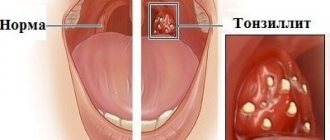
For every parent, there is nothing worse than a child’s illness. I would like to help in any way possible. One of the common pathologies is chronic tonsillitis - inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils. The main reason for its occurrence is weakened immunity.
It is less common in children under 3 years of age; children from 3 to 12 years of age are most susceptible. If you suspect such a disease in your child, it is worth making an appointment with a pediatric ENT specialist, as untimely treatment can lead to unpleasant complications.
What is pharyngitis?
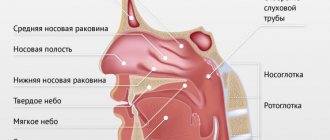
This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and its lymphoid tissue. With pharyngitis, the throat is sore, sore and irritated. The pain intensifies when swallowing. Pharyngitis usually develops with influenza and ARVI. Viral pharyngitis usually goes away on its own. Some other less common forms of pharyngitis may require treatment.
IMPORTANT! Information from the article cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication! Only a doctor can prescribe the necessary examinations, establish a diagnosis and draw up a treatment plan during a consultation!
Does a healthy child have a cough?
In 90% of cases, cough is a symptom of an acute respiratory disease with localization of the inflammatory process in the nose, nasopharynx and oropharynx or in the lower respiratory tract. However, the cough reflex is a mechanism for protecting the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract from various pathogens, including viruses.
Ciliated epithelial cells, making oscillatory movements, contribute to the formation of a protective mechanism called mucociliary clearance (MCC - a mechanism for cleaning the respiratory tract from foreign particles, including infectious ones):
– bronchi;
– trachea;
- nasal cavity. MCC in healthy children under normal conditions is the main mechanism for cleansing the trachea and bronchi.
Clearing the lower respiratory tract of foreign particles occurs due to the transport of tracheobronchial mucus and its subsequent elimination. Mucus has a bactericidal effect because it contains immunoglobulins and has certain properties - liquid, viscous, elastic.
Healthy children can cough up to 5-6 times a day, an infant up to 11 times during teething due to excessive salivation. A night cough is almost certainly a sign of illness.
With inflammation of the respiratory tract, mucus production may increase, sputum becomes more viscous, and the drainage function of the ciliated epithelium is inhibited.
In young children, the cough reflex is still imperfect. Therefore, with inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract in infants, cough may be absent. In infancy, it weakens the baby, makes it refuse to eat, and regurgitates food.
When to go to the doctor?
Take your child to the doctor if your child's sore throat does not go away after breakfast.
Call an ambulance immediately if:
- the child has difficulty breathing;
- he cannot swallow;
- The infant is drooling unusually, which may indicate an inability to swallow saliva.
If an adult has pharyngitis, visit a doctor in the following cases:
- severe or prolonged (more than a week) sore throat;
- throat hurts often;
- difficulty breathing, swallowing, or opening your mouth;
- earache;
- joint pain;
- rash;
- fever above 38.3 for more than three days;
- blood in saliva or sputum;
- pain when turning the head;
- nodes and tumors in the neck;
- Hoarseness, hoarseness lasts more than two weeks.
What to do if a child has a barking cough with fever
Parents of boys and girls under 6-8 years of age may have encountered nightly attacks of a loud barking cough when a child suffering from acute respiratory infections suffocates at a high temperature.
Acute attacks plus nasal congestion, sore throat, hoarseness, difficulty in breathing, and a preceding barking cough are a sign of acute stenosing laryngotracheitis or false croup (FC). The development of laryngeal edema, accumulation of mucus and muscle spasm against the background of inflammation can create a threat of asphyxia. LC is a complication of viral infections, most often parainfluenza, influenza, and can also occur with measles, rubella, chickenpox, diphtheria and scarlet fever. The likelihood of edema in a dry, overheated room in the autumn-winter period is quite high. Most often, the acute form of laryngotracheobronchitis develops in children of the second and third year of life (more than 50% of cases), somewhat less often - in infancy (6 - 12 months) and in the fourth year of life. In boys, this complication is observed almost 3 times more often than in girls. The cause of LC is not an allergy, but a virus. If a child has a seizure during which he experiences difficulty breathing, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you can take a number of measures on your own, having previously agreed with your doctor: lower the air temperature in the room and increase the humidity: you can hang the radiators with wet towels, turn on the humidifier, calm down yourself and calm the child. You can distract your baby with a tablet, give him a drink of cold mineral water without gas or a lukewarm compote. It is possible to carry out inhalation with a drug prescribed by your doctor. It must be remembered that a warming compress, which mothers love so much, is contraindicated at high temperatures and fevers, as well as during the active phase of an infectious disease, so it is better to avoid this measure. Since hyperthermia causes additional swelling, a pediatric antipyretic may be given at high temperatures.
