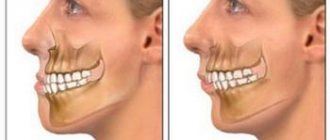
What is the cause of prognathia?
About 70% of children have some degree of distal malocclusion. What is the reason for such a common pathology? Dentists believe that genetics are to blame. The child inherits from the parents the shape of the teeth, the size of the jaw, as well as abnormalities of the masticatory apparatus.
But there are other factors that contribute to the formation of a prognathic bite:
- negative effects during intrauterine development - inflammatory diseases, lack of calcium and fluoride;
- chronic ENT diseases - if the nose is stuffy, the child begins to breathe through the mouth, which leads to narrowing and stretching of the upper jaw bone;
- bad habits - prolonged use of a pacifier, the habit of chewing pencils and other objects provoke displacement of the lower dentition;
- poor posture - incorrect position of the body leads to a constant tilt of the head forward, this disrupts the growth of the jaws;
- premature loss of baby teeth - removal of a temporary tooth ahead of schedule (for example, due to caries or crown fracture) causes displacement of adjacent crowns, so there is not enough space for the eruption of a new tooth.
Causes of progeny
Depending on its origin, progeny is divided into congenital (hereditary) and acquired. In the second case, factors contributing to changes in bite are:
- abnormalities in the structure of the pharynx, leading to breathing problems in a child of early years;
- birth injuries;
- edentulous upper jaw;
- the presence of supernumerary teeth on the lower jaw;
- habit of sucking your finger, tongue or upper lip;
- acromegaly;
- calcium metabolism failures resulting from various diseases;
- improperly attached or shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- habit of sleeping with your head on your chest;
- uneven wear of baby teeth during the period of mixed dentition;
- hyperfunction of the pituitary gland;
- macroglossia;
- the habit of sitting with your lower jaw supported by your hands;
- excessive passion for pacifiers and pacifiers;
- poorly performed surgical operations.
How to identify distal bite in a child?
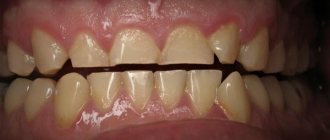
This type of teeth closure is always characterized by a discrepancy between the sizes of the upper and lower jaws. The upper molars may be displaced inward, and the incisors may be pushed forward at an angle. Sometimes the presence of three and diastemas (interdental spaces) is noticeable.
Distal occlusion as an independent type is rare. In 80% of cases, a combination of 2 pathologies is observed: prognathic and deep bites, when the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half. As a rule, there is no contact between the front teeth on both jaws.
During diagnosis, the dentist examines not only the occlusion (closing) of the molars and incisors, but also the profile of the face.
Prognathia is accompanied by the following external signs:
- overly rounded face;
- the lower third of the face is visually reduced;
- half-open mouth;
- deep crease on the chin;
- “fan-like” arrangement of teeth;
- The lower lip is located behind the upper incisors.
Treatment of progenia
Treatment of pathology at a young age
In the early stages of the disease, it is much easier to stop the development of the pathological process.
Treatment of progeny in young children comes down to the following measures in dentistry:
- eliminating factors influencing the formation of malocclusion;
- massage of the anterior zone of the alveolar process located on the upper jaw;
- correction of a shortened frenulum of the tongue;
- combating bad habits (through the use of the vestibular plate);
- normalizing the functions of swallowing, chewing, breathing and speech (using labial activators, training the orbicularis oris muscle);
- artificially establishing the child’s incisors in marginal closure by grinding their cutting edges (the technique is used to treat children under 4 years of age with a slight reverse overlap);
- the use of the Bruckle device and a cap with a chin sling and an extraoral rubber rod to displace the lower jaw (advisable for deep incisal reverse overlap);
- the use of plates with protracting springs located on the vestibular or palatal surface of the central incisors during the eruption of the latter;
- the use of occlusal pads in the presence of incisal reverse overlap not exceeding 2 mm;
- the use of the Wunderer activator, the Bashirova apparatus, the Hoffman activator, the Schwarz double plate, the Andersen-Goipl activator, the functional Boule apparatus and the Frenkel clasp activator for the treatment of severe dentoalveolar types of pathology.
Treatment of pathology in adolescents
Treatment of progenia in persons with a formed permanent dentition requires much more effort and time than treatment of this pathology in children. At the same time, to correct the bite in adolescents in orthodontics, the same devices are most often used as in the period of temporary occlusion, however, dentists in this case opt for the use of fixed devices.
Treatment of the disease in adults
In case of severe progeny in adults, the Brückle apparatus, arc devices with intermaxillary traction and brace systems can be used.
In this case, orthopedic treatment of pathology is reduced to the following measures:
- displacement of the lower jaw teeth lingually, and the upper jaw labially (using a wire ligature, protraction springs and devices operating on the principle of an inclined plane);
- reducing the length of the lower row of teeth by removing some teeth or eliminating spaces between them, as well as lengthening the upper row by moving the front teeth forward;
- sagittal displacement of both dentitions in the required directions.
