Inflammation: where does it come from?
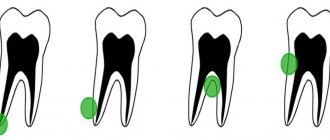
The most common cause of swollen gums is an inflamed tooth. In the vast majority of cases, swelling occurs as a result of chronic inflammation of the dental tissues under the crown and/or filling, lasting more than one day or even more than one week, against the background of progressive complicated untreated caries and/or after mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane.
Unfilled canals, improper treatment of caries - all this ultimately leads to gum swelling. Voids in the dental canals, perforation of the tooth root against the background of poor quality treatment involuntarily help the infection to spread further.
In this case, the swelling of the gums also affects the area of the diseased tooth, accompanied by a feeling of aching pain. For some people, the pain may be intermittent and only occur when biting.
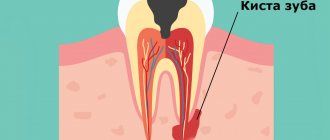
The usual swelling of the gums can also hide such serious problems as a dental cyst or an abscess on the gum.
Why is a cyst dangerous and why should you never delay its treatment?
Many people are so afraid of dentists that they do not seek treatment for cysts until the last minute, even when the disease develops pronounced symptoms. If you suspect that you have a dental cyst, but delay treatment, you are seriously risking your health, because a cyst is a dangerous disease that can cause severe complications.
Lack of treatment for a dental cyst can lead to:
- To the development of sinusitis if the tooth is located in close proximity to the maxillary sinuses;
- Inflammatory processes in the periosteum - flux, periostitis;
- Provoke an abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis.
If an infection from a cyst gets into the soft tissue, it can cause a life-threatening condition such as sepsis. Therefore, do not delay or put off cyst treatment until later. There is no need to be afraid that it will be painful: before the doctor begins to remove the tumor, he will definitely numb the tooth. Patients of our clinic in Moscow “Firadent” can take advantage of a special service - treatment of dental cysts under sedation.
Cyst symptoms
The cyst develops asymptomatically for a long time. Sometimes it makes itself felt by aching pain when pressing on a sore tooth or when biting into hard food. It is easy to detect on plain X-rays.
When immunity decreases, the cystic infection can worsen and begin to actively produce pus. This process is accompanied by severe pain in the area of the corresponding tooth, sometimes by increased body temperature and swelling of the gums. The cheek becomes noticeably swollen, the person feels unwell and weak, urgent consultation and diagnosis are required, and then urgent treatment.
Treatment of dental cyst
Treatment of the cyst can be therapeutic and/or surgical.
Surgical treatment involves resection of the cyst.
Therapeutic treatment lasts a long time. The doctor has to remove the pulp and re-treat the canals with antiseptics. After this, a paste with a long-acting antiseptic is placed in them. In some cases, the treatment procedure requires repeated repetition.
After a course of therapy, an x-ray shows how effective the treatment was. If the cyst has significantly decreased in size, the canals can be filled with a permanent filling - gutta-percha.
After this, the patient should periodically visit the dentist to assess the dynamics of recovery.
How to treat a dental cyst: a review of modern techniques
Treatment of a cyst on the root of a tooth can be surgical and conservative (medication). Conservative treatment of a cyst does not involve an incision in the gum and is therefore considered a gentle technique, however, the treatment process will not be simple, because it is carried out in several stages. It is also worth knowing that conservative treatment of cysts is effective only for small formations (up to eight millimeters) located in that part of the tooth root that the doctor can reach through the dental canals.
All stages of conservative treatment of cysts
Drug treatment of cysts is carried out in several successive stages:
1. The treatment process begins with anesthesia of the treatment area and installation of a rubber dam - a special latex lining that reliably isolates the diseased tooth with a cyst from moisture and saliva from the oral cavity.
This is important because saliva and wet breath may contain pathogenic microorganisms. 2. As soon as the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor will begin working on the tooth. He will drill out his crown to gain access to the canals and cyst.
