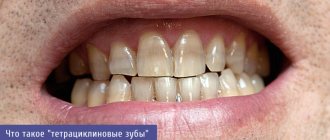
Tetracycline teeth are characterized by the appearance of unnatural shades in the tooth enamel and are caused by the penetration of large or small doses of the antibiotic tetracycline into the body. The route of penetration does not matter - oral administration of drugs and applications to mucous membranes, for example, are also to blame.
Tetracycline intervention occurs in several ways. Often the child receives the drug from the mother while still inside the womb. A pregnant woman, possibly as a result of self-medication or prescribed serious therapy, takes tetracycline. The baby is born with a pathology that becomes visible at the time of teething.
It happens that pediatricians prescribe tetracycline treatment to children under 14 years of age. At this age, the enamel has not yet completed its formation cycle, therefore it is vulnerable and capable of absorbing the medicinal component.
Antibiotics are used to treat diseases that do not require easy progression and self-treatment: pneumonia, ulcers, cholera. Tetracycline also has a good effect on painful skin formations, various rashes, bacteriological lesions, etc. The doctor is obliged to warn the patient about the consequences of such therapy. Not only the enamel is at risk, the marginal periodontium as a whole is also weakened.
Sometimes a change in the color of the enamel occurs in an adult who has not been treated with an antibiotic. But teeth are still called tetracycline teeth - for a similar external effect. The list of possible reasons includes:
- Products containing chemicals and dyes;
- Atypical manifestations of allergies;
- The influence of hard ultraviolet radiation;
- A special reaction of the body to an internal or external stimulus.
An antibiotic that has entered the body cannot be removed. Its danger lies in the possibility of delayed action. That is, a person is being treated now, but the reaction will occur years later.
What colors are tetracycline teeth?
Most often, the enamel in the cervical area of the tooth is affected - it is this area that is the first to form in the fetus. Dynamics of similar frequency are observed when tetracycline is deposited in the lateral parts, in the folds of the enamel. Sometimes all the teeth in a row show the same even shade, and sometimes the color is distributed in spots, making the teeth look mosaic.
The color palette is almost always shifted to the left side of the spectrum. Teeth acquire yellow, brown, orange and brown shades in various variations. Sometimes the enamel looks gray.
Recommendations from experts
Do not try to whiten enamel at home - it is not only ineffective, but also dangerous. For example, by doing your own teeth whitening with chemicals, you can significantly worsen the situation and damage your tooth enamel. To solve this problem, you need to consult a dentist.
NikaDent dentistry employs competent specialists. After examining the oral cavity and conducting diagnostics, specialists will determine effective tactics on how to restore the normal shade of tooth enamel. It is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as the enamel begins to change. Be healthy!
Diagnosis of tetracycline teeth
Treatment of teeth affected by tetracycline requires correct diagnosis. Human teeth can change color when exposed to a variety of dyes. This situation is familiar to smokers with teeth yellowed by nicotine, lovers of strong coffee, red wine, etc. Teeth can change color due to developing caries, darken as a result of nerve removal, or taking iron supplements.
Tetracycline teeth are easy to identify. Under UV radiation they begin to glow brightly, and the doctor determines the cause of the lesion.
Causal factor of the disease
The cause of tetracycline teeth is the use of tetracycline drugs, both in young children and in women carrying a baby. Taking tetracycline by pregnant women does not affect the health of the expectant mother, but it does affect the development of the child’s teeth. The color of the enamel does not change immediately, but gradually. It depends on some factors:
- From the individual characteristics of the body.
- From a balanced or unbalanced diet.
- From the body's response to the action of the drug.
- From ultraviolet exposure.
Remineralization of tooth enamel
The lack of mineral components during the formation of enamel is the main source of the formation of tetracycline teeth. When restoring enamel, applications with calcium gloconate and sodium fluoride are effective. The phonophoresis procedure is used. The goal of therapy is to supply ions of the main elements to the enamel: calcium, phosphorus and fluorine.
