From this article you will learn:
- why do gums bleed during pregnancy,
- what is pregnancy gingivitis,
- how to carry out treatment correctly.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
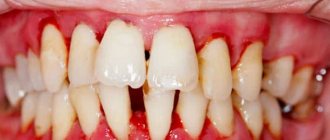
Inflammation of the gums during pregnancy is a process characterized by bleeding gums, as well as hypertrophy of the gingival papillae, which occurs due to an increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman. This condition is usually called the term “gingivitis in pregnant women”, and according to statistics, it is observed in 75% of women - for a period of 2 to 8 months. Most often, gingivitis occurs in the area of the front teeth, and it affects only the gingival margin at the necks of the teeth (including the gingival papillae).
Clinical studies show that more than half of all women with gingivitis during pregnancy already had a mild form of chronic catarrhal gingivitis at the beginning of pregnancy, which is practically asymptomatic. Thus, an increase in the content of estrogen and progesterone in most cases led to an exacerbation of pre-existing gingivitis, and was not the root cause of its development. We will tell you more about the causes of inflammation below, because... there are other factors to consider.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis –
But pregnant women can experience not only gingivitis, but also a more serious gum disease, in which inflammation spreads from the superficial part of the gums to deeper tissues. This disease is called periodontitis, and with it there is destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, destruction of the dental-gingival attachment, suppuration from periodontal pockets, and over time, tooth mobility also occurs. And this disease already indirectly affects the fetus, which requires mandatory treatment.
How is catarrhal gingivitis treated in pregnant women?
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women begins with professional teeth cleaning: plaque and tartar are carefully removed, and the teeth are polished using special brushes and pastes. The next stage is anti-inflammatory therapy. For this purpose, the dentist prescribes the use of anti-inflammatory rinses, applications and toothpastes. The correct diet is very important - you need to reduce the consumption of carbohydrate foods and avoid frequent snacking. And of course, you need to take good care of your oral hygiene.
Causes and symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women -
The development of the disease is usually associated with a restructuring of the hormonal balance during pregnancy - primarily with a high concentration of estrogens, progesterone, and prostaglandins. A number of authors also consider the phenomenon of toxicosis as an additional reason for the development of gingivitis in pregnant women. However, as we said above, there are additional reasons that are not related to hormones or any other changes in the body of a pregnant woman.
These changes relate, firstly, to changes in eating behavior. For example, women usually begin to consume significantly more carbohydrates (foods containing sugar, flour, starch). Moreover, a large amount of them is consumed between main meals, i.e. These are so-called snacks between meals. Naturally, after every cookie or bun in the middle of the day, women do not run to brush their teeth, but at most rinse their mouths with water or mouthwash.
Stuck food debris is an excellent breeding ground for soft microbial plaque, which also leads to its rapid growth. Pathogenic plaque bacteria produce toxins that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. Thus, the development of gum inflammation in pregnant women is caused by both changes in eating behavior and the observed insufficient level of oral hygiene.
1) Symptoms of the first half of pregnancy -
The first symptoms usually appear at 3-4 months of pregnancy, i.e. just when the most intense hormonal changes in the body occur. The symptoms of this period are more characteristic of the form of gingivitis, which is commonly called “catarrhal gingivitis” -
- bleeding gums,
- swelling of the gingival papillae and the marginal part of the gums,
- pain when brushing teeth,
- change in gum color from pale pink to red, and then to bluish.
At the same time, women’s complaints that their gums hurt during pregnancy can be associated not only with pain during brushing their teeth, i.e. when mechanical irritation of the gums occurs. If severe inflammation develops, pain can be observed even at rest.
Moreover, when soreness and bleeding gums appear, many women begin to “spare” their gums, starting to brush their teeth less often or less intensely (leaning more on mouth rinses). As a result, there is an even greater accumulation of soft microbial plaque in the area of the necks of the teeth, which only increases bleeding, as well as other symptoms of gum inflammation.
2) Symptoms of the second half of pregnancy -
Mild inflammation, which is manifested by swelling and bleeding of the gums, worsens in the second half of pregnancy (24stoma.ru). In many women, at this time, the growth of the marginal gums begins (polypous growth of gingival papillae). This type of gingivitis is called “hypertrophic”. It is especially pronounced in the area of the front teeth, as well as where there are overhanging edges of fillings and crowns that injure the gums.
