Treatment of acute and chronic dental periodontitis in the Implantmaster clinic is carried out under a microscope, by a specialist of the highest category, at low prices in Moscow. If tooth periodontitis is not treated in time, it will develop deeper and it will be impossible to save the tooth.
Periodontitis is one of the most serious complications of untreated caries, which affects bone tissue, the root canal, is a source of unbearable pain and requires immediate dental care. Periodontitis, the symptoms of which manifest as sharp pain in the affected tooth, is familiar to most people.
If doctors have the necessary knowledge and professional skills, patients can hope to receive high-quality treatment for periodontitis, the appropriate type and course of the disease.
In the innovative dental clinic "Implantmaster" in Moscow, periodontitis treatment is carried out with the participation of specialists of the highest category, who regularly improve their skills in the best clinics in Europe. We are accustomed to solving complex problems in the shortest possible time and satisfying the needs of even the most demanding patients. Our doctors are constantly improving, mastering new methods of treating periodontitis, using the most advanced materials, using modern equipment for diagnostics (CT of teeth) and treatment of periodontitis (Labomed Magna microscope), setting loyal prices for the services provided.
Next we will talk about methods of treating periodontitis. You will also learn about the main steps that are implemented in the treatment process and will be able to get acquainted with the indications for various treatment methods. You will learn about these and other points below.
What is dental periodontitis?
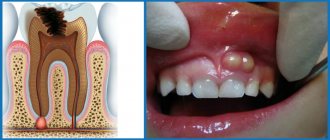
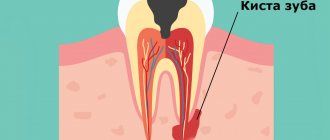
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the dental root canal and surrounding tissues. In most cases, periodontal damage is infectious. Along with infection, the causes of periodontitis can be acute tooth trauma or its chronic nature, advanced caries, untreated pulpitis, as well as allergies to medications. Any of these reasons, under a combination of circumstances, can cause inflammation of periodontal tissues. This disease usually occurs in acute or chronic form.
- Acute periodontitis . The occurrence of spontaneous localized, pronounced pain is observed; there is redness and swelling of the gingival margin around the causative tooth; the process of inflammation provokes the development of swelling of the soft tissues of the face.
- Chronic periodontitis . The most common periodontal disease, since the number of visits to the doctor for this pathology is low and to a large extent they are detected by chance. This is due to the fact that the pain syndrome is less pronounced than in acute periodontitis; they are often almost asymptomatic. Chronic periodontitis can only be reliably diagnosed using an image of the affected area. On a panoramic photograph of all teeth or a targeted x-ray of a tooth, you can examine the causative tooth and peri-root tissues, but it is better and more accurate to diagnose chronic periodontitis using computed tomography. These diagnostic methods are present in our clinic and are used by our specialists. Each of the various forms of damage to perihilar tissues has its own specifics that must be taken into account during treatment.
Why periodontitis is dangerous
Periodontal inflammation is the stage following pulpitis in the spread of infection from a carious tooth.
Its focus is located at the apex of the root and is a small cavity filled with pus.
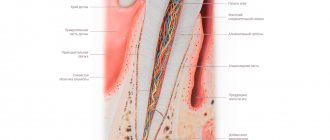
In the absence of therapy, the infectious-inflammatory process spreads to the periodontium - the intermediate tissues that separate the roots and neck of the tooth and the bone tissue of the gums.
Important! The periodontium surrounds the entire subgingival part of the tooth and plays the role of cement that fixes the tooth in the jaw. When it is damaged due to periodontitis, the likelihood of tooth loosening and loss increases many times over.
Most often, periodontitis is localized at the apical part of the root affected by pulpitis. If left untreated, the inflammation spreads further, covering the entire subgingival part of the tooth. As the disease develops, a purulent cavity forms around the roots, which sooner or later opens onto the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or onto the skin of the face. When it becomes chronic, periodontitis is accompanied by constant suppuration with the outflow of contents through a fistula - long-existing ducts, the walls of which do not grow together.
Indications and contraindications for conservative treatment of periodontitis
There are two main routes that can be followed when treating periodontitis: conservative or surgical. Each direction has its own specific indications and contraindications.