Treatment is carried out in the clinic, and in case of slight darkening, outpatient treatment at home is allowed. Up to 20 procedures will be required. If performed daily, therapy will end after three weeks or earlier. With a course of use every other day, it will take up to one and a half months.
In this case, the patient did not have any serious problems with aesthetics. I wanted to significantly lighten my teeth and improve their shape. If we were talking about traditional veneers, we would dissuade the patient from the procedure.
There is no point in sacrificing dental health for aesthetics. In this case, the patient did not have any serious problems with aesthetics. I wanted to significantly lighten my teeth and improve their shape. If we were talking about traditional veneers, we would dissuade the patient from the procedure. There is no point in sacrificing dental health for aesthetics.
With Luxneers you don’t have to choose between health and beauty - you can create a perfect smile without sacrifice! The teeth are not subjected to grinding and you can return to your “natural smile” at any time. The procedure is comfortable, installation is absolutely painless!
Find out more about Luxneers no-preparation veneers
Causes of the defect
This type of pigmentation occurs only in one case - the accumulation of tetracycline salts in the body. It is used quite rarely for the treatment of severe bacterial ailments:
- pneumonia;
- cholera;
- acne;
- ulcers.
The accumulation of the substance occurs in bone tissue, and it is impossible to remove it from the body. Moreover, a change in enamel may not occur immediately, but may be provoked by other reasons. Important! Medicines containing tetracycline are contraindicated in children under 14 years of age, pregnant women and women during lactation.
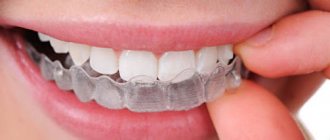
Tetracycline Teeth Whitening
After the initial stage of treatment, most patients with tetracycline teeth will require aesthetic therapy.
It is acceptable to try to whiten dark teeth if your doctor supports this method of restoring the beauty of your smile. The technique will show results if the initial darkening is slight and uniform. However, a situation often occurs when, after a short period of time, the teeth return to their previous color, neutralizing the results of whitening. The patient has to repeatedly subject himself to the procedure in an attempt to achieve harmony.
Any whitening methods acceptable for a particular patient are allowed - hardware and home use. If the result is persistently unsatisfactory, there is only one way out - to resort to dental restoration.
Prevention
The risks of tetracycline teeth are now a well-known problem, so doctors familiar with it try to avoid, if possible, recommending tetracycline antibiotics for pregnant women and children under 12 years of age. But if there are no other possibilities, then, unfortunately, you have to choose the priority of the general health of the mother and child. The doctor may try to make the course of antibiotic therapy as short as possible, since the inclusion of antibiotic molecules in growing dental tissues is a process that takes quite a long time.
Request a consultation
Restoration of tetracycline teeth with veneers
Veneers are a good way out if your own teeth, given by nature, are no longer pleasing. The term refers to extremely thin plates that are placed on the tooth and cover its front part like a shield.
There are a number of technologies for installing veneers. Designs are divided into direct and indirect. The cost of the former is quite affordable for any patient. They are made quickly; the technique is based on layering a composite material on the vestibular part of the tooth.
Hollywood veneers, like those of movie stars, are glued with a special glue; sometimes preliminary grinding of the enamel is required. By analogy with the previous ones, they are very similar to natural enamel, and the doctor enhances the identity by selecting a similar shade and transparency of the veneer according to the Vita scale. Mostly installed on incisors.
The third type of veneers combines expensive lumineers and ultraneers. These plates are attached to the teeth without preparing the enamel. They can be used to cover all teeth in a row, including chewing ones. An additional advantage of lumineers is their extraordinary whiteness and long service life.
