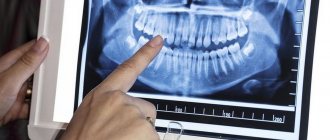
X-ray of the skull: when is it needed and how is it performed?
Radiography is a quick and reliable way to determine pathologies that are located within dense tissues.
The advantages of a skull x-ray are as follows:
- high information content of images taken in various projections;
- high efficiency;
- non-invasiveness and relatively simple technology for performing the procedure;
- accessibility - today head x-rays
can be taken in almost any clinic; - low radiation exposure.
When is a skull x-ray prescribed?
Survey X-ray of the skull
in different settings can be prescribed to patients who are concerned about:
- cephalgia, or, in other words, headache, of varying localization and intensity;
- trembling in the limbs;
- the appearance of a veil before the eyes or darkness;
- nosebleeds;
- painful chewing of food;
- decreased visual and hearing acuity;
- cases of fainting for no apparent reason;
- the appearance of asymmetry of the facial bones.
X-rays of the head are also indicated for mechanical injuries - bruises, blows, falls from a height, and so on.
Various specialists can prescribe an X-ray examination of the skull: a neurologist, a surgeon, an oncologist, an ophthalmologist and others.
What does the procedure show?
X-ray images clearly visualize:
- cheek bones;
- lower jaw bones;
- bony pyramid of the nose;
- sphenoid bone;
- eye sockets;
- temporomandibular joints;
- mastoid processes of the temporal bones.
If a more accurate and detailed diagnosis of the condition of the bone tissues of the skull is necessary, targeted images are taken, which can show the following pathological conditions:
- formed calcifications - can provoke pathological development of the cranial bones;
- partial calcification of tumors;
- hemorrhages and hematomas;
- fluid in the paranasal sinuses;
- fractures of the skull bones.
Using the X-ray method, it is possible to identify congenital pathologies of the skull, as well as increased intracranial pressure. The latter may be indicated by so-called impressions - marks similar to fingerprints that are located on the inside of the bone tissue.
TRG - lateral and direct image of the skull
TRG, teleroentgenogram, is an x-ray of the head. It is also called cephalometric, that is, measuring the head.
TRG is most in demand in orthodontics: for diagnosing occlusion and planning treatment: methods, stages, timing. To tell your doctor how long you will have to wear braces, bring him a TRG.
What will the TRG show in lateral projection?
The lateral projection of a teleroentgenogram is a profile shot of the skull. Based on this, the orthodontist will determine:
- Direction of growth of maxillofacial structures;
- Jaw angle;
- Size of jaws and teeth;
- Type of bite;
- Hidden injuries of the dental system;
- Soft tissue features (to improve profile aesthetics)
Front projection - more information
For this type of TRG, photographs of the skull are taken from the frontal view, from the side of the face and from the back of the head. Based on the results of TRG in direct projection, the orthodontist will determine:
- Features of the structure of the dentition (narrowing, widening);
- The plane of teeth closure.
- Degree of facial asymmetry.
Calculation and analysis of TRG
An integral part of orthodontic treatment planning is teleradiogram analysis. By directing you to the image, the orthodontist will indicate in the direction whether interpretation is required.
- Required - the calculation and analysis will be carried out for you by the orthodontist CosmoStom.
- Not required - your doctor will calculate and analyze TRH yourself.
Previously, calculations were done manually. The picture had to be printed, and the orthodontist would find key points on it. Next, the doctor, using tracing paper, a ruler and a protractor, calculated angles, distances, and proportions. The problem of measurement error inevitably arose, because even the thickness of a pencil introduced distortions into the calculation.
The digital revolution in dentistry has made it possible to automate these steps. TRG results are loaded into the program, where more than 80 points are set according to anatomical landmarks. The points are connected into diagrams, and then the doctor chooses which indicators he needs. The accuracy and reliability of such measurements have increased manifold. Now the orthodontist analyzes each case in more detail, and the effectiveness of treatment increases.
CosmoStom uses Romexis programs to calculate and analyze TRG, as well as its own unique software module “Cosmos”.
5 reasons to do TRG at CosmoStom
- Precision equipment: Planmeca ProMAX 3D (Finland) with high sensor resolution (5 pairs of lines per mm).
