Indications Prosthetic options Types of crowns Stages of prosthetics How to choose?
The incisors and canines make up the smile line; any damage or defect in this area becomes immediately noticeable. Restoration and reconstruction of the frontal group of teeth is the most complex process of all clinical options. When replacing the supragingival part of a tooth with an artificial crown, it is necessary to achieve a harmonious combination with the adjacent units and soft tissues. The best crowns for the front teeth should have a natural shade and degree of transparency, like real incisors. At the same time, be not only beautiful, but also quite durable.
Orthopedic dentistry uses different methods, technologies and materials to restore the frontal group of teeth. The doctor decides which crowns to put on the front teeth and which method of prosthetics to choose based on the clinical situation. The patient is offered several treatment options, from which he chooses the optimal one in terms of aesthetics and cost. The physical and optical properties of restoration materials are well studied today, which greatly simplifies the choice. An integrated approach to treatment allows you to create prosthetic structures with individual optical characteristics, achieving the best aesthetic result.
Indications for prosthetics
- Chipped crown (when the defect cannot be corrected by installing a filling);
- multiple cracks in the enamel;
- pathological abrasion of enamel;
- fluorosis;
- tetracycline teeth;
- color change (darkening, yellowing);
- destruction of the supragingival part of the tooth more than 70% with preservation of the root;
- thin, weakened enamel;
- replacement of an old restoration.
Prosthetic options depending on the clinical picture
- If you need to correct the shape, size, color of incisors, fangs, eliminate cracks, small chips, a good solution is ceramic or zirconium veneers. Thin dental onlays (up to 0.3 mm) require minor preparation of the enamel layer. They are fixed to the outside of the teeth with composite glue (bond).
- If there is extensive destruction of the supragingival part ( more than 60%
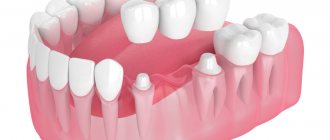
), a dental crown is installed. Before installation, the incisor and canine are given the desired shape (grinded), the root is strengthened with a stump insert (if necessary), the prosthesis is fixed to the support with dental cement. - If not only the supragingival part is destroyed, but also the root, implantation will help restore full aesthetics and functionality of the dentition. If the clinical situation allows, the implant is immediately loaded with a temporary crown, which is replaced with a permanent one after the implantation of the artificial root.
Immediate prosthetics for single defects is possible only for incisors and canines (up to the 5th premolar). The prosthetic structure is removed from the bite (made slightly lower in height). This is necessary to eliminate the risk of loosening the implant due to the load on the prosthesis.
Stages of bite deformation in children and adults
Doctors distinguish several stages of bite deformation.
The first is considered the easiest. It is diagnosed when the patient has a curvature of one or more teeth - they may have an irregular shape or length, an abnormal inclination and location, or may be rotated around their own axis.
The second or middle stage involves malocclusion throughout the entire row on one jaw or both.
To the third, most severe stage, experts include pathologies associated with the abnormal structure and size of the maxillofacial apparatus relative to the skull, violation of the position of the upper and lower jaws relative to each other, and the degree of closure of the teeth.
Important! Any, even the most minor, deformation of the bite, at a minimum, leads to a violation of the aesthetics of the smile and facial proportions, and at a maximum – to serious health problems. For example, to dental diseases and gastrointestinal pathologies, to respiratory failure, hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles and overload of the maxillofacial joint, to headaches, to early loss of teeth.
What kind of crowns are placed on the front teeth?
The front incisors are not used for chewing food, so when prosthetics for this group of teeth there are more requirements for aesthetics and restoration of correct occlusion. But the material of the prosthesis must be strong enough to withstand the load when biting. To create crowns, metal alloys, metal-ceramics, ceramics (porcelain), zirconium oxide, E-max metal-free ceramics, plastic, etc. are used. The cost, appearance, and durability of the restoration depend on the material.
Types of crowns for front teeth
Metal crowns
They are created from metal alloys, including precious ones, by casting or stamping. The high strength of the metal ensures long service without the risk of cracks and chips. Gold crowns are easily shaped and reproduce the anatomical shape of the tooth in detail. Designs made from metal alloys are inexpensive (with the exception of crowns made of gold), comfortable, strong, durable, but do not resemble natural teeth, and therefore are not suitable for prosthetics in the smile area.