Scientific article on the topic:
Changes in tooth color as a result of exposure to minocycline and tetracyclines, whitening methods for these diseases
Authors
Makarova E.S. Student at the Medical Institute, Penza State University, Department of Dentistry. Ryzhova S.A., Efremova A.V., Frolova K.E. - assistants of the Department of Dentistry, Medical Institute, Penza State University, Department of Dentistry
Annotation:
The article reveals the concept and general properties of tetracycline and its derivative - minocycline, as well as their effect on the color of teeth. A classification of the degrees of tetracycline staining of teeth is given. The author reviewed the indications for modern methods of teeth whitening exposed to tetracycline and minocycline.
Keywords:
Tetracycline, minocycline, tooth color, discoloration, tetracycline teeth, teeth whitening, office whitening, home whitening, aligners, ZOOM whitening, laser whitening, outpatient whitening.
Introduction
A snow-white smile is beautiful, white teeth, which are not only a sign of good health, but also a symbol of well-being and prosperity, but not every person can boast of it. One of the reasons for discoloration of the natural color of teeth is the consequences of taking tetracycline drugs (“tetracycline teeth”). To eliminate discoloration of teeth, patients seek help from dental clinics, where they are offered teeth whitening services.
Main part
Tetracycline (Tetracyclinum) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with a bacteriostatic effect. The drug is aimed at destroying gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Tetracycline has found wide use in the form of a drug for the treatment of various purulent skin diseases (including acne, furunculosis), inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract (pneumonia, bronchitis, tonsillitis, etc.) and the genitourinary system (syphilis, gonorrhea, etc.) [5, p. 63].
The use of drugs from the tetracycline group in medical practice has emerged since 1950, and the dental pathology associated with them (“tetracycline teeth”) was first depicted in 1956. The cause of the identified pathology is the use of tetracycline drugs during the period of calcification of temporary or permanent teeth. This is caused by the ability of tetracyclines to pass through the placental barrier, then be deposited in dentin and, to a lesser extent, in tooth enamel (it is assumed that the critical dose is at the level of 21-26 mg/kg and above). In this case, a tetracycline-calcium-orthophosphate complex is formed, which, under the influence of ultraviolet rays, acquires a darker color. The described process mainly occurs on the vestibular surfaces of the front teeth, which are most exposed to solar radiation when talking and smiling. The color of the oral surfaces of the anterior teeth and molars remains virtually unchanged. Tetracycline staining of teeth ranges from gray to black and yellow to brown. The change in tooth color depends on the tetracycline drug used (Table 1).
Table 1 – Classification of tetracycline pigmentations [11, p. 511]
| Tetracycline drug | Pigmentation of teeth |
| Chlortetracycline (Aureomycin) | Taupe |
| Dimethylchlortetracycline (Terramycin) | Wishing |
| Oxytetracycline (Terramycin) | Wanting (to the least extent) |
| Tetracycline (Achromycin) | Wishing |
| Doxycycline (Vibramycin) | No changes were noted |
| Minocycline | Black |
Teeth stained yellowish by tetracycline may fluoresce when exposed to ultraviolet rays. This property is possible in differential diagnosis with discolorations that are caused by other reasons [8, p. 5].
Minocycline is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetracycline of a new generation, which has lipophilic properties and is also well bound to plasma proteins. Minocycline is characterized by a bacteriostatic effect and a greater antibacterial effect than tetracycline or its analogues. This antibiotic is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and interacts poorly with calcium. People taking minocycline may experience internal pigmentation of the oral mucosa, as well as gums, teeth, and bones. Pigmentation occurs as a result of the formation of insoluble chelates with iron. There is a point of view that minocycline causes tooth staining as a result of its binding to secondary dentin. It should be noted that tooth pigmentation does not go away as a result of stopping the antibiotic [4, p. 105].
Depending on the dose used, tetracycline (minocycline) can not only change the color of the enamel, but also cause underdevelopment of tooth enamel (hypoplasia). It has been determined that even in adults, fully formed permanent teeth can change their color as a result of taking tetracycline-minocycline. This occurs due to the deposition of the antibiotic in the tertiary dentin, as well as when it is dissolved in saliva [3, p. 35].
Four degrees of tetracycline staining of teeth are determined:
I. Faint yellow, brown or gray staining, distributed evenly over the entire tooth surface, not streaked in certain areas.
