Inflammation of trigeminal neuralgia: causes
What are the causes of inflammation, neuritis, trigeminal neuralgia? The causes of trigeminal neuralgia are various inflammatory (inflammation), traumatic (damage), toxic, infectious (infections, including herpes - postherpetic neuralgia), allergic, infectious-allergic, metabolic effects. Compression of nerves (pinching) in bone, musculoskeletal and osteoarticular canals, prolonged microtrauma, especially in combination with hypothermia, and foci of focal infection also play an important role.
What methods are used in treatment
The treatment method depends on the extent of the lesion and is carried out after assessing the sensitivity deficit. With neuropraxia, recovery occurs on its own within 4-6 weeks . No medical attention is required since the nerve structure is not damaged.
With partial degeneration, symptoms subside two months after the injury. For a complete recovery, medical measures will be needed. Numbness for 9-12 months is dangerous due to irreversible degeneration of nerve cells . Microsurgical treatment can be urgent (for an open injury) or planned (for a closed injury).
Treatment tactics for closed injury
- For numbness that does not go away for three months - suturing, transplantation;
- For dysesthesia (perversion of sensitivity) for more than 3 months - revision, decompression, neurolysis, suturing and nerve transplantation;
- If hypoesthesia (decreased sensitivity) lasts for more than 3 months, partial unscrewing or removal of the structure, revision, transplantation, suturing is indicated.
Drug treatment
Indicated for chronic nerve inflammation syndrome. An important point is pain relief. Can be used:
- Antineuralgic drugs:
- Carbamazepine;
- Phenytoin;
- Baclofen.
- Antidepressants:
- Amitriptyline;
- Imipramine.
- Local products:
- ointments with capsaicin;
- acupuncture;
- electrical stimulation;
- physiotherapy.
Inflammation, trigeminal neuralgia symptoms
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders, the following symptoms: facial hyperemia (redness of the face) and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea (discharge of watery mucous discharge from the nose), hypersalivation (salivation, increased secretion of the salivary glands), Possible increased blood pressure (BP), chills-like trembling, difficulty breathing.
Trigeminal nerve, anatomy, innervation, where the trigeminal nerve is located
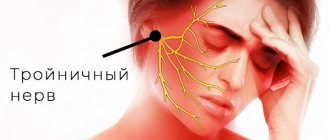
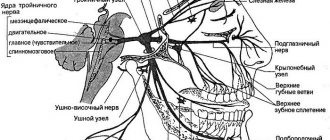
The trigeminal nerve, nervus trigeminus, the 5th pair of human cranial nerves is a mixed nerve that contains sensory, motor and autonomic fibers. The functions of the trigeminal nerve are varied.
The sensory fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the cells of the trigeminal ganglion, which is called the ganglium trigeminale. It is located in the recess of the pyramid of the temporal bone. The dendrites of these cells form 3 branches and 3 trunks.
1 branch of the trigeminal nerve, the first branch (nervus ophthalmicus) - the ophthalmic nerve passes in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, later through the superior orbital fissure into the orbit. Then it breaks up into branches, innervates such structures as the outer part of the conjunctiva, the skin of the outer corner of the eye, the upper eyelid, the lacrimal gland, the skin of the scalp to the temporal and parietal regions, the skin of the forehead, the skin of the root of the nose, the cornea, the frontal sinus, the main sinuses , nasal mucosa, nasal skin, posterior cells of the ethmoid bone.
2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve, second branch (nervus maxillaris) - the maxillary nerve passes (exit) through the round foramen and the pterygopalatine fossa. It further breaks down into branches and innervates the following sections: the skin of the temporal region (temporal region, temple), the skin of the zygomatic region (cheekbone), the mucous membrane of the posterior ethmoid cells and the main sinus, the vault of the pharynx (pharynx), the nasal cavity (nose), the soft palate, hard palate, mucous membrane of the tonsils (tonsils), skin of the infraorbital region (infraorbital region), wings of the nose, upper lip, gums of the upper jaw, upper teeth.
