Bruxism and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles are inextricably linked processes. Bruxism is a condition when the muscles of the jaw involuntarily spasm, as a result of which a person begins to grind his teeth. There is an increased tone of the masticatory muscles.
Very often, this problem becomes a serious obstacle to dental procedures, such as implantation, prosthetics, and installation of veneers. Bruxism can interfere with quality orthodontic treatment. Increased tone of the jaw muscles overloads the implants, and dentures are destroyed much faster.
Bruxism also has a negative effect on “native” teeth. The enamel is damaged and worn away, and the teeth become loose. Therefore, if such a problem arises, it is necessary to look for ways to solve it. Thanks to modern medicine, you can get rid of bruxism for a long time.
Symptoms of bruxism and the main causes of hypertonicity:
- the surface of the teeth grinds down, they become flatter;
- the enamel is damaged, fillings fall out, teeth begin to loosen, their integrity is violated, the gums become raw and bleed;
- crunching and clicking appears in the jaw when opening and chewing;
- teeth grinding occurs when a person sleeps;
- it is difficult to open and close your mouth, you feel tired and overstrained masticatory muscles;
- you often unconsciously clench your jaw, most of the time they are tense;
- malocclusions appear;
- the lower part of the face takes on a square shape;
- posture worsens.
Tension of the masticatory muscles - how it manifests itself with age
Let's start with the deep (medial and lateral) muscles. The medial one (No. 3 in the picture) is responsible for the movement of the jaw to the right and left. Have you noticed that some older (and not so old) women have an asymmetrical jaw - larger on one side and smaller on the other? This just indicates a spasm of this muscle on one side. Therefore, in order to have a symmetrical face without distortions, it must be relaxed.
The lateral (No. 1) masseter muscle pushes the lower jaw forward and pushes it back. It greatly affects the bite. I think everyone has seen this in others or maybe in themselves:
Here is a clear example of excessive tension in the lateral masticatory muscles - they literally pull the lower jaw inward.
But there is also the opposite situation - when the muscles are too weak, in hypotonicity:
The lower jaw then moves forward. Of course, now this is corrected with braces. However, with the help of exercises this can be done without them. And if you already wear braces, you can significantly speed up the results with exercises. This is confirmed by orthodontists.
Spasms of the temporal muscles lead to the fact that the eyebrows begin to float down and the face becomes gloomy. The habit of clenching your teeth (mostly unconsciously, from stress, anger, irritation) causes tension in the facial muscles of mastication - those at the corners of the jaw. This causes the oval of the face to float; the face may even become longer with age. Bruxism may develop, tooth decay may begin, and gum disease may appear - because chronic spasm of these muscles blocks normal blood circulation.
Botulinum therapy as a method of treating bruxism
Botulinum therapy is effectively used to relieve overstrain in the masticatory muscles, fights bruxism and can relieve involuntary teeth grinding at night.
In medicine, as in cosmetology, botulinum toxin type A is used. It is able to immobilize a muscle or relieve tension in it, acting locally. This effect lasts only for a certain period of time. But during this time the body manages to get used to the new state, and the overstrain disappears completely.
Botulinum toxin type A is a neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. It is capable of blocking impulses from the central nervous system sent to the muscles. In fact, botulinum toxin paralyzes them, breaking the connection between muscle fibers and the brain.
The drug is injected into the required areas, so it has an effect exclusively on the desired areas. Dosages of butolotoxin are completely safe, and its effect is reversible. After six months, it is completely eliminated from the patient’s tissues.
How to prevent trismus
There are 4 main ways to prevent trismus:
- massage your jaw muscles;
- train your jaw muscles;
- maintain good posture;
- Maintain proper oral hygiene.
This should be done even if there are no symptoms of trismus to prevent it. Follow the directions in the section below. If you have had surgery, ask your healthcare provider if it is safe before you have surgery.
You may need a timer or watch to help you hold the stretching position for the required amount of time. Breathe normally and do not hold your breath. If you feel pain, numbness, or tingling, stop immediately and call your healthcare provider.