II. Darker or more intense coloration, gray or yellow, without streaking.
III. Pronounced blue or dark gray staining in the form of horizontal stripes on the tooth surface.
IV. Severe pigmentation, the use of bleaching is ineffective.
These degrees of tetracycline pigmentation tend to increase with chronic exposure to artificial and sunlight. The severity of the lesion depends on three factors: time, duration of use, type of tetracycline and its dose, and the activity of tooth calcification.
Teeth whitening is a chemical effect of free radicals on dental pigment (chromatophore), located mainly at the enamel-dentin boundary, during which the color of dentin and enamel changes from dark to light. Increased efficiency can be achieved through external activation of various sources of heat or light [6, p. 62].
Measures to transform the color of teeth depend on the aesthetic needs of the patient. All indications for the use of whitening are relative. It has been determined that not in every situation the result necessary to satisfy the patient’s aesthetic wishes is guaranteed [7, p. 52]. In general, the indications and contraindications for office (professional, office) whitening, as well as for home whitening, are similar. There are internal (depulpless teeth) and external whitening. The doctor makes a decision on the best method of whitening for each specific clinical case. In some cases, it is more appropriate to combine different techniques (mixed bleaching).
Contraindications for teeth whitening:
- caries;
— inflated expectations among patients;
- periodontal disease at the time of exacerbation;
— endodontic diseases;
- exposed dentin and cracks, increased tooth sensitivity;
- allergic reactions in the patient to the drugs used;
— pregnancy and lactation;
— orthodontic treatment;
— crowns or extensive restorations in the smile area;
— general severe illnesses in patients;
- obvious gum recession and pigmented exposed tooth roots.
It is most advisable before the whitening procedure for “tetracycline teeth” to carry out remineralization - saturation of the enamel with strengthening substances: calcium, fluorine or phosphorus. For this, the patient is first sent for x-ray diagnostics to determine the depth of the affected tissues.
Preparations used for remineralization on tetracycline (monocycline) enamel:
— remodent: made from bone material of animal origin, remineralizes the enamel with a wide range of essential elements (magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, sodium),
— 0.2% sodium fluoride solution: saturates tissues with fluoride,
— 10% solution of calcium gluconate: enriches tissues with calcium.
Therapy is carried out through phonophoresis and electrophoresis. The duration of the course is about a month and consists of 15-20 procedures, applied for 3-5 minutes. The doctor prescribes the duration of treatment for each specific case. The therapy ends with coating the teeth with fluoride varnish, which protects them from carious lesions.
In situations of uniform staining of tooth enamel damaged by tetracycline (monocycline), whitening is possible. An attempt to whiten teeth with intense uneven staining will improve the cosmetic condition of the teeth slightly and not for long - the result of the procedure may be completely unremarkable, and in less than six months, whitening will need to be done again.
For cosmetic whitening purposes, vital or internal (external/external) methods are used. Internal bleaching is performed when deep-lying tissues are damaged. To do this, specialized preparations are infused into the pulp cavity to whiten the tooth from the inside. Let's consider modern methods for whitening teeth exposed to tetracycline (monocycline):
1. The home whitening method, which is carried out through the use of a special protective plate (mouth guard), made in a dental laboratory on a plaster model from an accurate impression of the teeth, including 5-6 mm of the vestibular and oral surface of the gums. The design and quality of the protective plate are important details, since the plate must reliably limit the area of influence of the bleaching gel, preventing it from entering the mucous membrane, and also prevent its dissolution by oral fluid [10, p. 35-36].
Initially, tetracycline (monocycline) lesions were considered a poor candidate for treatment with at-home bleaching. However, several successful studies in this area have shown that although home whitening is slower to work than age-related yellowing, success can be achieved over a longer period (3 to 6 months). In this case, the doctor must continue to monitor teeth and other tissues throughout the entire whitening period. Monthly follow-up examinations by the doctor provide motivation for the patient to continue treatment.
