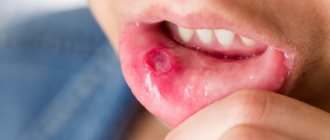
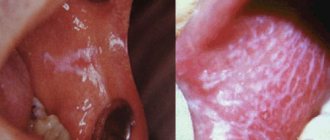
A sore and dry throat, pain when swallowing, weakness, and fever signal a disease of the pharynx.
Below in the article you will find the causes of the disease; the doctors who treat him; necessary medical procedures for treatment; as well as general information about the disease, its localization, features of diagnosis of diseases and their treatment. However, we advise you to consult a doctor, because self-medication in 90% of cases is fraught with the disease progressing to the chronic stage with extremely unpleasant complications. Make an appointment and consultation
COMPLICATIONS OF PHARINGITIS OR WHAT HAPPENS IF IT IS NOT TREATED OR TREATED INCORRECTLY
The most serious complications of pharyngitis are represented by autoimmune diseases that arise as a result of increased sensitivity of the body to the microbes that cause the disease... What does this mean? This means that strep throat itself is not very dangerous, BUT it can lead to very serious consequences if left untreated. In this regard, streptococcal pharyngitis is especially dangerous, as a result of which purulent and non-purulent complications can develop...
Purulent complications:
- A peritonsillar abscess is an inflammation in the peritonsillar tissue (the area around the tonsils), where an abscess forms.
- Retropharyngeal abscess - formed as a result of suppuration of the lymph nodes and tissue of the retropharyngeal space.
Non-purulent complications:
- Inflammation of the kidneys (post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis).
- Rheumatism.
With rheumatism, inflammatory nodules form in various tissues of the body. For example, if they form in the heart muscle, on the inner surface of the heart or, in the most severe case, on the valves, they can cause disruption of the flow of blood through the heart, which can lead to undesirable consequences, including the formation of heart disease... Inflammatory nodules can also be deposited in the skin, muscles, joints, which may result in swelling and pain...l
Enlarged lymph nodes
The body is one big system. Consists of many small ones, one of which is lymphatic.
It performs three important functions:
- maintains fluid balance between blood and tissues
- helps protect against bacteria and other attackers, is part of the immune system
- participates in the absorption of fats and fat-soluble nutrients in the digestive system
Consists of vessels, ducts, nodes and other tissues.
There are three types of vessels in the lymphatic system:
- milky Very small, absorb fats and fat-soluble nutrients from the intestines
- superficial - originate just under the skin. They tend to flow parallel to the veins. Over time they flow into deep vessels
- deep - pump lymph in deeper places, repeat the path of deep arteries
Lymph flows through these vessels - a transparent white liquid consisting of leukocytes and fluid from the intestines, which consists of proteins and fats - chyle. It is formed when fluid leaves capillaries due to pressure. Approximately 10% of the blood volume becomes lymph. Unlike blood, it is not pumped, but squeezed out through the vessels when we use muscles. Moreover, lymphatic vessels have practically no walls - just one name.
The place where the lymphatic vessels branch is called a node. They look like soft, small beans. Someone calls them glands, do not repeat after these ignoramuses: glands can only be endocrine.
In the lymph nodes, immune cells evaluate the presence of foreign materials. In total, there are more than 600 nodes inside us and each one can react to the invader.
Lymph is gradually squeezed out to two main channels - lymphatic ducts:
- the right duct drains lymph from the upper right quadrant of the body: the right sides of the head, neck, arm and chest
- The thoracic duct is much larger. It drains lymph from the rest of the body.
These two ducts, with lymph already filtered, empty into the veins under the collarbones.
There are a couple of organs that also belong to the lymphatic system: tonsils, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, fetal liver.
We are constantly attacked by dangerous microorganisms. First line of defense:
- physical barrier, e.g. skin
- toxic barrier, e.g. stomach acid
- good bacteria in the body⠀
However, pathogens often manage to enter the body. In this case, the lymphatic system gives the command to the immune system.
The lymphatic system produces two types of lymphocytes: T cells and B cells.
