Each person normally secretes mucus in the lumen of the bronchi. This mucus protects the bronchi and lungs from dust and infection from the inhaled air. If a person is healthy, then the production of this mucus is not accompanied by a cough. However, when inflammation occurs in the bronchial tree, there is a significant increase in mucus production and a change in its viscosity. A cough occurs and the person coughs up this mucus. Mucous discharge passes through the bronchi, trachea, laryngeal cavity and mouth before leaving our body. This discharge is called sputum. Sputum is also called discharge during inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract - nasopharynx, larynx.
The nature of sputum - its color, viscosity, smell - has important diagnostic significance. In classical medicine, there are such artistic descriptions - sputum in the form of “raspberry jelly” (suggests the presence of pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumonia). Or canary-colored sputum (may indicate pulmonary aspergillosis). Scarlet sputum may indicate hemoptysis or pulmonary embolism.
For chronic and acute pulmonary diseases, mucopurulent and purulent sputum is most characteristic. The sputum becomes cloudy and yellow instead of clear. Over time, the color of the sputum becomes yellow-green, and later takes on a purulent, green character. Sometimes the sputum has a putrid odor. The physical properties of sputum also change - it becomes viscous and viscous. It is difficult to cough up.
White lumps in the throat with an unpleasant odor: what is it?
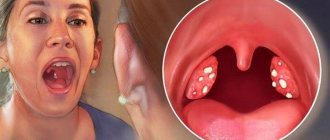
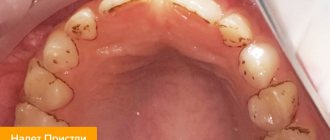
Small lumps that sometimes enter the mouth under certain circumstances are nothing more than tonsillar plugs or stones that form in special recesses of the tonsils - lacunae.
They can have different shapes, sizes, colors and textures, depending on their composition.
As a rule, people note white, slightly less often yellowish or even grayish bad-smelling balls. Sometimes they have a soft consistency, in other cases they are quite dense, which is due to the presence of calcium compounds in their composition.
White lumps formed in the lacunae of the tonsils are formed from aged and exfoliated cells of the mucous membrane, a small amount of food residues and various types of bacteria.
As a rule, these are staphylococci, streptococci, somewhat less frequently chlamydia and other microorganisms, that is, mainly representatives of opportunistic flora, which are constantly present in the oral cavity of every person.
Sometimes they contain pus. In such situations, they acquire a yellow tint and a characteristic odor.
When they appear, a person may feel significant discomfort, manifested by:
- sore throat;
- feeling of the presence of a foreign body behind the tonsils;
- bad breath.
Although often the formation of formations does not manifest itself in any way. A person becomes aware of their presence only when he coughs up part of the cork.
Associated symptoms
Chronic tonsillitis is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- Foul-smelling pellets are coughed up. This can happen during a conversation. Sometimes they even fly out when sneezing, causing discomfort to a person. Most often their size is small - no larger than a match head, but sometimes the plugs are quite large.
- White plaques on the surface of the tonsils can be observed in the upper layers, so they can be noticed when examining the throat. But sometimes they are concentrated in deeper layers of tissue, so they are not noticeable.
- Periodic sore throat. This unpleasant symptom is especially noticeable in the morning. Sometimes the soreness can be so pronounced that a person begins to choke.
- Sore throat, redness. This may prevent the patient from swallowing normally, making it difficult to eat and drink.
- A feeling that something is stuck in the throat, something is gnawing. Some patients note the presence of a lump in the throat.
- Bad breath. It is so pronounced that others can feel it.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- General deterioration of health, aches and malaise.
- Cough. It is associated with the desire to cough up something that bothers a person.
When coughing, lumps are not always cleared up, but thick mucus may come out. It may have a jelly-like consistency, making it difficult to cough up completely. The symptom is relieved by consuming throat lozenges or mints.
But in some cases, a person is not bothered by any symptoms. And he learns about the presence of some kind of pathology only by the lumps leaving the throat.
Yellow lumps from the throat with an unpleasant odor
When yellow lumps come out of the mouth, the first thing to suspect is the presence of a purulent process. This is due to the fact that it is pus that gives the infiltrate a yellowish tint.
But sometimes crumbs are coughed up that smell strongly of rotten, even in the absence of such pronounced inflammation. In such situations, their shade is a consequence of the long stay of tonsillitis in the lacunae.
