Cysts in the human body are closed cavities, a kind of capsule, with contents. Their localization can be very different, but dentistry deals with the treatment and prevention of cysts located in the oral cavity. They can range in size from microscopic, in which case they are very difficult to detect with the naked eye, to impressive, which significantly complicates the quality of life of patients. The causes of cysts and methods of their treatment often depend on where exactly they formed.
Let's consider each of the options in more detail.
Tonsil function
The tonsil is a lymphoid tissue located in clusters in the pharynx. The tonsils are one of the organs of the immune system that protect the internal environment of the body from harmful influences. There are six tonsils in the human pharynx: two paired and two unpaired; together they form the so-called Pirogov-Waldeyer protective ring. The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are located closest to the entrance of the pharynx, and these tonsils suffer more often than others. The lymphoid tissue of the tonsils supports general and local immunity. Lymphocytes mature in it and antibodies are produced.
The palatine tonsils play a vital role. They are the largest and differ in their structural features. Upon careful examination, it is clear that the surface has depressions or lacunae, smoothly turning into crypts or deep folds lined with mucous membrane. Only the lateral surfaces are covered with a capsule of connective tissue, and all the rest are in contact with everything that enters the pharynx.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Classification
Experts distinguish two types of tonsil cysts:
- Retention - formed after blockage of the ducts of the glands of lymphoid tissue, have a classic round shape, a thin capsule, filled with serous or purulent secretion. After emptying (evacuation of contents or spontaneous breakthrough), they are filled again.
- Dermoid or congenital - formed during intrauterine development, inclusions of embryonic tissue are always found in them. These true tumors, caused by genetic causes or harm suffered by the mother during pregnancy, are very rare. The capsule is usually dense and the contents are viscous.
Prevention
no specific methods for preventing tonsil cysts . We recommend that the patient give up bad habits (all types of smoking, excessive alcohol intake), adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition, and maintain oral hygiene.
At ENT Clinic No. 1 you can receive a full range of treatment for tonsil cysts and chronic tonsillitis. Highly qualified otorhinolaryngologists will select adequate conservative treatment using USOL therapy, laser exposure, phonophoresis and tonsil lavage. According to indications, an opening of the palatine tonsil cyst will be performed. If necessary, a streptate test will be performed and swabs taken from the throat and cyst contents to study the microflora.
Causes of retention cysts
The reasons for the formation of cysts are varied, but more often than others, factors such as:
- chronic inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx with periodic exacerbations - tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- autoimmune diseases accompanied by the production of a large number of lymphocytes;
- smoking, especially tobacco with a high tar content;
- injuries, including the habit of swallowing small bones;
- hormonal imbalance;
- occupational hazards, inhalation of aggressive aerosols;
- decreased immunity, especially local.
The formation of a cyst is caused by impaired drainage of the mucous lacunae of the tonsils against the background of the inflammatory process.
Manifestations of tonsil cysts
Symptoms of having a palatal cyst depend on its size and location. Cysts up to 1 cm in size usually do not manifest themselves, are invisible and painless. People, as a rule, do not even suspect their existence. Cysts can be discovered accidentally during routine examinations by an otolaryngologist.
You can suspect the presence of a cyst in the tonsil if you have bad breath with healthy teeth and normally functioning digestive organs. The smell comes from food particles that become trapped in the area of the cyst and begin to decompose there. As the size of the cyst increases, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- feeling of constant presence of a foreign body in the throat;
- sore throat or discomfort;
- difficulty and mild pain when swallowing solid food;
- hoarseness of voice.
Young children may begin to choke on food. If the cyst grows towards the pharynx, then a feeling of lack of air may occur, which is especially pronounced in children whose larynx is small. The existence of the cyst itself maintains chronic inflammation. The cyst excludes areas of the tonsil from immune protection.
Cyst on the gum: treatment and symptoms
The most common type is gum cyst , which can occur as a result of insufficient oral hygiene, the result of purulent inflammatory processes, trauma to the teeth or gums, and even as a complication of sinusitis, ARVI, or a common cold. The main reasons that lead to the formation of cysts on the gums are advanced caries and pulpitis, complicated by abscesses, gum pockets formed during periodontitis, perforation of dental canals due to unprofessional filling.