- Low radiation exposure: from 1.8 to 3.1 μSv. A person receives a similar dose after flying on an airplane or spending a weekend watching TV.
- We do the decoding, use our own TRG analysis module
- On weekdays and weekends we are waiting for you in the X-ray room.
- Convenient location: you can quickly get to CosmoStom on Volochaevskaya 19/1 from anywhere in Omsk.
Harmony of facial features
and a healthy, correct bite are calculated mathematically.
How does a teleradiogram work?
You can do TRG of teeth in 15 minutes. No pre-registration is required at CosmoStom. You just come to the clinic on Volochaevskaya 19/1 (stop “Rabinovicha Street”) in the X-ray room operating mode:
- Mon-Sat from 9:00 to 19:00
In the X-ray room:
- The patient usually stands. The head is fixed motionless so that the image is clear. Also, the same position of the jaw will allow you to take a repeat image in the future and measure the result of the treatment.
- The X-ray technician places the cephalostat in the desired position, asks you not to move, and starts the scan.
- The patient is waiting for the results in the lobby. In a few minutes he will be given a printed photograph or a disc with the recording.
- If calculation and analysis of TRG is required, the results will be ready within a week.
Price TRG
The cost of a teleradiogram depends on 2 factors:
- Only side projection or both?
- Is decoding necessary?
The answers to both questions should point in your direction. Be sure to take it with you to the clinic.
| Price, ք | With a discount, ք |
| Orthodontist consultation | 250 |
| TRG (teleradiogram) in 1 projection | 1100 |
| Calculation and analysis of TRG | 1650 |
Preparation for the procedure
Special preparation x-ray of the head
does not require. Before the procedure, the patient must remove all metal jewelry, glasses, and, if possible, dentures. If the dentures are fixed or a metal implant is installed, the radiologist must be warned about this in advance. Then, depending on the configuration of the X-ray machine, the patient takes a lying, sitting or standing position.
A lead vest or apron is placed on the patient's body to prevent exposure below the neck level. The head is secured with special clamps, since the first condition for obtaining a high-quality image is immobility.
Technique
To take an X-ray, the patient must stand up, sit near the X-ray machine, or lie down on its work table. It is important to remain still and not breathe while filming. If you need to take a picture in several projections, the doctor will tell you how to change the position.
X-ray of the skull in 2 projections
To obtain the most detailed and complete information about the condition of the nasal bones, photographs can be taken in two projections - frontal and lateral. In the first case, the patient faces the X-ray machine, in the second - sideways (left or right).
Interpretation of chest x-ray in Ufa
Results of examination of the chest organs and interpretation of the radiograph
After receiving the image, the radiologist makes a conclusion and passes it on to the attending physician, who referred the patient for radiography.
The description contains information about the location and size of the heart, respiratory organs, and the state of the vascular and lymphatic systems. If there are foreign objects, shadows, or neoplasms, this is also noted in the description of the study results. X-ray of the lungs allows you to evaluate their condition, size, shape, tissue structure, as well as the location of other organs of the chest. To obtain the most complete information about the condition of the lungs, the doctor needs an x-ray in 2 projections, where the lung tissue, domes of the diaphragm, the shadow of the heart and mediastinal organs, the bones of the spine, the shoulder girdle, and the sternum are clearly visible. Images of various organs and bones are superimposed on each other.
To correctly interpret the image, you need a clear idea of what healthy chest organs look like on an x-ray. For example, even subtle darkening, clearing, and an asymmetrical pulmonary pattern may indicate a serious illness. Regular examinations allow you to identify pathologies at an early stage and begin treatment immediately.
When decoding, the radiologist evaluates the quality of the image. Incorrect execution of the procedure (incorrect positioning of the patient, incorrect projection, etc.) does not allow an accurate conclusion to be drawn, so a re-examination may be required.
