Signs Causes Types Diagnostics Treatment methods Consequences Timing Prevention Doctors Work
Mesial occlusion is a violation of the closure of the jaw, when the lower one protrudes more forward and the upper incisors overlap. This causes the patient not only psychological problems, lack of proper aesthetics, possible discussions of the defect from the outside, but also affects health in general. And the treatment of mesial occlusion in adults and children is long and difficult. There is work to be done from all sides: myofunctional gymnastics, massage of the alveolar process, the use of orthodontic structures and periodic visits to dental specialists.
What is mesial bite
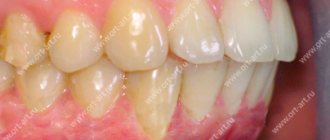
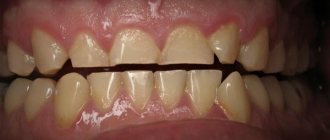
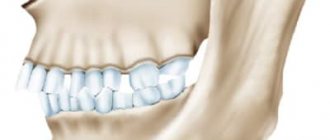
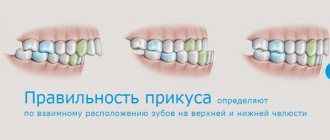
Mesial (medial) bite is an anomaly of occlusion when the jaws do not close correctly. The forward position of the lower dentition towards the upper is noticeable even visually.
The mesial jaw occurs in up to 10%
of the total amount (quite often pathology is observed in the Mongoloid race). And unlike distal occlusion, mesial occlusion is diagnosed less frequently. However, all ages are susceptible to it.
Mesial displacement of the tooth is sometimes combined with other types of anomalies - open, cross bite.
Varieties of progeny
Progeny can manifest itself in two forms:
- true;
- false.
True progeny
True progeny is a disorder in which both lateral and anterior teeth are in the reverse bite, and in the case of central occlusion, a space is formed between the front teeth of both dentitions. In this case, the main causes of pathology are developmental anomalies of the lower jaw.
Persons suffering from true progeny face serious disturbances in the functioning of the jaw apparatus. In particular, the unnatural arrangement of antagonist teeth deprives patients of the opportunity to bite off and chew food thoroughly, and excessive protrusion of the lower jaw causes them to experience significant psychological discomfort.
False progeny
False progeny is a malocclusion in which only some front teeth are in reverse relationship. The relative position of the remaining teeth on both jaws remains correct. Examples of false progeny include senile progeny or incomplete fusion of the alveolar processes and palate after surgery.
Signs
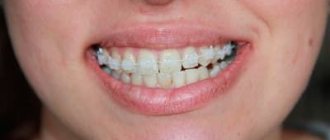
Progeny of the jaw, as mesial occlusion is also called, is expressed by the following signs:
- the upper incisors are covered by a third by the lower antagonists;
- “strong-willed chin” protruding forward, the expression seems angry;
- ⅓ of the bottom of the face is visually more massive;
- lower lip thickened;
- the profile is concave, “month-like”;
- the change of baby teeth begins with the lower teeth and occurs quite early;
- asymmetry of the temporomandibular joint due to mesial occlusion;
- jaw clicking, sounds when yawning, chewing.
In addition to external, facial signs, intraoral symptoms can manifest themselves not only by reverse overlap of the incisors, but also by direct bite. The teeth of the lower jaw are directed towards the oral cavity; there may be three, diastemas, and crevices. Chronic periodontal diseases are often diagnosed.
Pathology of the mesial jaw is accompanied by a speech defect. The patient complains of difficulty biting food and gastrointestinal problems.
Mesial occlusion is a feature of the Habsburg dynasty
A protruding lower jaw significantly changes the patient's face, usually causing an increase in the lower third of the face - between the base of the nose and the lower part of the chin, an increase in the volume of the lower lip and, against this background, a visual decrease and recession of the upper lip.
It was precisely these facial features that were characteristic of members of the royal Habsburg dynasty, which died out due to the high percentage of intermarriages. On the canvases of famous painters, male representatives of the family that ruled the Austro-Hungarian Empire for a couple of centuries are depicted with a typical “heavy”, noticeably protruding chin. It is known, for example, that Charles the Second Bewitched, the last Spanish king from the illustrious dynasty, could not speak or eat normally because of this anomaly.