The regimen for home whitening is determined by the patient’s current lifestyle, preferences and schedule. If the patient has the opportunity to wear mouth guards at night, use carbamide peroxide with a value of 10% at night for 8 hours on a schedule every other day. Many patients have the opportunity to wear mouth guards on both the lower and upper jaws at the same time. In this case, bleaching is carried out within two weeks. Some patients prefer to whiten the upper and lower jaws separately. This whitening regimen takes about four weeks. Good whitening results are seen with the selective use of high concentrations of carbamide peroxide (20 or 15%) for dark teeth (canines), in combination with 10% carbamide peroxide for teeth of lighter shades. Some patients are unable to wear aligners at night and prefer to do so during the day. The advantage in this situation is the more frequent refilling of the trays with whitening gel to achieve maximum effect. However, increased salivary secretion and occlusion pressure during the day reduce the concentration of the gel.
2. External office whitening is a more expensive procedure than home whitening. It is used for patients who do not have enough time to carry out home whitening or who have difficulties wearing aligners (don’t like the taste of the gel, gag reflex, etc.). The instant results of in-office whitening make it possible to motivate the patient to continue whitening at home.
In-office bleaching has the potential to initiate tooth dehydration, resulting in a falsely lighter shade immediately after treatment. In this regard, manufacturers have released a gel containing 10–20% water, which rehydrates teeth. Hydrogen peroxide with a value of 35%, intended for whitening, in the form of a combination of liquid and powder, is mixed until a gel is formed. A ready-made gel is also produced, into which you need to add liquid. A significant drawback of the in-office “powerful” whitening procedure is the caustic (Greek kaustikos - burning, caustic) nature of the 35-50% hydrogen peroxide used. It is important to carefully follow safety protocols when handling, applying, removing, and disposing of peroxide. It is necessary to protect and isolate the lips, gums, cheeks, areas of the eyes and face from tissue burns.
There are various combinations and options for methods for activating whitening. In some systems, activation occurs through a chemical reaction as a result of mixing two gels, others are based on the use of thermal or light activation, and there are also more effective double activation systems (we will consider further). To activate the whitening gel or accelerate the whitening effect, various types of light radiation are used. Initially, ordinary photocuring lamps were used, then plasma arc and laser lamps. Activation occurs through light exposure for 30 seconds for each of the teeth, the course consists of 3 sessions of 10 minutes. Thanks to the “fullsmileilluminator” system, both arches of the teeth can be illuminated simultaneously. The key safety issue regarding activating light is the generation of heat and its effect on the dental pulp [10, p. 15].
3. Office technique of double activation.
The Hi-Lite office whitening system has dual activation: light and chemical activation. It includes ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, which serves as a chemical activator, resulting in the whitening process being completed in 7-9 minutes. Additionally, the composition includes light-activated manganese sulfate, which can speed up the whitening process by up to 2-4 minutes. The technique uses a strong 19-35% concentration of hydrogen peroxide. A feature of the “Hi-Lite” (“Shofu”) material is the presence of a green-blue indicator color, initially blue and becoming white as it deactivates. This helps the dentist minimize the amount of time the bleach remains on the teeth and maximize the whitening results.
Briefly, the procedure is as follows:
— teeth are isolated with rubber dam in the usual way. The rubber dam is placed over all teeth to be whitened so that maximum tooth surface is accessible. It is important to protect the tissue surrounding the tooth from the bleaching material, which can cause significant inflammation of the gums;
— “Hi-Lite” material is placed on the teeth. Usually, the material is first applied to the area of the gingival half of the tooth, which is most stained with tetracycline (monocycline). By increasing the whitening time (number of applications) of the darker areas of the tooth, it is possible not only to lighten, but also to make the overall color of the tooth more homogeneous;
- the material is left for 6-10 minutes and then removed by wiping (when the whitening gel has turned from green to white);
- the process can be repeated (if necessary, up to six times per visit, depending on the type and severity of staining);
— teeth are cleaned with prophylactic paste.