They reach the lymph nodes, are filtered and activated upon contact with harmful organisms. From this stage, pathogens or invaders are declassified and become known as antigens.⠀
When lymphocytes are activated, they form antibodies and begin to protect the body. They can also produce antibodies from memory if they have encountered a particular pathogen in the past.
Activated lymphocytes travel further through the lymphatic system and enter the bloodstream. They are now ready to spread the immune response throughout the body through the circulation.⠀
Most lymph nodes are in the neck, armpits and groin. They increase for two reasons:
- response to infection - foreign material enters immune cells through lymph, which is removed from the infected tissue.
- direct infection of the lymph nodes - the nodes themselves can become infected and inflamed (lymphadenitis).⠀
Lymph nodes collect information from the bottom up. Inflammation suggests:
- ulnar lymph nodes - you need to look for scratches on the hands (maybe you have a cat?) and this is cat scratch disease
- axillary lymph nodes - women should pay attention to the breasts
- submandibular lymph nodes - check the throat: sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, pharyngitis
- occipital lymph nodes - a sign of rubella
- inguinal lymph nodes - worth checking for STIs
- popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes, with swelling of the legs - venous disease, diabetes mellitus
If the lymph nodes are swollen due to a cold or flu, you don’t need to bother the doctor; it will go away along with the flu.
When to see a doctor?
lymph nodes remain swollen for longer than 1-2 weeks
the enlarged lymph node is hard or cannot be moved
In addition to swelling, there is fever, itching, sweating, or unexplained weight loss
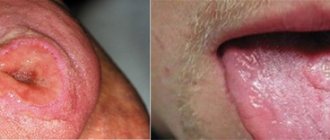
TREATMENT OF PHARINGITIS
First of all, with pharyngitis, it is necessary to exclude irritating foods from the diet (hot, cold, sour, spicy, salty), and also stop smoking and drinking alcohol. You need to drink a lot (1.5–2 liters per day), it is better if these are fortified drinks (for example, berry fruit drinks or rosehip decoction). Rinse with warm antiseptic solutions (furacillin, iodinol, etc.), lubricate (Lugol's solution in glycerin) or irrigate (for example, Ingalipt, Tantum Verde, Cameton) of the pharynx. Rinsing with a warm saline solution (1 teaspoon per glass of water), inhaling a solution of soda with vegetable oil, or instilling a warm solution of soda with the addition of glycerin into the nose also helps to alleviate the condition. To reduce body temperature, you can take antipyretics (paracetamol, aspirin - except for children). The doctor may also prescribe medications with interferon and lysozyme, antihistamines and vitamin-mineral complexes.
If it is determined that pharyngitis is of bacterial origin (the causative agent is most often hemolytic streptococcus), then, most likely, it will not be possible to do without antibiotics. They must be prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable. The drugs of choice are penicillins, and if they are intolerant, first generation cephalosporins and macrolides.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis is always long-term; in addition to eliminating the source of chronic infection in the nasopharynx, it includes treatment of concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine disorders, etc. With hypertrophic pharyngitis, the overgrown lymphoid tissue is cauterized by applying electric current or cold to it ( electrocoagulation or cryotherapy ). With atrophic pharyngitis, on the contrary, therapy is aimed at increasing mucus secretion and reducing symptoms of pharyngitis such as dryness (lubricating the pharynx with Lugol's solution in glycerin) and stimulating regenerative processes in the mucous membrane (vitamin A preparations, ATP).
in the treatment of chronic pharyngitis :
What to do if your lymph nodes hurt?
Treatment of lymph nodes depends entirely on the causes of inflammation. In order not to “overlook” the disease, it is enough to be attentive during a visual examination. With inflammation, the lymph nodes enlarge - the familiar, for example, submandibular relief becomes smoother. There are about a hundred diseases associated with this condition, so self-diagnosis is a bad idea. A much better decision would be to contact a therapist: he will be able to conduct a comprehensive examination, after which he will refer you to a specialist, depending on the nature of the inflammation.