In the modern world of dentistry, based on medical standards, the doctor should preferably use a conservative method for treatment. It is worth noting that the possibility of using a conservative method is determined by the condition of the affected tooth and the patient’s body. Indications for conservative treatment of periodontitis include both acute and chronic periodontitis, the appearance of cysts and granulomas, and tooth mobility.
But in some cases, surgical intervention should be used. The following are considered indications:
- obstruction of the root canals (impossibility of expanding them with modern endodontic instruments);
- the presence of a stump tab or pin that cannot be removed without damaging the roots;
- the presence of a deep bone pocket communicating with the periapical region;
- multiple perihilar cysts or those cysts that have grown into the maxillary sinus;
- perforation in the tooth cavity or root wall;
- large size of the periapical lesion (over 1 cm);
- ineffective conservative treatment methods;
- frequent exacerbations of the process (more than 1 time per month).
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years
Treatment methods for dental periodontitis
There are several conservative and surgical methods for treating periodontitis.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis
Drug therapy is used in the treatment of all forms of periodontitis. It is recommended to carry it out for extensive purulent lesions, as well as for tooth mobility. And only in the most extreme and difficult cases, surgical intervention is performed.
Conservative therapy is a gentle method of treating periodontitis in the vicinity of the gums, allowing you to eliminate the inflammatory focus without serious intervention. It is carried out using endodontic techniques for the treatment of periodontitis:
- mechanical treatment of canals with endodontic instruments: passage, expansion, giving the canal a cone shape;
- medicinal treatment of root canals: irrigation with antiseptic solutions, application of calcium hydroxide, other disinfectants and osteotropic agents;
- obturation of root canals.
Conservative treatment of periodontitis is always accompanied by antibiotics.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
Surgical treatment is resorted to if conservative therapy is impossible or ineffective. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- size of formations – more than 10 mm;
- impossibility of endodontic treatment of periodontitis: obstruction of root canals, orthopedic crowns, stump inlays or pins that cannot be removed without tooth destruction;
- cysts and granulomas in multiple quantities at the roots, growth of formations into the maxillary sinuses;
- perforation of the walls of the roots or the bottom of the cavity.
Surgical methods for treating chronic periodontitis or acute forms are varied and are selected depending on the clinical picture.
- Resection is the cutting off of the root apex (upper third) along with the surrounding pathological tissues. The operation is performed for periodontitis through an incision on the gum in any teeth, but best of all – 2- or 3-root chewing teeth (molars). In this case, the canals in the teeth must be tightly sealed along the entire length, except for the last third.
- Amputation is a manipulation similar to resection. It differs in that not a part, but the entire root of the tooth is removed, preserving the crown part. They are carried out on multi-rooted teeth of the upper jaw: more often on molars, less often on premolars. After this operation, it is necessary to perform a retrograde filling. Also, such teeth cannot be used as support for a prosthesis.
- Hemisection is similar to resection, but it does not cut off the root apex, but completely one of the roots along with the crown. This manipulation cannot be performed on single-rooted teeth.
- Separation is the most radical tooth-preserving operation for periodontitis. Only one part of the tooth remains, which is weakly stable, difficult to replace with prosthetics and will not last long.
- Replantation consists of removing the tooth, endodontic treatment outside the oral cavity, which is best done under a microscope, and returning the unit to its place. Our clinic has all the necessary equipment to carry out this operation - a Labomed Magna dental microscope, a panoramic image and a targeted x-ray of the tooth. Our specialists also have the necessary knowledge and qualifications.
- Removal is a last resort method in the treatment of periodontitis. It is carried out if other methods have been unsuccessful.
Physiotherapy for periodontitis
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used in addition to the main methods of treatment for apical periodontitis. They help relieve inflammation, normalize tissue trophism, accelerate healing, and also reduce the risk of complications.
When treating periodontal abscess, the following types of physiotherapeutic procedures are performed:
- Electrophoresis . The use of low-intensity current together with the introduction of drugs: antiseptic and anti-inflammatory. As a result, toothaches and inflammation are reduced, and healing is accelerated.
- Coagulation . The effect of high frequency and low voltage electric current on the affected area, which leads to the disappearance of the inflammatory process.
- Ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF) . A high-frequency electromagnetic field affects the source of inflammation. Inflammation is relieved and blood circulation improves. The method is prohibited for use for removing purulent contents - exudate.
