What can inflammation of the salivary gland ?
Read the answer to this question in this article. The human body is a complex mechanism consisting of a huge number of organs and systems. Several structures are responsible for performing the same function, constantly complementing each other. For example, different organs take part in the digestion process.
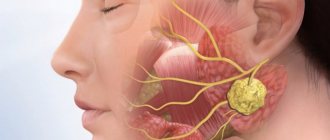
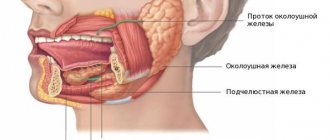
In the human body during normal development there are three pairs of salivary glands
The parotid gland is most often affected by various diseases. There are a number of diseases in which the sublingual and submandibular salivary glands become inflamed. If you do not start treatment on time or undergo inappropriate therapy, then serious complications may occur after such diseases, such as encephalitis, orchitis, meningitis, nephritis, neuritis and pancreatitis. However, do not worry, treatment often gives positive results. To avoid inflammation of the salivary glands, you just need to follow a few recommendations.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of pain under the tongue
Treatment of pain in the sublingual area should be carried out after a high-quality diagnosis to determine the root cause of the problem. Sometimes, pain in the frenulum under the tongue or in the surrounding tissues is treated by therapists or allergists, but in most cases this is done by dentists, because about 90% of all cases of treatment are associated with a dental problem.
Diagnosis of pain under the tongue is carried out in several stages:
- Initial appointment - the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out information about the nature and location of pain, and also examines the patient’s oral cavity;
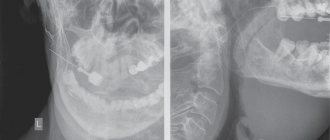
- A complete diagnostic examination is carried out in the absence of characteristic symptoms of common dental diseases. It is possible to use hardware techniques (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.);
- Differential diagnosis – a specialist differentiates the underlying pathology from similar diseases;
- Making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment - based on the data of the initial examination and diagnosis, the doctor establishes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes an adequate treatment regimen.
Note! The method of treatment and the choice of drugs to eliminate pain in the sublingual area directly depend on the root cause of the symptoms. For example, if your frenulum hurts due to a mechanical injury, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions for mouth rinsing will be prescribed, including: chlorophyllipt, hexoral, stomatophyte, alcohol tincture of calamus, stomatidine or others. If the pain is associated with the development of bacteria or fungi, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Three types of inflammation of the salivary gland
Depending on the disease, there are three types of inflammation, namely catarrhal, purulent and gangrenous. First of all, a swelling forms in the area of the salivary gland, which is often accompanied by pain. The inflamed area becomes red, and the skin there is tense and shiny. The exit site of the gland duct has a limited area of edema and inflammation.
In most cases, a specific liquid is released from it, similar to saliva or pus. Body temperature rises sharply to 39 degrees. Opening your mouth becomes more and more difficult and painful. If treatment is not started on time, the disease will develop into a more severe form with serious consequences.
Symptomatic features of pain under the tongue
Pain in the sublingual area can have various symptomatic manifestations. First of all, they are accompanied by different types of pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), as well as constancy or frequency.
If you consult a doctor, it is very important to correctly characterize the pain - this will allow the specialist to narrow down the range of symptoms for differential diagnosis. For example, you may have pain in the frenulum under your tongue or pain under your tongue on the right/left.
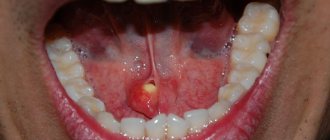
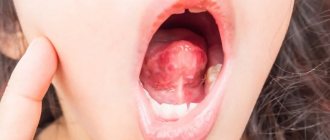
One of the characteristic manifestations of stomatitis or candidiasis is a white pimple under the tongue. Its presence may indicate the development of a fungal or bacterial process. If such a symptom is detected, treatment will include antifungal and antibacterial therapy with the prescription of antibiotics or special antiseptic rinses. The presence of pimples of a different color may indicate the presence of a wide range of problems, the identification of which requires a thorough diagnosis of the oral cavity or the entire body.
It is very difficult to diagnose this disease in the early stages.
In most cases, patients notice that something is wrong when the stone prevents the complete drainage of fluid. All this is accompanied by sharp pain, similar to salivary colic. At the site of inflammation, the tissues swell and become swollen. These symptoms are not constant, the pain either increases or disappears. During treatment, the stone is removed; if the situation is too advanced, sometimes the entire gland is removed.
