Dental periodontitis is an inflammation of an infectious nature that occurs at the membrane of the tooth root and affects the tissues of the oral cavity located next to it. Periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other dental diseases, because it has a clear symptom – severe and constantly increasing pain, which cannot be relieved by taking tablets from the pharmacy.
Treatment of periodontitis must be carried out urgently, because you risk not only losing a tooth, but also acquiring complications that are dangerous to the overall health of the body! How periodontitis occurs, what signs will help to identify the disease in a timely manner, how periodontitis is treated in dentistry, at what prices the service is offered in Moscow - we will talk about this in detail in this article.
Causes of dental periodontitis
Various reasons can lead to the appearance and development of dental periodontitis, but in the vast majority of cases the disease appears:
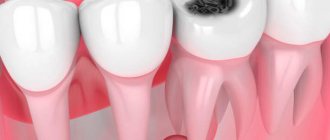
- Against the background of untreated dental caries and pulpitis;
- Due to poor quality treatment of tooth canals, or more precisely, mistakes made when filling the canals.
Less commonly, periodontitis occurs after injuries, incorrectly installed dental fillings, or violation of the dosage of dental medications.
Whatever the cause of periodontitis, its treatment cannot be delayed due to fear of dentists. It is important to understand that you will not stop the inflammation on your own, with pills or folk remedies, and the more it progresses, the less chance you have of saving the tooth. In addition, periodontitis can also affect neighboring healthy teeth.
How to identify periodontitis and not confuse it with caries or pulpitis? We already talked about the most striking symptom of the disease at the very beginning of the article, but the signs of periodontitis may vary depending on the form of the disease. Therefore, below we will consider the main types of dental periodontitis, as well as talk about their characteristic symptoms.
Take a short test and calculate the cost of treatment!
Take a short test
- Which teeth have caries?
- Visual assessment
- Reaction to stimuli
- Cost calculation
×
Manukyan Artavazd Genrikovich
Chief physician of the clinic
Permanent canal filling
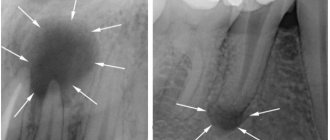
Permanent canal filling in the treatment of periodontitis is performed during the third visit to the dental office. Before proceeding with any manipulations, the specialist sends the patient for a control x-ray. The image will help determine the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment. If the percentage of bone tissue destruction has decreased significantly, permanent filling of the canals is performed.
The procedure begins with the removal of the temporary filling from the crown of the tooth, and then the canals are freed from the previously placed composite. The doctor will carry out an antiseptic rinse and then fill them to the apical part of the root with a composite. Upon completion of the work, the patient is given another x-ray to monitor the quality of the filling performed. Gutta-percha must be tightly packed into the canals to the very apex of the root, otherwise there is a high risk of relapse of periodontitis.
A couple of days later, the patient comes to the doctor for the fourth time and during this visit the crown part of the tooth is restored with a permanent filling to restore its aesthetics and functionality.