Is it possible to remove purulent plugs on the tonsils yourself?
Sometimes patients make attempts to remove all stones and plaques on their own so that their breath does not stink. But doctors warn that getting rid of tonsil blockages at home is fraught with serious consequences. By wielding a foreign object, the patient can disrupt the integrity of the lacunae and cause an infection in the throat.
At home, you can perform inhalations with compounds that have anti-inflammatory and disinfecting properties. To combat white formations on the tonsils, it is recommended to use herbal preparations, with which you can rinse your mouth or carry out inhalations. To increase efficiency, you can add cedar essential oil to the inhaler.
If white lumps on your tonsils don’t give you peace, you can try to get rid of them in several safe ways:
- Sometimes the plugs “come out” of the gaps if you press on them with your tongue. After the procedure, be sure to rinse your mouth.
- You can try removing the plugs with a soft-bristled toothbrush.
White balls in the throat and tonsils indicate inflammation in the pharynx, so it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe a treatment regimen. Remember that manipulations carried out at home do not guarantee getting rid of white formations in the throat and relieving chronic tonsillitis.
White lumps in the throat can appear against the background of diphtheria, sore throat, respiratory diseases; they form on the side walls of the throat, tonsils, and sometimes cough up on their own during coughing or sneezing. Effective medicines and traditional medicine methods will help eliminate the appearance of clots.
White lumps in the throat are a consequence of the development of the disease
Reasons for the appearance of white lumps on the tonsils
They usually occur in people suffering from chronic tonsillitis. This disease often results from the lack of proper treatment for the acute form of the pathology.
The following can provoke its aggravation:
- ARVI;
- weakening of the immune system;
- taking excessively chilled drinks, ice cream, etc.;
- overwork.
However, sometimes white lumps with an unpleasant odor on the tonsils are also found in absolutely healthy people who have a certain tissue structure of the tonsils and have previously had a sore throat.
White balls from the throat with an unpleasant odor in an adult
According to authoritative medical sources, almost always an expectorated white lump in an adult is the result of a current or past sore throat that has not been completely cured. Its appearance requires consultation with an ENT specialist.
The doctor will help you accurately determine the reasons for the formation of traffic jams, the degree of neglect of the pathology, and prescribe treatment appropriate to the situation, which will give maximum results.
At the same time, patients should be prepared for the fact that therapy can stretch over a fairly long period of time and may include not only medication, but also physiotherapeutic and medical procedures.
Also, to achieve stable remission, eliminate tonsillitis and the bad breath caused by them, the therapeutic course must be repeated every six months
and regularly be comprehensively examined for the possibility of damage to other organs and the development of complications.
Patients should be aware that in severe situations, surgery may be necessary.
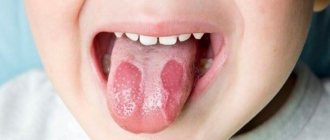
White spots in the throat in children
In a child, the reason why white lumps form on the tonsils can be a sore throat, which is also called acute tonsillitis. Its chronic form, especially in young children, is rarely diagnosed.
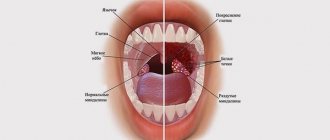
With tonsillitis, the tonsils may become covered with a whitish film or small individual spots. This is always accompanied by severe pain and severe persistent sore throat, fever and weakness.
At the same time, white lumps often appear on the throat due to candidiasis - a fungal infection of the mucous membrane, which can be a consequence of decreased immunity, severe infection or severe stress.
Gradually they appear in other parts of the oral cavity, sometimes they clear the throat, but more often the plaque remains unchanged.
Causes of the unpleasant phenomenon
The cause of white lumps in the mouth is chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tonsils of the palate . It can occur as a result of untreated acute tonsillitis, reduced immunity, smoking and other negative factors.
Due to constant inflammation in the tonsils, pathogenic flora multiplies. Bacteria accumulate and, together with waste products and food particles, form white or yellow lumps.
More often they occur due to streptococci and staphylococci. Less commonly, chlamydia, viruses, and fungi lead to their appearance. They are present in the oral cavity of every person, but in minimal quantities. Under the influence of certain factors, they begin to multiply excessively, leading to the formation of lumps. The lacunae expand, and general intoxication of the body is observed.
