There are a wide variety of dental diseases that damage the health of the teeth and oral cavity. Some pathologies - for example, primary caries - can be treated quickly and even without drilling the tooth; therapy for other diseases requires a whole course of procedures. For example, the treatment of periodontitis is always a complex process, since the disease affects not only the tooth itself, but also the tissues located next to it, which has a negative effect on the body as a whole.
If periodontitis develops to a certain stage, then all therapeutic measures may turn out to be useless and there will only be one way out - to remove the tooth. We will talk in detail about what periodontitis is, its forms, symptoms, and treatment methods in the following sections of the article.
Periodontitis: how does the disease appear and how does it develop?
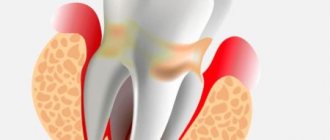
Periodontitis is a term dentists use to refer to an inflammatory process that affects the tissues that surround the tooth and help keep it in the socket. The causes of periodontitis may vary in etiology (origin) and the disease is classified into subtypes. Correct diagnosis of the subtype of periodontitis is of fundamental importance: on its basis, the specialist will select the most effective treatment methods. Below we will get acquainted in detail with the forms of the disease, and also consider in detail their characteristic symptoms.
Infectious periodontitis
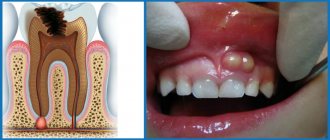
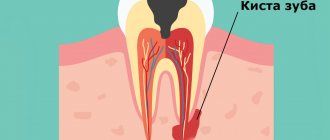
Dentists have to treat the infectious form of periodontitis in 90% of cases. The disease appears due to infection entering the root canals of the tooth and usually against the background of caries or pulpitis, the timely treatment of which was ignored. Infection in the canal cavities can also occur due to errors in endodontic treatment. The inflammatory process begins to actively develop from the moment pathogenic microflora enters the cavity of the dental canal. As inflammation spreads, not only soft but also hard tissues are destroyed; a granuloma can form, and if left untreated, a cyst.
IMPORTANT: The process of cyst formation can be asymptomatic, but the formation can grow to significant and dangerous sizes and lead to various types of pathologies, including deformation of the jaw joint.
Clinical researches
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Retrograde periodontitis
This form of the disease is quite rare. Periodontitis of this form begins to develop against the background of infection penetration into the periodontium through the blood flow or lymph flow.
Traumatic periodontitis
Periodontitis of traumatic origin appears against the background of trauma, when a person receives a sufficiently severe bruise. Some medical errors made during dental treatment can lead to traumatic periodontitis:
- A small piece of an instrument that was “forgotten” after treatment in the cavity of the dental canals;
- Re-filling of the dental canal, which consists of excessive filling of filling material, which ultimately protrudes beyond the apical part of the tooth root;
- Incorrectly restored natural tooth crown, prosthesis, which constantly injure the tissues of the oral cavity.
Toxic periodontitis
This form of periodontitis usually occurs after poorly treated caries, and can occur due to tissue irritation caused by certain medications.
Each form of periodontitis has its own symptoms, but inflammation in the periodontium can also be determined by some general signs:
- Pulsating and clearly localized pain, the intensity of which gradually increases. The pain impulse intensifies at the slightest attempt to touch the teeth, during the period of their closure, while eating;
- The appearance of elevated body temperature due to toothache;
- Feeling of fullness in the area of the inflammatory process;
- Swelling of soft tissues.
IMPORTANT: Severe symptoms during the development of periodontitis are not present in all cases. Some phases of the disease can occur without the slightest external signs at all, or the person feels slight discomfort, which he mistakes for ordinary caries. Professional dental examinations, which are recommended to be carried out at least once every six months, will help to identify periodontitis in a timely manner for treatment.
Complications of pulpitis
As a result of a tooth fracture or untreated caries, the enamel cracks. Saliva, bacterial plaque, and food particles penetrate into the resulting defects. Inside, all this is formed into a mass, which becomes an ideal substrate for the growth of microflora. Tissue infection begins.
Gradually, inflammation moves along the nerves, through the capillaries, goes beyond the dental canals, and spreads throughout the body along with the bloodstream and lymph.
Typical complications of advanced pulpitis:
- Removal of a tooth;
- Apical periodontitis develops when infection invades periodontal tissue;
- Inflammation of the soft tissues near the diseased tooth with swelling and pain – periostitis. The common name is flux. Often the complication becomes the subject of cartoons and causes smiles. In reality, there is nothing funny here at all;
- If you ignore inflammation and try to treat yourself, there is a high risk of developing phlegmon - a dangerous aggravation of the problem. Pus breaks out and spreads beyond the affected area. Surgery required;
- Maxillofacial abscesses. Unlike phlegmon, they form clear boundaries;
- Blood poisoning, otherwise known as sepsis. A terrible disease, treatment is long and difficult, death is likely;
- Amyloidosis is the process of intoxication of the body with toxic products from the source of infection in the tooth. The result is malfunction of vital organs. An extreme case is complete failure of a body part.