If necessary, the fight against progeny can be carried out using a combined hardware-surgical method.
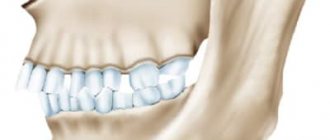
Forms of prognathic occlusion
There are 4 forms of distal occlusion of the dentition:
- I form – characterized by retrognathia (insufficient development) of the lower jaw, while the upper one is developed normally;
- Form II – macrognathia (excessive enlargement) of the upper jaw bone is observed, as well as the size of the upper crowns being too large. Lower jaw – without deviations;
- III form - 2 anomalies are diagnosed at once - the lower jaw is underdeveloped and the upper jaw is overdeveloped;
- IV form - only the anterior section of the upper dentition protrudes forward.
Prevention
If the pathology is not congenital, the formation of a pathological bite can be avoided by taking timely measures:
- Plan your first visit to the dentist when the child is 2-3 years old;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol (even in small doses) while planning pregnancy and while carrying a baby;
- prevent the development of bad habits: wean your baby off thumb sucking, get rid of pacifiers and bottles in a timely manner;
- From early childhood, teach to keep your posture straight, since the interconnection of all systems in the body has been proven. Slouching changes the tilt of the head, which contributes to the constant advancement of the lower jaw forward;
- Monitor the position of the child's head during sleep. The child should not get used to placing a pillow or fist under it. Excessive pressure on the jaw creates an incorrect bite. You should also avoid throwing your head back or pressing your head to your chest.
The main signs of progeny are a signal for immediate contact with the dentist. Pay special attention to your child, because it is in childhood that pathology is easy to correct.
Add a comment
Leave your comment
Consequences of distal occlusion in adults
Prognathia should be eliminated in childhood, preferably before the age of 14. If this is not done, a person will experience a number of problems in adulthood:
- firstly, a violation of facial aesthetics - abnormal occlusion always affects the appearance, because of this, self-esteem decreases and complexes arise;
- secondly, deterioration in the function of chewing and swallowing - due to poor closure of teeth, a person has to make approximately 30% more chewing movements compared to the norm;
- thirdly, speech disorders - a “lisp” and other speech therapy abnormalities occur.
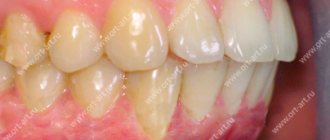
It should be taken into account that those with a distal bite have a greater risk of developing dental diseases - caries, gingivitis, and enamel erosion. This happens due to the increased load on individual dental crowns and periodontal areas. In addition, there may be problems with the jaw joint - pain when chewing and talking, deterioration in mobility.
Therefore, you cannot ignore the problem; you should contact your dentist in a timely manner. Treatment of distal bite in children and adults is carried out by an orthodontist. You can select such a specialist on our website through a convenient search system.
Classification
By severity:
- Gnathic form. Develops due to improper development of the cranial bones.
- Dentoalveolar. It is formed when the tooth roots are incorrect or when there are significant differences in the sizes of the lower and upper jaws.
The pathology may have a mixed form.
By localization:
- General. The defects extend to both the front and side elements.
- Partial. The anomaly concerns the front teeth.
By etiology:
- True progeny. The anterior and posterior teeth have an irregular position, with space present between the anterior units. Pathology reduces the functional abilities of the dentofacial apparatus, and protrusion of the movable jaw brings psychological discomfort.
- False. Affects only a few frontal units. The anomaly is more common in elderly patients and may also be a consequence of improper surgical treatment.
Surgery to correct mesial malocclusion
If conservative treatment methods do not help, the patient is referred for surgery to an orthognathic surgeon. To correct the anatomy of the jaws, an osteotomy is performed - the removal of bone fragments to give the jaw an anatomically correct shape.
Important! There are few specialists in orthognathic surgery, and Ukraine is no exception. Carefully approach the choice of a specialist, ask about his experience and successes. Feel free to ask questions like this.
Complications with mesial occlusion
If the mesial bite is not corrected, then in the future this leads to the following complications:
- Psychological problems . They arise due to irregular facial shapes. With such a defect, a person begins to be embarrassed about his appearance and feels insecure.
- Tooth decay . Due to the disruption of teeth closure, hard tissues are destroyed faster. With a mesial bite, only some teeth bear the main load. This speeds up their destruction.
- Disorders of the digestive tract . Violation of the chewing process leads to the fact that poorly processed food (relatively large pieces of food) enters the stomach. This impairs the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to the development of gastritis and dyspepsia.
- Disorders of the temporomandibular joint . When moving the jaws, clicks are noticeable. Subsequently, pain occurs. In severe cases, the person is unable to open or close their mouth.