To prevent tonsillitis from developing, it must be treated in an acute form. The disease is accompanied by severe sore throat, malaise, and weakness.
The chronic form of the pathology is almost asymptomatic, so a person may not notice when plugs form. Gradually, the white blood cells surround the bacteria present in the throat of the patient. In the absence of treatment, they are filled with deposits of magnesium and calcium salts, and therefore become hard.
Here are the main factors leading to their occurrence:
- Diseases of the nasal cavity that have a chronic course. As a result, the infection can spread to the throat.
- Improper oral hygiene. If you don't brush your teeth, a large number of bacteria develop in your mouth, which can get on your tonsils.
- Reduced immunity. Because of this, a person becomes vulnerable to any infectious diseases.
- Damage to the tonsils. An infection gets into the wound, causing a purulent inflammatory process to begin.
Diagnostics. When should you see a doctor?
In general, any person can periodically form white lumps with an unpleasant odor in the mouth. When this is not accompanied by discomfort or the formation of persistent plaque and these are not lumps of pus, no specific treatment is required.
But still, the appearance of such traffic jams should serve as a reason to contact a specialist and conduct an examination in order to determine the causes of their occurrence. For this purpose the following is carried out:
- UAC and OAM;
- ECG;
- immunogram;
- bacteriological examination of a throat smear.
These examinations are necessary to determine the existing chronic disorders and the presence of possible complications that chronic tonsillitis could cause.
How to treat white formations in the throat?
Since the main reason why white lumps appear on the tonsils is considered to be tonsillitis, in order to radically get rid of the problem it is necessary to fight this particular disease.
To eliminate it, and at the same time purulent lumps from the throat with an unpleasant odor, a set of measures is needed, including:
- washing the lacunae of the tonsils;
- antibiotic therapy;
- gargling;
- strengthening the immune system;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Drugs
The main direction of drug therapy is antibiotic therapy. To eliminate pathogens of the inflammatory process, the following can be used:
- Polydex;
- Isofra;
- Augmentin (Amoxiclav);
- Cefazolin;
- Rovamycin;
- Erythromycin.
To relieve pain, I advise patients to dissolve special lozenges, for example, Strepsils, Septolete, Lizak, Lisobakt, Faringosept and others.
In order to normalize body temperature, paracetamol (Panadol, Efferalgan-Upsa) and ibuprofen (Nurofen, Imet) are recommended.
Immunostimulants are also required.
They need to be taken in courses, both during the treatment period and after its completion, to ensure the persistence of remission and strengthen the immune system. These include:
- Lycopid;
- Imunofan;
- IRS-19;
- tincture of echinacea or ginseng;
- rosehip decoction;
- vitamin complexes.
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils
To remove the pellets from the lacunae (recesses) of the tonsils, it is necessary to carry out specific rinses, carried out in the otolaryngologist’s office. The procedure can be performed either using a syringe or a Tonsilor device.
Syringe rinsing is an old, but still frequently used technique, the essence of which is to pre-treat the tonsil mucosa with lidocaine and insert the tip of a special brass cannula into the mouth, which is placed on the syringe.
As soon as the anesthesia takes effect, an antiseptic solution is supplied through the cannula, the pressure of which mechanically helps to wash out the plugs and remove all pathogenic flora.
To perform the procedure the following are used:
- copper-silver solution;
- Ectericide;
- streptocide solution;
- Furacilin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin.
This manipulation takes on average about 10 minutes, but, despite preliminary premedication, it is quite unpleasant for the patient, especially if he has a strongly developed gag reflex.
During it, it is important for the patient to remain motionless, not paying attention to the discomfort, since a sudden, careless movement can lead to damage to the tonsils by the tip of the cannula and aggravation of the inflammatory process.
As a rule, at least 7–10 sessions are required to achieve good results. Without the proper skills, it is almost impossible to wash out all the accumulations from the winding gaps.
Remember
It is strictly not recommended to carry out such a procedure at home, as it can lead to injury or lack of effect.
A more modern and gentle procedure for washing the tonsils is the hardware method, which involves the use of the Tonsilor device. Its essence is to suck out all the plugs with a vacuum.
In addition, during manipulation, the mucous membrane is exposed to ultrasound, which has an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. The course of treatment consists of 5 sessions held every other day.