People experience illnesses individually. If the first organism resists for a long time and secretly, the second will develop an instant and severe reaction. Pulpitis means that two of the most important systems of the human body are already affected - the circulatory and nervous. Do not lead to pathology; try to treat caries in a timely manner.
Treatment methods for periodontitis
The treatment method for periodontitis will be selected based on the characteristics of the clinical case. Methods that are used to treat inflammation in the periodontium can be divided into two groups - conservative and surgical. However, the goal of any treatment method for periodontitis will be to obtain the following results: elimination of all tissues that are affected by the infectious process, elimination of inflammation, restoration of healthy tissue, as well as restoration of the aesthetics and functional qualities of the dental unit.
To accurately diagnose, determine the form of periodontitis and select the optimal treatment method, a number of measures are carried out: a thorough examination of the patient’s oral cavity, radiography, CT, OPTG.
Therapeutic treatment of periodontitis: features and key stages
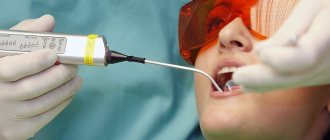
Therapeutic treatment of periodontitis is a complex, lengthy process and associated with certain difficulties. In particular, a fairly large amount of time is required to restore periodontal tissues damaged by inflammation; competent and high-quality treatment of dental canals will not be easy.
The complex of therapeutic measures for the treatment of periodontitis includes the following procedures:
- Drilling the diseased tooth to gain access to the canals;
- Work on expanding channels to a certain size, allowing for their high-quality processing;
- Painstaking cleaning of the canals from damaged and destroyed tissues;
- Flushing the canal cavity with antiseptic agents;
- Placement of antibiotic-impregnated linings into the tooth canals;
- Permanent canal filling;
- Restoration of the natural tooth crown.
Treatment of periodontitis may require repeated changes of medications in the canals, and therefore the patient is given a temporary filling for this period. After the inflammatory process can be completely eliminated, the tooth canals are filled with gutta-percha and a permanent photopolymer filling is placed on the tooth.
IMPORTANT: The more stages there are in the therapeutic treatment of periodontitis, the higher the price of the service as a whole will be.
When carrying out filling, it is extremely important to achieve complete sealing of the dental canals and all branches coming from them. After endodontic treatment of periodontitis, the doctor may additionally prescribe a number of medications for the patient to take that will help accelerate tissue recovery. Endodontic treatment of periodontitis can be supplemented by a number of physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UHF;
- Laser and magnetic therapy;
- Ozone therapy.
The need for additional physiotherapeutic procedures is determined by the dentist when drawing up a plan for the therapeutic treatment of periodontitis and based on the diagnostics performed and the characteristics of the clinical case.
Second visit
After a couple of days, the doctor at the appointment assesses the patient’s condition - whether there are any swellings, whether the temperature has risen, whether the lymph nodes are inflamed, etc.
If no complaints are received, the doctor removes the temporary filling and turundas with cresophen, and then obturation of the root canals with temporary filling material. Its task is to help the bone tissue partially regenerate in the place where the inflammatory process was noted at the root apex. In addition, the substance sanitizes and disinfects the tubule cavity. Calcium hydroxide-based pastes are mainly used as temporary fillings: Calasept, Metapex.
From above, all this is covered with a new non-permanent filling.
Operative (surgical) treatment of periodontitis
Surgical techniques for the treatment of periodontitis are used if conservative therapy turns out to be ineffective or initially inapplicable due to clinical reasons. In 90% of cases, doctors try to perform tooth-preserving operations, that is, resort to a type of intervention that will eliminate inflammation, but at the same time preserve the dental unit. These types of interventions in the treatment of periodontitis include:
- Resection of the root apex. It is indicated for use when cysts and granulomas are identified during diagnostic procedures. The essence of the operation is to remove all infected tissues along with the apical part of the tooth root;
- Cystectomy. During this type of intervention in the treatment of periodontitis, the formed cyst or granuloma is removed, and the apical part of the root is excised, in which inflammation has caused pathological tissue changes.
After the operations, treatment and hermetically sealed dental canals are also carried out.
