Relevance
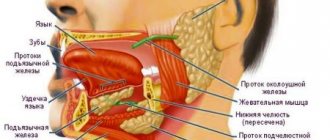
The surgical method of treating tongue tumors remains the main one in the specialized treatment of benign tumors and carcinomas in the initial stages of the malignant process. Despite the postoperative “discomfort” when eating, changes in speech function, the choice of radical surgery is determined by the need for rapid and complete removal of the tumor focus in the oral cavity with its final pathohistological examination and effective “medical profitability” in the treatment of these patients. The healing process of post-resection wounds of the tongue is influenced by the state of the microbiota and factors of local immunity of the oral cavity. Therefore, the study of indigenous microorganisms and the level of lysozyme in mixed saliva before and after surgical treatment of patients with oral cavity tumors is relevant for subsequent personal preventive measures [1, 3]. The use of local oral irrigations with various drugs is also a reasonable necessity and requires modern analysis and study in the changing conditions of the pharmaceutical market.
The purpose of the study was to study the nature of postoperative wound healing and the qualitative and quantitative composition of the oral microbiota, as well as the level of lysozyme in the saliva of patients with tongue carcinoma at the stage of surgical treatment with local application of a 2% solution of acid-soluble chitosan.
Tongue traumatism: theory
Before you begin treatment of the tongue, you should carefully study the nature of the injury and its causes.
Mechanical impact
The first type of damage - mechanical - is the most common cause of tongue injuries. Due to mechanical damage, ulcers and superficial erosions form on the tongue.
Conditions under which mechanical injuries occur are of a domestic nature:
- damage to the integument by dental instruments - probe, bur, disc;
- the occurrence of a wound under the influence of a sharp object - a bone, a knife, a fork;
- biting the tongue while eating, epileptic seizure;
- the appearance of tongue injuries from blows to the face.
Healing of a wound caused by mechanical impact occurs depending on the depth and area of damage to the mucous membrane.
Chemical burn
Chemical injury to the tongue, as the second type of injury, occurs due to contact with the mucous membrane of a chemical substance of an acidic or alkaline nature.
Under the influence of an irritant, chemical burns occur on the tongue. The latter are characterized by the appearance of dark-colored areas, scars, blisters and blisters on the tongue (in severe cases).
Instant rinsing of the mouth with solutions with neutralizing properties is the key to rapid restoration of the integument.
For chemical burns, it is preferable to seek help from medical institutions.
Painful influence from the outside
Damage to the mucous membrane by steam, hot water, fire, electric current or ionizing radiation is called physical trauma to the tongue.
Characteristic of this type of injury is pain that gradually subsides from the moment of injury.
The main danger of physical injury is the development of acute catarrhal glossitis (inflammation). Consultation with a doctor in complex stages of injury is mandatory.
Deep damage to the tongue caused by various kinds of external irritants can be accompanied by complications: abscess or phlegmon of the tongue.
Painful swelling and accompanying difficulties with swallowing and speaking are symptoms of an abscess. In later stages, with increasing inflammation of the tongue, the abscess turns into phlegmon. The victim requires emergency hospitalization and surgical intervention.
What types of wounds are there?
A wound is a tissue damage that is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes. The wound is accompanied by pain and bleeding.
The first sign is pain. It occurs due to damage to local nerve endings, and subsequently due to swelling, which puts pressure on the nerve and irritates it. In this case, pain can spread not only along the surface of the wound, but also along the damaged nerve.
The second mandatory sign of a wound is bleeding. It occurs as a result of damage to capillaries, veins or arteries. Bleeding can be weak and drip, for example, with a small cut, and severe when the integrity of the vein and artery is damaged.
The third sign of a wound is gaping. However, gaping appears only with deep wounds, for example, with abrasions it does not exist. Gaping is the divergence of the edges of the wound on either side of the axis of the cut. If there is severe gaping, the wound is usually sutured.
There are many types of wounds. For a person in everyday life, it is necessary to know several classifications. The first is based on whether there is an infection in the wound. Wounds may be aseptic, contaminated, or infected.
An aseptic wound is a pure injury to the skin. Usually these are surgical wounds that are performed in order to penetrate the internal organs. Children most often experience contaminated wounds. This means that microbes have entered the area of skin damage. At first, these are relatively safe wounds: local protective mechanisms inhibit the development of microorganisms. If a contaminated wound is not treated, it becomes infected: an infectious process develops, which is accompanied by inflammation, severe pain and suppuration. An infected wound can cause a strong reaction in the child’s body: body temperature rises, chills, drowsiness and apathy appear.