Causes
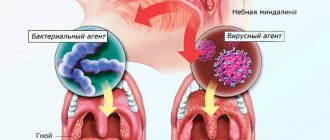
As a rule, this is a viral infection (ARVI), in some cases it is bacterial (streptococcus, pneumococcus). In addition, the cause of pharyngitis may be:
- allergies to dust, mold, pet hair, pollen. Since allergies cause a runny nose, fluid can drain down the back of the nasopharynx and irritate the throat;
- dry air, especially in the morning;
- tobacco smoke, chemical irritants;
- overstrain of the vocal cords (long performances, loud screams at sports competitions, etc.)
- gastroesophageal reflux - reflux of stomach contents back into the esophagus. May be accompanied by heartburn, a lump in the throat, and hoarseness.
- HIV. Pharyngitis may be a sign of a recent HIV infection in the body. Also, people who have been infected with HIV for a long time may experience secondary acute and chronic pharyngitis caused by cytomegalovirus, oral candidiasis and common viruses that cause acute respiratory viral infections. These complications can be dangerous in HIV-positive people.
- Malignant tumors of the throat, tongue, and trachea can also manifest as pharyngitis, coupled with hoarseness, noise when breathing, blood in saliva and sputum, and a “knot” in the neck.
Rare causes of pharyngitis can be a throat abscess and epiglottitis, a serious condition in which the epiglottis, which looks like a petal between the trachea and larynx, becomes inflamed and blocks air from entering the airways. As a rule, epiglottitis in children is caused by a hemophilus influenzae infection, against which it is necessary to vaccinate on time.
Not just a sore throat. We talk about pharyngitis in children
Your child has a sore throat. “Is it really a sore throat?” – did you think? This may be true, but there are other diseases that can cause a sore throat. One of them is pharyngitis. What it is? What are its reasons? How is it manifested and treated?
Our questions are answered by otolaryngologist “Clinic Expert” Voronezh Inna Stanislavovna Chirskova.
— Inna Stanislavovna, what is pharyngitis, and how common is this disease in children?
— Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, in particular the back wall of the pharynx. It occurs very often in children; it almost always accompanies colds - acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections. Moreover, in children this disease, unlike adults, in most cases occurs in an acute form.
Read more about ARVI here: What is ARVI?
— Is there another course of this disease besides acute pharyngitis?
— Yes, the course of pharyngitis can be either acute or chronic, but the second option is more common in adults.
— What are the causes of pharyngitis in children?
— Most often, the disease appears against the background of general or local (inhalation of cold air) hypothermia. Excessively dry air can also provoke pharyngitis, which is especially important during the heating season, as the mucous membrane of the pharynx dries out. To avoid this, you need to use special humidifiers.
Inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa can occur after drinking cold liquid (for example, water, milk, compote) or as a result of a burn to the mucous membrane when eating too hot food. Breathing air filled with chemicals or tobacco smoke can also make you sick.
All these factors lead to a weakening of both general and local immunity in the child, and his body is less resistant to infection.
The direct causative factors of pharyngitis are influenza viruses, enteroviruses, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, various types of herpes (this separate form of the disease is called herpetic pharyngitis), and the Epstein-Barr virus. Moreover, in young children, pharyngitis is of viral origin. Viruses are transmitted by airborne droplets and household contact.
Pharyngitis can also be caused by fungal infections, mainly Candida fungi (this form is more typical for very young children), and various types of cocci (a type of bacteria).
Let us separately highlight allergic pharyngitis as a reaction of the body to some food products, medications, or plant allergens.
With adenoiditis (inflammation of the adenoid tissue in the nasopharynx) in children, draining infected mucus causes and maintains inflammation of the back wall of the pharynx.
With reflux - the backflow of acidic stomach contents into the oropharynx - the back wall of the pharynx also suffers from the effects of acid. Fortunately, this doesn't happen often.
Read materials on the topic:
Herpes: how to recognize and cure? There is no need to panic, but you need to get treatment. What do we know about the Epstein-Barr virus? What to do if you suffer from heartburn?
— Please tell us about the signs of this disease. How does pharyngitis manifest in children?
— Symptoms of pharyngitis include intense pain in the throat, especially with an empty sip of saliva, dry throat, hoarseness, sore throat, dry cough, which can last for several weeks. Unlike chronic, acute pharyngitis in children always occurs with more vivid and pronounced symptoms, sometimes body temperature rises.
— Many parents know firsthand about such an illness as sore throat. How does it differ from inflammation of the pharynx and is it possible to determine at home whether a child has a sore throat or pharyngitis?
— Sore throat (or, in other words, acute tonsillitis) is an inflammation of the tonsils. Sore throat is always caused by pathogenic microorganisms. This is mainly pyogenic streptococcus - a very dangerous bacterium that causes a lot of complications. Bacterial sore throats can also be caused by other, no less malicious microbes - for example, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, moraxella. Bacterial infections require antibiotics. The doctor decides which ones specifically.