In most cases, tetracycline (monocycline) lesions can be reduced or removed by teeth whitening, and when whitening and porcelain veneers are combined, stunning results can be achieved.
4. “Corridor” whitening technique. This technique uses 35% carbamide peroxide, which is activated by heating the syringe under hot running water for several minutes before use. The gel is applied to the tray, excess material is removed, and the patient is asked to wait in the corridor. After 30–60 minutes, the patient is invited into the office, the trays are removed, the whitening gel is vacuumed off and washed out. During one visit, the procedure can be repeated 2-3 times. In some cases, to achieve the desired result, whitening is performed in several visits. As a rule, one session is enough to fulfill the aesthetic needs of most patients. “Corridor” whitening should be used for patients who value quick results, as well as in situations where the patient needs a “shock” start before undergoing home whitening.
5. Whitening using “ZOOM” technology is a hardware method that allows you to whiten tooth enamel up to 12 tones. It is produced by applying hydrogen peroxide or urea to tooth enamel. Then the surface is irradiated with a special “ZOOM” lamp. Under its action, oxygen begins to separate from the applied materials, which whitens tetracycline stains. For patients with a low pain barrier, this procedure activates painful feelings. Others feel slight discomfort. The procedure lasts approximately two hours, and upon completion, the sensitivity of the dental tissues increases.
6. Laser teeth whitening is a more gentle procedure, in contrast to whitening using the ZOOM technology. It makes it possible to whiten teeth enamel up to 12 shades. Also applies to hardware methods.
For whitening, one of two types of lasers is used: CO2 -, argon, neodymium: yttrium aluminum garnet (ND: YAG). There are two ways to use lasers for whitening - in combination or separately.
Lasers are used to enhance the activation of whitening materials. They provide the energy for hydrogen peroxide to break down into water and oxygen and then release the oxygen into the stained tooth. Lasers catalyze the oxidation reaction. The free oxygen radicals released in the process break divalent bonds into simpler, more stable, less colored chains.
The surface of the tooth enamel is covered with a specialized dental photosensitive gel, which also begins to release oxygen through the action of laser beams. The procedure lasts approximately 30 minutes, but more than one approach may be required to achieve a good result.
The result of whitening “tetracycline teeth” obtained as a result of the use of laser and ZOOM technology lasts for several years. After this time, the procedure will need to be repeated.
7. Outpatient whitening, which involves filling the tooth cavity under a temporary filling with a mixture of sodium perborate and water for one week. After this, the procedure is repeated until the desired degree of whiteness is achieved. Sodium perborate is unchanged in the form of a dry powder, but in the presence of moist air or water it decomposes into hydrogen peroxide, metaborate and pure oxygen. This option is a combined bleaching technique. Sodium perborate is mixed with hydrogen peroxide 30% or less, but not with water, until a thick paste is formed. The mixture is poured into the dental cavity for a week. When mixed with sodium perborate, hydrogen peroxide multiplies its effect and gives the best whitening effect. This procedure is fast-acting, and noticeable results are visible within a week [1, p. 40].
Conclusion
Thus, a correctly selected method of whitening tetracycline (monocycline) changes in teeth allows you to preserve dental tissue as much as possible, achieving good aesthetic results. The centuries-old history of this current dental trend has been complemented by innovative technologies of recent years. At the same time, many issues require further study.
List of used literature
- Akulovich A.V., Manasherova O.G. Modern teeth whitening technologies // Medicine. XXI Century. 2021. No. 12. pp. 23-26.
- Baytus N.A., Novak N.V. Laboratory study of fluorescence of pulpless teeth after bleaching // Postgraduate Bulletin of the Volga region. 2021. No. 5-6. pp. 85-88.
- Bodden M.K. Treatment of endemic fluorosis and tetracycline discoloration of teeth using microabrasion and overnight vital whitening. Clinical observation / MK Bodden, VB Haywood // Quintessence. – 2015. – N2. – pp. 45–49.