Depending on the nature of the damage, there are the following wounds:
- punctured - they occur when punctured by a narrow and piercing object, for example, when a child falls on a nail. Typically, a puncture wound bleeds slightly and hurts. Outwardly it may seem that this is a safe wound, but this is not so: large vessels, nerves are often damaged, and even an infection occurs;
- cut - occur upon contact with a sharp oblong object: a knife, razor, sharp scissors, a shard of glass and paper. With an incised wound, the tissue is usually slightly damaged. The wound bleeds heavily and hurts moderately;
- Chopped wounds occur when damaged by a heavy sharp object, such as an ax. Usually the bleeding is moderate, but the wound is very painful and gapes. May lead to serious condition;
- a bruise wound appears when struck with a blunt object or falling on asphalt. Most often, the bruised wound is located on the head, elbows and knees. The edges of a bruised wound are uneven and soaked in blood. It bleeds slightly and is moderately painful.
There are also bite wounds that occur when children are bitten by animals or other children. The difficulty with this wound is that in most cases it contains infection from the animal's oral cavity. This is how rabies, insect and snake poison, and putrefactive infection are transmitted.
The wound process consists of several stages:
- In the first seconds after skin damage, local blood vessels reflexively constrict and biologically active substances are produced - platelets, which adhere to the wound area and close the damaged vessel. The blood clotting system turns on, stopping the bleeding. In a healthy child, bleeding stops on its own within 15 minutes.
- Inflammation. Lasts 3 days from the moment of injury. Inflammation is manifested by pain, redness and local fever. Also, swelling in the form of a tumor appears on the wound within two hours.
- 2–4 hours after injury, leukocytes migrate to the area of injury. They absorb foreign particles and cleanse the wound of microorganisms.
- Healing phase. Begins 3–5 days after injury. Bioactive substances arrive to damaged tissues, which restore vascular and skin tissue.
- Epithelization phase. Begins 2 weeks after injury. The wound mark becomes pale and a scar forms. The epithelialization phase may be delayed if bacteria are present in the wound.
Treatment Basics
As mentioned earlier, treatment for tongue injuries depends on the nature of the injury. While a home first aid kit is sufficient to heal superficial injuries, eliminating the consequences of traumatic factors in case of serious injuries requires, first of all, consultation with a doctor who will select the necessary medications and prescribe recommended procedures.
What to do depending on the type of injury:
- The standard method of treatment or initial treatment of mechanical injuries is the use of antiseptics (alcohol, iodine, brilliant green). Rinsing with disinfectants helps in restoring the mucous membrane: furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate dissolved in water in a ratio of 1 to 3000 or baking soda at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 250 ml. Do not neglect plant decoctions with calming properties.
- Knowledge of chemical neutralizing reactions will be useful in case of chemical burns , because the “golden rule” of first aid for this is as follows: rinse with a neutralizing solution. Timely implementation of the necessary procedures will avoid further treatment. Blisters appearing on the tongue indicate severe damage. Opening of formations with subsequent processing should only be carried out by specialists. After neutralizing the blisters, doctors most often prescribe rinsing the mouth with disinfectants.
- Profusely bleeding wounds require immediate tamponade. It is unacceptable to independently remove foreign bodies from ulcers.
Treatment of abrasions in children
How to properly treat abrasions in children:
- Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin around the wound from dirt, dust, debris and other objects.
- Disinfect the wound: the abrasion can be treated with the following products: zinc oxide ointment, benzalkonium chloride cream, dexpanthenol cream, chlorhexidine, methyl blue, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green and 5% iodine solution.
- Usually, mild capillary bleeding occurs with abrasions. It is enough to apply a dry cloth or gauze to the damaged skin.
Biting your tongue - everyone knows this
Biting the tongue, cheek or lip is accompanied by painful sensations, as damage to the mucous membrane occurs.
Obviously, the initial goal after a bite is to reduce pain. So, what should you do if you bite your tongue, what and how to relieve pain and inflammation?
The main rule is to remain calm. Calm down and try to come to terms with the pain, because tantrums and tears will not help heal the damage.
And then you should do the following:
- Be sure to stop bleeding , if any. An elementary solution would be to repeatedly rinse with cold water: it will help narrow the blood vessels and reduce bleeding activity. A worthy alternative would be a piece of ice.