Treatment of mesial occlusion: myths and misconceptions
Some dental clinics resort to various advertising tricks, wishful thinking. This also applies to the treatment of mesial occlusion. Let's look at two main myths that can mislead the patient.
- Treatment with braces for gnathic forms. It is indeed possible to correct the anomaly with braces, but only if the reason is the incorrect position of the teeth. If such treatment is offered to you for gnathic forms of mesial occlusion, then contact another clinic. It is impossible to change an abnormal jaw with braces and other orthodontic structures alone. The situation can only be corrected through surgery followed by orthodontic treatment.
- Chin sling. Another misconception regarding gnathic forms of mesial occlusion is the ability to restrain jaw growth. For these purposes, they offer a special device - the so-called chin sling, which is installed on the child’s face. However, no devices will be able to restrain the growth of the jaw. This way you will only waste time. In addition, patients will not wear such masks and slings around the clock. It should be taken into account that wearing “restraining” structures on the jaw can worsen the functioning of the temporomandibular joint. Thus, you will not only not correct the reverse closure of your teeth, but you also risk developing other problems.
Important. In addition to the above incorrect treatment methods, you also need to take into account the mistakes that doctors themselves may make. In this case, it will be difficult for the patient to assess the correctness of the chosen treatment method. Therefore, if you have been prescribed a surgical operation, then do not be lazy - consult another specialist, find out an alternative opinion.
Treatment at the CIS clinic, Kyiv
At the Center of Israeli Dentistry, treatment of mesial occlusion is based on three pillars:
- Diagnostics. The most important stage for understanding further treatment strategy. To clarify the diagnosis, we use modern types of tomography, including three-dimensional images. It is noteworthy that the examination is carried out regularly and during treatment to monitor the result.
- Modern orthodontics . We often begin treatment by correcting the patient's posture, as this has a significant impact on the jaws. Only after this we begin treatment with modern braces and other orthodontic structures.
- Honesty . We never offer patients knowingly ineffective methods of bite correction. If during the diagnostic procedures it becomes clear that the patient needs surgical intervention, the orthodontist at the CIS clinic will speak directly about this.
Correction of mesial bite
Development factors
The main reason for the development of progeny is considered to be a hereditary predisposition.
Among others:
- disturbance of intrauterine development (in particular, transverse presentation of the fetus);
- improper development of tooth roots;
- lack of timely removal of primary incisors;
- hormonal imbalance;
- elongation of the fangs, which provokes incorrect position of the teeth when chewing food;
- abnormal enlargement of the tongue;
- holding foreign objects in the mouth;
- adenoid diseases;
- rickets and other metabolic disorders.
FAQ
What happens if mesial bite is not treated?
If mesial malocclusion is not treated, the consequences are disappointing in terms of both physical and mental health. First of all, we are talking about facial aesthetics. With a mesial bite, the face is disproportionate (the lower jaw is too massive). A person with such an overbite always seems stern and angry.
With such a bite, the chewing process is disrupted and teeth are quickly destroyed. So, the front teeth, closing, quickly rub against each other. The main chewing load is directed at several teeth, which leads to their rapid destruction. Since these teeth bear the brunt of the work, they are more susceptible to caries than others.
Mesial bite without treatment threatens chronic injuries to the oral mucosa. This occurs if the lower edges of the upper incisors reach the mucous membrane of the lower jaw. Constant trauma to the mucous membrane is fraught with the development of gum disease (in particular, periodontitis). In addition, the risk of developing a malignant tumor in the area of injury also increases.
Another problem of mesial occlusion is disruption of the temporomandibular joint. If the bite is not treated, then over time clicking will occur when working with the jaw. In the future, the problem is aggravated by pain in the joint area, headaches, and even jamming of the joint (when a person cannot open or close his mouth).
It is difficult for patients with mesial occlusion to undergo implantation or prosthetics. This fact must be kept in mind, since a reverse bite often leads to the loss of teeth that need to be replaced.
Is it possible to correct a mesial bite without surgery?
It all depends on the type of progeny. As a rule, dentoalveolar forms of progenic occlusion in childhood and adolescence respond well to treatment with orthodontic structures (braces and mouth guards). Orthodontic treatment of gnathic forms (when the anomaly is caused by the characteristics of the jaw bone) is ineffective. In this case, combined treatment with surgery is necessary.
How long do you need to wear braces for mesial occlusion?
Everything here is also individual. The duration of wearing orthodontic structures is influenced by both the type of progeny and the age at which treatment began. For some patients, 1 year is enough, while others need to wear braces for up to 2.5-3 years.
How much does mesial malocclusion treatment cost?
Depends on the type of treatment. The price of orthodontic treatment alone will be cheaper than combined treatment (with surgery). Let us remind you that during surgical treatment, braces are also used, which must be worn after the operation. The substantive cost of treatment is discussed only after diagnosis. First, you need to discuss with your doctor all questions about mesial occlusion (treatment, price, rehabilitation, possible complications, and so on).