The disease is manifested by an increase in body temperature above 39 degrees, intense sore throat and necessarily severe intoxication (poor appetite, weakness, tearfulness). The course of a sore throat, in comparison with pharyngitis, is much more severe and requires mandatory treatment by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable here.
Of course, the mother of such a child, suspecting he has a sore throat, can use a streptate test, which is sold in a pharmacy: this test will show whether the sore throat is caused by streptococcus or not. But further diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of the child must be carried out by a doctor, even if the test results are negative.
When we talk about sore throats, we cannot help but talk about their other forms - viral sore throats. They are very common in young children. They are caused by adenoviruses, enteroviruses, the Epstein-Barr virus and herpes viruses (the latter type of sore throat is called herpetic and is accompanied by the formation of rashes in the form of small bubbles with liquid on the tonsils and soft palate).
Fungal sore throats. They often proceed more easily, appearing in the form of a bright white, cheesy, easily removable coating on the tonsils. In this case, the child’s temperature remains subfebrile (stays within 37.1–38.0 degrees).
Read materials on the topic:
Take care of your throat! How to avoid “summer” sore throat? Viruses and bacteria - what is the fundamental difference?
— Which doctor treats pharyngitis in children? Is this always a doctor of one specialty?
— This disease is treated comprehensively. An ENT doctor (otolaryngologist) can determine the extent of damage to the pharynx, and several specialists can be involved in the treatment of pharyngitis - a pediatrician, a gastroenterologist, an allergist-immunologist, an infectious disease specialist. But the first person you should contact if you have a sore throat is, of course, an ENT doctor.
— How is pharyngitis diagnosed?
— The diagnosis of “pharyngitis” is made by an ENT doctor after an initial examination of the child. Then a swab is taken from the throat for flora. If necessary, the doctor can use the same streptatetest. Next, the child is sent for a general blood and urine test.
- Let's talk about the treatment of pharyngitis in children. What is it?
- First of all, both the child’s drink and food should not be hot or cold - only warm. Treatment, in any case, is prescribed by the doctor. According to his recommendation, local antiseptics are used to dissolve in the mouth (these can be tablets, lozenges), and an inhaler is used. There is no need to do any warming up, nor do you need to breathe over the steam. The child’s diet should not contain carbonated drinks, irritating foods - spicy, containing a lot of spices.
— Are there effective folk remedies for treating pharyngitis in children?
— Warm milk with butter and honey helps to soften the back wall of the oropharynx (unless, of course, the child is allergic to honey and tolerates milk well). To gargle, you can use warm decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs: decoctions of chamomile, eucalyptus, sage, calendula. The doctor will tell you how to prepare such products.
— How often do doctors have to deal with pharyngitis in infants? Are there any special features in the treatment of infants?
— Pediatricians work with infants. In such children, pharyngitis is often caused by fungi - the same candida. Treatment, as with older children, is complex. Infants cannot gargle, so they are given chamomile infusion simply to drink.
— Is it possible to somehow protect a child from pharyngitis?
— You should not smoke in a room where a child is often present. It is necessary to observe household hygiene: so that there is less dust, so that the air is fresh and not dry. Try to strengthen the child’s immunity; hardening will not hurt. Avoid hypothermia - no ice-cold drinks from the refrigerator. Avoid exposure to air conditioning and keep your feet warm.
Interviewed by Igor Chichinov
You can make an appointment with a pediatric otolaryngologist here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
How to get rid of a barking cough? Let's talk about laryngitis Immunity under control! We create a strong rear for a child How often is it? A child who is often ill at a pediatrician's appointment
For reference:
Chirskova Inna Stanislavovna
In 1995 she graduated from Samara Medical University. She worked as a general practitioner, and in 2002 she specialized in otorhinolaryngology. Since 2002, she has worked as a clinic receptionist. Since 2021 - ENT doctor at Clinic Expert Voronezh. Receives at the address: Voronezh, st. Pushkinskaya, 11.
Risks and measures to prevent pharyngitis
Pharyngitis most often affects children and adolescents; adults also get sick, but somewhat less frequently. Also, the risks of pharyngitis increase with dry air, throat irritation from tobacco smoke or chemical reagents, allergies, weakened immunity, chronic or frequent infections of the nasopharynx.
You can reduce the likelihood of illness in the same way as in the case of other nasopharyngeal infections: wash your hands, do not drink from the same cup with others, cover your mouth when coughing and sneezing (do not “share” your viruses), wipe the screen and keyboard of phones and other devices etc.
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Typically, the ENT examines the patient's throat, as well as his nose and ears, carefully palpates the lymph nodes, and listens to breathing using a stethoscope.
The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to diagnose bacterial pharyngitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child's throat, and within 24-48 hours the result is ready. Streptococcal pharyngitis will have to be treated with antibiotics.
We have our own laboratory in the clinic, so you can always take all the necessary tests with us!
Treatment
Viral pharyngitis usually resolves within 5-7 days. The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt - a teaspoon per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial pharyngitis is treated with antibiotics. You should not interrupt or stop the course, because this increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
You can make an appointment by phone: + .