- Ultra-high frequency therapy (UHF) . Microwaves are used to relieve pain and relieve spasms.
- Fluctuarization . It is based on the use of low-frequency current of varying amplitude and intensity. When used, pain is reduced, tissue nutrition is improved, purulent formations are resolved, and healing is accelerated.
- Laser therapy . Laser waves help eliminate inflammatory formations, disinfect, and stimulate repair. Mainly used for chronic apical periodontitis during endodontic treatment in teeth with canals of complex anatomical shape.
- Ultrasound therapy (US) . Ultrasonic waves provide micromassage, which has a positive effect on the treatment of chronic periodontitis in the acute stage.
- Ultraphonophoresis . Ultrasound waves are used to administer anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Magnetic therapy (MT) . Exposure to high or low frequency magnetic fields, static or intermittent, with pulses of various shapes, durations and frequencies. With the help of manipulation, inflammation, swelling, pain are reduced and reparative processes in tissues are stimulated.
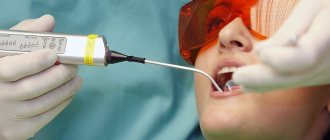
Treatment of periodontitis under a microscope
For innovative treatment of periodontitis in dentistry at a reasonable price, our Implantmaster clinic in Moscow has all the necessary equipment. Thanks to the multiple magnification of the pulp chamber and canals under the Labomed Magna dental microscope, during treatment our specialists can see the smallest areas of affected tissue, remove them and fully process the tooth canals.
- A clear, enlarged image of the dental cavity allows the dentist to preserve living tissue as much as possible when treating periodontitis under a microscope.
- During dental treatment under a microscope, the patient is in a chair in a lying position, and the doctor sits on the side of the patient’s head, which ensures their comfort.
- In case of periodontitis, dental treatment under a microscope allows the dentist to identify other problems that are just brewing. Such knowledge will help avoid negative consequences.
Also, the advantage of treating periodontitis under a microscope is the preservation of the tooth, with perforation on the roots. Thanks to the use of a microscope, the dentist can perfectly navigate inside the tooth cavity.
Read more about dental treatment under a microscope »
Signs
Clinical manifestations of periodontal inflammation depend on the form of the disease.
In the acute course, the symptoms are pronounced, often accompanied by the formation of a painful abscess on the gum, gumboil (deeply located abscess with intense swelling of the soft tissues of the gums and face), increased body temperature, etc. Acute inflammation can occur in two forms:
- Serous periodontitis occurs without the formation of a purulent cavity. Accompanied by constant aching pain that does not intensify when touching a tooth or biting food.
- Purulent periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of an abscess. Accompanied by sharp, bursting or throbbing pain, the intensity of which may vary. Flux is noticeable on the gum near the diseased tooth, and the soft tissues of the face on the affected side swell. The mobility of the tooth is increased, the pain intensifies when biting and touching the tooth.
In the chronic form, periodontitis is not as severe as acute periodontitis. There are three forms of the disease:
- Fibrous , the symptoms of which are sluggish inflammation without the formation of an abscess and fistulas. Pain with this form rarely occurs. An external sign is a change in the color of the enamel to gray, a change in its transparency. Signs of inflammation are visible only on x-rays.
- Granulomatous , the symptoms of which are periodic formation of an abscess. As it “ripens,” a duct opens on the gum, from which purulent contents pour out. Such ducts can form permanent non-healing fistulas. On x-rays, this form of periodontitis looks like a lesion with a diameter of up to 5 mm at the root apex.
- Granulating , the symptoms of which are chronic toothache, aggravated by biting hard, hot or cold food with a sore tooth. The gums near the tooth are constantly swollen and hyperemic. The opening of the fistula can open both on the oral mucosa and on the skin of the face.
Symptoms of any form of periodontitis tend to subside when the purulent cavity is cleared of its contents.
It is important to know! The main difference between periodontitis and pulpitis is the nature of the pain. With pulpitis, it is acute, painful, reminiscent of electric discharges, intensifying when the diseased tooth comes into contact with solid food particles, hot or cold air.