3. One of the most difficult stages of the treatment process is carried out - treatment of the dental canals. First, the dentist will expand their internal space with a special tool, and then rinse and treat them with antiseptic drugs. We have already told you about the importance of the quality of work with dental canals: if you make mistakes in this process, relapses of the disease are possible! At the Firadent clinic, the canals are processed by doctors using a dental microscope - a special device with powerful magnification, and therefore errors and inaccuracies in the treatment of the intracanal space are completely eliminated!
4. Manipulations are performed to block the source of infection (cyst), a drug is placed in the tooth that stops the development of the tumor and destroys it.
5. The tooth canals are filled with a special temporary filling material, a special paste that has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. A temporary filling is also placed on the tooth.
After completing all these steps, the doctor sends the patient home, prescribing antibiotics. After some time, you will need to come to the clinic again to evaluate the results of the treatment. A photograph of the tooth will be taken, which will show progress or lack thereof in treating the cyst.
Drug treatment of a cyst can last for several months; a permanent filling will be placed on the tooth only when an x-ray shows that there is no cyst and the inflammatory process has stopped completely.
IMPORTANT: When treating a dental cyst using medication, antibiotics are prescribed, and therefore some people have the opinion that if you buy drugs at the pharmacy and drink them without going to the dentist, you can cure a dental cyst at home. But this opinion is erroneous and dangerous: without the use of special drugs or canal treatment, the cyst will not go anywhere, it will remain on the root of the tooth and will continue to develop. In addition, self-medication with antibiotics is dangerous due to the high risk of side effects.
Treatment of an abscess on the gum
After examining the oral cavity and studying the image, the doctor identifies the cause of the suppuration and prescribes treatment, which can also be either conservative or surgical dental treatment under general anesthesia.
Conservative treatment: the canals are opened, then an antiseptic is placed into the tooth cavity. Within a few days, the drug destroys the infection, and the doctor refills the canals. The formation of pus completely stops, swelling and redness of the soft tissues disappear.
Surgical treatment: the doctor makes an incision in the gum or removes a tooth.
When are antibiotics needed for dental implants?
Modern research proves that one of the reasons for the development of peri-implantitis1 is a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity. That is, there are many “bad” bacteria compared to the good ones - these are anaerobic bacilli, streptococci and other cocci. In addition, unprofessional installation of implants or the choice of incorrect designs plays a big role. For example, during installation, a doctor may allow implants, which are in sterile packaging, to come into contact with the patient’s lips or tongue, that is, with saliva, where many pathogenic bacteria live.
If we are talking about the engraftment stage, then with insufficient oral hygiene on the part of the patient, in the presence of general problems with the body (especially viral and bacterial infections of the oral cavity or nose, including in a chronic compensated form), there is also a high risk of developing inflammatory processes.
Indications for antibiotic therapy:
- poor initial oral hygiene,
- difficult care of implants and crowns after their installation,
- one-stage implantation, in which prostheses are installed immediately,
- installation of implants against the background of periodontitis, periodontal disease or osteomyelitis,
- implantation of implants simultaneously with removal of tooth roots,
- multiple installation of implants,
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx,
- reduced immune status of the patient,
- bone tissue augmentation surgery combined with implantation.
The effectiveness of antibiotics in dental implantation
In practice, it has been proven that patients who do not take antibiotics at any stage of implantation are at a “high” risk of developing inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. And even in patients whose oral cavity maintains a “normal” balance of microflora, there is a risk of complications after surgery, because literally every little thing influences a favorable outcome: the state of health of the entire oral cavity, the professionalism and conscientiousness of the attending physician, the model of the implant used.
“We make sure to prescribe patients not only antibiotics, but also painkillers and antihistamines. They are taken in combination to relieve swelling, reduce inflammation, and speed up the rehabilitation of the body as a whole. We very often carry out complex dental restoration against the background of inflammatory processes of periodontal tissue, so antibiotic therapy is among the mandatory procedures after dental implantation.”
Bespalov Roman Dmitrievich, maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist, more than 25 years of experience make an appointment
Two-piece implants for delayed loading with a prosthesis usually have a porous coating. On the one hand, it ensures better osseointegration of the structure in the bone tissue. On the other hand, it is the rough outer surface that is the site of accumulation of bacteria, which leads to the development of peri-implantitis. In most situations, this is relevant after the implants have been implanted, since over time the bone tissue sags a little (this is a physiological process that is considered normal) and the top of the implant becomes exposed. But in the first months after installation, bacteria can also accumulate on implants. For example, if the structure is located slightly above the gum (due to incorrect installation or incorrect choice of model), as well as if the implant-abutment connection is not tight.