- Bondarik E.A., Polyanskaya L.N. Modern methods of teeth whitening // Modern dentistry. - 2011. - No. 2. – pp. 37-41.
- Vartanyan G.A., Kurinskaya O.A., Borisov B.P. Ethics of choosing a treatment method in dentistry // Scientific journal. 2021. No. 1 (14). pp. 61-64.
- Gazhva S.I., Volkomorova T.V., Kulkova D.A. Modern aspects of the problem of whitening in aesthetic dentistry // Modern problems of science and education. – 2012. – No. 6.
- Grigoryan M.M., Korotkaya A.R. Causes of dental discoloration and methods of its treatment by bleaching // Modern trends in the development of science and technology. — 2021. — No. 2-4. — P. 34-35.
- Greenwall L. Whitening techniques in restorative dentistry: An illustrated guide. Per. from English – 2nd ed. - M.: Publishing House "Higher Education and Science", 2009. - 304 p.
- Dubishchev A.V., Kulagin O.L., Dodonova N.A. Solid dosage forms. - Samara, 2013. - pp. 61-76.
- Eremenko O. Current aspects of the teeth whitening procedure // DentalClub. — 2021. — No. 1 (13). – P. 6.
- Zhatkina A.A., Suvyrina M.B., Vasilyeva V.V. The relationship between the level of personal self-esteem and the patient’s desire in the teeth whitening procedure // Current issues of modern medicine, materials of the 72nd final scientific conference of young scientists and students of the Far Eastern State Medical University with international participation. Far Eastern State Medical University. 2015. pp. 188-189.
- Ivanova I.P., Bakumenko M.Yu. Discoloration of teeth. elimination methods. patients’ attitude to this problem // Healthcare of the Far East. — 2015. — No. 2 (64). — P. 52-53.
- Kozitsyna S.I., Gritsay I.G., Makarova A.N., Kirienko A.Yu., Dmitrieva N.G. // What are veneers and ultraneers? — Institute of Dentistry. 2011. No. 3 (52). pp. 42-45.
- Krikheli N.I. Justification of a comprehensive program for increasing the effectiveness of treatment of discolorations and prevention of complications arising from bleaching and microabrasion of enamel of discolored teeth: abstract of a dissertation for the degree of Doctor of Medical Sciences / Moscow State Medical and Dental University. Moscow, 2021.
- Krikheli N.I. Features of treatment of patients with tetracycline teeth // Dentistry for everyone. — 2021. — No. 4. — P. 4-7.
- Krikheli N.I. Teeth whitening and enamel microabrasion in aesthetic dentistry. Modern methods / N.I. Krikheli. – M.: Prakt. medicine, 2021. – 205 p.
- Luzganova E.V. Modern approaches to teeth whitening and rules of oral hygiene // Science of the 21st century: questions, hypotheses, answers. — 2021. — No. 1 (22). — P. 14-17.
- Lutskaya I.K. Whitening and aesthetic restoration of teeth when their color and shape are disturbed // Modern dentistry. — 2021. — No. 1 (62). – pp. 35-39.
- Parkhamovich S.N., Tyukova E.A., Minchuk S.A. Optical perception of composite restorations in ultraviolet light // Modern dentistry. 2014. No. 2 (59). pp. 77-79.
- Semchenko I.M. Teeth whitening techniques: method. allowance / I.M. Semchenko, A.I. Delendik. – Minsk: BSMU, 2021. − 24 p.
- Sumenov M., Radyshevskaya T.N. Methods for making veneers // Dentistry: science and practice, development prospects: Materials of the scientific and practical conference within the framework of the VI All-Russian Olympiad in Dentistry with international participation, dedicated to the 80th anniversary of Volgograd State Medical University. 2015. pp. 109-112.
- Terekhova N.V. The effectiveness of clinical whitening of pulpless teeth in young people / N.V. Terekhova // Present and future of postgraduate education: materials of the rep. scientific-practical conf., dedicated 75th anniversary of BelMAPO. – 2021. – T.2. – pp. 486–488.