Stages of treatment of chronic periodontitis
How many visits to the dentist’s office will be needed for complex treatment of periodontitis will depend on the stage of inflammation (acute periodontitis, chronic, chronic in the acute stage), as well as the chosen treatment tactics. Periodontitis is often treated in several stages and requires about two or three visits to a dentist; installation of a permanent restoration is not advisable until the inflammatory process is eliminated.
- Preparatory stage : diagnosis using a panoramic photograph of the teeth, a targeted X-ray of the tooth, as well as control using CT; carrying out anesthesia.
- Opening the carious cavity or removing the previous filling material to access the pulp chamber, removing the nerve bundle.
- Expansion of root canal orifices.
- Treatment of canals with antiseptic solutions, application of medications, physiotherapy.
- Installation of a filling using temporary filling material.
- Removal of temporary filling material , treatment of the canals with antiseptic solutions (this stage is repeated until the inflammatory process subsides; several months of treatment may be required).
- Control x-ray and placement of a permanent filling.
During visits for periodontitis, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing with disinfecting solutions are prescribed for treatment at home.
Diagnostics and treatment of tooth canals
The first place in the treatment of periodontitis is a thorough examination of the patient’s health status, after which the specialist prescribes x-rays. In our clinic, for the convenience of patients, we have CT technology, the ability to take panoramic images of all teeth, as well as targeted radiography of a specific tooth. Thanks to the X-ray image, the diagnosis is made with maximum accuracy. It is also possible to study in detail the number of canals in the roots of teeth, their length and shape. Next, an injection with anesthesia is made into the area of the causative tooth, without which treatment of periodontitis can cause pain and discomfort.
After pain relief occurs, the doctor will perform the following manipulations:
- Removal of all carious tissue from the causative tooth, as well as part of the adjacent unaffected enamel and dentin for better access to the mouths of the root canals;
- In a previously untreated tooth, the doctor will remove the inflamed pulp. In a previously endodontically treated tooth, the tooth canals are unfilled;
- Expansion of the tooth canals using manual and mechanical endodontic instruments, followed by rinsing with an antibacterial solution;
- Placement of medication with enhanced antiseptic effect into the channels;
- Afterwards, a temporary filling is placed;
- The patient is consulted on oral care at home, anti-inflammatory drugs and antiallergic medications are prescribed;
- The next visit to the doctor will take place after completion of the first stage of periodontitis treatment - three days later.
Temporary filling of tooth canals
When you return to a dentist-therapist during the course of treatment for chronic periodontitis, the area for further manipulation is examined. The specialist must clarify whether the patient has complaints of pain, swelling in the gum area of the causative tooth or other discomfort. In the absence of these negative phenomena, temporary filling of the root canals of the tooth is performed.
To do this, first of all, the temporary filling and the antiseptic drug placed in the tooth canals are removed. The canal mouths are carefully treated with an antiseptic and then filled with a special medicinal material that contains calcium hydroxide, a substance that kills pathogenic microorganisms and stimulates the regeneration processes of bone tissue in the area of the apex of the tooth root. Temporary filling of root canals is carried out for a long period - from a month to three. At the end of the visit, the dentist closes the tooth cavity with a temporary filling.
Permanent filling of tooth root canals
During the third visit to the dentist during root canal treatment, a permanent filling is performed. First, the specialist sends the patient for a control x-ray, which determines the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment. If there is a decrease in destroyed bone tissue, permanent canal filling is performed.
The procedure begins with the removal of a temporary filling from the crown of the tooth, then the canals are freed from the previously laid healing material. The doctor rinses the root canals with an antiseptic and then fills them to the root apex with a composite. At the end of the work, the patient is given a final x-ray to control the quality of the filling performed. Gutta-percha pins must be tightly compacted in the canal to the very apex of the root, otherwise there is a high risk of relapse of the disease.
You may have toothache after periodontitis treatment. Normally, they last 3-5 days and gradually fade away. If the pain does not subside or returns with renewed vigor, retreatment is necessary.
The patient should come to the doctor for installation of a permanent restoration of the crown of the tooth at the next, fourth visit. The filling material in the root canals becomes denser, and the discomfort after intervention in the canals disappears.
Temporary and permanent root canal filling
After the operation to remove pus for acute periodontitis, 3-4 days should pass, and then the patient visits the clinic again. During the second appointment, the doctor performs the following manipulations:
1. Thoroughly rinses the canal cavities with antibacterial solutions, and then puts an antiseptic in them.
2. Places a temporary filling on the tooth.
The patient is sent home, but is warned: at the slightest sign of pain, he should immediately seek professional dental care.