Massage your jaw muscles
Press your index and middle fingers against your cheekbone. Use your fingers to massage the masseter muscle, which is attached to the lower jaw (see Figure 3). As you move your fingers, look for areas that are tender or tight. Massage these areas with circular movements of your fingers for 30 seconds. Do this 2-3 times a day.
Try not to clench your jaw when you are stressed or out of habit. This will help relax your jaw muscles.
Figure 3. Massage the jaw muscles
Train your jaw muscles
Perform these exercises 3 times every day. You can do them standing or sitting. Use a mirror to help you do the exercises correctly.
These exercises will help stretch the muscles well, but should not cause pain. If an exercise causes pain or discomfort, try doing it with less effort. If pain or discomfort persists, contact your healthcare provider.
Range of motion and stretching exercises
Your head should remain in one position while performing these exercises. Repeat these steps 5 times.
- Open your mouth as wide as possible until you feel a good stretch but no pain (see Figure 4).
Hold this position for 10 seconds. Figure 4. Opening your mouth as wide as possible - Move your lower jaw to the left (see Figure 5). Hold this position for 3 seconds.
- Move your lower jaw to the right (see Figure 6). Hold this position for 3 seconds.
Figure 5. Jaw shift to the leftFigure 6. Jaw shift to the right
- Make circular movements with your lower jaw to the left.
- Make circular movements with your lower jaw to the right.
Passive stretching exercise
Figure 7. Press your thumb and index finger against your teeth.
Repeat these steps 5 times.
- Press your thumb against your upper teeth in the middle of your jaw.
- Press the index finger of your other hand against your lower teeth in the middle of your jaw (see Figure 7).
- Open your mouth as wide as possible. Place additional emphasis with your fingers so that your mouth does not close. You should feel a slight stretch, but not pain. Hold this position for ______ seconds.
Maintain proper posture
Correct posture means sitting and standing with your ears, shoulders, hips, knees and ankles aligned horizontally (see Figure 8). To have correct posture, it is necessary to maintain good tone and stretch in the muscles of the neck and shoulders. The following exercises will help you with this.
Figure 8. Correct posture
Do them 2 times every day. You can do them standing or sitting with your arms at your side.
Neck stretch
Repeat these steps 5 times. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds.
- Tilt your head forward (see Figure 9).
- Tilt your head back (see Figure 10).
Figure 9. Head tilt forwardFigure 10. Head tilt back
- Turn your head to the right (see Figure 11).
- Turn your head to the left (see Figure 12).
Figure 11. Turning the head to the rightFigure 12. Turning the head to the left
- Tilt your head, trying to bring your left ear closer to your left shoulder (see Figure 13).
- Tilt your head, trying to bring your right ear closer to your right shoulder (see Figure 14).
Figure 13. Head tilt to the leftFigure 14. Head tilt to the right
Chin retraction
Figure 15. Retraction of the chin when pulling the head back.
Repeat these steps 5 times.
- Looking forward, tuck your chin.
- Pull your head back so that your ears are level with your shoulders (see Figure 15). Stay in this position for 3 seconds.
Scapula compression
Repeat these steps 5 times.
- Tuck your chin in as described in the exercise above.
- Squeeze and squeeze your shoulder blades together as hard as possible (see Figure 16).
- Stay in this position for 3 seconds.
Figure 16. Squeezing the shoulder blades together
Maintain proper oral hygiene
- Brush your teeth and tongue in the morning after sleep, after every meal and before bed.
- If you have removable dentures, remove and clean them every time you brush your teeth. Don't go to bed with dentures in your mouth.
- Floss your teeth once a day before bed.
to come back to the beginning
Main stages of treatment
The first step is preparation for the procedure. It's simple. For a few days, it is necessary to eliminate alcoholic beverages from the diet, and also reduce caffeine consumption. Before the procedure, you should not take antibiotics or blood thinners.