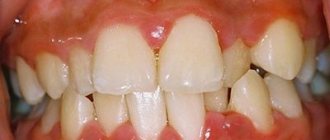
Signs of acute periodontitis
Symptoms of acute periodontitis are always pronounced. Among them:
- Acute aching pain, the intensity of which is constantly increasing;
- Pain increases when trying to eat;
- If treatment for periodontitis was not started on time, attacks of pain will appear more and more often, and the intervals between them will become shorter and shorter;
Against the background of intense pain, a person cannot eat, speak, sleep, and may develop an elevated temperature. In the acute form of periodontitis, significant tumors and swelling often appear in the area of the diseased tooth. The cheek may also swell. This occurs due to the active accumulation of pus in the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
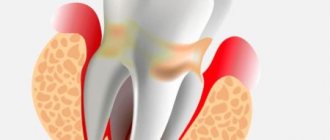
Periodontal anatomy
The periodontium (from Latin perio - around, around; odontos - tooth) is a complex of tissues surrounding the tooth and holding it in the socket. It includes the gum, dental cement, alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, which is located between the dental root and the alveolar plate and communicates between the alveolar bone and the cement of the tooth root. The periodontium consists of many blood and lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, and periodontal fibers. The thickness of periodontal fibers depends on age and averages 0.2 mm, becoming thinner over the years. The periodontal ligamentous apparatus is represented by groups (bundles) of fibers that have different directions, connecting all areas of the periodontium into a single system, stretching between the teeth, from the cement of one tooth to the cement of another. The ground substance of the periodontium occupies about 60% and is an amorphous gel-like substance, 70% consisting of water. A large amount of base material and water in it are factors that play a huge role in providing shock absorption. A characteristic feature of the cellular structure of periodontal tissue is the ability for rapid renewal, but with age this process becomes slower. The structural integrity of the periodontium is ensured by the enamel attachment, the cells of which are completely renewed within 4–8 days. This ability to renew provides mechanical protection of the entrance to the marginal part of the periodontium and reduces the risk of negative factors affecting it. The periodontium performs the most important functions. Plastic – ensures the growth and development of teeth due to the activity of osteoblasts and cementoblasts; trophic – provides nutrition to the cement base of the tooth and the alveolar plate; supporting-retaining – ensures fixation of the tooth in the alveolus; shock-absorbing - distributes chewing pressure due to the ligamentous apparatus; protective – prevents the entry of pathogenic microorganisms and the spread of inflammatory processes 3.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a very insidious form of the disease, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is extremely rare for a person to feel a slight pain when trying to bite something on a sore tooth; sometimes unpleasant sensations appear when consuming hot food and drinks.
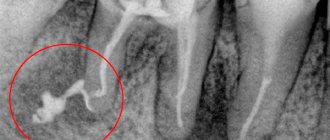
Chronic periodontitis of the tooth is diagnosed with an x-ray, which clearly shows the process of bone destruction at the apex of the tooth root. This form of the disease has its own classification, according to which there are: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis. With fibrous periodontitis, there is almost no pain, which is why it is most often recognized either in the acute phase or during an examination by a dentist and x-rays.
Treatment of this form of periodontitis is quite simple and is carried out in 1-2 visits to the doctor. Granulomatous chronic periodontitis most often develops asymptomatically, but under the influence of certain external factors it easily turns into an acute form. The disease has its own characteristic symptom, manifested in the formation of granulomas - capsules with pus, which separate tissues affected by inflammation from healthy ones. The treatment process for granulomatous periodontitis is long and complex, it can last for several months and even require surgical intervention!
Dentistry “New Line Dent”: treatment of periodontitis without pain and with a quality guarantee
In almost every article on our site, we try to convey to the reader the following important information: the quality of dental treatment always depends on the level of professionalism of the doctor, the equipment of the clinic - materials, tools, diagnostic equipment. These are the criteria that you should rely on when choosing dentistry for the treatment of periodontitis and other dental diseases.
In our dentistry in St. Petersburg “New Line Dent” all conditions have been created for you to have high-quality dental treatment, without pain and with comfort. We work with the best materials, equipment and tools, and each doctor in our clinic is an experienced, qualified specialist who is responsible for the quality of his work.
Come to New Line Dent for healthy teeth and a beautiful smile!
How does the acute phase of chronic periodontitis manifest?
When exacerbated, chronic periodontitis of the tooth expresses itself with the same symptoms as the acute form of the disease. That is, there is a strong, aching pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Typically, chronic periodontitis enters the acute phase when the immune system is weakened, the flu, ARVI, or simply severe hypothermia are present. If, during an exacerbation of the chronic form, a fistula appears in the gum area, pus will flow from the area of inflammation and the pain in the tooth will gradually subside.
