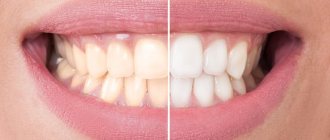
Today, many patients when visiting dentistry complain about the loss of the natural shade of tooth enamel. Why does enamel become dull and lose its natural color? There are actually a huge number of reasons, and it is to them that we will pay attention today, but a little further. Now we note that this problem can be dealt with using modern teeth whitening technologies, Zoom whitening, Brite Smile, Opalescence, which are successfully used in medical science.
External discoloration
External discoloration is a superficial change in the color of teeth that does not affect the structure of the tooth itself. The cause is a hard, pigmented plaque that settles on the tooth enamel. On the surface of the enamel coating there are a large number of microscopic grooves and cracks, where food dyes and tobacco smoke resins are retained.
Frequent consumption of coffee, strong tea, red wine, smoking, combined with insufficient oral hygiene lead to enamel staining in yellowish or brownish tones.
Changing the color shade of tooth enamel: varieties
There are two types of loss of natural tooth enamel color:
- Internal change. Occurs in the inner part of the tooth structure - dentin. The tooth becomes covered with gray, yellow spots or darkens.
- External change. The process takes place in the outer layer; deterioration is indicated by the appearance of yellow spots, white stripes, and dips on the surface of the tooth.
It is worth noting that external discoloration can be treated with special whitening technologies. Internal change is more difficult to cure. Its treatment may require aesthetic methods, such as veneers.
Internal discoloration
Internal discoloration of teeth is formed due to deep changes in the hard tissues of the tooth: dentin and enamel.
The following factors can lead to changes in the shade of tooth enamel.
- Consuming water with high fluoride content. Excess fluoride, settling on the surface of the enamel, makes it matte and softer. Subsequently, dyes accumulate in these areas, changing the color of the enamel.
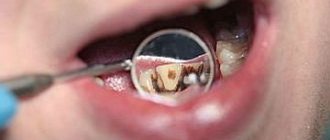
- The carious process, causing demineralization and destruction of the organic matrix, promotes the penetration of microorganisms deep into the tooth tissue. Brown and black spots form at the site of the lesion.
- Long-term use of certain medications - tetracyclines, hormones.
- Natural aging. With age, the processes of enamel remineralization slow down, it becomes thinner, and in combination with external factors, its darkening develops.
- Violation of the rules of endodontic treatment. With poor quality treatment, pathogenic microbes continue to multiply in the root canals, the waste products of which are sulfide compounds. These compounds, penetrating through the dentinal tubules into the hard tissues of the tooth (dentin, enamel), stain them dark.
- Pulp removal. A change in the color of pulpless teeth is observed when certain filling materials are used in their treatment:
- filling with Foredent or paracin gives the tooth crown a pink color;
- the silvering method causes a gray or dark gray coloration of the enamel;
- the use of iodoform-containing pastes leads to yellowing of the tooth.
- When tooth depulpation occurs, trophic processes are disrupted, which leads to a deficiency of mineral and organic components. As a result, the optical density of dental tissues changes, and consequently, the color of the tooth.
- Trauma that leads to damage to the vascular bundle of the pulp. Significant hemorrhage changes the color of the tooth from reddish to pink or orange. The combination of necrosis of pulp tissue together with iron heme gives a gray, blue, brown color.
Tooth pigmentation - symptoms and treatment
A doctor can make a diagnosis of “teeth pigmentation” by collecting all the necessary data after a survey and examination. If necessary, additional studies are performed.
In modern medicine, there are not many methods for diagnosing tooth pigmentation, so choosing the right one is not difficult. These include:
- visual inspection of clinical manifestations;
- radiography - allows you to evaluate the internal structure of the tooth and identify deviations;
- computed tomography (CT) is a fairly modern research method that is beneficial for both the doctor and the patient (the doctor receives a higher quality image, and the patient receives approximately 90% less radiation); allows you to study the image in 3D format and monitor the dynamics of treatment;
- microscopy - magnifies the area under consideration approximately 25 times, makes it possible to study the structure of the enamel and the extent of the lesion;
- rheodentography - allows you to determine the functional abilities of the pulp, as well as assess the depth of the lesion;
- electroodontodiagnosis is a method of studying the condition of the pulp and periodontium (soft tissues surrounding the root of the tooth) using a dosed electric current that affects the nerve without damaging the tissue membrane of the pulp [8][9].