When a cyst on the gum has just formed, its symptoms are vague. There is only slight redness and mild pain when chewing food. In most cases, these signs go unnoticed and patients consult a doctor only when the cyst transforms into a vesicle with purulent contents and pain increases. In addition, there may be a slight increase in body temperature, deterioration in the general condition of the body and inflammation of the lymph nodes. At the appointment, if the doctor has doubts about the diagnosis, he recommends taking an x-ray to clarify the clinical picture of the disease and make recommendations for further treatment.
When a gum cyst is diagnosed, treatment is usually carried out surgically. The mucous membrane is cut, and the cyst itself is removed. Sometimes it is also necessary to remove part of the tooth. Fortunately, in most cases, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the tooth can be saved after disinfection of the gum cavity and drug treatment. Therapeutic methods are effective at the first stage of cyst development. In such a situation, the dental canals are thoroughly cleaned, disinfected, and treated with a drug that dissolves the granuloma membranes, which allows the pus to come out. Then the channels are filled with a paste that regenerates damaged bone tissue.
Diagnosis of a cyst
As a rule, detecting a cyst does not cause any particular difficulties, since the pharynx can be clearly seen even with the help of a backlit frontal mirror. The main thing is to contact an otolaryngologist for examination. ENT doctors use various instruments during examination - spatulas, elevators, and, if necessary, endoscopes.
The cyst is determined in different parts of the tonsils, on the surface or in the depths. It has the appearance of an opaque round formation, similar to a ball, whitish in color, elastic and mobile. There may be no signs of inflammation of surrounding tissues.
You cannot touch or put pressure on the cyst yourself - it can burst, and its contents are unknown. At best, the purulent contents will enter the stomach, and at worst, it will spread to other organs.
The doctor examines cysts larger than 1 cm very carefully, without damaging the surrounding tissues, trying not to touch the capsule.
Diagnosis of a cyst includes puncture (puncture and removal of contents). If necessary, the resulting material is examined in the laboratory to understand the nature of the disease. If a malignant process is suspected or blood is leaking from a cyst, treatment begins immediately, without waiting for the end of the examination.
Depending on age, general condition and concomitant diseases, the doctor may prescribe other clinical tests. The blood coagulation system, the functioning of the heart and lungs are required to be examined.
Salivary gland cysts
Symptoms of a salivary gland cyst
Depending on which gland it forms in, the symptoms of a salivary gland cyst can be distinguishable.
Small gland cyst
If a small gland has undergone a neoplasm, then the cyst is noticeable on the surface of the mucosa from the lower lip, and less often - on the mucosa of other parts. The small gland cyst does not exceed 1 cm in diameter and grows slowly. In appearance, it is a round elastic movable sphere protruding above the mucous membrane. It is practically imperceptible to the patient. If accidentally bitten or damaged by hard food, the cyst opens and secretes a viscous fluid, after which it closes again and mucus accumulates inside it again.
Sublingual gland cyst
Its location is under the base of the tongue. Such a cyst has a spherical or oval shape and a bluish light tint. When the cyst is located near the mylohyoid muscle, it takes on an hourglass shape.
A cyst of the sublingual gland can cause inconvenience because, as it increases in size, it provokes displacement of the frenulum of the tongue. Its incorrect position causes difficulties while eating and talking. Periodically, the cyst may spontaneously empty and be filled again with transparent or translucent secretion due to the fact that the gland continues its work.
Submandibular gland cyst
This cyst manifests itself as a fluctuating, round-shaped formation with a soft, smooth surface, located in the lower jaw, closer to the jaw joint. It can also spread to the sublingual area of the oral cavity and manifest itself as swelling of its bottom. In advanced cases, a submandibular gland cyst causes facial deformation. Like other types of similar neoplasms, this cyst can empty and fill again with liquid contents.
