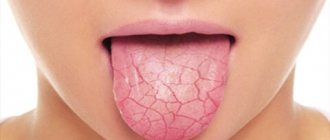
Glossitis is an inflammatory disease of the tongue, which can act as an independent pathology or be a symptom of other diseases of the internal organs. Sometimes a change in the shape or color of the tongue may be the only sign indicating a problem in the body. Therefore, it is important not to ignore painful changes in the oral cavity.
Self-medication can lead to chronic glossitis, which is characterized by severe growths and the appearance of ulcers. Seeing a doctor will help you make a correct diagnosis and cope with the disease in a short time.
Why does the disease occur?
The culprits of inflammation on the mucous membrane of the tongue are pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria) that the local immune system cannot cope with. Most often, glossitis is caused by the herpes virus. It can remain in a latent (sleeping) state for many years after infection and not bother a person in any way. But when immunity decreases, it becomes more active and begins to multiply.
Other possible reasons:
- thermal or chemical burns;
- allergic reaction to toothpaste,
- drinking tongue-burning drinks;
- frequent mechanical injuries from the edges of decayed teeth or sharp edges of fillings, biting the tongue;
- abuse of spicy foods;
- excessive passion for mouth fresheners, rinses with aggressive composition.
People over 50 years of age, smokers, and lovers of caramel and lollipops are at risk. The oral cavity is an ideal place for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, therefore, ignoring hygiene and chronic dental pathologies also cause inflammatory processes in the tongue area.
In most cases, glossitis acts as a symptom of disorders of the digestive system, dysbacteriosis and autoimmune diseases.
How to treat
The treatment methods used will directly depend on the reasons that provoked the development of glossitis, so high-quality diagnosis comes to the fore.
It is impossible to say for sure which doctor treats glossitis, since it will depend, again, on the reasons that caused the disease: you should start by visiting a dentist, who, in turn, may need to consult a therapist and even a surgeon.
If glossitis is a consequence of diseases (syphilis, gastrointestinal problems, anemia), then it is necessary to eliminate these diseases.
To reduce pain, the doctor may recommend applying local lotions with Lidocaine, Pyromecaine and other anesthetics. This procedure can actually be carried out at home. In order to speed up recovery, the tongue is regularly cleaned of plaque with a cotton swab soaked in Chymotrypsin. If there are ulcers, lotions with Iruksol are prescribed. Traditional medicine methods are also allowed, for example, rinsing with a decoction of chamomile or soda, lubricating the affected areas with propolis and much more.
There are quite a few treatment options: the doctor will be able to choose the most effective one, so at the first signs of illness you should not delay visiting him.
Classification of glossitis and their characteristics
Based on external manifestations, there are 3 groups:
- Catarrhal
The inflammatory process affects only the superficial layers of the tongue. Characterized by redness, swelling and plaque formation. The main reason is a fungal disease of the oral cavity (candidiasis) or a burn of a muscle organ. In rare cases, catarrhal glossitis is a consequence of advanced stomatitis or vitamin deficiency.
- Purulent
The most severe form. The pathological process spreads deeper, causing pain and severe swelling. Sores with purulent contents form on the surface of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by high fever and intoxication. Treatment by a specialist is required.
- Ulcerative
With this type, multiple ulcers form on the surface of the tongue, which can bleed. The person experiences severe pain, which leads to a decrease in appetite. Speech disturbances are possible due to swelling and hypertrophy. Provoking factors are inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral cavity.
There is also a form of glossitis called folded. This is a congenital disease, the clinical manifestations of which are folds on the surface of the tongue. Treatment is not required, as this form does not cause pain or discomfort. In some cases, aesthetic correction is possible.
