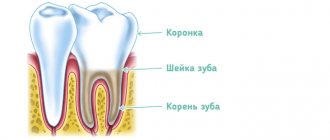
- Treatment of caries and pulpitis of milk teeth
- Treatment of caries and pulpitis for children and adolescents under 16 years of age
- Children's prevention and hygiene
- Tooth extraction for children
- Anesthesia for children
A grown-up person who already has his own opinion at a dentist’s appointment is a big responsibility for the doctor.
The psycho-emotional sphere of school-age children and adolescents is not formed and is vulnerable, so parents reduce control over hygiene and the condition of their teeth, but physiologically, the teeth and the entire dental system require increased attention, because At this age, the child enters a phase of active growth. Therefore, we draw the attention of parents to the fact that it is very important not to miss this period - it lays the foundation for the health of your children’s teeth for the rest of their lives. It is necessary to ensure that the process of changing teeth and forming a permanent bite is completed correctly and to correct all violations in a timely manner, if any are detected. And most importantly, preserve the newly erupted permanent teeth - at this time they are most susceptible to caries. We will tell you in detail how to do everything correctly and avoid mistakes on this page.
Why do we need a special approach to the treatment of caries and pulpitis in mixed dentition?
A child’s new permanent teeth are very different in structure from the teeth of an adult – they have fragile, not yet mineralized (not saturated with minerals) enamel and unformed roots. In order for a tooth to “mature” it will take from 3-4 months to 1.5 -2.5 years for the mineralization of the enamel, and up to 4 years for the formation of roots. Those. in fact, the formation of full adult teeth is completed by the age of 16.
Until this age, a teenager has “special” teeth, so until the age of 16, he should be treated by a pediatric dentist, no matter how much he would like to be an adult and see an “adult” doctor. Only a pediatric dentist has sufficient skill in treating permanent teeth that have not yet fully formed - he has not only the knowledge for this (any dentist theoretically knows how to treat “young” teeth), but also the necessary daily experience. And the absence of relapses of the disease and complications in the future depends on correctly performed manipulations.
Is chewing gum good for you?
The cult of chewing gum and whitening toothpaste at a young age does not add health to your teeth. Not only do teenagers chew gum for more than 15 minutes (this process can take several hours), but they also use it repeatedly. Chewing gum really cleans the mouth. However, only in the first minutes. Afterwards, it becomes a breeding ground for bacteria and plaque on thin enamel. Within a few hours in the mouth, 2 cubes of chewy sweetness can cause caries.
Striving for a stellar smile can lead to complete destruction of the enamel. Therefore, when at the age of 30 you want to show off your white teeth, you will have to spend a lot on replacing them. To prevent this from happening, you should contact a dental clinic, where they will select a program for gentle enamel cleaning. to become the owner of a “ Hollywood smile ”. Firstly, thanks to professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. The dentist, using a sand-saline solution and an ultrasound machine, literally removes plaque from the teeth. This method can lighten the enamel by a tone or two, but not lighter than the natural color. This procedure is necessary in youth. It is not only possible, but also must be carried out every six months. Thanks to which your teeth will be healthier and cleaner.
Sometimes doctors offer gel teeth whitening. This is a long-lasting and invisible way to whiten and make your teeth lighter. Its advantage: safety for health and a very stable result. And lastly, clinics often use whitening strips. They contain peroxide and work many times better than any other method. However, due to the acid content, teenagers should avoid it.
Causes of caries and pulpitis of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
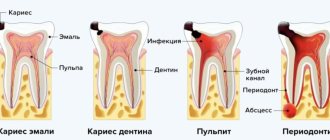
There are 2 main causes of caries - the presence of caries-pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity and an increased concentration of carbohydrate breakdown products, which create an environment for the proliferation of bacterial colonies. The acid released during their vital activity washes minerals out of the tooth enamel, it becomes porous, brittle and begins to break down - this is how caries forms. Read more about the mechanism of development of caries disease, types of caries and its symptoms in our article Treatment of caries in adults - they are completely identical in children.
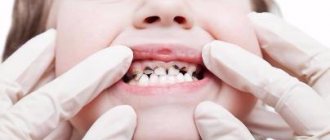
Diet, of course, matters, but it is difficult to explain to teenagers that a passion for sugary soda and snacks undermines the health of their young permanent teeth. A grown-up child is trying to get rid of parental control and care, including dental hygiene, and his parents allow him to do this - after all, the child is already big. Unfortunately, our children at any age do not like to brush their teeth, and they do not know how to do it correctly. This approach leads to the fact that children aged 9-12 years are included in the main risk group and have the highest rates of caries and pulpitis.
The lack of habit of visiting a pediatric dentist at an earlier age leads to fear of the doctor; the teenager desperately resists going to the clinic - who wants to “give up”? At this age, the child does not want to show himself as “not cool.” As a result, 70% of children’s visits to the clinic are due to acute toothache, and this is almost a 90% chance of having pulpitis. Having received such a diagnosis at such an early age, there is a very high probability of not saving your tooth until adulthood.