Causes
The etiology of the causes of mesial occlusion is different. They can be congenital, acquired, genetic:
- heredity, structural features of the skull, facial skeleton in a generation;
- pathologies in intrauterine development, when a pregnant woman took strong medications or suffered a serious illness;
- short bridle;
- underdeveloped jaw (upper) or premaxillary bone;
- bad habits (thumb sucking, upper lip, for example);
- early eruption of lower primary teeth (however, any deviations in eruption can be the cause of mesial occlusion);
- osteomyelitis and other bone diseases;
- macroglossia (large tongue);
- removal of baby teeth ahead of schedule;
- previous rickets;
- supernumerary teeth.
In recent years, the percentage of detection of mesial occlusion has been increasing; scientists see the problem as a genetic predisposition.
Incorrect position during sleep (head lowered on the chest), habit of holding a fist, hands under the chin (sitting) can affect malocclusion.
Classification
In dentistry, the classification of mesial occlusion is quite expanded and expanded over the last century. Even back in 2004, Persin L.S. proposed his own system of 9 classes, based on the experience of previous years.
- lower macrognathia (hyperdevelopment of the jaw);
- lower prognathia (the jaw protrudes significantly forward);
- upper micrognathia (underdevelopment of the jaw);
- upper retrognathia (displacement of the jaw deeper into the skull);
- superior micrognathia and inferior macrognathia;
- superior retrognathia and inferior prognathia;
- upper micrognathia and lower prognathia;
- superior retrognathia and inferior macrognathia;
- habitual protrusion of the lower jaw forward.
Mesial occlusion is distinguished by prognathia, which can be:
- true;
- false.
True
- pronounced facial asymmetry, severe speech impediment. It appears at an early age. This is macrognathia of the lower jaw and/or its prognathia. Correction of mesial occlusion must begin at the age of 5-7 years, for now in the form of therapy.
False
- the lower jaw is of normal size, and the upper jaw is underdeveloped and/or recessed into the skull. This type of jaw progeny cannot always be noticed at first glance. But x-rays and computed tomography give a clear understanding of the pathology.
Classification of the degree of curvature:
- First degree
- visually imperceptible anomalies, the size of the gap between the teeth is up to 2 mm, the lower incisors protrude slightly. - Second degree
- a “strong-willed chin” appears, the gap increases to 10 mm, the fangs of the lower jaw constantly touch the mucous membrane of the upper lip. - Third degree
- the lower jaw moves forward and it is clearly noticeable that it is larger than the upper jaw, the gap is more than 10 mm between the teeth, the incisors do not touch each other. Other abnormalities may be present—dental crowding is one of them.
The third degree of curvature is dangerous because almost always such mesial displacement of the teeth turns into an open bite. And it may not be possible to correct a mesial bite with braces.
Another type of displacement separation by shape:
- dentoalveolar
- the lower jaw can fall into place on its own, move back with normal closure of the lateral teeth; - gnathic
- in this case, spontaneous shift is impossible; - mixed
.
We have not described all types; there are many classifications in the medical literature, as well as clinical cases.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis begins with a visual examination by a doctor, and this should be an orthodontist. To determine the degree of mesial occlusion, the following studies and actions will be needed:
- assessment of facial anomalies, asymmetry;
- measuring the proportions of the jaw using measuring instruments;
- X-ray, teleradiography, orthopantomography;
- CT scan;
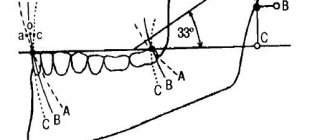
- on the articulators, clarify the inclination of the incisors to the temporal region;
- use bite pads;
- taking impressions of the jaw.
When palpating the TMJ (temporomandibular joint), the patient may feel pain and discomfort. To determine further treatment: how to correct mesial occlusion without surgery or whether it cannot be avoided, complete information about the current condition is necessary. And all innovative diagnostic methods are used.
Features, methods, stages of treatment
The choice of correction method is influenced by the patient’s age and the degree of pathology.
Correction of mesial bite in children
The best period to correct any malocclusion is childhood. It all starts with a massage of the alveolar processes, then:
Myogymnastics
- for the little ones, up to 5-6 years old. Special oral exercises will allow the jaws to grow harmoniously. For older children, myotherapy is prescribed in addition to the main treatment.
Trainers
for patients 5-8 years old they help correct the bite. For 4-8 months they are worn at night. It is a silicone two-jaw mouth guard. Acts on the jaw muscles.
Plate
. From 8 years old, an orthodontic plate is offered. Plastic base with metal arches correcting mesial occlusion. There are many types and modifications: Frenkel activator, Bruckle apparatus, Andresen-Goipl Activator, etc. The choice of whether it will be a classic plate, with springs or another depends on the degree of pathology.