As a secondary disease, glossitis can be a sign of various diseases of the internal organs. In this regard, the following forms are distinguished:
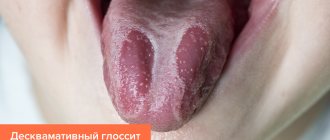
- Desquamative or “geographic tongue” - the external surface of the tongue with this form is similar to a geographical map, that is, lines, grooves, and bright red spots are observed. It occurs in pregnant women due to changes in hormonal levels, as well as in people suffering from chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. A desquamated tongue is often a symptom of parasitic diseases or liver dysfunction.
- Villous - the main symptom is the proliferation of filiform papillae on the surface of the muscular organ. Subsequently, they become like villi. This form occurs with candidiasis or frequent injuries to the tongue. Taking certain medications and smoking can also cause villous glossitis.
- Gunterovskaya is a sign of B12 deficiency and folate deficiency anemia. The surface of the tongue is smoothed and appears shiny. The color is bright red, the papillae atrophy.
- Rhomboid (median) - characterized by thickening of the epithelium with the formation of diamond-shaped pathological areas. Has a chronic course. People with gastritis or low acidity in the stomach suffer from this form. There are flat, tubercular and warty glossitis.
The most dangerous form is considered interstitial, as it acts as a precancerous condition. Without treatment, the cells of the tongue affected by glossitis become malignant, which leads to cancer formation. Also, such glossitis is a characteristic sign of syphilis.
Causes
Due to the fact that the causes of glossitis have not been identified for certain, it would be more correct to talk about risk groups of patients who are more susceptible to developing this disease. The following can be considered as provoking factors that can cause the onset of the disease:
- Disturbances in the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Disorders of the nervous system.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Weakened immunity.
- Pregnancy.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Avitaminosis.
- Dysbacteriosis, including those caused by long-term use of antibiotics.
- Heredity.
Desquamative glossitis is a chronic disease. It is absolutely not contagious. In about half of the cases it develops together with a folded tongue and glossalgia.
Main manifestations of pathology
Symptoms vary. The severity and nature of the disease depends on the form of glossitis and the cause of its occurrence. Characteristic manifestations:
- discomfort or pain when talking or eating;
- change in tongue color - from pale pink to brown;
- swelling, changes in the size and shape of the organ;
- ulcerative lesions, sometimes with purulent contents;
- bleeding wounds;
- the appearance of plaque;
- smoothing of the taste buds, causing the surface of the tongue to become smooth.
An increase in temperature does not always occur. At the initial stage, a person feels only pathological changes on the surface of the tongue; changes in general well-being occur only as a result of the development of intoxication.
In a complicated course, without the necessary treatment, the pathology manifests itself:
- increased salivation;
- bad breath, even with good oral hygiene;
- difficulty swallowing;
- speech disorders due to swelling and deformation of the tongue;
- change in taste or its complete absence;
- burning.
With the villous form, there is no unpleasant painful sensation. But the main symptom is the formation of the so-called “hairy tongue”. Dark, dense growths of a dark color, similar to villi, appear on the surface of the organ. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after examination and examination.
Symptoms
Depending on the type of disease (and there are quite a few of them), typical signs will vary. Nevertheless, there are general symptoms that are similar for all forms.
First of all, glossitis changes the appearance of the tongue: growths that are dense to the touch are formed on it or areas are formed whose color differs from the healthy mucous membrane (the shade can vary from red to burgundy). In addition to visual changes, there are other symptoms:
- burning of the tongue, often accompanied by swelling;
- increased salivation;
- feeling of a foreign body in the mouth;
- changes in taste sensations (foods may acquire an unusual taste, sometimes a person becomes completely unable to perceive the taste of food);
- difficulty swallowing;
- change in diction (speech becomes slurred; in order to express a simple thought, a person has to make serious efforts, because due to pain it is difficult for the patient to pronounce words clearly).
If treatment is neglected, there is a high probability that the disease will enter the chronic stage: its onset is indicated by a change in the structure of the tongue and a noticeable increase in its size.
