Caries is a pathological process that occurs in dental tissues and leads to the formation of cavity defects in them.
The choice of method for diagnosing dental caries depends on the stage of its development and the location of damage to the teeth.
While caries is at the spot stage, it is extremely difficult to identify its presence on your own, since the disease can be practically asymptomatic. Most often, it can only be detected with the help of special tools and modern equipment at a dentist’s appointment.
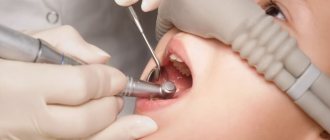
It is easier to diagnose medium and deep caries, both for the person himself and for the doctor - for this he uses a mirror and a probe.
Methods for diagnosing caries
Self-detection of the disease
A person can independently detect the presence of caries when brushing his teeth or visually examining the oral cavity in the mirror. Damaged areas have white or dark brown spots. You should especially carefully inspect the areas near the fillings. If a change in the color of tooth enamel is accompanied by unpleasant sensations while chewing food or drinking hot or cold drinks, this indicates the occurrence of caries.
You can also independently detect the disease using ordinary dental floss. If the floss becomes damaged while brushing your teeth, this may be the first sign of developing a disease.
If during a self-examination any of the signs of caries are detected, it is necessary to urgently visit a dentist to prevent the development of the disease and save the tooth. It is worth remembering that self-diagnosis will help detect the disease only in 10 cases out of 100.
Visual diagnosis of the disease
First of all, the dentist conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity. He pays attention to the presence of pronounced spots, as well as the appearance of areas with roughness on the enamel. Using a probe, the doctor detects uneven areas and asks the patient about the presence or absence of discomfort during the diagnosis. Using a mirror, each tooth is carefully examined from all sides.
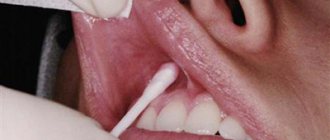
Drying
The process is carried out to diagnose the primary stage of disease development. The tooth is isolated from the separated saliva and dried using cotton swabs. Damaged areas do not have shine; as a result of drying, they become matte. This indicates the presence of the disease.
Diagnosis of the disease using staining
To stain the enamel, special caries markers are used (most often methylene blue). The principle of this method is that the affected areas become visible after staining. If the area of enamel does not have carious damage, the blue substance flows smoothly from the tooth. Damaged rough areas absorb the product into their pores and thereby enable the dentist to determine not only the exact location of the lesion, but also its boundaries.
Some clinics use a pink filler, fuchsin, to diagnose caries, which is applied with a special swab. After the diagnosis, the product is washed off.
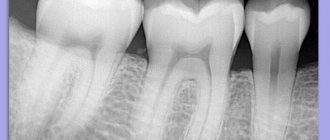
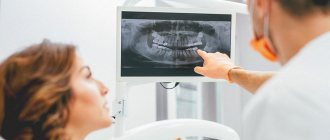
X-ray
Diagnosis using x-rays is effective in the following cases:
- To identify the course of the disease in a latent form.
- To detect deep caries.
- If the suspected area of carious formation is hidden between the walls of the teeth or is located under the gum.
In the photograph, damaged areas appear lighter than healthy tooth tissue. The disadvantage of this method is that it does not detect the disease at an early stage.
Panoramic shot
An orthopantomogram provides complete information about the state of the human dental system and allows you to detect damaged areas. A dental tomograph is used for diagnosis. The advantage of this method is that the radiation dose is several times less than that of an X-ray machine, and the information obtained as a result of the examination is more accurate.
The procedure is carried out as follows: a digital sensor and a radiation source are placed in the oral cavity, which begin to move in the opposite direction to each other. As a result, only the affected area is visible in the image, and healthy areas are a blurry spot.
Thermal diagnostics of the disease
This method is based on the reaction of teeth to temperature irritations. The intensity of irritation is determined using hot or cold water, less often - ether. The teeth are irrigated from a special syringe, or a cotton swab, previously soaked in cold or hot liquid, is applied to the damaged area for a short period of time. The conclusion about the presence of a disease or its absence is made based on the patient’s pain. If the pain goes away after a few seconds, this indicates that the patient has caries; if the discomfort lasts longer, the patient may have developed pulpitis.
Studying the disease using electroodontometry
This method is differentiated and is rarely used in practice. It is used to detect pulpitis and at the same time diagnose caries.
EDI is based on the use of electric current, with the help of which the condition of the nerve elements of the pulp is determined. Nervous tissue becomes excited as a result of the effect of current on dental tissue. Before the procedure, the tooth is isolated from secreted saliva and thoroughly dried, after which an active electrode is placed on its damaged areas.
The pain of the procedure is minimal - the current effect stops immediately after the first tingling sensation appears in the patient.
Transluminescence
In most cases, this method is used to detect other dental diseases, but it is also used to detect caries. The procedure is carried out in a dark room. A bright light source is pointed at the damaged tooth. Carious formations differ from healthy tissues by the presence of a dark hemisphere on them. During this diagnosis, the patient does not experience pain.