Metal ceramics
Metal-ceramic crowns for the front teeth are one of the popular prosthetic options due to their low cost (except for restorations made of gold, palladium, and platinum). They have a durable metal base, onto which a layer-by-layer ceramic mass is applied, identical in color to natural enamel. The one-piece casting method minimizes the risk of complications since there is no gap between the inside of the prosthesis and the support.
The cladding is carried out in layers - each subsequent layer is subjected to thermal treatment (baking) to achieve the highest adhesion of the metal to the ceramics. Manufacturing technology allows us to achieve a natural-looking prosthesis. But this aesthetics is not enough to make an incisor or canine look natural.
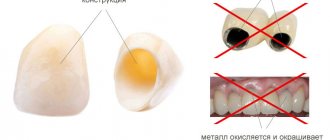
Living teeth are capable of reflecting, transmitting, and scattering light. The metal base does not have this property - when natural light hits the teeth, the difference between natural and artificial crowns is noticeable (the base shines through the coating). Another unsightly disadvantage is discoloration and receding gums around the base of the crown (gray neck). The reason is metal oxidation due to prolonged contact with the mucous membrane. Also among the main disadvantages are accelerated abrasion of the enamel of the antagonist tooth, chips of the ceramic veneer, and an allergy to metal.
The metal base of the metal-ceramic crown is slightly visible through the gums
Modern orthopedics offers a more aesthetic result - metal-ceramic crowns for the front teeth with shoulder mass. In such structures there is no exposed metal ledge - they are completely covered with ceramic cladding. The metal does not come into contact with the mucous membrane, which eliminates cyanosis of the gums around the prosthesis. But the manufacturing technology of such models is more complex, which affects the cost of restorations.
Ceramics
Ceramic crowns for the front teeth are made from dental porcelain by firing or casting. Due to the optical properties of the material, all-ceramic structures look identical to living teeth. They are biocompatible, do not stain, do not oxidize, and last 7-10 years
.
Porcelain dentures are light, thin, and do not require deep preparation of the supporting units. The disadvantages of such restorations include:
- higher cost than metal-ceramic structures;
- fragility of the material (under heavy load, porcelain cracks and crumbles);
- impossibility of bridge prosthetics.
If the crown part is severely damaged (if only the root remains), installing crowns on the front teeth involves the use of metal-free inlays or pins. Metal structures are not used, since they will shine through the ceramics and can crack the restoration. Solid ceramics are fixed only to your own tooth.
E-max ceramics
Today, metal-free solutions have come to the fore, developed in accordance with the latest advances in robotics. E-max glass ceramics based on lithium disilicate are free of all the disadvantages of dental porcelain and allow you to create beautiful, incredibly durable prosthetic systems. The manufacturer offers blanks of five different levels of transparency, which, when making a crown, ensures a smooth color transition from the gingival part to the cutting edge, achieving a natural restoration.
Advantages of glass ceramics:
- Leucide ceramics are very durable, wear-resistant, and suitable for restorations of frontal and chewing units. It recreates in detail the structure of natural enamel and relief.
- Depending on the manufacturing method, E-max crowns can be pressed (E-max PRESS) or milled (E-max CAD).
- 3D milling using CAD/CAM technology is automated, which allows you to create thin, light, durable restorations that cannot be distinguished from living teeth.
The only negative (and that is relative) is the cost. E-max frontal crowns are more expensive than metal-ceramics or porcelain analogues. But this disadvantage is compensated by high strength, natural appearance, inertia of restoration, and durability. Average service life – 15-20 years
. They are inferior in strength only to zirconium prosthetic systems.
Emax is used for single restorations, as part of bridges on the front 4 teeth. Pressed models are not used for bruxism. Excessive mechanical load can lead to damage to the restoration. In such situations, only milled structures are suitable.
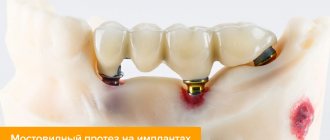
Zirconium dioxide
Zirconium crowns for the front teeth are made automatically, by milling on a computer-controlled machine. Ultra-strong, bioinert, hypoallergenic material allows you to create thin, lightweight restorations for any part of the jaw. Products made using CAD\CAM technology up to 0.4 mm thick. This minimizes trauma to dental tissues during preparation. Thanks to optical properties close to natural enamel, a smooth exit of the crown from the gum is ensured - the color of the restoration is rich in the center, more transparent at the cutting edge.