Only thorough prevention can reliably protect a teenager from dental problems - regular professional hygiene and preventive procedures - such as remineralization and sealing of fissures of fragile teeth - they are effective and painless. We talk about this in more detail in the article on Children's prevention and hygiene.
What should you do when the third molar is cut?
Often the eruption of the third molar on the upper jaw is completely asymptomatic. On the lower jaw, this is only possible if there is space. If there is not enough space, the wisdom tooth begins to erupt to the side, pushing the adjacent tooth, which is accompanied by pain and inflammatory symptoms around the third molar.
It also happens that the third molar partially erupts and part of it remains in the bone tissue. The erupted part of the tooth is covered, like a hood, by the mucous membrane, and food debris can get under it, which leads to inflammation of the mucous membrane around this tooth. The dentist at the 32 Dent clinic can eliminate the symptoms of inflammation by washing the contents of the pocket formed under the overhanging mucosa.
If the third molar lies in the bone tissue at an angle in relation to the adjacent teeth, it is recommended to remove it. In order to avoid dislocation of a nearby tooth and injury, wisdom teeth should be removed no earlier than 17 years of age.
How is the treatment of caries of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years old at the GALA DENT clinic?
Treatment of caries of permanent teeth in children should be carried out with maximum consideration of the psychological factor and must be done by a CHILDREN'S dentist with full local anesthesia and, if necessary, sedation. Read more about anesthesia for children.
We select the anesthetic drug and its dose individually for each young patient and use the latest generation of anesthetics that are safe for children.
Dental treatment under general anesthesia is not advisable, because it affects the child’s entire body and is justifiably used only in the most extreme cases, although to parents the “put to sleep and cure” option sometimes seems to be the best way out.
Uncomplicated caries of permanent teeth in children is treated in the same way as in adults. First, anesthesia is performed, then the tooth is thoroughly cleaned of damaged tissue and filled. For permanent teeth in children, we use high-quality photopolymer (light-hardening) filling materials, the same as for adults, with precise color matching to the natural color of the enamel.
Also, do not forget about the restoration of the chewing surface of the tooth - for adolescents this is a very important stage of treatment, because the correct formation of the entire dental system, which is in a period of active growth, depends on the quality of interdental contacts.
The total duration of treatment for one visit to the dentist in adolescence should be no more than 40-50 minutes.
Advice for teenagers
In order for a young man to smile widely, he needs to monitor and care for his dental health correctly:
- Brush your teeth and floss twice a day to avoid plaque deposits;
- limit the consumption of sweets and starchy foods, create a diet of foods that do not harm teeth;
- undergo regular dental examinations;
- if a malocclusion develops, visit an orthodontist, who will recommend the best treatment option - braces, dental plates;
- if a teenager is involved in active sports, then he should wear protective mouthguards to protect his teeth and gums from injury;
- avoid bad habits such as smoking, which causes plaque deposits, bad breath and can lead to cancer;
- if you want to somehow express yourself and make yourself a piece of jewelry, for example, tongue or lip piercing, you don’t need to do it in unsanitary conditions, it’s better to go to the dentist, talk about your desire, and he will advise what measures should be taken;
- It is impossible to whiten your teeth at home, but you can maintain whiteness after professional whitening with the help of whitening pastes; in no case should you use chemical elements to make your smile snow-white on your own, without the supervision of a doctor.
It is important for parents to understand that teenagers are children, but they cannot simply be ordered around. They need to be taught, mentored, and shown a positive example of a healthy lifestyle. And it is very important to teach him to take care of his oral and dental health and regularly visit the dentist and make visits to the doctor every six months a habit that he will take with him into adulthood.
Causes of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children and adolescents under 16 years of age in mixed dentition
The tooth is nourished through a neurovascular bundle called the pulp. Its inflammation is called pulpitis.
- Typically, pulpitis develops as a complication of untreated caries, when the carious process “goes” deep into the tooth tissue, destroys the pulp chamber and bacteria infect the pulp. Such a diagnosis requires serious intracanal (endodontic) treatment.
- In adolescence, children have a habit of not telling their parents that something is bothering them, so very often they do not receive timely treatment. As a result, patients often come to the appointment already with severe pain, complications and deterioration of their general condition (fever, headache, weakness)
- Read more about other non-carious causes of pulpitis, its main forms, symptoms and possible treatment methods in Treatment of pulpitis (dental canals/endodontic treatment).
We keep the tooth alive!
The main task of a pediatric dentist is to preserve the tooth and its internal tissues (nerves). This is the only way the tooth can finally form, the enamel will reach the required thickness, and the roots will grow and become stronger. Therefore, the adolescent dentist must strive with all his might to help the nerve survive, in whole or in part.
