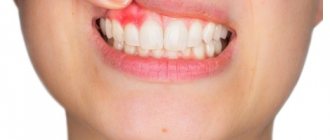
Like any part of our body, our gums can also become injured. The tactics of the planned treatment depend on the volume and nature of the damage received. Only with properly organized treatment will trauma to the gums not leave serious consequences. When any oral disease appears without the necessary treatment, manifestations of a weakened body and complications are possible.
Despite the fact that the gums are protected from the outside by the muscle tissue of the lips, they are easily exposed when talking, eating, or laughing. This is facilitated by the fact that facial muscles in humans are quite well developed. Therefore, gums can easily suffer injuries of varying severity.
Why does pain occur?
Soft tissue may hurt due to:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- A wisdom tooth that is starting to erupt
- Getting food between teeth
- Injuries received as a result of a fight, blow or bad fall
- Suppuration.
One of the causes of pain is injury. In dental practice, they are usually divided into two categories:
- Mechanical damage to the gums. A fairly common type that occurs in both adults and children. The reasons can be very diverse, but they are all related to physical effects. Falls or impacts may cause damage in one way or another. People often injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity and teeth during sports activities. Mechanical injuries are easier to diagnose because their presence can be determined visually during an examination by a doctor. They are accompanied by swelling, bruising and bleeding. An experienced dentist will help solve the problem, write out prescriptions, and select appropriate medications.
- Chemical. This category includes injuries caused by exposure to harsh chemicals. There are situations when a person, in a hurry and confused, drinks vinegar instead of water, resulting in a burn to the oral cavity. Exposure to various acids will inevitably lead to serious consequences. Teeth also suffer.
Causes of scratches on the gums
Gums play a big role in the development and condition of the dentition. Gum tissue, surrounding the surface of the teeth, protects them from infection. Therefore, any damage to the mucous membrane of the gums can lead to destructive processes in the periosteum and infect the periodontium.
Very often, the causes of scratches on the gums are quite banal; they appear due to carelessness:
- When using a hard toothbrush, damage to the mucous membrane occurs, leading to microtrauma.
- The habit of chewing and gnawing foreign objects (pens, pencils, matches, toothpicks). Careless movement can injure your gums.
- Eating solid foods (lollipops, grilled candies, crackers, seeds).
- Damage to the gums by a medical instrument during treatment, tooth extraction, or when installing a prosthesis.
You can scratch your gums with the edges of teeth that are broken or poorly polished. Poor-quality dentures also injure your gums.
However, children are much more likely to injure their gums. Many babies often have the habit of sucking their fingers, pulling toys into their mouths, while damaging the mucous membrane with a nail or a sharp edge. As a result, a painful wound remains on the gum.
A child can get a scratch if:
- eruption of the first tooth, the sharp edge of which can injure delicate tissue;
- accidental bite with the primary incisors located in the front;
- independent attempts to eat with a spoon or fork;
- unexpected falls during the game.
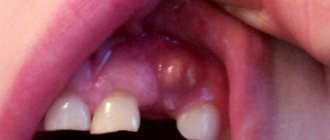
Typically, a scratch on the gum does not cause much discomfort and heals quite quickly. But if pathogenic bacteria get into the wound, the cut can become inflamed and lead to complications that will require long-term treatment.
Mechanical damage to the gums: how to treat
Damage to the gums is a serious problem, which in some cases requires the intervention of a specialist. It is better not to self-treat gum damage. But you can familiarize yourself with general recommendations on how to behave immediately after an injury:
- Use an antiseptic solution and rinse your mouth twice a day
- Take painkillers
- Eat on the other side so as not to provoke an attack of pain
- If possible, consult a dentist as soon as possible to avoid suppuration and other complications.
Acute and chronic injuries
Acute gum injuries include injuries resulting from soft tissue injury:
- Too hard bristles of a toothbrush
- Fish bone
- toothpick
Bruised gums are possible from falls and fights. Thermal burns are also possible if you consume too hot food or drink.
Chronic injuries include those that a person receives as a result of prolonged exposure to irritating agents on soft tissue:
- Food constantly stuck between teeth
- Poor quality filling that extends beyond the tooth
- Orthodontic devices (braces, plates)
- Poorly fitted clasp on a prosthesis
- Edges of a crown on a tooth
Mechanical injuries may be accompanied by slight bleeding. And with chemical and thermal injuries, erosion forms at the site of damage. With chronic injuries, purulent discharge may form on the gums. In advanced cases, surgery may be required. But more often local treatment is enough. Minor injuries can be treated with special healing balms prescribed by the dentist.
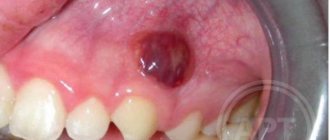
Scratch on the gum and possible complications
Infection of even a small scratch leads to swelling of the gums and the appearance of small bumps, causing discomfort when chewing. The tissue around the wound becomes inflamed, acquires a reddish tint and increases in volume.
Consultation with a doctor is required for the following symptoms of exacerbation:
- the appearance of swelling and a change in the color of the scratch to whitish;
- leakage of ichor or cloudy liquid;
- tugging or throbbing pain that spreads to other parts of the oral cavity.
These signs indicate that a purulent inflammatory process has begun. The infection can spread to the roots of the teeth, disrupting blood circulation, causing acute gingivitis, pulpitis or other complications.
In addition, inflammation is accompanied by constant pain, which interferes with eating, sleeping and disrupting normal functioning. The wound reacts especially acutely to the ingress of pepper, salt, and spices. All this can lead to the development of stomatitis and rashes.
That is why any scratch cannot be left unattended. It is necessary to immediately inspect the damaged area and treat it.