The second step is the introduction of butolotoxin. The procedure lasts about twenty minutes. The required dose is divided into three to four injections. The injection needles are very thin, so the procedure is virtually painless.
The third step is the rehabilitation period. Butolotoxin acts instantly, but gains its full strength after two weeks. After injections, it is not recommended to overheat or cool the treated areas. Sports and facial massage should be excluded.
Getting rid of a nightmare
Brux checher
We should immediately warn you: bruxism today, despite all the progressive achievements of modern dentistry, remains an open and not fully studied topic. And also a serious problem in terms of diagnosis and treatment. But this does not mean that treatment can be postponed.
For effective treatment of bruxism, it is necessary to pay attention to two aspects: dental (mandatory visit to the dentist) and psychological (constant work by the patient on himself).
Visit to the dentist
Diagnosis and treatment of bruxism begins with a visit to the dentist. After a thorough examination of the oral cavity, the doctor determines signs of grinding and, if necessary, treats damaged teeth. For an objective diagnosis of the disease, a specialist uses a brux checker - a special mouthguard. The item is selected separately for each patient, and then inserted overnight.
Brooks checker (Brux checher) was developed by Professor Sadao Sato from Kanagawa Dental College (Japan). It helps the dentist both at the diagnostic stage and at the treatment stage of bruxism. Brooks checker allows you to identify occlusal obstacles and select the appropriate treatment method. To make a brux checker, only an impression of the upper and lower jaw is required and then a special mouthguard is made.
Based on the prints on the bruxchecker, the dentist analyzes the nature of the violations and identifies deficiencies. If necessary, the patient can be referred for consultation to a periodontist or orthodontist to replace crowns and correct the bite.
For mild cases of bruxism, dentists recommend protective orthodontic mouth guards . Special jaw pads form a barrier between the teeth to prevent them from touching.
Drug treatment of chewing movements consists of taking calcium-containing drugs and magnesium .
Implantation for bruxism
Implants can be placed if an integrated approach has been taken to the procedure. In cases where the dental system has not worked correctly for a long period of time, dentists perform treatment using complex implantation.
If excessive tension in the jaw muscles was caused by a reason such as psychosomatics, then the patient is referred for examination to a specialized specialist. Only then can you begin to restore your teeth.
Contraindications
In some cases, it is contraindicated to relax the chewing facial muscles by performing light gymnastic exercises.
It is recommended to refrain from the procedure if:
- allergic reaction in the acute stage;
- inflamed facial nerve;
- high body temperature;
- high blood pressure;
- there are rashes, irritation or acne on the skin;
- fragile blood vessels and pathologies associated with blood clotting;
- sinusitis, rhinitis.
If a sharp pain is felt when performing any exercise, then the complex is performed incorrectly or is contraindicated. It is recommended not to perform it again or to consult with your doctor.
Prevention of bruxism
Preventive measures for hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles of the jaw imply measures that can prevent bruxism. Treatment of this disease without diagnosis and examination by a qualified specialist can be hazardous to health. As soon as you notice the first signs of this pathology, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will prescribe diagnostics that will help identify a possible problem and effectively eliminate it.
The patient may need to be examined by specialists such as a neurologist or psychotherapist. Increased tone of the masticatory muscles has different etiologies. Doctors in these areas can prescribe various treatments, such as physical therapy, magnesium-based medications. All this is decided on an individual basis.
Preventative measures may help if approved by the patient's physician. You can easily massage the cramped areas. There is a set of exercises that can reduce the manifestations of bruxism. They must be done daily before going to bed.
Stressful situations must be avoided. You should rest more, get enough sleep, and spend a lot of time outdoors. Avoid caffeine and take baths with herbs that have a sedative effect. These measures will be an excellent prevention of muscle spasms, and will also enhance the effect of complex treatment.
Contact the Denta-Labor dental laboratory for solutions to issues regarding the protection of your teeth during bruxism.
Jaw Information
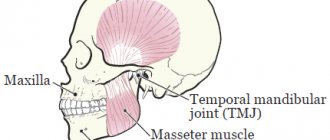
The jaws are a pair of bones that form the base of the mouth and teeth (see Figure 1).