There are 2 forms of hypertrophic gingivitis -
- Edema form - in which the gingival papillae are enlarged, bluish, soft to the touch, have a loose consistency or polypous growths.
- Fibrous form - when the gingival papillae are still enlarged, but become dense to the touch (due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue).
How are treatment methods chosen depending on the stage of pregnancy?
The first trimester of pregnancy is associated with the risk of spontaneous abortion, so during this period interventions should be as necessary, and the indications for them are acute pain or severe swelling of the gums. Tartar can also be removed, but it is still better to postpone this manipulation for a while. In the second trimester, you can carry out complex treatment, including professional cleaning and taking antiseptics. And in the third trimester, a visit to the dentist should be as short as possible, so you should limit yourself to only hygiene procedures.
Treatment of gum inflammation during pregnancy -
Treatment of gingivitis at the dentist can begin at the end of the 1st trimester, starting from the 9th week (by this time the fetus has already completed organogenesis).
Accordingly, after this period it is already possible to remove dental plaque with ultrasound - the safety of this has been shown in clinical studies (Lopez et al. 2002, 2005). Such periodontal therapy can then be safely carried out throughout the entire 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Therapy for gum inflammation in pregnant women will depend on the form of gingivitis, i.e. from the predominance of symptoms of catarrhal or hypertrophic form. Let us recall that a symptom of hypertrophic gingivitis is the growth of the gingival margin (gingival papillae).
1) Treatment of catarrhal form of gingivitis in pregnant women -
The catarrhal form of gingivitis develops in pregnant women against the background of insufficient hygiene and an increase in microbial plaque. Changes in hormonal levels are more of a provoking factor here than the root cause of the development of gingivitis. Let us remember that this form is primarily characterized by bleeding and swelling of the gums, as well as their pain when brushing your teeth. Treatment will include the following activities:
- Removal of dental plaque –Previously, it was believed that pregnant women could only remove dental plaque using hand instruments - special sharp curettes. However, there is now a lot of research that ultrasonic cleaning is the most common safe procedure (after 8 weeks of pregnancy). However, it is recommended not to set the ultrasonic scaler to the highest power, and also not to work too aggressively with the ultrasonic tip in deep periodontal pockets.
Regarding the removal of dental plaque with hand instruments, the opinion of doctors has now changed dramatically. This is due to 1) the high traumatic nature of this method for the gums, 2) high traumatic potential is always accompanied by bacteremia, i.e. entry of bacteria into the bloodstream. - Anti-inflammatory therapy – a 10-day course is usually prescribed, consisting of antiseptic rinses, as well as applications with special anti-inflammatory gels. Below we list several tools to choose from.
Antiseptic rinses: a) Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (instructions) course 10 days (no more), 2 times a day in the morning and evening after oral hygiene. Rinse your mouth for a full minute each time. b) rinsing with non-alcoholic infusions of herbs: chamomile, sage, eucalyptus. V) Fluoride rinses: Fluoride not only strengthens teeth, but also has a caries-static effect on plaque and therefore reduces inflammation in the gums. When choosing rinses, make sure that they do not contain alcohol or antibiotics (for example, triclosan).Applications of anti-inflammatory drugs a) MetrogilDenta gel (instructions) contains metronidazole 10 mg and chlorhexidine 0.5 mg. This drug is not recommended for pregnant women only in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, but can be used in the 2-3 trimesters. During lactation, the issue of stopping breastfeeding for the duration of use should be decided. b) CholisalGel (instructions) contains choline salicylate and cetalkonium chloride. Use in pregnant women is possible, but with caution, i.e. as prescribed by the dentist.
Such anti-inflammatory gels are applied to the marginal part of the gums, interdental papillae - primarily from the front surface of the teeth. After application, it is advisable not to eat or rinse your mouth for 2-3 hours (you can drink). Apply 2 times a day in the morning and evening after, for example, rinsing with chlorhexidine 0.05%. The course is no more than 10 days.
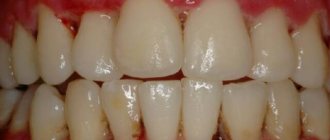
Photos Before and After Gingivitis Treatment –
In addition, it is worth noting the great importance of maintaining a proper diet. Those. It is vital to avoid frequent snacking between meals and consumption of sugary drinks. If you eat cookies or candy, you need to go brush your teeth. Also, as an additional therapeutic measure, you can use special anti-inflammatory toothpastes that will help cope with swelling and bleeding of the gums.
