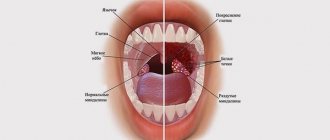
The tonsils or palatine tonsils are an important protective organ located in the human throat. It serves as a barrier to pathogenic bacteria, dust particles and food, and also produces antibodies. In chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, the tonsils do not have time to clear themselves, which leads to the accumulation of pus and mucus on their surface.
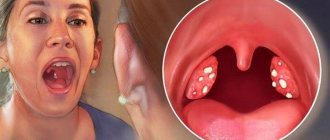
Outwardly, this pathology resembles white lumps in the throat with an unpleasant odor. The affected area becomes inflamed, which leads to increased activity of pathogens. Tonsil masses may go away on their own, but it is recommended to consult a doctor to prevent possible complications.
Symptoms:
- red, swollen tonsils with white or yellowish coating or streaks;
- a sore throat;
- difficult and/or painful to swallow;
- fever (temperature above 38.0);
- cervical lymph nodes are enlarged;
- hoarse or hoarse voice;
- headache;
- stiff neck muscles;
- abdominal pain (especially in young children).
In infants:
- drooling due to pain in swallowing;
- anxiety;
- refusal to eat
- With chronic tonsillitis, your breath may smell bad.
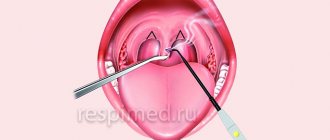
Surgical intervention (opening a tonsil cyst)
In cases where drug treatment is unsuccessful or when the patient experiences obvious, persistent symptoms, the doctor recommends surgical intervention, which helps prevent relapses in the future.
Before opening the cyst, the otolaryngologist performs local application (irrigation, lubrication) anesthesia, opens the cyst with a scalpel and evacuates the contents. After the intervention, the doctor treats the site of the process with antibacterial drugs and prescribes antiseptic therapy.
If necessary, upon completion of the intervention, the otolaryngologist can take the contents of the cyst for analysis or material for histological examination.
If repeated cystic formations occur, the cyst refills with contents, then the most effective method is considered to be surgical intervention, i.e. complete removal of the cyst with its membranes.
Complications of tonsillitis
- Labored breathing.
- Sleep apnea (holding your breath during sleep).
- Spread of infection to the tissue near the tonsils (peritonsillitis), peritonsillar abscess - accumulation of pus behind the tonsil.
- Acute cervical lymphadenitis is inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
Streptococcal tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- acute rheumatic fever, affecting the joints, heart and other organs;
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to serious consequences, including kidney failure).
Treatment with antibiotics significantly reduces the likelihood of complications after streptococcal sore throat.
Possible complications
It is believed that if the white balls are caused by chronic tonsillitis, then you need to worry less. In this case, they will go away on their own with proper treatment. The greatest danger is intoxication of the body, as well as the risk of developing intestinal dysbiosis, since bacteria developing on the tonsils enter the digestive tract. In addition, there is a possibility of the formation of secondary stomatitis and caries on the tooth enamel.
A long-term illness leads to severe discomfort for a person, since an unpleasant odor is difficult to hide during a conversation. In the future, it may be intensified by diseases of the oral cavity.
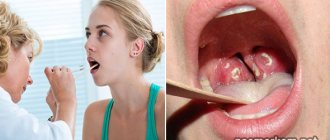
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
- For tonsillitis, the doctor will examine the child's throat, as well as his ears and nose, where there may also be inflammation.
- The doctor will examine the child's skin, since streptococcal sore throat sometimes causes a specific rash. This is what is called “scarlet fever” - it is not some kind of separate disease, but a sign of damage to the body by streptococcus.
- The doctor will feel the cervical lymph nodes - as a rule, with tonsillitis they swell.
- The doctor will feel the spleen to distinguish a sore throat from mononucleosis, which also causes swollen lymph nodes.
- The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to distinguish streptococcal tonsillitis from viral tonsillitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child’s throat and within 24-48 hours the result is ready.
- In some cases, a general blood test may be needed, the results of which can also indicate the viral or bacterial nature of the disease. It is usually taken if the streptococcal test is negative, but the course of the disease leaves the doctor in doubt.
About the clinic
Euromed Clinic is a multidisciplinary family clinic in the center of St. Petersburg.
- Calling a doctor to your home
- 24/7 therapist appointment
- Tests, ultrasound, x-ray
- Whole body diagnostics
- Hospital and surgery
- Vaccination
Find out more about the clinic
Treatment methods
Conservative treatment:
- washing the tonsils;
- inhalation;
- rinsing;
- ultrasonic influence;
- laser therapy.
These procedures cleanse the tonsils, increase blood circulation, have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, which has a positive effect on the recovery process of the tonsils and their proper functioning.
If conservative methods do not produce results, then surgical treatment is resorted to.
Treatment of tonsillitis
The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt and soda - a teaspoon of salt and a small pinch of soda per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial tonsillitis (usually streptococcal tonsillitis) is treated with antibiotics. It is dangerous to interrupt or stop the course because it increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
GBOU "NIKIO im. L.I. Sverzhevsky" of the Moscow Department of Health
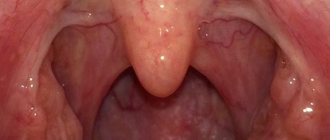
Hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil
The lymphadenoid tissue of the root of the tongue is presented in the form of two clusters of large follicles located in rows or in random groups. These clusters are separated by a central groove extending from the middle of the lingual epiglottis fold to the largest, final, circumvallate papilla on the root of the tongue. Therefore, it is more correct to talk about not one, but two lingual tonsils. The number of large follicles in a 1-year-old child is 10-12, and in a 5-year-old child it is 20-30. At the age of 35 to 40 years, the maximum number of follicles (35-40) is observed with a simultaneous increase in their size. After 45 years, the number of follicles decreases and the size of each of them decreases (A.I. Tseshinsky, 1951).