When is a visit to the dentist necessary?
It is advisable to seek help immediately as soon as the following symptoms appear:
- General health has deteriorated significantly
- subfebrile body temperature is within the range of 37.2? C - 37.5? C
- a slight increase in the level of leukocytes in the CBC was noted
- formations (seals) detected
With a weakened immune system, the injured area can take quite a long time to heal. If, after examination, the dentist determines that the gums (or teeth) are damaged as a result of the impact of the denture, the patient will be referred to an orthopedist.
Summary -
In this article, we briefly listed the main stages of treatment necessary to quickly relieve inflammation. Removing dental deposits from teeth and anti-inflammatory therapy will relieve redness, swelling, bleeding of the gums, the gums will become denser, pale pink in color, and bad breath will disappear. However, the treatment of a disease such as periodontitis does not end there.
In the case of deep periodontal pockets, and when the gums move away from the teeth, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability that splinting of mobile teeth will be required, as well as one of the surgical methods for treating periodontitis (for example, flap surgery or open curettage of the gums). During flap surgery, a thin strip of marginal gum is removed, which is loose and not attached to the teeth and, accordingly, this reduces the depth of periodontal pockets, as well as the rate of progression of periodontitis.
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.V.).
How to treat mechanical gum damage
To help the patient, the doctor will first eliminate the causes of inflammation:
- if necessary, remove the foreign body
- will replace low quality fillings
- will consider alternative options to replace uncomfortable dentures
- recommend a new toothbrush
If the gums are damaged by a toothbrush, the accessory must be replaced, choosing it according to the degree of stiffness of the bristles. Your doctor will help you make your choice. Below we will consider how doctors suggest treating mechanical damage to the gums:
- Treatment and procedures for pain relief of the damaged area. Applications with lidocaine solution help. Some dentists recommend propolis preparations to patients for these purposes.
- Treatment of inflammation. To prevent infection, the drugs Chlorhexidine, Miramistin or furatsilin will be prescribed. You can also use traditional medicine: decoctions of chamomile and sage. Gels against gum inflammation show a good effect: Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal.
- Healing procedures. Gels, ointments and balms containing vitamin A and E work well.
If the size of the damage is small, then sutures are not required. It is better to check with a professional about treating gum damage rather than trying to prescribe medications on your own.
Folk remedies
If you receive a wound on your gum, you should not wait for unpleasant consequences. It’s better to start preventing inflammation right away. To do this, it is not necessary to use powerful pharmaceutical antiseptics. It is enough to use simple recipes from traditional medicine based on herbal ingredients. They rarely cause side effects and do an excellent job with non-healing scratches on the mucous membrane.
The following formulations quickly and easily eliminate redness and burning due to infection:
- Calendula tincture diluted with plain water. The wound is thoroughly rinsed with it and applied as a compress to the jaw.
- A piece of propolis: it is used to prepare an alcohol infusion. A soft cake is also made from a natural component, which is left on the inflamed area of the gum for half an hour several times a day.
- Chamomile flowers and sage leaves mixed in equal proportions. From these plants you can prepare a decoction that will become an excellent antiseptic, help remove purulent contents and complement the main traditional treatment.
- A mixture of dried St. John's wort, oak bark and flax seeds will improve the microflora and remove the cause of infection in the oral cavity.
To speed up treatment, the patient will have to switch to soft or highly chopped food, and temporarily give up hot seasonings and sour pickled foods. The correct choice of hygiene products will help to avoid the recurrence of scratches on the gums: a high-quality toothbrush and toothpaste, rinsing solution. It is important to give up such a bad habit as smoking and increase local immunity, which will be able to resist any infection in the future.
Preventive measures
It is rare to avoid gum injury under certain circumstances, but there are some preventive measures you should know:
- Try to eat carefully. Without being distracted by conversations or watching movies. This will minimize the likelihood of mechanical injury or burns.
- Teeth should be treated on time. Immediately after the onset of painful sensations, you should consult a dentist.
- Prosthetic procedures take place in reliable and certified clinics.
- Do not self-medicate under any circumstances; do not take antibiotics or other serious medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- Try to brush your teeth properly. If necessary, use a soft-bristled brush.
About gum damage in a child
Children can often damage their teeth and gums due to their active lifestyle. Parents should always pay great attention to proper teeth cleaning. Quite often, young children injure themselves with toothbrushes. In most cases, there will be a slight bruise that will go away on its own over time. If an injury occurs as a result of a blow or fall, bleeding comes from the gums, and the tooth is noticeably loose, the first thing to do is contact a pediatric dentist.
Young children are not prescribed “adult” drugs, so you should not try to cure a child by simply giving him an anti-inflammatory drug. Under no circumstances should you risk the health of children whose immune systems are not yet stable. Even if only the mucous membrane is visually damaged and the tooth is intact, this does not mean that the root or nerve of the tooth is not damaged. A doctor's examination is necessary to close any access of infection through the damaged area. Treatment of gum injuries in children begins with a visual examination and is carried out taking into account the intensity of the damage. In controversial situations, the pediatric dentist may prescribe additional tests, for example, computed tomography. Remember, regular preventive examinations for children and adults always contribute to oral health.
conclusions
Carefully monitor the health of your teeth and oral cavity. Use dental floss and irrigator carefully. In case of gum swelling, pain and bleeding, it is better to immediately seek professional help. This will allow you to stop the problem in a timely manner and prevent it from developing into periodontitis.
Don't neglect professional teeth cleaning. Remove tartar and plaque at least once a year. More often if you have dentures, implants and/or smoke.
Strictly follow your doctor's instructions, especially with regard to taking antibiotics and using medicinal ointments and solutions.