→ Rating of toothpastes for bleeding gums
Treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis –
This form of gingivitis is characterized by the growth of the marginal gums and gingival papillae, and high bleeding. Mild forms of hypertrophic gingivitis, as a rule, heal on their own in most pregnant women immediately after childbirth. If the cause of gum growth is the overhanging edges of fillings and crowns, then they need to be corrected. Local treatment during pregnancy should consist of maintaining good hygiene, removing dental plaque, and, if necessary, anti-inflammatory therapy.
More severe forms of the disease may require active treatment - courses of sclerosing therapy (injections of sclerosing solutions into the gingival papillae) or surgical correction of the gingival margin. This treatment is carried out after childbirth. You can read more about the treatment of hypertrophic gingivitis here .
Signs of violation
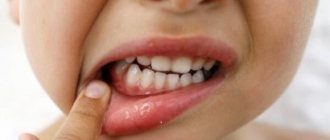
If your gums bleed during pregnancy, you can assume the presence of gingivitis. During different periods of pregnancy, this disease manifests itself in different ways. Typically a woman complains about:
- inflammation and swelling of soft tissues;
- bleeding even with minor mechanical stress;
- feeling of constant itching;
- transformation of the gingival papillae - they cease to be pointed and become dome-shaped;
- pain when chewing solid foods;
- elevated body temperature.
There are three forms of gingivitis:
- Light. Only the gingival papillae are damaged.
- Average. The inflammatory process has spread to the gums.
- Heavy. The entire gum is inflamed.
The disease can affect one or more teeth, or affect the entire dentition. In any case, treatment must be carried out as soon as possible.
Treatment
If your gums become inflamed, bleeding or swollen, it is important to consult a doctor immediately and follow the prescribed hygiene measures. The doctor will prescribe treatment, perform the necessary manipulations and prescribe procedures that can be performed at home.
Depending on the intensity of the disease, various medical interventions are required - from simple cleaning to tissue removal.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is highly not recommended to carry out treatment with potent drugs and carry out dental cleaning procedures with laser or ultrasound.
During the first trimester, you can visit a doctor who will determine the need for immediate intervention or prescribe a treatment plan for a later period.
The safest time for treatment is considered to be the second trimester. The last trimester is also suitable for carrying out procedures, if the patient is feeling well, there is no dizziness and problems with low blood pressure.
Therapy in a clinic setting
Any modern clinic has good equipment and professional specialists who are ready to treat both simple and complex cases.
The sooner you contact a dentist, the faster you can receive qualified services and save yourself from unpleasant symptoms of the disease. The help of a periodontist in the fight against gingivitis can be divided into several stages:
- Initial examination and determination of the shape, location and degree of gum damage.
- Professional removal of plaque and stone.
First of all, a procedure is carried out to remove deposits and clean plaque. To do this, they first disinfect and anesthetize the diseased areas, and then clean out the deposits manually or using modern equipment. - Disinfection of the oral cavity with solutions, for example, Chlorhexidine.
- Anti-inflammatory procedures. To restore proper vascular-tissue permeability, lotions are applied to the gums. They last from several minutes to several hours. Ointments that are harmless to the child are used as effective remedies.
- Electrophoresis and vacuum massage procedures. To reduce swelling and normalize the functioning of blood vessels, one to five procedures are performed.
At the end of the treatment, the periodontist prescribes an individual system of care and hygiene, which includes rinsing, cleansing and diet.
Home and folk recipes
To provide first aid and prevent gingivitis, there are a number of measures that can be taken at home to mitigate the signs of the disease and eliminate severe pain.
Among these methods, the most effective is rinsing the mouth. It is recommended to carry it out with special solutions:
- decoctions of herbs (lingonberry, chamomile, oak bark);
- means "Rotokan" or "Maraslavil";
- soda solution;
- hydrogen peroxide (diluted with water);
- kefir (infused for at least 3 days).
Gels of the “Metragil-Denta”, “Lakalut”, “Cholisal” series and other preparations are also used for oral care.
In order to stop bleeding and remove inflammation, you can use folk recipes. Fir oil and a paste of honey and sea salt should be applied to problem areas.
Linden infusions, Kalanchoe juice or brewed oak bark also alleviate pain and inflammation. It is important to apply the products using gauze or straining the decoctions so that small leaves do not fall between the gums.
How can oral health affect a child?
Recent research shows that severe gum disease, accompanied by red, swollen or bleeding gums, can harm the health of an unborn baby.
