Alveolitis is an inflammation of the socket (alveoli) left after tooth extraction. This pathology does not always develop; its development depends on many factors. The disease is characterized by severe pain in the area of the hole formed after surgery, general weakness, fever, headache, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, bad breath and other unpleasant symptoms.
Alveolitis is not only physically painful, but also a dangerous disease. In the absence of proper treatment for several days, the inflammatory process can result in limited osteomyelitis, purulent melting of the jaw bone, and then surgical intervention will be required again.
With timely diagnosis of pathology and proper sanitation of the socket, the treatment prognosis is favorable. The main thing is to detect the symptoms of the disease in time and begin to treat it.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the healing of the hole, dentists distinguish several main forms of dental alveolitis:
- Serous. The initial stage of the disease usually appears 2–3 days after tooth extraction. This form is characterized by continuous pain that worsens while eating. Although the patient does not yet complain of feeling unwell, his lymph nodes are not enlarged, but he already feels that the disease is progressing.
- Purulent. If the serous form of alveolitis is not treated, the disease turns into a purulent form. Most often it is diagnosed 6–7 days after tooth extraction. The painful sensations can no longer be ignored, the pain intensifies, radiating to the ear or temple. Exploring the affected area also causes severe pain. Purulent alveolitis is characterized by a dirty gray coating inside the socket, significant swelling around the wound, thickened alveolar process and other problems. The patient's general health deteriorates significantly. Lymph nodes enlarge and become painful on palpation. Often the patient cannot even eat or open his mouth.
- Hypertrophic. At this stage, the symptoms of the disease subside. The patient notes a decrease in body temperature, improved well-being and decreased pain. However, at the hypertrophic stage, dangerous tissue proliferation occurs, which is clearly visible upon examination. When touched, pus is released from the inflamed area, and the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint.
Ask a Question
Restrictions
It is logical to perform a preservation operation after the removal of permanent molars, within the so-called sevens, second molars (except for wisdom teeth, eights), since when baby teeth fall out, bone tissue does not resorption. There is no upper age limit for performing an operation aimed at preserving the natural contours of the alveolar process.
Causes of inflammation
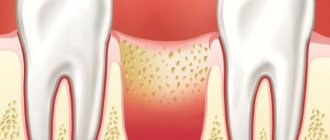
The disease can develop only after tooth extraction. Most often, the hole formed after removal heals within a day after the operation, and the patient feels better. But if the blood clot that covers the open wound moves or becomes deformed, an infection can penetrate into the hole, in which case alveolitis of the gums develops. As a result, the surface of the wound heals for a long time, and the patient suffers from complex discomfort.
Predisposing factors for the development of inflammation:
- Surgical injuries during complex removal. The more complex the operation, the more pronounced the postoperative inflammation of the bone tissue will be, and the more likely the release of direct plasminogen activators.
- Complex extractions associated with tooth segmentation, osteotomy, detachment of the mucoperiosteal flap. Complex operations increase the chance of developing alveolitis 10 times.
- Removal of wisdom teeth. The denser, less vascularized bone tissue adjacent to the figure eights is prone to the formation of dry sockets.
- General diseases of the patient. Alveolitis often occurs against the background of concomitant diseases. For example, patients with diabetes mellitus or immunocompromised patients are more susceptible to alveolitis due to impaired healing processes in the tissues.
- Taking oral contraceptives. The estrogen contained in these drugs may indirectly enhance the fibrinolytic process, causing the breakdown of the blood clot.
- Smoking. The direct connection between smoking and alveolitis has been repeatedly proven clinically. According to studies, the risk of socket inflammation in smokers increased 4-5 times compared to non-smokers. The incidence increased by more than 20% in patients who smoked 1 pack per day and by 40% in patients who smoked immediately before and after surgery.
- Dislocation of a bunch. If the socket is handled carelessly and there is negative pressure (for example, due to drinking through a straw), alveolitis may develop.
- Bacterial infections. Dentists agree that bacterial infections are the main risk factor for dry socket.
- Poor oral hygiene. The incidence of alveolitis increases significantly with poor oral hygiene.
- Excessive use of local anesthetics. According to some studies, excessive use of an anesthetic with a high concentration of a vasoconstrictor can provoke ischemia and make it difficult for the socket to fill with blood. This condition also increases the risk of alveolitis.
In fact, alveolitis is a fairly rare disease. According to statistics, it affects approximately 3% of patients who have undergone tooth extraction surgery. More often than not, the socket is not formed properly when lower incisors and molars are removed.
But alveolitis is especially common when removing lower wisdom teeth: according to experts, in approximately 20% of cases, the removal of “eights” with difficult eruption is complicated by alveolitis. In addition, it is believed that the risk of developing the disease is inextricably linked with age. This is explained by the fact that metabolism slows down, immunity is weakened, and the regenerative abilities of the body deteriorate.