Characteristic symptoms of the course of inflammation are also a change in the consistency of the lymph node (it can become soft from suppuration, or hard due to the development of cancer cells of the lymph tissue), the occurrence of painful sensations during palpation or swallowing, redness of the skin at the site of the lesion, as well as apathy and fatigue characteristic of many diseases , headaches and fever, which is inevitable during inflammation.
If the lymph nodes in the neck hurt from a sore throat or any other disease in which such sensations are only a symptom, then the pain will go away along with the end of the underlying disease. Mild symptoms (mild pain or tingling when swallowing or pressing, general weakness and frequent colds) indicate a general deterioration of the immune system.
In the second case, the most common treatment method is ultra-high frequency therapy - a painless and discomfort-free procedure performed using special equipment. Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed by a doctor in case of urgent need, but in general it is enough to adhere to bed rest, take vitamins and drink plenty of warm fluids. Echinacea tincture will help ease the course of the disease - a truly magical plant, a natural antiseptic that eliminates inflammation and strengthens the immune system. Decoctions of mint, chamomile or calendula will help you feel better, and rinsing with salt and soda will help fight inflammation.
Remember that inflamed lymph nodes should under no circumstances be heated, rubbed, or an iodine mesh applied to this area. Such procedures aggravate the course of the disease and accelerate the spread of infection.
CAUSES OF PHARINGITIS
The main cause of pharyngitis is inhalation of cold or polluted air, exposure to chemical irritants (alcohol, tobacco). Infectious pharyngitis can be provoked by various microbes (strepto-, staphylo-, pneumococci, as well as viruses (influenza, adenoviruses) and fungi (candida). Pharyngitis often develops as a result of the spread of infection from any source of inflammation adjacent to the pharynx. This is how pharyngitis develops for sinusitis, rhinitis, dental caries.
According to the etiological factor, acute pharyngitis can be divided into viral, bacterial, fungal, allergic, traumatic (as a result of a foreign body or surgical intervention) and caused by exposure to irritating factors (hot liquid or steam, acids, alkalis, radiation, etc.).
Chronic pharyngitis is usually classified not according to etiology, but according to the nature of the changes developing in the mucous membrane: catarrhal (simple), atrophic (subatrophic) and hypertrophic. These forms of chronic inflammation are often combined.
Thus, the presence of diffuse atrophic changes in the mucous membrane can be combined with focal hyperplasia of the lymphoid tissue of the posterior pharyngeal wall or tubopharyngeal ridges.
Why does inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck occur?
So why does inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck occur? Lymph nodes are an integral part of the human immune system, part of its defense, a kind of biofilter that helps prevent the development of many diseases. If the filter becomes clogged and simply cannot cope with pathogenic microorganisms, inflammation occurs. Thus, if your lymph nodes hurt, it means there is an infection in your body that threatens your health. In total, nine pairs can be classified as cervical lymph nodes, one way or another connected with the area of the face or neck. They are located near the ears, jaw, above the collarbones and even under the tongue, so the occurrence of pain in these areas may indicate inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Most often, the cervical lymph nodes become inflamed due to a sore throat or ear infection. Also, the cause of the painful condition can be ARVI, which peaks in the autumn and spring periods, influenza, any diseases of the oral cavity, from stomatitis to caries. The lymph nodes located next to the ears become inflamed with otitis media. The location of the lymph nodes plays an important role in determining the source of infection, since they usually signal disease in nearby organs.
Much less often, pain in the lymph nodes occurs due to metabolic disorders, alcoholism, thyroid disease or simple allergies, however, it would be wrong to completely exclude these options.
In addition, inflammation of the lymph nodes, unfortunately, can be associated with serious problems, for example, mechanical damage (trauma) to the lymph node itself or nearby tissues, as well as cancerous degeneration of lymph tissue cells.
Be that as it may, inflamed lymph nodes are a sign of dysfunction of the immune system. In this regard, there is a common misconception that pain in individual nodes, their enlargement, may indicate the presence of AIDS in a person. This is not an entirely correct statement, since HIV-infected people suffer from enlargement of entire groups of lymph nodes.