- The maxilla is the upper jaw bone.
- The mandible is the lower jaw bone.
- The temporomandibular joint is where the lower jaw attaches to the skull.
- The masseter muscle is the muscle that connects the lower jaw to the skull.
Figure 1. Bones and muscles of the jaws
The opening and closing of the mouth is controlled by many muscles and nerves located around the jaws. Most people can open their mouth 35–55 millimeters (1.4–2.2 inches), which is the width of three fingers (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Normal open mouth height
to come back to the beginning
Consider treatment with Botox injections
In severe cases, botulinum toxin injections into the masticatory muscles can be used to reduce the manifestations of bruxism. After administration of the drug, the muscles partially relax and the spasm is relieved. This is followed by relief from headaches, toothaches and other unpleasant symptoms. Botulinum toxin lasts up to 6–8 months, then the muscles regain sensitivity and the ability to contract. This should be enough time to stop grinding your teeth.
There is no way to get rid of bruxism once and for all. But with an integrated approach, you can get a good result: reducing the load on the temporomandibular joints, restoring enamel, and improving the quality of sleep.
Week schedule
You can relax the chewing muscles of your face within a week by doing simple exercises. Gymnastics should last no more than 15 – 20 minutes.
The weekly class schedule is shown in the table:
| Day of the week | Types of exercises |
| Monday | Stroking and relaxing the masticatory muscles, “Cork”, “Swing”. |
| Tuesday | Stroking the masticatory muscles, “Bucket”, “Cat”, exercise with fists. |
| Wednesday | Stroking and relaxing the masticatory muscles, “Ladle”, “Cat”. |
| Thursday | “Traffic”, “Swing”, exercise with fists. |
| Friday | “Cork”, “Bucket”, strengthening the front surface of the neck. |
| Saturday | Stroking and stretching the masticatory muscles. |
| Sunday | Stroking and stretching the masticatory muscles. |
When performing gymnastic exercises, it is recommended to adhere to the following precautions:
- You should perform the exercises carefully, constantly listening to your own feelings during the gymnastics process;
- to prevent lymphatic stagnation and morning swelling, the complex should be carried out in the morning or 2 hours before bedtime;
- Before starting the procedure, it is recommended to consult with an instructor;
- Muscle overstrain must be avoided;
- It is advisable to master the exercise technique gradually.
First aid
If a spasm appears suddenly and there is no one nearby, you should do the following:
- Take a comfortable relaxing position (preferably sitting or lying down).
- Gentle massage of the lower facial region (2-3 minutes), without intense pressure. There is no need to touch painful areas.
- Alternately applying cold and warm (for 20-30 minutes with a 10-minute interval).
To relieve spasm, it is recommended to relax and abstract from problems.
Further treatment
To draw up a treatment plan, a preliminary diagnosis of the cause of the spasm is necessary. An examination of the patient's oral cavity is carried out in the dental office. To relax the muscles, the doctor injects Botox.
Depending on the diagnosed pathologies, treatment is carried out:
- To reduce pain, a blockade is performed using anesthetics.
- To treat inflammatory processes, the patient is prescribed antiseptic rinses and antibiotic therapy.
- To eliminate abscesses, incision and drainage are performed.
- If nervous disorders of the nervous system are detected, the patient is indicated for neurological treatment.
- The patient undergoes oral sanitation and treatment of carious cavities. If the spasm is caused by errors in prosthetics, it may be necessary to correct the bite using orthopedic structures.
- The reconstruction of the jaw apparatus is carried out by a dental surgeon.
- To normalize muscle tone, physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed: massage, procedures.
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Treatment prognosis
If trismus is associated with internal factors, then treatment lasts several weeks. Serious disorders of organs and systems with concomitant trismus require complex treatment aimed at treating the underlying pathology. Most infections require long-term treatment, and the result depends on the initial condition of the patient and timely seeking medical help.