Parotid cyst
The parotid type of cyst, like others, has the shape of a ball with an elastic structure. A cyst forms on the mucous membrane inside the mouth near the auricle. Typically, a parotid cyst affects only one side of the mouth, which can cause facial deformity due to swelling of one cheek. The skin over the site of the cyst does not change color or structure. On palpation, the gland affected by the cyst does not show signs of fluctuation and does not cause pain.
In the absence of treatment and subsequent infection, the cyst can be complicated by abscess processes, accompanied by hyperemia of the skin and pain in the ear area. In this case, opening the mouth becomes very difficult, fluctuation and a slight increase in temperature in the tissues of the cheek are observed.
Treatment of palatal cysts
Tonsil removal
- Cost: 75,000 - 105,000 rubles.
- Duration: 30-40 minutes
- Hospitalization: 1-2 days in hospital
More details
Treatment of cysts is determined by many factors, primarily the size of the cyst, its location, growth rate and the age of the patient. At first, they always try to carry out a high-quality course of conservative treatment, especially anti-inflammatory treatment. Treatment is carried out both general and local.
The radical and best way to treat cysts is surgery, which can be performed in different ways. Small cysts located superficially are removed along with the capsule. After this, a slight scar remains on the tonsil, which soon resolves.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not feel anything. In most cases, the intervention is performed on an outpatient basis, and the person goes home the same day.
A cyst of significant size, especially one located deeply, is removed along with part of the tonsil. If there are several cysts or the location is such that it is impossible to get to them, the tonsil is removed completely and a tonsillectomy is performed.
Pleomorphic adenoma of the minor salivary glands in the palate
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common mixed benign tumor of the salivary glands. It is especially common in women in middle age. Approximately 80% of all cases involve the parotid gland, and about 7% involve the minor salivary glands. Histologically, this tumor is represented by both epithelial and mesenchymal elements, and is usually encapsulated in large salivary glands.
Mostly, tumors of the minor salivary glands are malignant (almost 50%). It has been established that the smaller the salivary gland, the greater the likelihood of tumor malignancy. The error of histological diagnosis varies from 1 to 14%. The difficulty of diagnosis lies not only in differentiating a benign neoplasm from a malignant one, but also in further, more detailed classification of the tumor.
The palate is the most common location of the minor salivary glands, followed by the lips and cheeks. PA appears as a painless firm formation and, in most cases, does not cause ulceration of the mucous membrane.
Ultrasound, CT and MRI may be used depending on the location and size of the tumor. The optimal treatment for PA is wide surgical excision of the formation along with the affected edges.
This clinical case examines a pleomorphic adenoma at the junction of the hard and soft palate.
Description of a clinical case
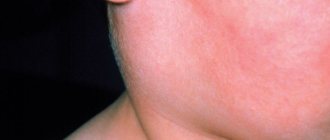
A 43-year-old woman was admitted to the clinic with complaints of a painless mass to the right of the junction of the soft and hard palate (Photo 1).
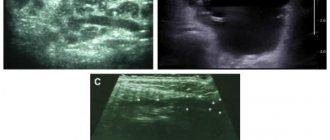
There was no somatic pathology in the medical history; the patient did not undergo drug treatment. Intraoral examination revealed a firm, approximately 2 x 2 cm, well-circumscribed, oval-shaped swelling to the right of the junction of the soft and hard palate (Figure 1).
Photo 1: Formation on the hard palate.
Also, palpation of the formation identified a tumor of soft consistency with well-defined boundaries.
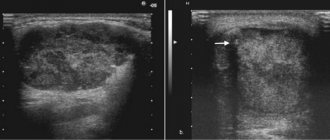
Photo 2: Orthopantomogram
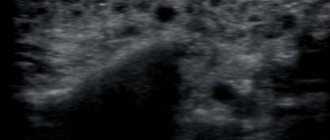
The orthopantomogram revealed changes in the bone structures and hard palate (Photo 2). MRI showed a well-defined mass on the palate (Figure 3). An incisional biopsy was prescribed. Histological examination revealed a keratinizing structure and myxoid degeneration (Figure 4). The cells were clustered into islands and layers separated from the myxoid matrix (Figure 4). Based on the data obtained, the final diagnosis was made: pleomorphic adenoma of the minor salivary glands of the soft and hard palate. The tumor was completely excised under local anesthesia, and the diagnosis was confirmed by repeat biopsy (Figure 5).