As a rule, to diagnose ordinary pigmentation, it is enough only to collect complaints, an anamnesis (history of the disease) and a visual examination. Doctors resort to more serious studies, such as CT scanning and a microscope, in case of deeper lesions of the dental cavity and periodontium.
To choose the right treatment method, it is very important to establish a correct diagnosis and not confuse a pigment spot with caries. The latter, unlike dark pigmentation, has a cavity bottom that is not only dark, but also loose.
Superficial caries must also be differentiated from a whole group of non-carious tooth lesions, such as enamel hypoplasia, fluorosis, wedge-shaped defect, erosion and necrosis of hard dental tissues.
With caries, the spot is most often a single one. It is localized in the grooves on the chewing surface or one of the contact surfaces (between the teeth), less often on the neck of the tooth. With hypoplasia and fluorosis, the spots are multiple and localized in places atypical for caries: areas of the labial (cheek) and lingual surface of the tooth crowns.
Spots with hypoplasia are usually white with clear boundaries and have a smooth and shiny surface. They are located at the same level of the crowns of several symmetrically located teeth.
How to restore the color of tooth enamel?
In many cases, with the exception of diseases and pathologies, patients have every chance to influence and change the color of tooth enamel for the better, without even going to the dentist. The surest way is to eliminate all foods and drinks that contain food colorings.
In difficult cases, various modern technologies, professional teeth cleanings help restore whiteness, and in the most difficult cases, prosthetics are performed.
There are many ways to restore the natural color of enamel; by contacting our center, each patient can count only on quality, namely the complete restoration of tooth enamel.
A beautiful smile is the key to success!
Smile with us! The dentists at our Center will help you make your smile sparkling for a long time. The department is equipped with the latest technology and has everything necessary to perform high-quality work: a modern dental complex, high-quality X-ray equipment and the latest generation materials. Each patient is guaranteed high-quality treatment and an individual approach to teeth whitening. If, after whitening, you need to replace old fillings with defects with new ones or cure caries, all these problems can also be solved in our dental department.
Remember that beautiful teeth are your calling card in our modern world!
What is whitening?
We will talk about bleaching - a chemical oxidation process, as a result of which, under the influence of oxygen, organic substances are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. During oxidation, organic substances are oxidized to intermediate products that are lighter than the original ones. During this reaction, the oxidizing agent (substance H2O2 - hydrogen peroxide), which has a free radical with a non-polar electron, gives it to the oxidized substance. The substance being bleached accepts a non-polar electron and is thus oxidized. The low or high percentage of strong free radicals depends on the acidic or alkaline environment in which the ionization process occurs. Back in the middle of the second half of the 19th century, articles were published about teeth whitening under the influence of hydrogen peroxide. Currently, modern bleaching systems use carbamide peroxide, chlorides, urea peroxide and hydrogen peroxide, one of the decomposition products of which is atomic oxygen. The intensity of tooth color is determined by the number of paired C=C compounds. Oxidation leads to the formation of a simpler, single carbon compound, which reduces pigmentation, i.e. teeth whitening. Whitening does not affect the surface of fillings and artificial crowns, so after it is completed, color differences may appear, to eliminate which replacement of the fillings or crowns covering the teeth is indicated.
Professional approach
Our clinic prefers the OPALESCENCE whitening system manufactured by Ultradent. We also use in practice and offer patients Rembrandt oral hygiene products. Opalescence, Rembrandt and Colgate are among the few whitening systems that are recognized and trademarked by the American Dental Association (ADA). The Opalescence teeth whitening system is registered by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. Opalescence gel contains 20% water, which helps to avoid hypersensitivity or reduce it, without drying out or dehydrating the enamel. The active ingredient in the Opalescence system is carbamide peroxide. Whitening pastes contain various flavoring additives - neutral, banana, menthol and watermelon flavors. Various concentrations of urea peroxide are available (Opalescence 10%, 15%, 20%) with and without fluorine. 35% Opalescence X-tra with carotene is intended for whitening only in the doctor's chair. The procedure for using the home version of Opalescence is not complicated, but requires strict adherence to the instructions. On the first visit, the dentist determines the initial color of the teeth, studies the medical history, removes dental plaque, and takes impressions of the dentition for subsequent production in the laboratory of individual aligner reservoirs in which the whitening gel will be placed. On the second visit, the mouth guards are tried on, they are adjusted, the patient is taught the technique of applying the gel, the procedure for use, the daily or night protocol for use is explained, and a particular toothpaste is recommended. On the third visit, the achieved result is assessed. The whitening effect is comfortable for the patient and others when the shade of the teeth is lightened by 2-4 tones. Attention!