But this does not mean that periodontitis has gone away on its own; the inflammatory process will continue to develop and will manifest itself again under favorable external factors, which we discussed just above. Based on the type of periodontitis, a treatment regimen is selected. The price of the service depends on the regimen chosen for treating the disease. We will tell you below about all the stages of treatment of dental periodontitis in different forms and prices for procedures. But no matter in what form periodontitis develops, its treatment always begins with diagnosis.
Diagnosis of periodontitis involves examination of the oral cavity, x-rays, and examination of patient complaints. All this together helps to accurately diagnose the form of periodontitis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
Temporary filling
During a second visit to a dentist-therapist during the course of treatment of chronic periodontitis, the area of manipulation is examined. The specialist will also clarify whether the patient has any complaints of pain, swelling in the gum area or other discomfort. If such negative phenomena are not observed, temporary filling of the dental canals is performed.
For this purpose, the temporary filling is initially removed, as well as the antiseptic placed in the tooth canals. The canal openings are thoroughly washed with an antiseptic and then filled with a special type of composite material used for temporary filling. This composite contains calcium hydroxide, a substance that destroys pathogenic microflora and also catalyzes the process of bone tissue regeneration in the area of the upper zone of the tooth root. Temporary filling of canal cavities is done for a fairly long period - from two to three months. The dentist then places a temporary filling in the crown of the tooth.
Price
The cost of periodontitis treatment is always strictly individual and consists of a combination of factors. These include diagnostics at the initial and intermediate stages of treatment, the diagnosis made and the algorithm of treatment measures adopted on its basis, the number of visits, drugs, equipment and technologies used in treatment, the work of specialized specialists if necessary, the level of qualifications of the doctor.
Periodontitis is a very serious disease of the teeth and the dental system as a whole. Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner and attempts at self-medication can lead to serious complications, including those that can threaten your life. At the first appearance of symptoms, you must urgently visit the dental clinic! Be prepared for long-term treatment, which involves multiple visits to the doctor, since the treatment of periodontitis consists of several stages, each of which cannot be started without diagnostically proven effectiveness of the previous one. Only this approach to treatment, combined with the professionalism of the doctor and the patient’s strict, vigilant attitude to all prescriptions and recommendations, is a guarantee of high-quality treatment and reliable protection against relapse for several years.
According to antiplagiat.ru, the uniqueness of the text as of October 16, 2018 is 99%.
Key words, tags: caries, pulpitis, bone tissue destruction, cyst, odontogenic cyst, flux, OPTG image, tooth-preserving operations, resection of the apex of the tooth root, cystectomy, root amputation, dental microscope, preservation, tooth extraction .
1 I. Zimin “From the history of dentistry.” 2 “Teeth and dentistry. Essays on history” / K.A. Pashkov. – M.: Veche, 2014. – 240 p.: ill. 3 Britova, A. A. Endodontics. Diseases of the dental pulp and periapical tissues: textbook. manual, 3rd ed., rev. and additional / A. A. Britova; NovSU named after. Yaroslav the Wise. – Veliky Novgorod, 2021. – 171 p. 4 https://elestom.ru/recommends INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DENTAL DISEASES ICD-C-3 BASED ON ICD-10. 5 https://elestom.ru/recommends INTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF DENTAL DISEASES ICD-C-3 BASED ON ICD-10. 6 https://mkb-10.com 7 Kleshchenko A. V. Improving the technique of unfilling root canals of teeth obturated with gutta-percha: Dissertation of a candidate of medical sciences: 01/14/14 / Kleshchenko Alexander Viktorovich; (Place of defense: Moscow State Medical and Dental University). - Moscow, 2011 - 93 p. 8 Report of the American Society of Microbiology based on the work. Author: Tobjörn Bengtson, presented by the Faculty of Clinical Medicine, School of Health Sciences, Örebro University, Sweden. * NOS is an abbreviation for “not otherwise specified,” meaning “unspecified” or “unspecified.”