However, any washing technique cannot be used if:
- acute period of acute respiratory infections, accompanied by fever;
- cancer;
- tuberculosis;
- pregnancy.
Almost always, completing the full course of treatment leads to stable remission, which lasts from 6 months to several years.
If you follow the otolaryngologist's recommendations aimed at strengthening the immune system, you can increase the duration of remission indefinitely.
Rinsing
One of the most common and accessible ways to eliminate the problem of coughing up white lumps with an unpleasant odor is to rinse with antiseptic solutions:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Furacilina;
- regular baking soda or pure sea salt without flavorings or other additives;
- Miramistina;
- infusions of chamomile flowers, calendula;
- saline solution or water with a few drops of essential oil, for example, cloves, juniper, tea tree and others.
Rinse thoroughly and for at least 30 seconds, tilting your head back. In the presence of an acute inflammatory process, the manipulation is repeated up to 6 times a day, and if only lumps fly out when coughing and sneezing, 2 sessions are enough: in the morning and in the evening.
Physiotherapy
To increase the effectiveness of the therapy, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UHF, which helps eliminate edema;
- ultrasound therapy necessary to eliminate inflammation;
- UV irradiation, which quickly kills pathogenic microflora;
- laser therapy, the purpose of which is to relieve swelling and inflammation.
All of them help restore normal functioning of the tonsils, their blood supply and eliminate swelling of the palatine arches. To achieve a pronounced result, 10–12 procedures are required.
What gives the yellow-green color to purulent sputum?
The respiratory organs are an open system of tubes devoid of valves, membranes, sphincters, etc. The air we breathe contains microorganisms in addition to organic and inorganic dust. These are viruses, bacteria, fungi. Once inside the respiratory system, they can be removed from it with the help of mucus and villi. In this case, a person will not even feel the presence of foreign objects in the bronchi. But during illness, microbes gain an advantage, multiply quickly, and come into conflict with the human immune system. They die, the protective cells die, and the surrounding tissue is damaged. Complex cytotoxic reactions occur. All these “military” actions lead to a change in the color of sputum. The more pronounced the inflammation process, the more purulent the sputum will become. In chronic long-term processes, sputum acquires a green-brown character and becomes viscous. In this case, the patient may cough up sputum in the form of casts of the bronchi. Green color.
The purulent nature of sputum can occur in acute and chronic lung diseases. In any case, this symptom cannot be ignored. Treatment measures must be carried out quickly and effectively.
Sputum interspersed with dark gray lumps may indicate mold growth or a tuberculosis infection.
The canary-colored sputum is characteristic of pulmonary aspergillosis.
Klebsiella pneumoniae causes a cough with sputum the color and consistency of “raspberry jelly.”
Yellow sputum is characteristic of acute diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes. Such sputum can occur in any pulmonary disease from acute bronchitis to pneumonia.
Green sputum is more typical for chronic lung diseases; this may be bacterial associations of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Such as Haemophilus influenzae + Staphylococcus aureus. Or Pseudomonas aeruginosa P. aeruginosa in combination with streptococci. Occurs in patients with bronchiectasis, COPD, and cystic fibrosis.
Thick green sputum with an odor indicates a lung abscess, abscess pneumonia. Pathogens can be S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, gram-negative bacilli, Streptococcus pyogenes Haemophilus influenzae.
The presence of blood in the sputum may indicate a pulmonary embolism, cancer, or problems with the larynx.
What to do?
In acute diseases, purulent sputum does not appear immediately, but usually on the 4th day of the disease. If coughing up such sputum is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, then the help of a doctor is necessary. No need to self-medicate!
In COPD, bronchiectasis, and obstructive bronchitis, sputum may become purulent within one to two days. Often green-yellow color of sputum is constantly present in a person suffering from chronic pulmonary diseases. During exacerbations, it becomes intensely green and coughs up large quantities. Patients with chronic lung diseases should have an individual plan prescribed by a pulmonologist for preventive and urgent action in connection with the appearance of purulent sputum. If you do not have such a plan, remind your doctor that you need one. If your active actions do not help within 5-7 days, contact a pulmonologist.