Filling materials are not bleached. Old fillings need to be replaced, since the whitened teeth will be much lighter, but this should be done no earlier than after 14-15 days. During this time, all cabamide peroxide leaves the tooth tissue, and the shade of the enamel stabilizes. Then you can proceed to the restoration of teeth and select the shade of the composite material that matches the shade of the bleached enamel.
How to treat discoloration at home
You can try to remove pigmented yellow and brown plaque with tooth powder or baking soda. The main thing here is not to overdo it and not damage the enamel layer. Highly abrasive pastes must be used very carefully - paste with charcoal can erase the enamel or leave scratches on it. It is recommended to use such toothpastes no more than 2-3 times a week.
There are ways to combat discoloration online using lemon juice and hydrogen peroxide. Most likely, such methods will not harm the teeth, but the effect will be insignificant.
More effective methods are based on a high concentration of hydrogen peroxide or urea. These are various sticks, strips, mouth guards with gel of dubious production from the mass market. These medications often cause tooth pain and sensitivity. These methods are not suitable for treating internal discolorations; you should visit a dental clinic and consult a dentist.
Caries
Children at an early age are characterized by the so-called “bottle caries”, which develops on several teeth at once due to the habit of falling asleep with a bottle of sweet nutritional mixture. Such food is to the taste not only of children, but also of microorganisms that rapidly multiply in the oral cavity in the presence of a carbohydrate substrate.
The hard dental tissues of toddlers are poorly mineralized, so when the surface layers of enamel are destroyed, they are quickly saturated with food coloring, acquiring a dark and sometimes even black color. Often, with a sufficient content of calcium salts in food, the carious process is stopped, the dentin becomes denser, but the dark color of the eroded surface remains.
With a lack of calcium, the carious process covers a significant area of the tooth surface, leading to its rapid destruction. If it is not possible to close large defects with a filling, then the dentist stops the destructive phenomenon using the silvering method - the enamel is treated with silver nitrate, which, when combined with protein molecules, forms an antimicrobial protective film. The disadvantage of this method is the blackening of the damaged areas, so the method is used on the front teeth only in young children.
Injury
Children's outdoor games are accompanied by injuries that do not immediately manifest themselves. When a tooth is bruised, the thin blood vessels entering through the root apex may rupture, forming a hematoma in the pulp chamber. The crown part of the tooth remains intact, but changes color. If a child’s tooth has darkened after a blow, it is necessary to see a dentist for treatment. Otherwise, inflammation of the baby tooth can affect the development of the permanent follicle, which is located deep in the bone.
Dental specialists will tell you what to do if a child’s tooth has darkened. To detect hidden problems and eliminate them in a timely manner, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations with a dentist. Doctors at the Shifa clinic will teach the child the rules of hygienic care and select a toothbrush and toothpaste appropriate for his age. If you have darkened teeth, our specialists will create a personalized program for restoring dental aesthetics. The clinic has all the necessary equipment to make your child’s teeth beautiful and healthy.
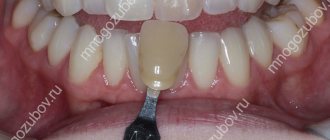
Definitions of tooth color
When making dentures, technicians are guided by a special tooth color chart. According to the Vita scale, which is used by almost all dental clinics in the world, natural teeth can have only a few shades: brown, yellow, gray and red. Depending on the intensity category, colors are designated by numbers from 1 to 4. Thus, if a dentist talks about tooth color under the index A1, he means the lightest shade from the reddish-brown range of the table, accordingly, A2 will be slightly darker, A3 - even darker. Index B corresponds to the yellow tone of the teeth and varies in the same way according to the lightness of the shades (B1, B2, and so on). The gray shade is indicated by the Latin letter C (C1, C2, and so on), and reddish-gray teeth - D (namely Latin, not Russian D). The numerical index of the scale indicates the intensity of the color and starts from one, so tooth color 0 actually does not exist.