Orthodontic cap
. The child will have to stay in it for 6-8 hours. It looks like a corsage with elastic bandages that puts tension on the back of the head and chin.
Bracket systems
. Mesial bite can be corrected with braces from the age of 12. The structure is not removable. The impact of a metal arch with brackets on the teeth and jaw is constant. They wear it for about a year.
Braces with and without ligatures to correct bite
Treatment of mesial occlusion in an adult
For adults, treatment begins with braces or inexpensive orthodontic plates. But they will have to be worn twice as long as children. Since it is not always possible to correct a mesial bite without surgery, implantation and prosthetics are sometimes necessary.
In case of severe pathology, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention. There are 2 types:
- gentle
_
For effective correction it is necessary to remove the teeth
. - traumatic
_
This is an operation
directly on the jaw. Its excision and forced fixation of the correct position using a structure made of titanium plates and screws. Stitches and plaster splints are applied and must be worn for 2 weeks. To consolidate the result, either braces or retainers are used.
Treatment of progeny in children
If it is necessary to correct such a bite in a child under 11 years of age, he will be shown functional orthodontics using removable appliances.
Children with progeny will need to use trainers or elastic mouth guards, which have a beneficial effect on the growth of the upper jaw and slightly inhibit the development of the lower jaw. Since these devices need to be worn only a few hours a day, they are prescribed even to children of five or six years old. Additionally, a palatal expander is used, which should be worn by the child while sleeping at night.
The “Full Order” clinic in St. Petersburg corrects abnormal occlusion in children and adults and guarantees high treatment results.
Consequences
If you do not correct the mesial bite, you can expect unpleasant consequences:
- recurrent migraines;
- jaw clicking when yawning and talking;
- pain appears when opening the mouth wide;
- facial muscle spasms;
- digestive problems;
- speech defects become stronger;
- aesthetics and appearance are lost, the face changes not for the better.
From the teeth:
- increased abrasion of enamel (even on baby teeth);
- interdental caries;
- bruxism;
- open bite.
The neglected condition of teeth and bone tissue due to mesial occlusion directly affects the impossibility or difficulty of implantation. This pathology cannot be ignored and correction should begin as early as possible.
Types of pathology and its treatment
Progeny is divided into two types - true and false. True toothache is extremely difficult to treat; it causes the formation of gaps between teeth, chewing dysfunction, and problems with the digestive system. Closing teeth or eating food becomes extremely uncomfortable and difficult.
False progeny is quite similar to true progeny, but it affects only the upper dentition. The teeth retain their natural inclination, it is possible to chew and close the teeth, there are no serious violations on this side.
At an early stage, treatment will be most effective; correction does not require much effort. Treatment options during this time include:
- elimination of all bad habits that led to pathology;
- massage;
- correction of the frenulum, if necessary;
- lip muscle training;
- methods of artificially directing incorrectly positioned incisors;
- the use of special tools: occlusal pads, wire arches, reducing the length of the entire dentition.
In advanced cases of pathology, treatment will be more complex and lengthy. In the absence of corrective measures, the pathology will only worsen; it will not go away on its own.
Forecast and timing
90% of cases of mesial occlusion can be corrected by correction. It is better to start with baby teeth or mixed bite. Children's bones grow, and the probability of putting everything in its place in 1-2 years is extremely high. Correcting mesial bite with braces guarantees a positive result. This can be seen in the before and after photos.
Adult patients may need to consult several doctors: dentist, orthodontist, orthopedist. Treatment will not be quick - 1.5-4 years. And only following the doctor’s recommendations will help not only achieve results, but also consolidate them.
Treatment of progenia in adults
In this case, correcting the bite without braces in adults does not justify itself, so the patient should tune in to long-term therapy, which will definitely produce results.
If the patient has a skeletal type of mesial occlusion, then the only way to eradicate this problem is surgery and subsequent orthodontic therapy with brackets.
Surgery can change the size and position of the bones to give the patient a functional bite. In addition, with the help of this type of treatment, the patient will acquire more harmonious facial features, and in order to straighten the dentition, the doctor will ask him to choose one of the braces systems available today.
If the patient has a dentoalveolar type of mesial occlusion, then orthodontic appliances are able to move the lower teeth forward and the upper teeth back and thus overcome the problem.
If you suspect that you or your child have this type of dentition anomaly, you should not panic, because today’s orthodontics can work real miracles - you just have to consult a doctor and he will definitely recommend the best solution to the problem.