3rd branch of the trigeminal nerve, third branch (nervus mandibularis) - the mandibular nerve leaves the skull through the foramen ovale (exit point, exit point), innervates the following areas: mucous membrane of the cheek, mucous membrane of the lower gum (lower gum), skin of the corner of the mouth (angle mouth), skin of the external auditory canal, anterior part of the auricle, temple, all lower teeth, skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip.
The motor fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the motor nucleus nucleus motorius nervi trigemini. The core is located in the bridge tire. Fibers extending from the nucleus leave the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. They innervate the masticatory muscles and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. The axons of the trigeminal ganglion cells form a root and go to the bridge, where they divide into 2 branches.
The descending branch forms the descending spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for conducting temperature and pain sensitivity. It ends in the nucleus spinalis nervi trigemini. The descending spinal tract and its nuclei are analogous in their function and structure to the posterior horns of the spinal cord. The nuclei and path are divided into 5 segments, as a result of which the innervation of the facial skin in the Zelder zones is located in a ring.
Therapy results
The prognosis of microsurgical and therapeutic treatment is influenced by:
- age, health status of the patient;
- skill and experience of the surgeon;
- the duration of the period between injury and surgery.
In 80% of cases of neurotmesis operated on in the first 5 months after injury, partial restoration of the function of the mandibular nerve was observed. Delaying surgical intervention systematically reduces the chance of recovery. Seeing a neuromicrosurgeon a year or more after injury has only a 10% chance of success.
Primary trigeminal neuralgia, secondary trigeminal neuralgia
There are primary trigeminal neuralgia (idiopathic, essential, typical) and secondary trigeminal neuralgia (symptomatic trigeminal neuralgia).
With primary neuralgia (mainly of central origin), attacks occur for no reason or are provoked by any movements of the facial muscles.
Secondary neuralgia is usually a complication of the primary disease, has a predominantly peripheral genesis and is often caused by pathological processes in the dentofacial area. The pain is almost constant, periodically intensifying in the form of attacks lasting up to several hours.
Classification and stages of disease development
Depending on the affected area:
- Intrabulbar (intraocular) neuritis, optic papillitis. This is an inflammation of the intraocular part (disc) of the optic nerve. More often develops in children.
- Retrobulbar neuritis. Damage to the nerve section lying between the eyeball and the optic chiasm. Forms of retrobulbar neuritisSource: Retrobulbar optic neuritis. Kukhtik S.Yu., Popova M.Yu., Tantsurova K.S. Bulletin of the Council of Young Scientists and Specialists of the Chelyabinsk Region, 2021: axial - a bundle of axons passing in the optic nerve is involved in the pathological process;
- peripheral - inflammation covers the nerve sheaths and spreads deep into the nerve trunk with the formation of a large amount of exudate under the sheaths;
- transversal - the process affects all layers of the optic nerve.
According to the etiology of the lesion:
- infectious:
- parainfectious (post-vaccination, after acute respiratory viral infections);
- demyelinating;
- ischemic;
- toxic;
- autoimmune.
According to the severity of the flow:
- spicy;
- chronic.
According to the prevalence of the lesion:
- mononeuritis – inflammation of one nerve (the vast majority of cases);
- polyneuritis – involvement of both optic nerves in the process (less than 1% of cases).