Treatment quality criteria
The main criterion for the quality of an alveolar socket preservation operation is its independent complete healing and maximum preservation of bone tissue, preservation of the natural contour and volume of the alveolar ridge, improvement of the condition of soft tissues and simplification of further stages of treatment. If the operation is successful, there will be enough bone tissue in the socket to install a dental implant. Separately, it is worth highlighting the advantages of condomization for the doctor and the patient - this is improved long-term treatment results, more predictable aesthetics and, of course, saving time for the doctor and the patient.
Symptoms of alveolitis
As a rule, the patient ignores the first symptoms of inflammation without due attention, considering them to be the norm after surgery. After tooth extraction, as already noted, pain within 24 hours is considered normal. As the hole heals, the pain subsides and completely disappears after a few days.
If the patient develops an inflammatory process, then the unpleasant sensations do not subside after a day or two, and 3–5 days after the operation, severe, throbbing pain in the socket occurs, which intensifies as the infection develops.
With alveolitis, patients may complain of both unbearable and moderate pain. Pulsation and pain are focused, as a rule, only in the removal area. However, in rare cases, the pain radiates to half of the face.
Other characteristic symptoms of alveolitis are:
- a sharp rise in body temperature;
- tooth sensitivity to hot/cold food;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- decreased appetite;
- increased salivation.
In rare cases, the disease causes weakness, increased fatigue, and secondary infectious foci appear on the oral mucosa.
Classification of periodontal diseases.
As Carl Linnaeus said, knowledge begins with classification. And the most popular classification in the world is the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10)
- By 05.3 chronic periodontitis;
- By 05.2 acute periodontitis:
- other.
- desquamative;
- ulcerative;
- hyperplastic;
- simple marginal;
- By 05.1 chronic gingivitis:
- K.05.0 acute gingivitis.
- simple;
- difficult;
- other.
- By 05.4 periodontal disease.
- By 05.5 others.
- By 05.6 unspecified.
- By 06.0 gum recession.
As you can see from the classification, the main periodontal diseases are gingivitis, periodontitis and gum recession. Now we will briefly tell you what kind of animals these are.
Diagnostics
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of acute pain, which does not subside either 24 hours or 2–3 days after tooth extraction. Sometimes a dentist can identify chronic alveolitis during routine oral examinations. In this case, an empty socket without granulation tissue appears in place of the impacted tooth. The bone is already visible at the bottom of the hole.
The dentist will be able to determine the presence of tissue changes during the examination; radiography and radiovisiography of the affected area may also be prescribed.
Contraindications
Preservation surgery is subject to the same restrictions as any osteoplastic surgery. Separately, I would like to note that it is not recommended to preserve a hole after tooth extraction in a state of acute pain, since the risk of complications increases. But in each specific clinical case, the actions of a professional dentist are strictly individual. Sometimes situations arise when you have to take risks, but this is due solely to medical indications. In any case, it is necessary to understand that performing a tooth extraction operation and subsequent preservation on a planned basis is better than as part of emergency care.
Treatment of alveolitis
When the socket becomes inflamed, the main thing is to eliminate the source of infection, prevent the development of inflammation and preserve the dentition. In order to alleviate the patient’s condition, the dentist uses the following therapy methods:
- Mechanical cleansing of the hole, washing out purulent residues with a solution of nitrofural or hydrogen peroxide.
- Anesthesia of the hole. The pain syndrome is relieved with the help of local applications with anesthetics and analgesics. To do this, the doctor applies the lotion for half an hour and then removes it to prevent the proliferation of microbes in the area. The dentist will advise the patient to repeat the procedure several times a day. Taking painkillers orally is not recommended.
- Taking antibiotics. In the presence of concomitant diseases, alveolitis is treated with antibiotics.
With the right approach, the signs of alveolitis subside 2-3 days after the start of treatment. If therapy was not started on time, residual pain may drag on for 2–3 weeks.
With the permission of the dentist, additional treatment of alveolitis with folk remedies is possible:
- Sage rinses. To prepare the solution, brew a large spoonful of dry sage in 250 ml of boiling water, leave the mixture for an hour, wrapping the container in a towel. After this, the liquid should be filtered and used for rinsing.
- Gargling with chamomile flowers. To prepare the composition, brew a large spoonful of chamomile flowers in a glass of water for 15 minutes, insulating the container with a towel. The infusion should be strained and rinsed your mouth up to 12 times a day.
- Poplar buds. To prepare, take half a glass of buds, pour into a glass container and pour in 500 ml of vodka. The product should be infused for 10 days in the dark and cool, then filtered, soaked in cotton swabs and applied to the inflamed area.