The salivary glands under the tongue extremely rarely. But at the same time, the disease develops at a rapid pace and can have adverse consequences.
In order to maintain your health, first of all, you must adhere to the rules of hygiene and if you experience the slightest discomfort, immediately consult a doctor.
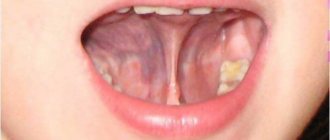
Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
Causes of pain under the tongue
Modern medicine knows dozens of different reasons that can cause unpleasant and painful sensations under the tongue in an adult, teenager and child: from a banal mechanical injury to the frenulum, leading to tissue damage, to allergic reactions causing swelling. At the same time, there is a list of the most common causes observed in most patients.
The main causes of pain under the tongue:
- Mechanical injuries to the frenulum and muscle tissue are the most common cause of sublingual pain. As a rule, it is observed in people with a short frenulum. It is injured due to stretching, as well as in the event of mechanical trauma to tissues, for example, during eating, hygienic brushing of teeth, etc.;
- Dental pathologies of the oral cavity – stomatitis, dental problems (caries, periodontitis, periodontitis), gumboil, etc.;
- Infectious inflammation of the oral cavity - pain often manifests itself with sore throat. During this period, it is painful for a person to eat, swallow water and saliva, stick out his tongue or simply chew;
- Cellulitis or abscess of the floor of the mouth is a significant accumulation of pus in a small area of the floor of the mouth. Causes “bursting” of internal tissues, putting pressure on peripheral nerves - this provokes pain and tactile discomfort;
- An allergic reaction can be the body’s response to various irritants. Causes swelling of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, accompanied by discomfort or pain in the sublingual area;
- Asymmetry of the hyoid bone - an anatomical disorder in the growth of the hyoid bone, can provoke excessive or nonspecific pressure on the peripheral nerves, causing pain;
- Neuralgia is a general disease of the nervous system that manifests itself in its various parts. It is often a consequence of nervous shock and is accompanied by a feeling of painful numbness in the oral cavity;
- Diseases of internal organs and body systems - some areas of the tongue may reflect (irradiate) pathologies of internal organs, which is accompanied by painful sensations in the sublingual area;
Note! Most of the above problems that provoke the development of pain in the sublingual area can be caused by bacterial infections (streptococci), fungi (candidiasis), and herpes.
Pain Relief Methods
Before suppressing pain localized under the tongue, it is important to establish the cause of this symptom.
If the frenulum ruptures, it is necessary to apply a disinfectant composition to the injury site and seek medical help.
Inflammation of the sublingual salivary gland is treated with the following medications:
- antiseptic;
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers.
If foci of suppuration are detected, the cavity is additionally drained.
Normalization of nutrition plays an important role in eliminating pain under the tongue. It is recommended to give preference to soft, pureed dishes at room temperature. Active saliva production speeds up the healing process. To do this, acidic foods such as sauerkraut or citrus fruits are introduced into the diet.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Pain under the tongue is a symptom, not a separate disease. It occurs when an organ is injured or against the background of various pathologies. It is possible to suppress pain only if the factor that provoked it is eliminated.
Causes of tongue tingling
Physiological factors
Tingling, burning throughout the tongue occurs after eating spicy foods and some spices.
Unpleasant sensations occur directly during eating and last for several hours. To reduce discomfort, a person drinks cool water and rinses his mouth. The tingling sensation is accompanied by increased production of saliva, which must be constantly swallowed. Externally, the tongue is unchanged, sometimes due to irritation and increased blood flow, it looks bright pink. The second typical reason is drinking too hot drinks or food. A superficial burn of the tongue occurs, which manifests itself as painful tingling, burning and tingling. With mild damage, symptoms persist for 12-24 hours, after which increased sensitivity of receptors to hot or spicy foods persists for several days.
Dental diseases
Constant tingling occurs when the tongue is traumatized by the sharp edges of carious teeth, incorrectly selected crowns or dentures. Discomfort is felt in the same place where maximum friction or scratching of the tooth on the surface of the tongue occurs. An epithelial defect is formed in this area, so when spicy food enters, the tingling intensifies.
Xerostomia
Low saliva production causes the tongue to dry out, which results in a painful feeling of tightness and tingling. Symptoms are aggravated by talking for a long time or eating dry solid food. Gradually, xerostomia progresses, so burning, tingling, and discomfort persist constantly. To alleviate the condition, patients regularly rinse their mouths and drink water, but such manipulations only help for a short time.