Permanent filling of the canals is carried out during the third visit. The treatment procedure can be carried out in the absence of complaints from the patient about any discomfort, as well as in the complete absence of pus in the canal cavities. The canals are filled with gutta-percha composite to the upper root zone. Restoration of the aesthetics and functionality of the tooth is done on a subsequent visit, and at this point the course of periodontitis treatment is considered complete.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
In the acute stage of periodontitis, two phases are distinguished: intoxication and exudation (appearance of discharge). As the disease develops, the patient first experiences aching and sparse swelling, and then the gums in the area of inflammation pulsate, so treatment cannot be delayed.
Acute periodontitis is divided into serous and purulent. In the second case, pus accumulates at the apex of the tooth root. The main goal in the treatment of acute purulent periodontitis for the doctor is to remove exudate. To achieve this, cleaning the tooth cavity and correct treatment of the canals may be sufficient, but in advanced cases, it may be necessary to resort to dissecting the periosteum to install drainage.
Emergency dental care in the treatment of periodontitis
While emergency care is provided to the patient during the treatment of periodontitis, it is primarily necessary to open the causative tooth in order to create an outflow of purulent exudate that has accumulated at the apex of the root. If acute periodontitis is accompanied by swelling of the gums, before treatment, an incision is made opposite the apex of the tooth root.
With an open tooth cavity, without a filling, the patient needs to walk around for several days, after which a second visit to the dentist will take place. For the entire period without a filling, when eating and drinking, it is necessary to close the cavity with a cotton swab, and then remove it - this will prevent pieces of food from entering the mouth of the canals, and will also avoid a possible relapse of inflammation.
The stage of providing emergency care as part of the treatment of acute periodontitis is a loyal service at a price. Its approximate cost is in the range from 2000 to 3000 rubles. But you should know that this is not the end of the treatment and it must be continued.
After the tooth cavity is opened during the treatment of acute apical periodontitis, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics and oral baths, as well as antihistamines.
Is it possible to cure periodontitis on your own?
It is important to understand that treatment of such a serious disease as periodontitis simply cannot be carried out at home. It is impossible to relieve inflammation either with pharmaceutical drugs, much less with decoctions, tinctures, or rinses according to traditional medicine recipes. Even if you start taking antibiotics on your own, periodontitis cannot be cured, since the source of the disease is an infection located in the dental canals. To eliminate this source, the channel cavities must be thoroughly cleaned.
Don’t experiment with your health - come to our dentistry in Moscow - Vanstom. We are located in the center of Moscow, next to the Baumanskaya metro station. Treatment of any form of periodontitis in our clinic is carried out professionally, using modern techniques and drugs, and therefore we guarantee you high quality services. To make an appointment with a Vanstom specialist, simply dial our contact phone number.
Prices for periodontitis treatment at Implantmaster
Treatment of caries by filling tooth surfaces
- Anesthesia
- Cavity preparation (preparation, medicinal treatment, application of a gasket)
- Filling with light-curing composite
- Grinding and polishing the filling
- X-ray images
Price : from 3,000 ₽ to 8,050 ₽, depends on the number of tooth surfaces affected.
Treatment of caries by placing a ceramic inlay “E-MAX” or “CEREC” or “EMPPRESS”
| from 20,000 to 28,000 ₽ |
Unsealing all tooth canals
| from 4,000 to 8,500 ₽ |
Filling all tooth canals
| from 6,500 to 11,500 ₽ |
| Removing a foreign body from a tooth canal (pins, fragments of instruments, etc.) | 3 000 ₽ |
| Application of medicinal paste into the tooth canals | 2 000 ₽ |
| Sealing tooth fissures | 2 000 ₽ |
| Treatment of caries without drilling the tooth using the “Icon” method | 3 000 ₽ |
| Complete restoration of a tooth with a light-curing composite (Tooth restoration) | 9 500 ₽ |
Prices for periodontitis treatment services vary, depending on:
- severity and form of the inflammatory process;
- the volume of manipulations performed;
- quality of the anesthetics used;
- status and location of the clinic;
- equipment and materials used in treatment.