One must think that the main cause of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil in adulthood is inflammatory processes in the oropharynx. In some cases, hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil develops as a compensatory process in individuals who have had their palatine tonsils removed (B. S. Preobrazhensky).
Symptomatology and diagnosis of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil.
Severe enlargement of the lingual tonsil can cause mechanical difficulty in breathing and voice production. Such cases, however, are very rare. Typically, patients with hypertrophy of the lingual tonsils complain of a feeling of pressure projected into the area of the hyoid bone, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, cough, and sometimes laryngospasm . These complaints are not pathognomonic for hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil. Therefore, their assessment requires caution. Sometimes patients with hypertrophy of the lingual tonsils complain of coughing paroxysms. In such cases, mechanical irritation of the lingual tonsil using a probe can provide some assistance in diagnosis. If cough occurs only when the lingual tonsil is irritated, then it seems likely that it is the receptive field of the cough reflex.
When making a differential diagnosis, you need to keep in mind the following diseases.
- Inflammatory processes in the area of the root of the tongue. They can be caused by a banal infection (abscesses and phlegmon of the root of the tongue), tuberculosis, syphilis and various fungi (actinomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, blastomycosis, moniliasis). These diseases differ from hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil by the asymmetry of the lesions, their greater density and more saturated color. Histological (biopsy), serological and bacteriological examination helps.
- Tongue root cysts. In this area, there are retention cysts of the mucous glands and very rarely - cysts formed from elements of the thyroglossal duct. They are distinguished by a smooth-stressed surface.
- Benign tumors - adenomas and mixed tumors of the salivary glands are more common. They are also distinguished by their smooth surface and significant density.
- Malignant tumors - cancer and lymphoepithelial tumors are usually observed. Diagnosis is simple for ulcerated tumors.
- The goiter of the tongue root is distinguished by a pink, smooth surface covered with a network of highly developed venous vessels. It has a significantly higher density than hypertrophied lymphadenoid tissue. In some cases, the thyroid gland is absent in its usual place, which can be confirmed by palpation of the neck in thin individuals. Research with radioactive iodine helps, which, after ingestion, is concentrated in the thyroid tissue, as a result of which strong gamma radiation is detected in the area of the root of the tongue.
Treatment of hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil.
With moderate hypertrophy, patients are prohibited from smoking and eating spicy foods. Sometimes alkaline rinses and lubrication with iodine-glycerin are beneficial. Some authors recommend cauterization with lapis and galvanocauter. The use of radiation therapy has been proposed. With severe hypertrophy of the lingual tonsil, its surgical removal is indicated. It can be removed piece by piece by “biting” under the control of a laryngoscopic mirror. Some authors prefer to perform complete enucleation of the lingual tonsils along with the capsule. Such intervention is especially advisable in cases where there are significant inflammatory changes in the hypertrophied lingual tonsils or if these tonsils are the cause of repeated phlegmonous inflammation in the area of the root of the tongue, damage to the kidneys, joints and other organs. Before the operation, a detailed clinical examination of the patient is necessary, studying the blood picture, its coagulability, counting the number of platelets, etc.
We perform removal of the hypertrophied lingual tonsil using a holmium laser (Ho:YAG) with a radiation power of 4.8 W (energy - 0.6 J, frequency - 8.0 Hz).
Treatment of tonsil cancer
For any prevalence, excluding metastatic stage 4, surgical treatment is recommended at the first stage - removal of the tumor and lymph nodes affected by metastases.
If surgery is not possible, radiation is carried out in combination with chemotherapy or chemotherapy is performed sequentially, and then radiation therapy, and again the issue of surgical treatment is resolved. But if the cancer is completely regressed as a result of conservative measures, you can stop there; if there is any remaining cancer in the irradiation zone, removal is suggested.
The metastatic process is subject to systemic treatment - cytostatics in combination with immuno-oncological drugs. The spectrum of cytostatics is quite wide; 4 monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated effectiveness.
Causes of tonsil cancer
Not so long ago, it was assumed that the leading role in the etiology belongs to the use of strong alcoholic beverages in combination with aggressive smoking or the tradition of chewing psychoactive plants and herbal mixtures - nasa and betel by some eastern peoples.
In recent years, it has become established that the malignant process is caused by the activity of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, similar to cervical carcinoma.
Risk factors include occupational hazards - tension in the vocal apparatus and chronic inflammatory processes - tonsillitis, tonsillitis.
Stages of the disease
The staging of tumors with intracellular DNA inclusions of human papillomavirus type 16 (16HPV) and without it differs.
For virus-negative neoplasms, everything is simple:
- Stage 1 - local formation up to 2 cm, without metastases in the lymph nodes;
- 2 tbsp. - tumor less than 4 cm and lymphatic collector without signs of cancer;
- 3 tbsp. - neoplasm more than 4 cm with “clean” lymph nodes or less and there is a node up to 3 cm;
- 4 tbsp. suggests either a primary tumor of any size with distant metastases, or a very widespread lesion of the oropharynx with a large conglomerate of lymph nodes on the same side, or a not very large cancerous node with lymph nodes on the opposite side of the neck.
When staging papillomavirus cancer in stages 1 and 2, metastatic lymph nodes are possible, and stage 4 - only with distant metastases from any tumor and lymph nodes.