- Cotton swabs soaked in 2% Lidocaine help in the fight against painful sensations . Another variation to reduce pain is eye drops with an anesthetic - Tetracaine, Alcaine.
- It is important to disinfect the entire oral cavity : brush your teeth thoroughly and rinse your mouth.
- Maintain regular rinsing : it is advisable to wash away the remains of eaten food after each meal.
- Use antiseptics such as Antiangin, Trachisan, Furacilin in the form that is optimal for you: spray, lozenge or solution.
- Avoid eating rough, cold or hot foods . During the restoration of the oral mucosa, it is advisable to create a daily menu of liquid soft foods at medium temperature: purees, soups.
- Avoid cold foods - ice cream, frozen juice and other foods with temperatures below zero - they slow down the healing process.
- Take a course of vitamins to help restore damaged areas. The optimal solution would be to include vitamin C and group B in the diet.
Do not forget to adhere to sanitary and hygienic measures: do not reach into the oral cavity with dirty hands, do not put pressure on the resulting injury.
Never pour iodine or brilliant green or peroxide into a wound: give preference to treating the environment around the injury. Antibiotics can only be used as prescribed by a doctor.
In practice, there are cases of tongue biting. In such a situation, it is important to remain cool, act quickly and in an organized manner: place the “particle” in a bag filled with ice and go to the hospital. To relieve painful sensations, it is permissible to ingest cold food: suck ice cream, frozen juice, ice, drink water.
What to do if the wound does not heal for a long time
The wound may not heal for a long time. This occurs due to several factors: the skin is not cleaned after injury, blood flow is complicated due to inflammation, or the regeneration mechanism is disrupted. Because of this, complications arise:
- Seroma is an accumulation of inflammatory fluid (exudate) in the wound cavity. Seromas most often occur when dirt, microorganisms, or foreign bodies remain in the wound;
- wound hematoma. It appears due to the fact that after the wound the bleeding did not stop completely, and drops of blood gradually soaked the surrounding tissue. Hematomas also occur as a result of diseases in which blood clotting is impaired;
- necrosis of soft tissues. Occurs due to severe and massive tissue damage or cutting of blood vessels. Early signs of necrosis: in the first days after injury, the skin is pale, has a bluish tint and is cold to the touch;
- malignancy is a process when tissue cells acquire the characteristics of a tumor. Malignization occurs when a chronically non-healing wound.
In addition, the wound may not heal for a long time with poor immunity, diabetes, long-term use of glucocorticoids and vitamin deficiency. The only correct option is to consult a surgeon: at home it is impossible to assess the condition of the wound and provide proper medical care.
Traditional medicine at the service of the people
Here is a selection of recipes for solutions, the use of which will help disinfect, heal wounds and reduce pain:
- A decoction of bedstraw helps to cope with tongue pain . Brew 1 tablespoon of dried herb with boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain the resulting mixture. The decoction is suitable for both rinsing and internal use.
- Sage tincture is an assistant in the fight against pain during the treatment of oral injuries. By brewing 2 tablespoons of the substance with half a liter of boiling water and letting the infusion “rest” for 30 minutes, you will get an excellent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory medicinal drug. Rinse frequency: 5-11 times a day.
- Pour 1 tablespoon of chamomile 250 ml of boiling water and let it brew. Use the strained solution after meals and before bed to heal wounds and relieve inflammation.
- St. John's wort tincture is a panacea for pain caused by a tongue injury. Use 40% alcohol and dried herb in a ratio of 5 to 1, respectively. Add 30-40 drops to 250 ml of water and rinse your mouth.
- Finding potatoes in a cellar or drawer is not difficult, but peeling them is a matter of two minutes. Feel free to use sliced raw vegetables to relieve pain from burns.
The best way out is to avoid injury
Statistics show that most tongue injuries are mechanical in nature, which, in turn, is evidence of negligence. To avoid damage to the oral cavity, follow these simple rules:
- do not get lost in thoughts while eating;
- When eating, do not be distracted;
- do not talk with your mouth full of food;
- Chew your food thoroughly and slowly.
Often the cause of wounds is a malocclusion or unsuitable dentures. An improperly growing or filed tooth also poses a risk to the integrity of the oral cavity.
Be extremely careful and remember that it is better to prevent a traumatic situation from occurring than to suffer trying to cope with its consequences. If you observe suspicious symptoms, be sure to seek help from a dentist or ENT doctor.