The reason for an incorrect examination result may be:
- Additional artifacts are shadows of various metal products that can obscure foci of pathology and disrupt the holistic perception of the image by the doctor
- Completeness of the image - due to incorrect positioning of the screen, the apexes, fields, and sinuses of the diaphragm may be displayed incorrectly
- Insufficiently clear and contrasting image - occurs when the X-ray machine mode is selected incorrectly. Modern equipment allows you to select the radiation dose for people of different sizes. For example, for patients with significant body weight, obesity, stronger radiation is required to obtain a clear radiograph. When digitizing an image, it is possible to change the contrast of the image
- Body position - if the patient is positioned incorrectly, exhales untimely, the shoulder blades open, or the screen or x-ray tube is not installed correctly, the x-ray image is likely to be distorted
X-ray interpretation protocol
Any qualified therapist will recognize serious pathological changes and damage on an x-ray. However, to draw a detailed conclusion and identify diseases at an early stage, a detailed analysis of the radiograph is necessary. For the convenience of radiologists, an algorithm has been developed according to which a transcript protocol is drawn up.
- The exact name of the examination - the anatomical area of the image is indicated, in which projection (lateral, erect) it was taken
- Assessment of pulmonary field symmetry
- Are pathological fields detected or not (focal, diffuse infiltrative), clearing in the lung tissue
- Description of the pulmonary pattern (if it is disturbed, this indicates pathological changes in the blood vessels of the lungs)
- Description of the roots of the lungs - whether the structure of the lymph nodes is disrupted or not, pathological changes in the large bronchi are present or not
- Description of the shadow of the mediastinal organs - especially important when diagnosing heart disease
- Description of the arch of the ventricles of the heart, large vessels
- The condition of the diaphragm and pulmonary-phrenic nodes of the sinuses - an assessment is made of the symmetry of the diaphragm, the angle of the sinus, whether it is filled or not (presence of effusion during pleurisy)
Inflammatory processes and tuberculosis
When analyzing a radiograph, diseases associated with tissue inflammation and pulmonary tuberculosis should be clearly distinguished. Tuberculoma in most cases is localized at the apex of the pulmonary tract, its shadow is round, often with clearing in the center - the focus of destruction. The expanded roots of the lungs are clearly visible.
Inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia) is clearly visualized on an x-ray. It looks like an infiltrative shadow against the background of an intensified pattern of the lungs; the focus of pneumonia is often surrounded by clearing - local compensatory emphysema.
How dangerous is the research?
X-ray is a non-invasive and painless procedure. It can also be called relatively safe, since the radiation exposure is minimal. At the same time, of course, x-rays are not a procedure that can be repeated many times in a row. There are certain norms and frequency that must be observed.
Contraindications for
An absolute contraindication for head x-rays is pregnancy. There are also relative restrictions. These are children under 15 years of age, mental illness, serious condition.
X-ray of the skull: decoding
When interpreting an X-ray of the skull in 2 projections, specialists evaluate the dimensions and features of the location of the bones, as well as the structure of the nasal sinuses. These indicators must correspond to the norm for the age category of the subject.
X-rays also make it possible to partially analyze the condition of the soft tissues of the brain (although for an accurate diagnosis of this organ it is better to use MRI or CT). The images can visualize tumor growths, and their location and size can be assessed. The main sign of a malignant neoplasm will be the presence of darkening of an uneven structure. If the tumor is benign, its contours will be smooth and clear.
Normal indicators
Let's figure out what a skull x-ray
in cases where there are no pathologies. When describing the images, the radiologist evaluates the size, shape, thickness and location of the skull bones, as well as the vascular system, the condition of the nasal sinuses and cranial sutures. All of the listed characteristics must correspond to the patient’s age.
X-ray of the skull for head trauma
The main questions that a specialist should answer based on an x-ray for a head injury:
- Is the integrity of the bones of the skull damaged?
- If there is a fracture, is it accompanied by the entry of bone fragments into the cranial cavity?
- Are the eye sockets, sinuses and ears damaged?
- Is there damage to the brain due to compression by the deformed bones of the skull?
The most common injuries to the calvarium are linear fractures (cracks) of its bones. In most cases, they appear in the place where the force was applied. By the way, this fact greatly facilitates the process of identifying a fracture/crack. The fracture is visualized as a sharp strip, in some places diverging in different directions, with uneven edges. Depending on the complexity, the fracture may have a different position, direction, and size. Multiple fractures can affect one or both halves of the skull. The most unfavorable situation is when the fracture passes to the cranial suture and causes its divergence.