For this purpose, doctors at Babyboom Pediatric Dentistry use materials that are biologically compatible with dental tissues. By supporting them and constantly monitoring the regeneration process (which, fortunately, occurs much faster and better in adolescents than in adults), the doctor helps the pulp tissues recover even after very deep caries.
How does the treatment of pulpitis of permanent teeth in children and adolescents differ from the treatment of adults?
Newly erupted “young” permanent teeth do not yet have formed roots. Therefore, if pulpitis in a teenager is to be treated, the doctor must first find out, using x-rays, whether the roots of the diseased tooth have formed or not. If the roots are not formed, then the treatment of the tooth canals is carried out as sparingly as possible.
Unfortunately, the method of partial removal - amputation of the pulp, which is often described on dental websites as acceptable in this case, does not work well in practice. It gives too many complications and a 100% guarantee that the tooth canals will need to be re-treated, so this method of treatment is practically not used in our clinic.
You also need to remember that if you do not seek dental care in a timely manner or if a doctor makes a mistake, pulpitis in adolescents quickly becomes complicated and turns into purulent forms, periodontitis (inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth) and even sepsis (blood poisoning).
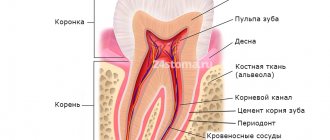
What does the dental formula look like in a medical record?
The dental formula of an adult, as well as a child, in the medical record of a dental patient looks in the form of a schematic table (Fig. 5), which will reflect only the serial numbers of permanent or baby teeth.
Directly in this formula, the doctor will mark the missing teeth (in this case, the number is crossed out with a cross), which teeth are affected by caries, pulpitis or periodontitis, as well as which of them have crowns or bridges. Dental formula in the form of a table in the medical record –
Is it possible to restore a dead nerve?
If the nerve does die, our dentists can help restore it. We have a unique revascularization technique that helps “bring back to life” pulp tissue. In this case, the doctor carries out the work, dividing it into several stages:
- The dental canals are sterilized and cleaned.
- Filling the channels with medicine and the patient's blood cells.
- Sealing the canal.
- Over the course of several months, a special tissue appears that replaces the functionality of the nerve and allows the tooth to develop and grow, and the roots and enamel to become stronger.
During the treatment process, doctors will monitor the process of pulp restoration using computed tomography.
Typical problems
The norm is the arrangement of permanent teeth in a row without “tipping” to the side or “protruding”, which indicates a harmonious process of replacing temporary teeth with permanent ones.
The formation of improper closure of teeth and, as a result, their crowding in the area of chewing and frontal teeth occurs in the case of early removal of chewing temporary teeth and displacement of permanent teeth forward.
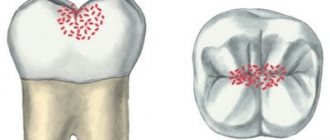
Poor oral hygiene in nine to twelve year old children is a common problem. Its appearance is explained by the peculiarities of the child’s psychological development during this period. The result is the development of caries in permanent “young” teeth. The sixth chewing teeth, that is, the first molars, are most often affected in the area of the natural grooves of the teeth (fissures). Remaining unnoticed, fissure caries develops very rapidly, leading to pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve of the tooth).
Features of the period
In the dentition of a nine-year-old child, the lower and upper incisors, as well as the first permanent molars, are emerging, and baby molars and canines are still present. Normally, the permanent teeth are located without “tipping” to the side or “protruding.”
The process of forming the roots of already erupted permanent teeth (lateral and central incisors, first molar) is completed by the age of ten. In this way, these teeth are “stabilized” in the bone.
Resorption of the roots of the first primary molar (fourth primary tooth) occurs at nine to ten years of age. During the same period, it is replaced by a permanent one (first premolar) on the upper jaw, and after some time - on the lower jaw. Resorption of the roots of the second primary molar (fifth primary tooth) and temporary canine begins at ten to twelve years of age and is replaced by the second premolar and canine, respectively. The permanent canine is the last one to erupt.
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones is completed by the 12-13th period and at this moment the child should have 24 teeth, that is, 12 teeth on each jaw.
Why are braces better than removable appliances?
Recently, parents are increasingly choosing braces instead of plates. Modern children live an active life - they attend clubs and sports clubs. With this rhythm, parents, who themselves usually work a lot, cannot control the child all the time. Children often forget to put on records and lose or break them. And in orthodontic treatment, regularity and continuity are important. If you do not wear the device for more than 1-2 weeks, it will not fit and you will have to make a new one. Each repair and replacement is subject to payment. As a result, treatment becomes unproductive and expensive.
The braces cannot be removed or lost, but they are quite difficult to remove. In addition, they do not need to be cleaned and washed separately; it is enough to use a brush and a special brush when brushing your teeth as usual.
The most important advantages of braces are the speed of alignment, the ability to correct complex pathologies and a more stable result.