The postoperative period passed without complications and relapse.
Photo 3: MRI. Axial view showing a clearly visible mass.
Photo 4: Histological examination revealing keratinizing structure and myxoid degeneration, x40
Photo 5: Complete tumor removal
Photo 6: 3 weeks after surgery.
Discussion
PA occurs most frequently in the parotid salivary glands (56.7%), followed by the submandibular salivary glands (31.1%), palatine minor salivary glands (8.9%), and buccal minor salivary glands (3.3%).
A large number of tumors of the minor salivary glands are malignant (almost 50%). It has been established that the smaller the salivary gland, the greater the likelihood of malignancy of the tumor. Thus, differential diagnosis is vital.
Among all tumors of the salivary glands, malignant neoplasms such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma and polymorphic poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma are distinguished. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common of all malignant tumors of the salivary glands.
The most vulnerable area after the parotid salivary gland is followed by the glands of the hard palate. Typically, such tumors are asymptomatic, grow slowly, have a different consistency, a bluish or red tint, and clinically resemble a mucous cyst. Adenoid cystic carcinoma most often occurs on the palate. It appears as a painful, slowly growing mass that affects surrounding structures and occurs in middle-aged people. Polymorphic poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma is also more often localized on the palate and usually presents as a slowly growing swelling. In the population, this disease predominates in older women.
Ultrasound, MRI and CT are used in diagnosis. In our case, MRI and CT were used. The CT scan was unremarkable, while the MRI revealed a mass on the palate.
Clinically and histopathologically, this formation can be mistaken for malignant; however, PA is a benign tumor that recurs quite rarely. The literature contains data on 2-44% of relapses. Wide surgical excision is the most preferred therapy. The occurrence of relapse may be associated with inadequate surgical treatment and removal of the tumor. In this clinical case, the tumor was completely enucleated.
Conclusion
The purpose of this report was to describe the diagnosis and treatment of a pleomorphic adenoma that was found at the junction of the soft and hard palate in a 43-year-old woman. The tumor was completely excised along with the affected edges. Recovery was uneventful with a short recovery period (Photo 6).
Authors: Firdevs AKPEK, Mustafa TEK, Orcun TOPTAS, Fat ih OZAN
Prevention of palatal cysts
It is important to understand that a cyst is usually formed as a result of a long-term inflammatory process. Carrying a bag of pus in the throat is extremely harmful; it is a source of chronic infection. Microbes have access to the bloodstream; if the body is weakened, this can lead to diseases of the heart, joints and kidneys.
ENT doctors at CELT have extensive practical experience in treating tonsil cysts. Specialists are ready to help people of all ages, including children, as well as those who have unsuccessfully tried treatment in other clinics. The main thing is to cooperate with your doctor to complete treatment until complete recovery. You can safely contact our clinic with this problem.
Symptoms of tonsil cyst
A small cyst may not be noticed on its own; generally, it does not cause any discomfort. Often this is an accidental finding by an otolaryngologist during a routine examination or during treatment of another pathology. Feelings of discomfort become apparent when the cyst on the tonsil becomes larger, 0.5-0.7 cm or more.
The most common cause of tonsil cysts is chronic infections. In most cases, it occurs against the background of chronic tonsillitis. In this regard, a common and first symptom is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. However, other signs of a tonsil cyst are possible:
- sensation of a foreign body in the throat, feeling of a lump, tingling in the throat;
- soreness;
- pain when swallowing;
- voice change;
- getting water or food into your nose.
Our services in otorhinolaryngology
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Taking ENT smears | 600 |
| Videoendoscopy of the upper respiratory tract | 2 400 |
| Radio wave removal of skin (mucous) neoplasms of ENT organs | 4 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions