29.11.2019
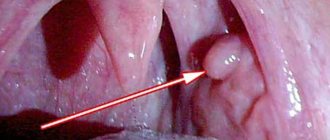
A growth on the mucous membrane of the mouth, located on the upper palate, causes discomfort to the wearer, sometimes accompanied by pain. A lump on the roof of the mouth occurs due to several completely different diseases. Each disease has its own characteristics and causes, but their clinical characteristics are similar. Without the qualified help of a doctor, it is impossible to determine an accurate diagnosis and effective method of therapy.
Types of tumor
A tumor on the roof of the mouth always indicates the onset of an inflammatory process in the human body. Tumors can be benign or malignant.
Malignant formation
Problems with the development of a malignant tumor are not limited to disturbances in speaking and eating. The lump, the cause of which is cancer, impairs articulation, complicates the ability to communicate or completely eliminates it.
Oral cancer is typical for men and is a local metastasis of other malignant tumors in the head. It is a rare cancer.
Such malignant lumps are classified as growths on the roof of the mouth. The tubercle can pop up due to a benign inflammatory process, so it is impossible to express a clear opinion about the diagnosis.
Understanding the reasons for the appearance of a tumor is important for determining the course of treatment. The causes can be accurately diagnosed by conducting clinical studies of the compaction.
Benign formation
A cyst on the roof of the mouth is not a fatal diagnosis; it is diagnosed with a number of benign tumors. Such tubercles are caused by insidious but curable diseases:
- growth of blood vessel tissue (angioma);
- cyst;
- pemphigus (erosion);
- myxoma.
Therapy
The tactics for treating cones is determined depending on the type of growth that has arisen on the palate. Complex therapy is often used, including:
- taking medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs;
- surgical removal of the growth.
If a malignant tumor is present, radiation therapy is prescribed.
Conservative therapy for growths on the palate is based on the use of vasoconstrictor and sclerotic drugs. They are indicated for angioma. During the treatment process, 70 percent ethyl alcohol is injected into the tumor, which disinfects the mucous membrane before surgery.
Preliminary determination of lump symptoms
A lump on the palate is the cause of a dental disease or inflammatory process. Each type of growth has its own causes and subtleties of symptoms, and therefore requires separate consideration.
Angioma
Angioma is a tumor in the palate caused by disruption of processes in the tissues of the blood vessels of the soft palate. The shape of the cone resembles a rolled corkscrew. The tubercle has a blue or purplish-black characteristic color. The ball is a product of a disorder in the development of blood vessels, so the color is caused by the excess amount of blood in the formation.
Pressure causes bleeding, which should not be experimented with. There is a pulsating response to pressure.
Such a lump on the upper palate is life-threatening for the patient. Bleeding is difficult to stop, and large blood loss is fatal.
At the first signs of such compaction, you must seek qualified help.
Cyst
A lump in the mouth on the palate is classified as a cyst when a hard ball appears on the palate and its size does not exceed 12 cm. The cyst appears due to a disorder of the sebaceous glands. It won’t hurt, but it will make it significantly more difficult to eat, and then completely disrupt the correct functioning of these secretions.
A cyst on the palate requires surgery and can only be treated with it.
Pemphigus
Children are most susceptible to developing pemphigus. It pops up in the shape of a white ball at the top of the mouth. The bumps are a consequence of erosion and later develop into ulcers. When pressed it bleeds and hurts. Diagnosed by visual examination and using the Nikolsky method.
If the tumor is not removed, erosion will develop into massive exfoliation of the oral epithelium, disruption of digestive processes, and general weakness. If there is no treatment, the bumps become widespread. Pressure causes rupture of tumors, the contents of which cause intoxication of the body.
Myxoma
A myxioma is a hard, white growth at the top of the mouth. The disease affects the hard part of the palate, and upon visual examination it is almost invisible; pressure on the tumor is not felt. This significantly complicates diagnosis and delays the patient’s visit to the doctor.
The diagnosis can be confirmed or refuted by a biopsy of the palate.
Oncological disease
Cancerous lump is classified into two diseases:
- Hard palate cancer - starting from the bone tissue between the nasopharynx and the palate, the disease spreads to all mucosal tissues.
- Cancer of the soft palate - a lump appears due to an oncological process in the muscle and mucous tissues of the mouth.
Additionally, the oncological tubercle on the roof of the mouth is divided according to the tissue from which the spread of the disease began:
- Cylinder - the maternal tissue is the tissue of the glands, the cancer spreads quickly and invades the oral cavity;
- Adenocarcinoma - begins expansion of the mouth from the soft tissues of the cavity;
- Squamous cell carcinoma is a malignant formation that begins to develop from the tissues of the mucous membrane.
Causes and types of lumps
Basically, growths on the upper palate are formed from:
- muscle tissue;
- epithelial tissues;
- blood vessels;
- connective tissue;
- organic liquids.
The most common cause of a lump is considered to be an inflammatory process in the oral cavity. Because of it, the flow of blood and other fluids through the vessels is disrupted.
The formation of a lump on the palate is promoted by colds and infection of the body. The main causes are cyst, angioma, myxoma, pemphigus.
Other provoking factors are fistula, epulis, exostosis.
Treatment is the use of anti-inflammatory, sclerotic, vasoconstrictor drugs. If the tumors are malignant, radiation therapy is prescribed.
The development of neoplasms in the oral cavity can be provoked by:
- congenital predisposition;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- damage to the mucous membrane;
- dental errors (installation of unsuitable dentures, untreated fillings, etc.);
- viral infection;
- diseases of internal organs and other factors.
The nature of the clinical picture depends on the type of growth.
Angioma
Angioma is a benign tumor that appears due to dilation of blood vessels. Less commonly, the tumor is formed from the lymphatic ducts. This tumor is called lymphangioma, and when pressed it causes pain.
Sometimes a lump on the roof of the mouth indicates trauma: burns, damage to the mucous membrane during eating (cutlery, solid food, fish, poultry or fruit bones), rubbing with the base of a removable denture.
In this case, it is enough to eliminate the root cause factor, as well as carry out antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and reparative treatment.
Dentist
Novikova Olga Alexandrovna
8 years of experience
The growth formed due to the proliferation of blood vessels is of two types:
- Simple angioma. Externally it has a reddish-blue surface. A simple angioma is formed due to the coagulation of blood vessels.
- Cavernous angioma. Has a dark burgundy tint. Formed in the cavernous cavities of the mouth.
The first type of tumor occurs due to disruption of the capillaries running along the palate. Cavernous angiomas are formed due to the proliferation of venous vessels. The endothelium grows around such compactions, due to which the neoplasms have a hard shell to the touch.
Cyst
Cystic cavities rarely occur on the palate. They usually do not exceed 1 cm in diameter. The appearance of a cyst is caused by a malfunction of the salivary gland, which is caused by:
- mucosal injuries
- narrowing of the salivary ducts;
- inflammation of the gland;
- congenital anomalies.
Cystic cavities do not cause pain. Without treatment, pus forms in them, which leads to an abscess.
Pemphigus
Pemphigus, or epidermolysis, is a benign white neoplasm. The tumor first appears in childhood. The main cause of pemphigus is congenital predisposition.
The development of epidermolysis triggers carious processes in the oral cavity. Having reached a certain size, pemphigus opens up on its own, and painful erosions remain in its place. The latter eventually turn into ulcers. This transformation is explained by the fact that in pemphigus the connection between epithelial cells is disrupted.
Myxoma
Myxoma is a type of cystic cavity that is formed due to the proliferation of capillaries. Growths of this type are characterized by a bumpy surface. The main cause of myxoma development is considered to be inflammation of local tissues.
Diagnosis of the neoplasm is carried out through hypoxia and x-ray examination. Additionally, a biopsy is prescribed to rule out a malignant tumor.
Other neoplasms on the palate
The most common neoplasms on the palate also include:
- Fistula. A characteristic sign of this neoplasm is the presence of a small hole through which pus comes out.
- Exostosis. Formed due to protruding bone tissue.
- Epulis. It is a small ball that is attached to the base by means of a thin stem. Epulis is more often detected in women.
Almost all growths on the palate interfere with chewing and swallowing food. Less commonly, the formation of cones is accompanied by pain. Sometimes they bleed when pressed.
Due to the fact that some of the cones are formed due to the proliferation of lymphatic or blood vessels, the development of growths on the palate causes swelling of the oral mucosa. At the same time, the lymph nodes located near the jaw enlarge.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of a lump
Modern medicine has not created a complete list of reasons why bumps may appear. Doctors' reasoning is based on hypothetical cause-and-effect relationships. The appearance of a lump on the palate is caused by:
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol, oral drugs);
- The presence of micro and macro injuries to the oral cavity (surgeries, scratches of the upper parts of the oral cavity);
- Availability of dentures;
- Viral infections;
- Intrauterine disorders (hemangioma is a congenital disease and acquired from the mother);
- Violation of the activity and integrity of the mucous membrane (typical of angina);
- Congenital and acquired dysfunction of the glands (the main cause of cysts).
There are two more hypothetical reasons for the appearance of malignant tumors:
- Eating too hot and spicy foods, constantly disrupting the structure of the cells of the oral cavity;
- The presence of papillomatosis or leukoplakia - diseases that are precancerous lumps that can develop into an oncological disease.
Preventive actions
Professional oral hygiene plays an important role. The procedure is carried out in a dental office at least once every six months. You should spend more time in the fresh air, eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, and alternate rest with moderate physical activity. Hardening has a positive effect on the body. The main thing is that the patient follows a number of simple rules:
- Chewing organs should be cleaned morning and evening;
- Rinse aids should be used after meals every time;
- Food that is too hot should not be consumed;
- Enrich your diet with useful microelements and vitamins to improve immunity;
It is necessary to avoid stressful situations, give up bad habits, and regularly diagnose the body. Such actions prevent the development of inflammation and diseases of the oral cavity.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the method by which a lump on the roof of the mouth will be treated, the causes of its occurrence are studied. The diagnostic procedure is carried out by a dentist.
Regular visits to the dentist are important to prevent the disease and determine whether a lump has appeared on the roof of your mouth. It needs to be treated at an early stage.
For diagnosis use:
- Radiography;
- Biopsy;
- Blood analysis;
- Radioisotope study;
- Ultrasound.
If you comprehensively examine the ball on the roof of your mouth, this will confirm or deny the presence of a malignant formation, and if it is absent, it will determine the exact diagnosis of a benign one.
Treatment of cones
The treatment methodology depends on the specific case. The approach is determined by:
- the presence of pain;
- part of the cavity that has been infected (upper, lower);
- time elapsed since the onset of the disease;
- reaction of the cone to pressure.
Treatment of angioma
Removing a lump of this type occurs in three stages:
- Drug treatment and treatment;
- Surgery;
- Radiation therapy.
At the first stage, alcohol is used: it constricts blood vessels and helps eliminate high blood loss during surgery.
Then, in the case of the capillary form, radium therapy is used, it consolidates the effect of treatment, and sometimes can act as an independent drug and cure the disease completely.
It is prohibited to treat the cavernous form of angioma with radium. It can help transform the lump into a malignant one, which can greatly worsen the patient’s condition.
Treatment of pemphigus
A lump of this type that appears on the palate is treated mainly with antibiotics and a diet that includes a high content of proteins and vitamins, but without salt.
If such a lump appears, it is necessary to use disinfectant solutions. In severe forms, blood transfusions are used.
Treatment of myxoma and cysts
In these forms of the disease, the attending physician prescribes antiseptic drugs and prepares the cavity for surgery (if there are signs of accelerated growth of the lump into the tissue).
Additional methods of electrical treatment are also used, which make it possible to artificially kill tissue without the use of a scalpel, but all methods of this type are dangerous, thanks to them, a malignant formation may appear in place of a benign one.
Treatment of cancer
Cancer requires immediate intervention by a qualified specialist. The earlier the stage of the disease, the less harm the treatment and the disease itself will cause to the body. If a cancer lump appears, the following treatment approaches are used:
- Radiation therapy – the cancerous growth is irradiated with X-rays. In the early stages, it completely cures the disease.
- Surgical intervention - not only the harmful lump is cut out, but also the tissue around it, in order to exclude relapses. Such an intervention leaves defects on the face, which can later be corrected with plastic surgery.
- Chemotherapy - taking cytostatics.
For the cancer in question, chemotherapy is effective only in combination with radiation and surgery.
It is easier to defeat any disease at its inception stage. But in the case of bumps on the palate, it is better not to have the disease than to treat it later.
The root causes of the disease have not been fully established. Therefore, following the hypothetically formed rules will not completely protect you from the disease, but it will definitely reduce the chance of developing a similar problem. A preventative visit to the dentist will ensure timely treatment, even if the lump pops up unnoticed.
Category Miscellaneous Published by Mister dentist