- Tyukova E.A., Minchuk S.A. Fluorescence in the practice of a dentist // New methods of prevention, diagnosis and treatment in dentistry. Collection of materials of the Republican scientific and practical conference with international participation, dedicated to the 50th anniversary of the Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Belarusian State Medical University. Under the general editorship of S.A. Naumovich. 2021. pp. 439-442.
- Chirkova N.V., Bogatyreva Yu.A., Vecherkina Zh.V., Kartavtseva N.G., Urusova G.G. Analysis of the definition, frequency, etiology, pathogenesis of dental discoloration // System analysis and management in biomedical systems. - 2021. - T. 16. - No. 3. - P. 509-512.
- Chirkova N.V., Bogatyreva Yu.A., Vecherkina Zh.V., Chirkova K.E. Clinical rationale for the use of whitening toothpastes in patients with dental discoloration // Integration processes of world scientific and technological development. Collection of scientific papers based on the materials of the International Scientific and Practical Conference. In 2 parts. Under the general editorship of E.P. Tkacheva. 2021. - pp. 151-154.
Opinion on the treatment of tetracycline teeth
Tetracycline is a time-tested antibiotic. Even if a person abstains from taking pills, tetracycline ointment is often used for herpes, conjunctivitis, and acne, which is extremely helpful. But in adults, brown teeth of this etiology are rare. A person is born with tetracycline teeth.
Treating damaged enamel and restoring color will not be cheap. In this case, a person has the right to choose - try whitening and then move on to installing veneers, or immediately agree to aesthetic therapy with ceramic onlays or crowns.
Tetracycline teeth whitening that skips the remineralization step will do nothing. It is also unacceptable to practice self-medication and purchase various whitening strips, pencils and gels without consulting a doctor. It is easy to damage teeth, but restoring the lost beauty of a smile can be extremely difficult, time consuming and expensive.
Install Luxneers veneers! With them you will forever forget about the problems of tetracycline teeth
Make an appointment
Or call +7(985)532-21-01
Tooth root caries treated or removed
Do fissure dental caries need to be treated?
Retrograde pulpitis: diagnosis, causes, treatment, complications
Removal of a wisdom tooth cyst
Treatment of wisdom tooth caries if it hurts
Hypoplasia of dental enamel, diagnosis and treatment
Tetracycline teeth treatment, whitening, veneers
Symptoms of tetracycline pigmentation
The depth of enamel damage depends on the amount of accumulated tetracycline in the body. If its concentration is low, only the natural color of the enamel will be changed. At significant doses, a pathological change in the color of the surface of all teeth is observed. Tetracycline does not cause caries, therefore, with noticeable external defects, the teeth do not have painful symptoms. Often, not the entire tooth is stained, but only certain parts of it. Depending on how long tetracycline was in the body, enamel pigmentation will have the following degrees of damage:
- Subtle and uniform color change.
The teeth are colored brown, gray or yellow without stains or structural changes in the surface. At this stage, the problem is solved by in-office whitening, provided there are no contraindications.
- Complete and profound change in tooth color.
This degree of change occurs with long-term use of the antibiotic. The return of whiteness is possible with deep, sometimes even internal bleaching.
- Deep discoloration at the junction of teeth and gums.
Such symptoms accompany underdeveloped enamel, and the problem can only be solved by applying veneers.
Can it be avoided?
In order to protect yourself from defects, you should be careful about the medications you take. Use tetracycline only as prescribed by a doctor; usually, therapists and other specialists prescribe antibiotics only when absolutely necessary.
In the event that an infant or an older child falls ill, and the pediatrician prescribes a tetracycline-containing drug, the dosage should be observed as accurately as possible, it should be reduced by him, and do not continue the course more than indicated.
Teeth exposed to this antibiotic cause discomfort to their owner. In order to avoid such problems, you should approach any course of therapy wisely and not self-medicate.