A low risk of developing inflammation of periodontal tissue while taking antibiotics occurs in the following cases:
- when choosing two-piece implants with an antimicrobial coating in the apex and when using abutments with a similar smooth antimicrobial coating,
- when choosing implantation methods that use one-piece one-piece implants with a smooth body or a neck that remains above the gum. In addition, such implants are fixed in deeper parts of the bone, which are not subject to inflammatory processes, so the risk of peri-implantitis (especially when taking antibiotics) is noticeably reduced.
Abscess on the gum due to periodontitis
With this disease, ulcers often form. The drugs only temporarily relieve discomfort, but the pathological process continues to develop, gradually destroying the bone tissue of the jaw.
Timely intervention by the dentist allows you to remove the source of infection and achieve 100% cure.
Antibiotics, rinses, physiotherapy - all this is included in the treatment of purulent infection. It is important not to let the process take its course, because complicated purulent infections are extremely difficult to treat.
What are the consequences of negligence?
As a rule, aching pain speeds up the patient, and few people delay a visit to the doctor. And this is correct, because even if there are no painful symptoms, swelling of the gums is quite enough to urgently consult a dentist for consultation, diagnosis and treatment (after which the swelling soon goes away).
In the absence of qualified and timely assistance, the patient may develop very serious complications. Thus, a slight inflammation can quickly affect the entire gum and even the jaw bone. And this will require a long and serious treatment with antibiotics, in addition, the prospect of inevitable surgical treatment of teeth in a dream looms before him - to eliminate the source of infection.
Removal of a cyst without tooth extraction: surgical treatment methods
If the diagnosis shows that the cyst has managed to grow to a significant size or the patient turns to the dentist in the later stages of development of the formation, an operation to remove the cyst is prescribed. There is no need to worry: in most cases, it is possible to remove the cyst, but at the same time save the tooth; sometimes, along with the cyst, one of the roots of the tooth is removed - completely or partially.
There are several methods for surgical removal of a cyst: the specific technology is selected individually for the patient, taking into account the characteristics of the clinical case. We will analyze all the surgical methods for removing a cyst and find out when and what method is used.
Hemisection for removal of a dental cyst
This surgical method for treating a cyst involves removing the purulent capsule itself, as well as part of the tooth root and its crown. Hemisection is recognized as a complex method of cyst removal and is performed when it is impossible to use other treatment methods. Hemisection is applicable only for teeth that have several roots, and since after it the tooth partially loses its chewing functions, it will need to be restored not with a filling, but with a crown.
Removal of a cyst using cystectomy
This cyst removal technique is used most often. It is considered the most gentle method of surgical removal of a cyst, but requires experience, qualifications and care from the doctor. When performing a cystectomy, treatment begins with canal treatment, after which an incision is made in the gum next to the diseased tooth, and the dentist removes the cyst along with part of the tooth root.
Cystotomy to remove the cyst
The operation is considered simple for the doctor and minimally traumatic for patients, but it has a disadvantage - after cystotomy, when removing the cyst, the tissue takes quite a long time to recover.
The essence of the technique is to remove the anterior wall of the cyst through an incision in the gum and pump out the pus that has accumulated in the capsule. Cystotomy to remove the cyst is performed when the tumor is large, as well as in cases where the cyst is formed at the base of the jaw and the bone tissue is very thin.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the treatment of dental cysts with laser. This technique is considered an innovation, as it began to be used for the treatment of cysts in Moscow dentistry relatively recently. Laser removal of a dental cyst is carried out in several stages:
- The tooth is drilled out so that the doctor has full access to its canals;
- The cyst is removed with a laser;
- The canal cavities are disinfected with laser radiation;
- The canals are filled, the tooth is restored with a filling.
Laser removal of a dental cyst has many advantages, including painless surgery, fast tissue restoration, and the ability to save the tooth. However, there are also disadvantages: the price of laser cyst removal is high, the cost of the operation will be higher than the price of cyst removal by other methods.