Luminescent diagnostics
This method involves examining damaged tissue using ultraviolet light, which is passed through a special filter. During the procedure, healthy tissues become snow-white, and damaged areas become dark. The boundaries of carious formations are clearly visible. The procedure is painless for the patient.
Laser-induced diagnostics
For the procedure, special devices of compact size, domestic or imported, are used. With their help, the teeth are illuminated with a laser beam, which helps to identify the affected area. During diagnosis, the patient does not experience any discomfort.
Fissurotomy diagnostics
The procedure involves opening the tooth enamel in places where it has darkened. This method is used not only for diagnosis, but also for treating diseased areas, as well as to determine the size of suspected damage.
The enamel is opened in the area of the dental fissures, after which the doctor assesses the degree of damage and the size of the area. The resulting holes are sealed with a special agent that has an antibacterial effect and prevents the further development of the carious process. Asepta offers toothpastes enriched with minerals in an easily digestible form. They strengthen the enamel, which is the best prevention of caries. You can choose a paste for basic use and combine it with ASEPTA PLUS REMINERALIZATION to achieve maximum effect.
Using silk thread to detect disease
This method is one of the simplest, cheapest and safest for the patient. Used to identify carious formations on the walls between teeth. The diagnostic process is carried out as follows: the dentist inserts a silk thread into the gap between the teeth, after which he begins to slowly lower and lift it. If the thread catches, becomes damaged or breaks, this indicates the presence of a disease.
However, this method is imperfect, since the thread can be damaged in the places where the filling is installed or if the patient has tartar.
Device "Diagnodent"
This device is considered the most effective way to detect caries. With its help, you can easily identify the disease even before a visual examination by a doctor.
The device is a small control panel equipped with two displays. The principle of its operation is based on the ability of a damaged tooth to reflect laser beams differently than they are reflected from a healthy one. Any deviations from the norm are detected by the device, and the received information is displayed on the screen. In addition, the device beeps when even minimal carious lesions are detected.
Advantages of diagnostics using a caries detector:
- The disease is detected at an early stage.
- Affected areas are found even on the contacting areas of the teeth.
- The device diagnoses caries in the root of the tooth.
- The device detects the presence of dentin damage under fillings.
- During the diagnostic process, the degree of dental damage is determined with maximum accuracy.
- The procedure is harmless.
- Painless diagnosis.
- The device can be used to detect diseases in young children and pregnant women.
Radiography
An image is taken of a small area of the jaw, more often to diagnose the condition of one tooth. It allows you to evaluate the characteristics of bone tissue, the tooth itself, the tissues around it and its root (gums, bone, ligaments).
X-rays in dentistry are used to:
- diagnose hidden caries, pulpitis, inflammation or cracks of the root canals;
- collect information about the dental system before implantation, prosthetics or monitor their results;
- assess the volume of bone tissue during sinus lift;
- check the quality of root canal treatment (must be filled without voids or pores);
- assess the structure of the dental system before and after orthodontic treatment;
- perform an accurate diagnosis if the patient’s complaints correspond to several diseases.
There are several types of X-rays used in dentistry.
Intraoral, dental. Performed to obtain an image of a single tooth or small area. The picture is taken using a radiovisiograph - a digital camera that captures an x-ray signal. The technology allows you to obtain high-resolution images: the doctor can see the condition of the canals, hard tissues, etc., and identify diseases at the initial stage. Radiation exposure with digital radiovisiography is minimal, which allows the method to be used for primary and intermediate diagnostics, when assessing the results and quality of treatment. The image is taken in a few minutes: a sensor is placed in the patient’s mouth on the side of the tooth being examined, and a pulsed radiation source is placed near the face. The image is available for viewing immediately.
Panoramic. It is performed to assess the structure and condition of the jaw as a whole, allows you to identify foci of inflammation or infection, pathology or disease of the TMJ, and assess the condition of the maxillary sinus and periodontium. Panoramic photographs are needed in preparation for implantation, prosthetics, and orthodontic treatment. They are performed using a special apparatus. The radiation dose is higher, but remains safe.
CT scan. It is used in planning sinus lifting, bone grafting, implantation, and other surgical interventions, and in diagnosing periodontal diseases. The photographs are taken in certain projections and used to build a three-dimensional model of the jaw. Computed tomography is very informative. The study provides information about the localization of inflammation (including intraosseous), the presence of tumor-like formations, their structure, size, features of the location of the root canals, etc.
How to diagnose the disease in pregnant women?
Caries in pregnant women is one of the most common diseases. Diagnosis of the disease begins with a detailed questioning by the doctor of the patient about the nature and intensity of pain, as well as the presence of other diseases. After collecting information, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the oral cavity and diagnoses the teeth for the presence of caries using a probe, mirror, dental floss, etc. Pregnant women are not prescribed x-rays to detect the disease, as this can harm the fetus. Usually the dentist limits himself to a visual examination or recommends the Diagnodent device.
Why is differential diagnosis needed?
The essence of the differential diagnostic method is to use a combination of all of the above methods to establish an accurate diagnosis. An experienced dentist decides on the appropriateness of a particular diagnostic method. The need to use differential diagnosis is due to the fact that in some cases caries can be easily confused with other dental diseases.