Diseases characterized by purulent sputum
- COPD,
- Bronchiectasis,
- Pneumonia,
- Chronic purulent obstructive bronchitis,
- Lung abscess, abscess pneumonia,
- Pulmonary tuberculosis,
- Cystic fibrosis,
- Purulent processes in the nasopharynx,
- Pulmonary aspergillosis,
- Non-tuberculous mycobacteriosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diseases of the respiratory organs leading to expectoration of purulent sputum is a set of measures that includes examination, auscultation, and percussion of the chest.
Mandatory x-ray examination. Computed tomography of the chest organs (CT CT) is considered more informative.
Functional breathing tests - respiratory function, body plethysmography and diffusion tests are often necessary.
Sputum examination is an important stage for prescribing treatment and assessing the prognosis of the disease. Routine sputum tests are important to assess the severity of inflammation (by counting the number of leukocytes in the sputum) and eosinophils. A general sputum test can help identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Fragments of mycelium or pseudomycelium of fungi.
The microbiological method (sputum culture) answers the question of what is the name of the microorganism that causes purulent, mucopurulent inflammation in the lung tissue. The sputum is sown on special nutrient media, the colony is counted and the name of the pathogen is determined. Detection of H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis and S. Pneumoniae.
For example, risk factors for Pseudomonas infection include recent hospitalization (2 days within the past 90 days), frequent use of antibiotics (4 courses within the past year), severe COPD, isolation of P. aeruginosa during a previous exacerbation, stable period of Pseudomonas colonization, and systemic use of glucocorticoids.
It will require the prescription of antibiotics aimed at destroying these particular microorganisms.
How can we help?
First, it is necessary to treat the disease leading to cough with purulent sputum. Be it an acute or chronic disease. The presence of hemoptysis is an urgent reason to consult a doctor.
- If the disease is caused by bacterial flora, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
- If we are dealing with influenza and bacterial pneumonia that has developed against it, a combination of antiviral drugs and antibiotics is needed
- If the cause of purulent sputum is a fungal infection, then it is necessary to treat with antifungal drugs
- If tuberculosis is detected, then use anti-tuberculosis drugs.
For a rapid response to treatment, bronchoscopy may be effective. These are manipulations in which a flexible endoscope is inserted into the bronchus, which sucks out purulent sputum from the bronchi, and with the help of it you can pour an antiseptic and antibiotic into the bronchus. But the method is traumatic, unpleasant and dangerous with complications.
An alternative to bronchoscopy can be considered hardware coughing technologies - intra-alveolar percussion devices, vibration vests, exercise therapy sets, breathing simulators and coughers for home use.
What not to do?
It is absolutely forbidden to squeeze out stones on the tonsils, or attempt to pick them out with cotton swabs, a toothbrush or other objects, since this will help remove only a small part of the formation, but will cause great harm to the body.
During such manipulations, the patient injures the mucous membrane and promotes the movement of plugs deeper into the lacunae.
All this is fraught with, at a minimum, the occurrence of painful sensations and aggravation of inflammation, and in the worst case, blood poisoning (sepsis).
When is surgery necessary?
If left untreated, pathogenic bacteria can infect the tonsils so severely that over a certain period of time they cease to perform their barrier function and become a source of infection, from where it spreads throughout the body and can cause damage to other organs.
In such situations, huge plaques form on the tonsils, white lumps regularly come out of the throat, smelling disgusting, and the patient is constantly plagued by discomfort in the throat.
In such situations, conservative therapy often no longer produces the expected results, and the otolaryngologist may recommend the patient to remove the tonsils. This operation is called tonsillectomy.
This surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia and can be performed either by classical surgery or by more modern methods: laser, radiofrequency ablation, etc. The procedure takes little time and is characterized by a short and simple recovery period.
Causes
If the state of the body has reached the point where white lumps come out of the throat, then it can be said that the person has developed chronic tonsillitis. Scientists have concluded that the tonsils are an integral part of the immune system. This means that the appearance of caseous plugs can be provoked by a weakened immune system. Therefore, smokers, alcohol drinkers, and people living in unfavorable environmental conditions are at risk.
One of the reasons for the appearance of white lumps can be infection. Usually a strong body quickly copes with this kind of problem, but if it weakens, it can no longer overcome it. The infection is actively developing, inflammation occurs and, as a result, caseous plugs. People who have breathing problems to varying degrees should be especially careful, for example, if the bridge of their nose is bent.