The standard cost of treatment includes:
- anesthesia;
- if necessary, remove the previous filling material;
- channel processing;
- temporary filling.
More detailed information can be obtained on the clinic’s website or by calling the helpline.
Causes
There are several causes of the disease:
- Traumatic. The disease occurs due to a bruise, sharp biting on a hard object, or a blow to one tooth. Another possible cause is injury during root canal treatment with dental instruments.
- Infectious. It develops due to the penetration of microorganisms into the tissues surrounding the tooth root. Typically, periodontitis occurs due to Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus.
- Medication. Occurs due to the effect of potent drugs on the peri-apical tissues of the tooth. Signs of the disease appear within a few hours after exposure to the drug.
The inflammatory process can occur slowly or very quickly. This does not depend on the cause of its occurrence.
Errors in the treatment of periodontitis and complications after
There are different types of errors and complications in the treatment of periodontitis. If the basic rules of the treatment process are violated (failure to follow the protocol for root canal treatment, ignoring X-rays, insufficient qualifications of the doctor or lack of follow-up therapy), the likelihood of complications is high. In this case, the failure of treatment lies with the doctor. But even compliance with all conditions does not guarantee success. So, if after installing a permanent restoration the previous symptoms persist for 5 days, there is a need for a repeat X-ray of the tooth. Based on the image, re-treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of periodontitis at each stage should be accompanied by a control x-ray to observe the dynamics of the inflammatory process.
Regardless of the reasons that could cause the recurrence of periodontitis, it is necessary to re-treat again with the implementation of all protocols for the technique and safety.
If all measures are not followed, the following complications are possible:
- inflammation of nearby areas of the jaw;
- formation of purulent exudate in the area of the causative tooth;
- the appearance of phlegmon;
- osteomyelitis;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
Periodontitis, like any other inflammatory process, requires attention from the doctor equally as from the patient. Otherwise, the treatment time for periodontitis will increase significantly.
Answers to popular questions
How long can it take to treat periodontitis?
Treatment of inflammation of periodontal tissues is a very long process. On average, 3–5 visits to the dentist may be needed (depending on the clinical case). The entire process sometimes takes several months.
Why is periodontitis dangerous?
The danger of the disease lies in its consequences. If inflammation is not treated, the following may develop: 1. periapical abscess; 2. diffuse purulent inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue (phlegmon); 3. fistula in the gum; 4. destruction of the jaw bones (osteomyelitis); 5. blood poisoning; 6. unit falling out of the hole, etc.
How can I tell if I have chronic periodontitis?
The following alarming signs may indicate the chronicity of the process: • wave-like appearance of aching pain; • the appearance of a fistula opening on the gum with purulent discharge; • increasing the sensitivity of the segment when chewing. At the first suspicion of the presence of a pathology, consult a doctor and undergo diagnostics.
Is it possible to treat periodontitis at home?
It is impossible to cure periodontitis at home on your own , since the cause of the disease is pathogenic microflora in the dental canals. The only way to remove them from the canals is to treat them with antiseptics and seal the canals, and this can only be done by a specialist. However, by waiting for a visit to the dental clinic, you can relieve symptoms of periodontitis and reduce pain before treatment. Antiseptic agents that do not irritate the mucous membranes can be used for oral baths 4-5 times a day. Doctors also recommend rinsing with a solution of salt and soda in order to relieve swelling and reduce the inflammatory process. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for pain relief. These may help relieve symptoms, but are not treatments.
Author:
Vivid symptoms of periodontitis
The disease periodontitis cannot be confused with anything. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the patient has severe periodic aching pain in the projection of the tooth;
- there is an increase in pain at the moment of biting;
- pain during periodontitis increases when the tooth is tapped with a hard object;
- the pain worsens at night and during the cold season;
- a purulent, inflamed sac around the gum, on which a fistula with purulent contents subsequently forms;
- mobility of the affected tooth is observed;
- Gaps appear between teeth;
- with periodontitis, bleeding gums are diagnosed;
- temperature rises;
- When sick, sleep is often disturbed;
- there is general weakness.
Very often, when a patient feels pain while biting food, he begins to chew on the other side, thereby freeing the pathological tooth from the load. During this time, the acute stage gradually turns into a chronic one, and the destructive process intensifies.