Dental pathologies are diagnosed in approximately a third of the world's population. Such defects require treatment by an orthodontist using special devices. The reasons for the development of improper jaw closure are poor posture, congenital malocclusions, and feeding habits in early childhood. As a result, speech defects appear, the chewing process worsens and the shape of the face changes.
To choose the right orthodontic appliance, it is necessary to determine what kind of bite should be obtained as a result of the treatment.
general information
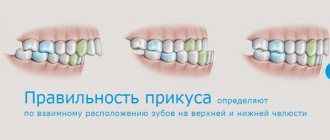
In medical terminology, occlusion refers to the relationship of teeth. The dentist analyzes the state of the chewing muscles and the temporomandibular joint at the moment when the jaws are clenched.
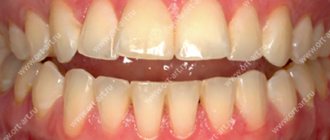
Bite is the position of the teeth in relation to each other when the jaws are fully closed.
There are physiological and pathological or, respectively, correct and incorrect bites.
A physiological bite in humans ensures high-quality functioning of the dental system (chewing food), clear diction, free breathing and an attractive smile.
With a correct bite, the face is harmonious, the lower and upper jaws are formed proportionally, the load on all teeth is carried out evenly, the vertical axis of symmetry of the face crosses the junction between the front incisors. This allows a person to chew food thoroughly without injuring soft tissue or periodontium and without overloading the temporomandibular joint.
VII PERIOD - from 12 to 15 years (period of formation of permanent dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- planned sanitation of the oral cavity, mandatory consultation with a periodontist to identify periodontal diseases and their treatment
- oral hygiene training, individual selection of hygiene and prevention products
- identification of postural disorders, flat feet, torticollis, therapeutic exercises and consultation with an orthopedist. Swimming, fitness classes
- identification of gastrointestinal dysfunctions, introduction to food hygiene, consultation with a therapist
- identification and elimination of calcium deficiency
- determination of skeletal ossification disorders and consultation with an endocrinologist
- introduction to risk factors
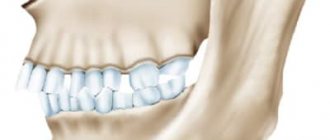
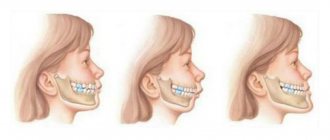
Physiological types of occlusion
Orthognathic
It is recognized as the standard type of occlusion, as it creates the most suitable conditions for processing food during chewing.
- The upper row of teeth overlaps the lower one by a third.
- When the jaws join, the teeth come into close contact with each other.
- There are no gaps or cracks between the incisors.
Biprognathic
Signs of bite:
- The upper and lower incisors are located with a slight vestibular inclination - towards the vestibule of the mouth.
- Contact between the incisors is maintained when closing.
- The upper canines overlap the lower canines by several millimeters.
Direct bite or orthognathic
This type of bite is diagnosed when, when closing the jaws, the upper teeth touch the cutting edge of the lower row of teeth. There are no voids, cracks or crowding of teeth. Correct occlusion of the chewing teeth is observed.
General overview
In order to diagnose malocclusions, various biometric studies of the jaw are carried out. It is impossible to carry out such measurements directly in the oral cavity. Therefore, biometrics is carried out on diagnostic models created in the dental office.
Each prototype performs a diagnostic function and serves as a control sample to test the effectiveness of various orthodontic treatment methods.
A constructive bite is an anatomically correct closure of the teeth, which the orthodontist strives to recreate in patients individually. The bite is distinguished by individual biometric indicators and is recreated using wax templates.
Each template is marked with:
- Name and age of the patient;
- medical history number;
- date of the study.
This approach eliminates the possibility of medical error during the study and helps to record its results. When studying prototypes, the size of individual units or dentition matters.
When the construction of teeth is considered incorrect
The main signs of malocclusion:
- Complete or partial absence of tooth contact during occlusion.
- Impaired chewing of food.
- Sound pronunciation defects.
- Changes in the shape of the face due to jaw deformations.
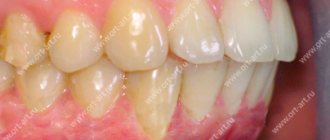
Pathological types of bites
Pathological occlusion is diagnosed if there are structural deviations from normal anatomy in the structure of the dentofacial apparatus, and disturbances in the functioning of the masticatory muscles and the temporomandibular joint are also detected.
Mesial
A distinctive feature of this type of abnormal bite is the advancement of the lower dentition in relation to the upper one.
Patients with mesial occlusion have a characteristic appearance - a massive protruding chin, a receding upper lip, and a concave facial profile. There are chewing disorders and speech defects.
Deep
With a deep bite, the upper incisors cover more than 50% of the lower incisors. In some cases, the upper incisors, when closing the teeth, reach the gums of the lower jaw and injure them.
Although orthognathic, biprognathic, and straight bites are normal, these types of bites can cause the following problems: damage to the enamel, chipped crowns, and injuries to the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Open
The main sign of pathology is the presence of a vertical gap between the dentition in the area of the frontal or chewing teeth.
An open bite is often formed against the background of narrowing of the alveolar arches, which is why the teeth have an irregular shape and are crowded.