For example, to distinguish hypoplasia from caries, a caries marker is used, pulpitis from caries - thermal diagnostics and EOM, non-carious lesions from caries - an x-ray.
It is almost impossible to carry out differential diagnosis using only visual examination methods.
What happens if the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner?
Advanced stage of the disease will most likely require surgical intervention. If you do not respond to painful sensations and try to drown out the pain with medications, very soon the process of decay will begin in the carious cavity. A granuloma may form around the root, which over time turns into a cyst. If you ignore the pain and do not consult a dentist for surgical treatment, the patient will lose the tooth.
Untreated caries can also trigger the appearance of periodontitis or pulpitis (treatment).
Periodontitis is characterized by inflammation of the periodontal tissues, which leads to severe pain and the need for tooth extraction. Pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental nerve. When it appears, the patient feels severe pain while eating and drinking. In an advanced stage, the patient may experience pain constantly.
If caries is not treated, the presence of an inflammatory focus in the oral cavity can cause the following consequences:
- The occurrence of chronic allergies.
- Joint diseases.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Biochemical methods
This is mainly a biochemical blood test. It is performed to detect signs of inflammation and changes in metabolic processes. Periodontal disease, especially in people over 40 years of age, is often accompanied by changes in lipid levels. A short (several indicators) or extensive biochemical analysis can be performed. Close attention is also paid to the composition of cells, their color, the presence of microbes, cell adhesion, etc. As a result of research, it is possible to establish the intensity of the development of inflammation and the direction of development of the pathological process.
Up to contents
Prevention measures
Prevention of caries is aimed at strengthening the mineral structure of teeth. First of all, you need to pay attention to your diet and provide your body with enough vitamins. The minimum content of carbohydrates in food and adherence to the diet have a beneficial effect on the condition of the enamel. It is necessary to eat enough vegetables and fruits, as they are a kind of “natural brush” for cleaning your teeth. Nuts, milk and cottage cheese, onions and sesame seeds help strengthen teeth.
To strengthen the enamel, you can additionally take medications containing fluoride (but only after consultation with your doctor), as well as calcium gluconate, fluoridated salt and fluoridated water.
Regular brushing of teeth will reduce the likelihood of developing the disease. The procedure must be carried out twice a day. The optimal size of the brush should reach the length of three teeth in the human oral cavity. It is not recommended to save on purchasing toothpaste, since high-quality products contain useful microelements that prevent the occurrence of caries.
Healthy sleep, proper rest and lack of stress also minimize the risk of illness.
It is necessary to undergo examination by a dentist twice a year to detect the disease at an early stage and treat it. Only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
One of the methods of preventing the disease is timely cleaning of plaque and tartar. The doctor can carry out an effective anti-caries procedure for enamel remineralization using special means, as well as carry out fluoride prophylaxis.
Tests before implantation
Dental implantation, like any other procedure involving surgery, requires careful preparation. Neglecting the implantation protocol is fraught with its rejection and inflammatory processes. Therefore, it is important to pass all the necessary tests before implantation. This will allow:
- Identify hidden problems with gum tissue;
- Eliminate reactions to anesthesia and the use of medications;
- Determine the condition of the patient’s bone tissue;
- Assess the patient's general condition before surgery.
A complete list of tests that can be prescribed by a dentist before implantation:
- Clinical general blood test;
- Analysis of glucose levels in the patient's blood serum;
- Syphilis test RPR HBsAg;
- APTT;
- Fibrinogen test;
- Determination of prothrombin;
- INR;
- Determination for Antithrombin III;
- Thrombin time analysis;
- Determination of the presence of antibodies to HIV 1 and 2;
- Determination of the presence of HIV antigen 1 and 2;
- Qualitative test Anti-HCV-total;
- Urine analysis for protein and creatinine content.
Tests for periodontal disease
Periodontal disease is an extremely dangerous disease, which has a pronounced systemic-dystrophic nature in relation to periodontal tissues. Often, to get rid of a disease, it is necessary to jointly diagnose and draw up a treatment plan from specialists in several fields - a general dentist, periodontist, and therapist. Therefore, in the process of preparing for therapy, the doctor can prescribe the widest possible list of laboratory tests. The results of the study make it possible to identify which system of the patient’s body has weakened, which led to the development of periodontal disease.
Clinical researches
Laboratory studies have proven that regular use of professional toothpaste ASEPTA REMINERALIZATION after 4 weeks improved the condition of the enamel by 64% and reduced tooth sensitivity by 66%.
Sources:
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Microbiological studies
This is a determination of the composition of the oral microflora and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. The reason for the importance of the study is not only the huge role of the microbial factor in the development of inflammation, but also the large number of cases where the disease is particularly resistant to traditional therapeutic interventions. Microbiological tests make it possible to determine the causative agent of inflammation, determine which antibiotic will be most effective in eliminating it, and also determine the treatment tactics for a specific form of periodontitis. Microbiological studies are also important because new microbial associations are emerging and their resistance to common antibiotics is increasing. Analysis of oral samples is usually performed before and after treatment to control its quality.
Up to contents