The strength of zirconium restorations is superior to all others, including metal-ceramics, which allows them to be used in bridges of any length. Since zirconium has a snow-white tint, crowns for the frontal zone are made with ceramic veneering, providing the artificial tooth with a natural appearance. The exception is Prettau zirconium materials, which are painted with special liquid dyes, making it possible to avoid layer-by-layer application of ceramics.
The cost of prosthetics with zirconium is 1.5-2 times higher than with metal-ceramics. But the service life of zirconium restorations is 20-25 years or longer
, which compensates for the price.
Plastic dentures
Plastic crowns are placed on the front teeth as temporary, protective restorations. The patient wears them while permanent structures are being made. The advantages of plastic structures are ease of manufacture and low price. But such restorations have more disadvantages - allergies, inflammation of the gums, rapid loss of aesthetics (the prosthesis absorbs foreign odors, coloring pigments), fragility, short service life. Although the declared service life of plastic models is up to 2 years, after only 1-2 months
their aesthetic condition deteriorates significantly.
Service life of dental crowns made of different materials
The most short-lived are temporary crowns on teeth (plastic). In second place in terms of durability are products made of metal-plastic. The longest service life of structures is 5 years. However, patient reviews “speak” of premature darkening and deformation of the crowns.
Metal-ceramic dentures, which are successfully fixed to both the front and chewing teeth, usually last about 10 years. Artificial teeth made of ceramics remain the same in appearance and functionality for 10-15 years.
Metal crowns made of metal alloys last a long time and last at least 15 years.
Expensive materials - zirconium dioxide and aluminum oxide - last up to 20 years. The long service life justifies their high cost.
The service life of prosthetic structures is determined not only by the quality of their manufacture, but also by the care they are provided after installation.
Stages of prosthetics
- Preparation
- assess the general condition of the oral cavity, take an x-ray, carry out hygienic cleaning (removal of plaque, tartar), treat caries, gums, change old fillings. - Preparation
- the front tooth is ground down for a crown, the stump is given the desired shape. According to indications, depulpation, treatment, and filling of dental canals are carried out. In case of severe destruction of the supragingival part, the root is strengthened with a stump insert. The prepared support is covered with a temporary plastic structure to protect tissues from destruction, chemical and temperature irritants. - Taking impressions
– the doctor takes impressions of the patient’s teeth using an impression tray with impression material or a digital scanner. The obtained data is transmitted to the dental laboratory. - Making a crown
- based on models, an orthopedic system is created in the laboratory using casting, pressing, and milling. At the manufacturing stage, the model is tried on the patient, and adjustments are made if necessary. - Installation
- the finished crown is fixed to the support with dental cement. The crown on the front tooth implant is installed using a cement or screw method.
Disadvantages that everyone needs to know about
Is it possible to correct crooked teeth with crowns? Structures cannot be treated. They only mask the defect, make it possible to achieve external attractiveness, but do not correct the cause of the pathology, i.e. broken bite. Therefore, their installation is advisable only if the anomaly is minor and does not threaten the health and functionality of the maxillofacial apparatus.
Another significant drawback: installing a crown is an irreversible process. Underneath it, you need to sharpen and depulp the tooth, and after removing the structure, it may even need to be removed. After all, a depulped unit is destroyed much faster than one in which there is living pulp. And in this regard, braces and any orthodontic devices benefit, because... after a course of treatment they can be removed; they do not require such sacrifices, although, of course, you have to wait a long time to get a positive result.
Important! Crowns do not allow you to change the incorrect location of the roots of the teeth and do not eliminate the cause of the anomaly. Therefore, it would be more correct to say that they do not straighten teeth, but only quickly restore their natural shape and color, and correct only individual defects.
Some patients believe that if they install a crown, they will not be at risk of caries or any other dental disease. However, this is a misconception. An inflammatory process can also develop under the structure if the canals were poorly treated, it was installed incorrectly, or due to insufficient hygienic care for the oral cavity.