Symptoms: lengthening of the lower third of the face, slightly open mouth, hypertonicity of the facial muscles, impaired diction, difficulty breathing, inadequate chewing of food.
Cross
Due to the displacement of the lower jaw to one side, the dentitions close like scissors crosswise, and underdevelopment of the jaw on one side is noted. Facial asymmetry is pronounced.
Distal
This is a variant of a pathological bite, in which the lower dentition moves back in relation to the upper one. In this case, the frontal (front) group of teeth does not connect, and the chewing teeth contact incorrectly, which creates the preconditions for blocking the normal development and growth of the lower jaw.
Facial signs of distal bite:
- protrusion of the upper jaw;
- shortening of the upper lip and lengthening of the lower lip;
- sloping chin.
Dystopia
A type of abnormal bite when the teeth on the upper or lower jaw are located outside the dentition and not in their place. In addition, with dystopia, the teeth are often turned around an axis.
Other signs
There are indirect signs of malocclusion.
- Reduced height of tooth crowns.
Typically, the front teeth are rectangular in shape. If they become square, this may be due to thinning enamel. The thickness of the enamel on the cutting edges and chewing cusps of the tooth is about 2 mm. Due to an incorrect bite, the enamel wears off and the teeth become more square in shape. This is a clear sign of an “age-related” smile, but for young people it is not the norm (unless the teeth were square from the very beginning).
Worn teeth
- Increased tooth sensitivity.
The reason is the same - the enamel becomes fragile and thin. Teeth begin to ache from hot and cold, sometimes from sour and sweet.
- Pain or clicking in the jaw joints.
They are often unnoticeable because many people eat mostly soft foods and do not spend much effort chewing. Problems with the jaw joints usually appear when trying to chew solid food. Most often, the cause of dysfunction is malocclusion. The jaws are positioned incorrectly relative to each other, so the joint is loaded unevenly.
- Discomfort when chewing or biting.
The more complex the disorder, the more noticeable it is that when chewing the load is distributed incorrectly. With an open bite, for example, some of the teeth do not close together at all, so it is difficult to chew food well.
- The symmetry of the smile is broken.
The easiest way to determine this is to look at the centers of the upper and lower jaw. They must match.
- Some teeth have a wavy edge.
The permanent teeth grow with wavy edges. And only then do they gradually grind down and become straight. This happens due to chewing. If one of the teeth is slanted or turned so that its edge is higher than all the others, it will remain wavy because it will not grind down.
Wavy edge of teeth
- The symmetry of the face is broken.
This sign needs to be assessed by looking not at the teeth, but at the face as a whole. Normally, the nasolabial folds are symmetrical. If only one of them appears, this indicates that the jaws are located asymmetrically.
- Obtuse angle between neck and chin.
If the lower jaw is too small or pushed back, a double chin may appear at a young age. This is due to the fact that due to the position of the lower jaw, the angle between the neck and chin is flattened.
Perhaps your chin looks small due to problems with your bite
If you have any doubts about the health of your teeth, consult a doctor - only an orthodontist can make a final diagnosis at an appointment, after which, if necessary, treatment can be planned.
Causes of malocclusion
The formation of a bite is a complex and lengthy process that begins at the stage of intrauterine development and ends only when a person reaches puberty.
- Genetic factor. One of the leading reasons for the formation of malocclusion is heredity, which determines the size and shape of the teeth, the width and length of the dentition, the height of the hard palate, as well as the nature of the location of the teeth (sparse or crowded).
- Quality of nutrition and maternal diseases during pregnancy.
- Birth injury. Jaw injuries received during childbirth lead to displacement of the temporomandibular joint, and subsequently to the formation of a pathological bite.
- Incorrect selection of nipples during artificial feeding, when the child does not make enough effort to obtain milk, as when sucking at the breast, which causes underdevelopment of the lower jaw.
- Untimely introduction of solid foods into the diet during teething. In the absence of chewing, the muscles of the dentofacial apparatus, on which the development of the jaws largely depends, are not strengthened.
- Behavioral factors: sucking pacifier, upper lip, fingers; sleep with the head thrown back.
- Irregularities in the timing and sequence of teething.
- ENT pathologies due to which the child is forced to breathe through the mouth for a long time: chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, deviated nasal septum, adenoids.
- Diseases affecting bone growth and development.
All these factors can cause improper closure of the dentition and form a pathological bite.
VIII PERIOD - from 15 to 21 years (completion of the formation of permanent dentition)
Prevention and treatment of dental anomalies:
- sanitation of the oral cavity, hygiene, use of individual care and prevention products
- mandatory professional hygiene
- observation by a periodontist, consultation and treatment of periodontal diseases
- identification of dental anomalies and their orthodontic treatment
- introduction to food hygiene
- elimination of calcium deficiency
- restoration of crowns of damaged teeth
- restoration of bite height, alignment of occlusion, selective grinding of teeth
- timely prosthetics
- monitoring the eruption of 3 molars (wisdom teeth) and their timely removal
- identification of incorrect habitual postures, posture disorders,
- prevention and treatment of osteochondrosis
- sports, fitness, swimming
- eliminating risk factors
- formation of useful habits and skills
- surgical treatment of severe deformities of the maxillofacial area