Scientists have found that women with severe gum disease are 7 times more likely to have preterm birth before 32 weeks than women with healthy gums. Another study looked at women with gingivitis and more severe gum disease and found a threefold increase in the risk of giving birth before 37 weeks.
Current research into gum disease during pregnancy shows a risk of prematurity comparable to that of alcohol consumption and slightly higher than that of smoking. Premature babies may have a wider range of health problems immediately after birth than full-term babies.
Women with gingivitis may also have low birth weight babies during pregnancy. Studies have shown that if you have gingivitis during pregnancy, you are 3 times more likely to have a low birth weight baby. This estimate is comparable to the risk associated with smoking during this period.
Why you need to treat gum disease
Some expectant mothers put off treatment for bleeding gums. They think that this problem can be dealt with after childbirth. This attitude towards the disease is incorrect. Only with good immunity can the body independently cope with inflammation and prevent its rapid progression. In all other cases, competent dental therapy should be carried out.
Under the influence of pathogenic microflora, which actively spreads when gingival tissue is damaged, the epithelium begins to collapse. If at the very beginning this process is reversible, then it will be quite difficult to correct the situation.
At some point, the pathogenic flora that has spread spreads to the periodontium. It gets damaged. This is manifested by tooth mobility. If you do not start treatment even with such symptoms, you can lose some units at a young age.
Doctors know of cases where the infection has affected the jaw bones. Then an irreversible change in the facial skeleton occurs, and fistula tracts are formed.
Don't start gingivitis. After undergoing professional hygiene and simple drug treatment, you will recover very quickly.
What measures are prohibited during pregnancy?
- Use arsenic.
- Carry out dental prosthetics and teeth whitening procedures.
- Use anesthesia (for pain relief, gentle agents are used that do not contain adrenaline).
Situations where doctors may forget about a patient’s pregnancy due to inattention are quite possible. Therefore, it is very important for the woman herself to monitor the actions of the dentist and specify each drug that is supposed to be introduced into her body. If the sensations are too painful, you can resort to anesthesia. The stress of a pregnant woman can cause more harm to the unborn child than the use of an anesthetic drug.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.
What is the danger
Bleeding is a fairly common and dangerous problem for pregnant women. It occurs most often in the first stages of pregnancy, and in the second and third trimester it takes on an acute phase. What are the dangers of bleeding and inflammation of the gums?
Plaque on teeth contains microbes and toxins that will enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This negatively affects the development of the fetus, causes a risk of infection, and also provokes the onset of labor ahead of schedule.
Gingivitis in its advanced form leads to another unpleasant disease - periodontitis, when the impact of bacteria occurs not only on the gums, but also on tissues and bones.
The effect of gingivitis on the mother's body
Gingivitis brings discomfort, pain and dangerous complications that can contribute to tooth loss.
It is very easy for viruses and fungal infections to take root and penetrate the body in the presence of various forms of gingivitis. In addition, every meal causes irritation and pain.
Inflammation of the gums contributes to the spread of toxins throughout the mother’s body and leads to problems of internal organs, thereby weakening the entire woman’s body.
The effect of gingivitis on the fetus
Any inflammatory process in the body can provoke infection of the fetus and affect its development in the womb.
In addition, the baby may encounter problems after birth. Weak immunity, low weight and special susceptibility to caries are just some of the possible consequences for the baby from gingivitis in the mouth of a pregnant woman.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is not recommended to use antibiotics. They will have a short-term effect, but can affect the fetus in unpredictable ways and cause developmental abnormalities. It is important to find and eliminate the cause of gingivitis.
Clinical researches
Analysis of the results of clinical studies revealed the significant effectiveness of Asepta products for moderate periodontitis. The use of Asepta mouth rinse turned out to be quite effective. In addition, no phenomena of mucosal irritation or brown staining of fillings were recorded. This indicates that the use of this rinse for a two-week period provides an obvious clinical effect in the absence of negative side effects.
Sources:
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Symptoms of diseases that cause bleeding gums
Since bleeding is associated with gingivitis and periodontitis, you should be aware of other symptoms of these diseases.
Signs of gingivitis
- Redness or bluishness of the mucous membrane
- Sore gums, especially when brushing
- Edema
- Unpleasant odor Signs of periodontitis
- All signs of gingivitis
- Loose teeth
- Exposure of necks and roots of teeth
- Fan-shaped divergence of teeth
- Suppuration from periodontal pockets