- A soda rinse solution can also be an effective addition in the treatment of alveolitis. You should take a large spoonful of powder in a glass of warm water or mix soda with water to obtain a paste-like mass, which then needs to be used to treat the hole.
- Burdock leaves. To prepare a medicinal decoction of burdock leaves, you need to pour 20 grams of raw material with 2 glasses of water, and then simmer the mixture over low heat for about 40 minutes. The resulting solution should be cooled and filtered, and then used for rinsing.
- Aspen bark. Pour 1 tablespoon of crushed aspen bark into one glass of boiling water. It is important to leave the solution in an airtight container for 3 hours, and then use 100 ml of strained warm liquid at least 3 times a day.
- Anise infusion. To prepare the infusion, pour 1 tablespoon of anise into 200 ml of boiling water, and then keep in a thermos for 50 minutes. The liquid should be filtered and used to rinse 3 times a day.
Prevention
The best prevention of pathology after tooth extraction is to be attentive to yourself and follow all the surgeon’s recommendations. While the hole is healing, give up bad habits, eating too hot, spicy, sweet foods, and if possible, switch to pureed foods. And if you suspect inflammation, contact your dentist as soon as possible.
Under no circumstances should the first symptoms of alveolitis be ignored. Against the background of inflammation, more serious problems may arise:
- Phlegmon is an acute diffuse purulent inflammation.
- An abscess is a purulent inflammation of tissues with their melting.
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic process that can develop in the bone and bone marrow, as well as in the surrounding soft tissues.
- Periostitis is inflammation of the periosteum.
- Sepsis is a severe systemic inflammatory reaction.
- Tissue necrosis is local tissue death.
Modern methods of treating alveolitis make it possible to quickly relieve the symptoms of inflammation and avoid the complex consequences of the disease. The sooner the patient consults a doctor, the less likely it is to develop complications.
Tooth tissue
- Enamel: The most durable tissue in the human body, covering the surface of the dental crown. In terms of hardness, enamel is equivalent to crystal, since 97% of this tissue is inorganic.
- Dentin: the main hard tissue of the tooth. It consists of 70% hydroxyapatite, as well as water and organic material, fibers consisting of collagen, and dentinal tubules.
- Cement: tissue that covers the surfaces of the root and neck of the tooth. It is similar in hardness to bone. Cementum connects the alveolar bone to the tooth via the periodontal ligament.
- Dental pulp: loose tissue consisting of connective tissue fibers located in the tooth cavity. Rich in nerves and vessels (lymphatic and circulatory). Supplies dentin with nutrients.
Considering how a tooth is structured, one cannot exclude nearby tissues that support and strengthen the tooth.
- Periodontal ligament: fibrous tissue connecting the tooth root and alveolar bone.
- Alveolar bone: The jawbone that supports the tooth - it contains the sockets where each tooth is seated.
- Gums: soft tissue covering the alveolar bone.
- Gingival sulcus: a small space between the tooth and gum, the depth of which is between 1 and 2 mm. If this space deepens due to inflammation, a gum pocket is formed.
Based on their chewing function, teeth are classified into 4 types:
- The front teeth are incisors, used for cutting and grasping food.
- Fangs are cone-shaped teeth located next to the incisors, involved in holding and tearing food.
- The back teeth are small molars (premolars) and large molars (molars) that grind food.
Knowing the structural features of teeth, it is easier to find a common language with a dentist. You will feel confident and better understand the essence of the manipulations being performed.
Structure of the human tooth:
Treatment of alveolitis in STOMA clinics
Surgeons at STOMA clinics are required to examine patients and give recommendations on how to care for the hole formed after tooth extraction. If problems arise after extraction, the patient can always call the clinic and clarify whether inflammation has really begun and what to do to reduce pain.
At any time after removal, the patient can contact our clinics. The attending surgeon will examine him and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Feel free to call us at any time and consult about your condition. The sooner we start treating alveolitis, the lower the risk of complications.
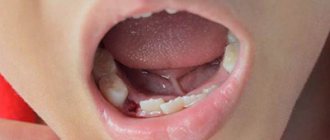
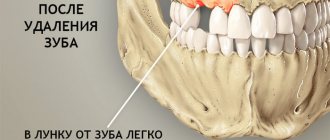
Alveolitis photo of the hole
Often the hole may look normal, that is, without pronounced deviations, but this can be seen in the photo. But here you can consider the presence of a narrow inlet. It is also not very clear whether a clot is present in this case. Of course, making a diagnosis under such circumstances is very difficult. To do this, the doctor will have to conduct a full examination, which is performed using modern technology. And only because of the constant, very often in the form of increasing pain, smell from the open socket, tumor of the gingival tissue, can alveolitis be suspected.