Tingling tongue
Glossalgia
With this pathology, the patient complains of a variety of painful sensations: tingling, pinching, rawness. Symptoms are not associated with ingestion of food or hot drinks. The tingling sensation is most pronounced on the lateral surfaces and tip of the tongue. The localization of sensations changes periodically. Externally the language has not been changed. Secondary glossalgias are manifested by:
- Endocrine disorders
: diabetes mellitus, Cushing's disease, hypothyroidism. - Gastrointestinal pathologies
: gastritis and gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis and cholecystitis. - Damage to peripheral nerves
: neuropathy of the glossopharyngeal nerve, ganglionitis of the sublingual autonomic ganglion, sympathalgia. - Diseases of the central nervous system
: encephalitis, neurosyphilis, residual effects after a stroke. - Connective tissue diseases
: scleroderma, dermatomyositis.
Glossodynia
Paresthesias are observed, manifested by tingling, burning, and a sensation of “crawling goosebumps” that have no apparent cause. At first, the discomfort symptoms affect only the tip of the tongue, but gradually they spread over its entire surface like an “oil stain.” The root of the tongue is the last to be affected, but often no tingling occurs in this area at all.
Discomfortable sensations last for 3-5 minutes and appear several times a day. As glossodynia progresses, episodes of paresthesia lengthen and are accompanied by a feeling of enlargement and swelling of the tongue. The pathognomonic feature of the disease is the absence of tingling at the time of eating. Therefore, people constantly chew something, which ultimately leads to weight gain and dental caries.
Desquamative glossitis
Periodically during the day, patients experience an unpleasant tingling and burning sensation in the mouth. Tingling spreads over the entire surface of the tongue or to its individual areas that are affected by the inflammatory process. It is common to experience increased discomfort while eating, especially when eating hot or spicy foods. Symptoms bother the patient for several weeks or months.
With desquamative glossitis, unlike glossalgia and glossodynia, the appearance of the tongue changes. Bright red foci of inflammation appear on its mucosa with detachment of the epithelium, noticeable cracks or furrows form. In areas of desquamation, pain and tingling are most pronounced. The wounds heal quickly, then new erosions form elsewhere - an ever-changing “geographic pattern” on the tongue.
Hypovitaminosis B12
Tingling and pinching of the tongue is caused by atrophy of the papillae and the development of Gunter's glossitis. Discomfort is observed constantly, it is not associated with food or other external factors. With increasing deficiency of vitamin B 12 and the occurrence of macrocytic anemia, the symptoms worsen. Patients complain of a constant painful burning sensation and pain when eating. The tongue becomes bright red, “polished” and shiny.
Oral candidiasis
Tingling of the tongue is characteristic of chronic candidiasis, while in the acute form, severe burning and pain are more common. The feeling of discomfort extends not only to the back of the tongue, but also to the mucous membrane of the cheeks and the red border of the lips. Patients notice a thick grayish plaque, after peeling it off, bright red inflamed areas of the epithelium remain. With the development of chronic atrophic candidiasis, tingling is complemented by severe dry mouth.
Allergy
Paresthesia in the tongue is one of the signs of a food allergy or reaction to animal fur or plant pollen. In this case, the tingling is combined with painful itching, to relieve which patients try to “scratch” the back of the tongue with their teeth, which increases the discomfort. Symptoms appear against the background of other allergic manifestations: lacrimation, sneezing, digestive disorders.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have the slightest discomfort or pain in the space under the speech organ, you should visit a therapist. Consultation with an allergist may be required. Most often, dentists deal with problems of the floor of the mouth. It is important to regularly visit the hygienist. Professional oral cleaning prevents many dental and soft tissue problems.
In case of frenulum injuries, rinsing with romazulan, chlorophyllipt, and stomatophyte is prescribed. The disease requires repeated rinsing: in the morning, after meals, in the evening. The affected area is treated with antiseptic drugs and agents to relieve the inflammatory process. If the salivary glands are affected, therapy should be started before an abscess appears. Medicines are injected into the pathological gland, antibiotics, drugs for salivation, and a course of physiotherapy are prescribed.
When an abscess forms, the patient needs a surgeon to clean out the gland cavity. As a preventive measure, dentists recommend proper oral care. It is necessary to take care of the gum tissue, prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microbes, treat caries in a timely manner, and clean the oral cavity twice a day. You need to visit the dentist once every six months. Patients with a shortened frenulum and asymmetry of its structure need to be careful to avoid injury.