Projections in X-ray diagnostics
A radiographic projection is an image on a plane obtained when X-rays pass through a given body onto a plane (for example, onto a film in a cassette).
There are many different projections in X-ray diagnostics, but the following standard and additional projections remain the main and frequently used projections. In this case, standard projections are mainly performed in a lying position.
Standard projections:
- Right lateral projection.
- Left lateral projection.
- Ventrodorsal projection.
- Dorso-ventral projection.
Additional projections:
- Oblique projections.
- With a horizontal course of rays - lateral, straight.
Now let's take a closer look.
The right lateral projection (RLP) is performed with the animal lying on its right side, and if the area of study is the thoracic region, abdominal cavity or survey image, then the thoracic limbs should be retracted strictly forward so that they do not block the chest and spine and the sternum should lie parallel to the table, and the ribs should be in superposition.
The left lateral projection (LLP) is performed similarly to the right lateral one, but with this projection the animal lies on its left side.
The position of the animal when performing the lateral projection.
Ventro-dorsal projection (VDP) is the position of the animal lying on its back, while the sternum and spine should be in superposition throughout, and the pelvic limbs should be retracted evenly back.
The position of the animal when performing the ventro-dorsal projection.
The dorsoventral projection (DVP) is similar to the ventrodorsal one, but the animal lies on its stomach.
The position of the animal when performing a dorsoventral projection.
Oblique projections are projections when the animal lies on its side at an angle of 45º to the table surface (see figure). Such projections can be performed both on the right side and on the left. And other variations are also possible depending on the area being studied.
The position of the animal when performing oblique projections.
With horizontal ray path - with this projection, X-rays pass horizontally (from the side). These projections can be performed both in a lying and standing position, and can be lateral and straight.
The position of the animal when performing direct projections with horizontal rays.
The position of the animal when performing lateral projections with horizontal rays.
The position of the animal during lateral projections with horizontal rays.
Projections in X-ray diagnostics are selected based on the area of study and preliminary diagnosis.
It should be borne in mind that if the area of interest is the chest, then only the chest is imaged. From a survey image, it is impossible to evaluate any indicators for examining the chest due to the fact that, firstly, the image is distorted due to the inclination of the X-rays passing along the periphery (the further the object is from the center to the edge, the greater the distortion). Secondly, we will not see small details that should be taken into account when describing the chest and making a correct diagnosis. The same situation occurs when examining the abdominal cavity, head, etc. Therefore, survey photographs should be used very rarely and only in emergency cases.
Therefore, before the owner and the animal go for X-ray diagnostics, it is necessary that the doctor, at a minimum, conduct a full clinical examination, make a preliminary diagnosis and, only on this basis, determine the area of study and the necessary projections.
To identify pulmonary pathology, the following are necessarily used: right lateral and ventro-dorsal projections.
To identify metastases: right lateral, left lateral and ventro-dorsal projections.
For cardiology: right lateral and dorsoventral projections.
To examine the trachea (including to identify collapse): lateral during inhalation and exhalation, straight, oblique cranio-caudal tangentially.
To examine the abdominal cavity: right lateral and ventro-dorsal.
However, do not think that for the same pathology there will be a standard number of images, this is not the case. For each specific case there will be a different number of projections due to the pathophysiology of the ongoing process and the anatomical structure of the animal. In some cases, in order to identify and correctly make an x-ray diagnosis, 2 projections are enough, but in some cases, 4 projections are completely insufficient. Therefore, the main standard projections are initially performed, and then additional projections are made as necessary.
It should also be taken into account that in order for the image to be obtained qualitatively, a well-positioned and fixed animal is important; for this it is necessary that at least 2 people come with the animal for X-ray diagnostics.
I would also like to note that when you come for X-ray diagnostics, you must have a referral for X-ray diagnostics with you, which you can read and print on our website or in the VKontakte group.
You can take an x-ray in Tver at our veterinary clinic “Doctor Ay and Oy” at the address: Tver, T. Ilyina St. 1 B. If you have any questions, please call; (4822)737-077
Source of the VK article “Doctor Ay and Oy” - 2015
radiologist Alexandrova Maria Sergeevna