Trigeminal nerve, symptoms of trigeminal nerve damage, pathology
Damage to one of the sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve results in a disturbance of all types of sensitivity on the face of a peripheral type in the zone of innervation of this branch. In this case, symptoms : pain, decreased reflexes, extinction of reflexes. When the optic nerve is damaged, the conjunctival reflex, corneal reflex, and superciliary reflex are affected. When the motor part of the mandibular nerve is damaged, the mandibular reflex suffers. When the trigeminal nerve ganglion is damaged, all types of sensitivity in the area of 3 of its branches are lost, herpetic eruptions (herpes, herpetic blisters), and trophic disorders are often observed. A lesion of one of the sensitive nuclei in the pons results in a dissociated type of sensitivity disorder - superficial or deep. When the nucleus and oral parts of the spinal tract are damaged, a violation of superficial types of sensitivity in the mouth and nose occurs. If the caudal region is affected, sensitivity is impaired in the area of the outer part of the face. When the optic thalamus and the posterior third of the posterior limb of the internal capsule are affected, contralateral hypersthesia is observed on the face, trunk (body), and limbs (arms, legs) according to the hemitype. When the motor nucleus and its fibers are damaged, peripheral paresis occurs, which is characterized by symptoms such as insufficient muscle tension when chewing, muscle atrophy, retraction in the temple area, angle of the lower jaw, deviation of the lower jaw towards the affected side when opening the mouth. If bilateral peripheral paresis occurs, the lower jaw droops, as a result of which a man or woman cannot chew, cannot close his teeth, or close his mouth. Central paresis of the masticatory muscles on one side does not occur, since the corticonuclear fibers approach the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve from both hemispheres of the brain. With bilateral lesions, chewing becomes slightly more difficult (difficulty chewing), and the mandibular reflex is significantly enhanced. Small children have difficulty sucking.
Injury Prevention
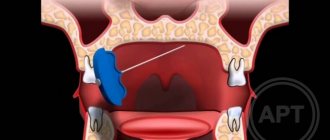
Prevention is high-quality preparation for surgery and professional performance of manipulations. A thorough study of the structure of the patient’s mandibular canal, the parameters of the alveolar process and the topographical position of the nerve fiber prevents neurological complications.
For this purpose the following are assigned:
- orthopantomogram;
- computed tomography - 3-dimensional scanning.
Complications will be avoided:
- correct formation of the implant bed;
- careful implantation of the dental structure;
- lateralization (change in the position of the nerve) when it is close to each other.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov, how to treat trigeminal neuralgia in Russia
Sarklinik provides comprehensive treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in children and adults, treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (nervitis, first, second, third branches) in Saratov, Russia, which includes effective reflexology methods. You can cure trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov!
Sarklinik knows how to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, how to cure neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis ! The following types of neuralgia are treated: neuralgia of the 1st (first) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 2nd (second) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 3rd (third) branch of the trigeminal nerve in children and adults. On the website sarclinic.ru you can see a doctor online for free. If you have neuropathy, nerve damage, pain, a cold, the trigeminal nerve hurts on the left, right, you have a cold, a cold, inflammation on the face, paralysis, paresis, you don’t know how to relieve the pain , then contact a doctor at Sarklinik.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Aniram | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Vegetative vascular dystonia: treatment of VSD, how to treat VSD, symptoms, signs
Panic, panic attacks: treatment, symptoms, causes, how to fight, get rid of
Trigeminal nerve, inflammation, treatment, trigeminal neuralgia, symptoms, how to treat
Neuralgia and neuritis, intercostal neuralgia: symptoms, treatment in Saratov
Hypothalamic syndrome, treatment of hypothalamic syndrome, how to treat
Comments ()
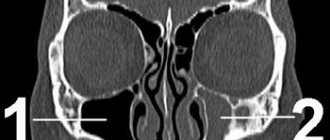
Diagnosis of the disease
Modern medicine has in its arsenal many diagnostic techniques that make it possible to determine the type of neuralgia and the cause of its occurrence:
- visual examination and questioning of the patient;
- X-ray of the jaw;
- MRI of the brain and blood vessels;
- laboratory analysis of urine and blood;
- electromyography.
Diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist, but additional examinations by other specialists are often required: dentist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist. Particular attention is paid to differential diagnosis, since neuralgia may resemble other diseases in its symptoms, in particular glaucoma, otitis media, ethmoiditis, Slader syndrome, etc.