glands under the tongue are often involved in the inflammatory process. An important role is played by what pathogen led to the disease, as well as how it progresses. In this case, inflammation can be gangrenous, purulent, catarrhal.
Treatment
You should consult a doctor even if the formation does not bother you or hurt. Therapy should be aimed at combating factors that provoke the appearance of abscesses, as well as strengthening the immune system. In most cases, sores and ulcers disappear after using local remedies: ointments, sprays. In more serious cases, specific therapy is prescribed.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the cause of the ulceration.
If the sores under the tongue are the result of mechanical action, then treatment with hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, propolis, and soda solution is prescribed.
Ulcers and sores are painful, so the specialist prescribes painkillers based on corticosteroids. Sores and ulcers under the tongue that are caused by herpes can be cured with the help of antiviral drugs. Candidal stomatitis is treated with antibiotics. In addition, the patient is prescribed vitamin C. Antiallergic medications are often recommended.
Ulcers caused by HIV infection are treated with drugs to restore the immune system.
There is a list of universal remedies that combat the appearance of sores in the mouth. These include:
- iodine and brilliant green;
- drugs based on lidocaine;
- Cholesal;
- mouthwash ;
- churacilin.
Ulcers under the tongue caused by tuberculosis are treated with chemotherapy. Syphilitic abscesses are treated with medications.
Drugs with anti-inflammatory properties will help relieve swelling and discomfort.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to consult a specialist.
As a conclusion
You should not self-medicate if the situation gets out of control. At the slightest change in the condition of the tongue and mucous membranes, it is best to go to the hospital.
If the disease is chronic, such as a stomach ulcer, then to avoid complications you should take medications prescribed by your doctor and also follow a diet.
The tongue is an organ in the mouth that consists almost entirely of muscle tissue. Part of its surface contains taste buds, and it performs important functions in chewing, swallowing and speaking. Swelling of the tongue is a pathology in which its volume begins to exceed its standard dimensions.
If the swelling occurs instantly, it may be a sign of an acute anaphylactic reaction. Otherwise, there are a number of other factors, from illness to injury, that could cause a swollen tongue.
Prevention
To avoid consequences, you should regularly visit a dentist, observe the rules of oral hygiene, do fluorography in a timely manner, avoid mechanical and chemical injuries to the tongue, avoid alcohol and smoking, and adhere to a diet.
Nutrition should be balanced, rich in microelements and B vitamins. A mandatory condition for maintaining health is taking medications that stimulate the body’s protective functions.
Sores under the tongue can be a signal of a serious disease, therefore, if discomfort and pain appear in the oral cavity, as well as in the presence of lumps and small wounds, the patient should consult a doctor in order to begin timely treatment and avoid negative consequences.
Why does swelling of the tongue still occur?
We list the most common reasons why an organ may swell:
- an allergic reaction resulting in Quincke's edema;
- glossitis disease or an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue;
- hypothyroidism or diseases of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases, when the tongue may suddenly swell;
- injury caused by a broken piece of tooth, or incorrect prosthetics;
- disruption of the metabolic process;
- malignant formations;
- complications caused by piercing, etc.
An experienced doctor will help determine the true cause of swelling of the tongue, who will diagnose the oral cavity under the careful supervision of the patient.
Doctors treating frenulum pain under the tongue
When the frenulum of the tongue hurts, you should visit a therapist. The doctor will conduct an examination and diagnosis, and then refer you to one of the following specialists:
- Dentist;
- Neuropathologist;
- Oncologist;
- Surgeon;
- Nutritionist;
- Psychologist.
© shutterstock
How inflammation develops
To prevent such inflammation, teach your child to follow simple hygiene standards. It is very important to brush your teeth regularly. If a child finds a wound in his mouth, it should be immediately treated with brilliant green or iodine. Invite your child to rinse his mouth thoroughly with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, a weak solution of potassium permanganate or soda. All these products have an antibacterial effect. If swelling or painful redness appears, take your child to the doctor immediately. He will recommend how to proceed further. Don't risk your child's health and don't waste time on self-medication! Under no circumstances should this swelling be rubbed, iced, or heated. Because of this, the abscess can burst inside.
How to treat an abscess in children
To identify an abscess, a puncture is often performed. This will make it possible to find out which specific pathogen caused the abscess. Also, the doctor will immediately determine which antibiotic is most effective against it. Most often, treatment is surgical. The doctor opens the abscess, cleans it, treats it with antibacterial agents, prescribes antibiotics and other drugs. Physiological procedures support the treatment. For a superficial abscess, the doctor will administer anesthesia with novocaine. Once the autopsy is performed, treatment will be the same as for normal wounds.
As a result, we emphasize once again that it is easier to avoid such inflammation than to treat it later. Just don't forget about basic hygiene. Well, if symptoms of the disease appear, immediately go to the doctor.
Possible consequences
If the swelling is not eliminated in time, then negative consequences will not keep you waiting. They may appear as follows:
- chronic or acute respiratory dysfunction;
- violation of a person’s aesthetic appearance (almost constantly open mouth with tongue hanging out);
- psychological discomfort;
- speech distortion;
- malocclusion;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- tooth decay and loss.