Drug treatment
The diagnosis is usually made by visual examination. To clarify the causative agent of inflammation, a scraping from the surface of the tongue is prescribed for further laboratory testing. The patient is also referred for consultation to specialized specialists - a gastroenterologist, immunologist, endocrinologist or hematologist. If glossitis acts as a symptom of a pathology of internal organs, then therapy will be aimed at the underlying disease.
Treatment is complex. Local methods include:
- Treatment of affected areas with antiseptic solutions.
- The use of anti-inflammatory ointments with a wound healing effect.
- Rinse with herbal decoctions in consultation with your doctor.
To increase the body's immune strength, vitamin therapy is carried out. For severe pain, analgesics are prescribed. In case of purulent form, it is recommended to take antibacterial drugs. But such treatment is prescribed only after identifying the exact cause of the disease. After the acute period is over, the oral cavity is sanitized if necessary.
The prognosis is favorable, but only if you consult a doctor. Self-medication leads to worsening of the disease. Frequent complications of glossitis are abscesses, phlegmon and oncological formations. These conditions require surgery.
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to visit the dentist regularly, treat chronic diseases of the internal organs, and carefully monitor oral hygiene.
What is glossitis?
What do we know about the tongue as an organ? We know that it is located in the mouth, which helps us articulate and pronounce words correctly, helps us mix food, feel all the diversity of existing tastes, that they can be shown indignation, and in some African countries, a demonstration of it can be used to declare war.
Such a significant number of different physiological and social functions may one day be compromised. And the name of this threat is glossitis.
Despite the absolutely clear location of this organ, there are big questions about which doctor deals with its problems: a dentist, gastroenterologist, maxillofacial surgeon or otolaryngologist. This is not an easy question, and sometimes you can endlessly go from one specialist to another. But let's finally understand this intriguing matter.
Answers on questions
What diagnostics are carried out before treatment?
The dentist examines the patient, collects medical history data: complaints, data on the patient’s general health (presence of chronic diseases). If necessary, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed: a smear (culture) from the oral cavity for microflora.
How to treat hairy tongue in adults?
The doctor prescribes complete sanitation of the oral cavity: removal of stone, plaque, and carious teeth. Selects individual home hygiene products. Prescribes a diet that includes plenty of fluids and solid vegetables. Smoking is prohibited. If necessary, the dentist prescribes rinsing solutions and antibacterial agents.
Types of disease
There are three forms of desquamative glossitis. Superficial is the classic form, involving clear, shiny and smooth spots or stripes of bright red color. Where there are no spots, the mucous membrane is healthy and looks normal. The patient with this form experiences a slight burning sensation.
The hyperplastic form of the disease is associated with the occurrence of focal compactions - due to hypertrophy of the papillae of the tongue and plaque. It comes in yellow, white or grey. If you ask the patient what he feels, he will note the feeling of something foreign, unnecessary in the mouth.
There is also a lichenoid form, characterized by migration of lesions, enlargement of fungiform papillae and a distinct burning sensation. More often it is caused by external factors, for example, allergies, hypersensitivity to those materials that were used in prosthetics and dental implants.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of desquamative glossitis of the tongue is not easy, because sometimes it is necessary to exclude many diseases. For this purpose, different methods are used in laboratory studies:
- microbiological;
- biochemical;
- morphological;
- immunological;
- serological.
Patients undergo blood, stool, and saliva tests, and, if necessary, receive consultations from additional specialists. This is a dermatologist, allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, and often also a psychotherapist.
Preventive techniques for glossitis
Most often, the disease is much easier to prevent than to treat.
For this reason, dentists advise following the following preventive techniques:
- following the rules of dental and oral hygiene;
- systematic preventive examination in the dental office;
- reducing the use of hot spices that irritate the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- giving up cigarettes and alcoholic beverages.
Timely and high-quality treatment can easily eliminate glossitis, while the complete absence of therapy leads to irreversible and sad consequences.