Another surgical method for treating periodontitis is an operation to amputate the apex of the tooth root. But it is possible only on multi-rooted teeth and taking into account the healthy state of the other roots of the dental unit. During intervention for the treatment of periodontitis, the crown part of the tooth can be preserved completely or partially removed. In our dental clinic in St. Petersburg you can receive services for safe and painless treatment of periodontitis. At all stages of the treatment process, dental specialists will use ultra-modern dental techniques and instruments to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment as a whole and guarantee the absence of complications.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in teeth with previously treated canals
Retreatment of tooth canals with periodontitis is an extremely difficult undertaking, during which the dentist will have to thoroughly clean the cavities from filling material. Only a truly competent and experienced specialist can perform such work in the treatment of periodontitis, because in the course of it it will be necessary to use different methods of cleaning the canals (using specialized reagents and files) and act in fact “blindly”.
After the tooth canals are completely freed from gutta-percha, they need to be thoroughly sanitized. At this stage of treatment of periodontitis, the care and literacy of the dentist are also important, because sanitary treatment of the canal cavities should ensure the complete exclusion of recurrence of inflammation in the future.
Typically, the canals for periodontitis are washed with a specialized solution, after which the doctor places medicine in their cavities and closes the tooth with a temporary filling. In the treatment of periodontitis, a pause is made, which is necessary for the complete cessation of the inflammatory process and the beginning of regeneration of tooth tissue. As soon as the desired effect in the treatment of periodontitis is achieved, secondary permanent filling of the canals and restoration of the tooth crown with a photopolymer filling are performed.
Methods for filling root canals
There are several basic techniques used in the treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis:
- One-paste method
The channel is filled with a plastic, subsequently hardening material. The method is outdated and gives a large number of complications. - Single pin method
First, the root canal is filled with a special paste, and then a gutta-percha pin is inserted into it. The percentage of complications is lower, but this method is also gradually being phased out. - Filling with “thermophile”
A more modern method, also based on the use of an initially plastic material - heated gutta-percha. The fluid state allows the material to densely fill all cavities inside the canal, which significantly reduces the risk of complications. The disadvantages of the method include high requirements for the doctor’s qualifications and relatively high cost. - Gutta-percha condensation method
This method ensures even more dense filling of the canal lumen with filling material. Currently, the method is one of the most common. The procedure is performed in several stages.
Traditional medicine: can its recipes help with periodontitis?
It is important to understand that periodontitis is a serious disease that affects the entire body as a whole and is fraught with serious complications. Its treatment cannot be carried out at home, since the infectious process occurs deep in the root canals of the tooth and it is important to thoroughly clean them of all tissues affected by inflammation. Only a doctor can do this - in a clinical setting and using a specialized instrument.
Remedies from folk recipes will be absolutely useless in the fight against periodontitis and, moreover, they can aggravate your condition. For example, hot compresses for periodontitis can provoke an acceleration in the rate of spread of inflammation.
Herbal decoctions and tinctures are powerless against periodontitis. They can only temporarily make the pain less pronounced, but in this case the inflammation will actively develop, affecting an increasingly larger area of tissue. If you are bothered by even a minor toothache, a reasonable solution would be to immediately consult a dentist. Remember that it is not always possible to save a tooth with periodontitis (especially with an advanced stage of inflammation).
Periodontitis treatment time
If you have been diagnosed with periodontitis, you should prepare for a lengthy treatment process. You will have to visit the dental clinic more than once, and in addition, strictly follow all the recommendations that the specialist will give you during the treatment process. Violation of medical recommendations can lead to complications that will increase the complexity and duration of periodontitis treatment. In the simplest case, when treating periodontitis, you will have to visit the dentist two or three times; treatment will be longer if it is supplemented by physical procedures and will require repeated placement of antibiotics into the tooth canals and consultation with highly specialized specialists. Remember that high-quality treatment of periodontitis will imply mandatory control photographs after each stage.
Radiography will allow you to track the positive changes achieved after certain procedures for the treatment of periodontitis, and evaluate the quality of canal filling. Only this approach guarantees a stable and positive result in the treatment of periodontitis and eliminates relapses of inflammation and complications.
How to check the quality of canal filling?
Quality control of fillings is an integral part of the treatment process and is performed at every stage. X-ray control is especially important after filling. It allows you to identify areas of insufficiently dense obturation, detect pins or sealer residues protruding beyond the root apex, identify fragments of files and other defects. All this can lead to severe pain after treatment, as well as to the development of complications.
The x-ray image should clearly show the canal cavities, densely filled with filling material. There should be no enlightenment. The filling material should reach the very top of the canal.
Following simple rules of prevention also helps to avoid complications. Pain after treatment can last from several days to a month and does not always indicate ineffectiveness or low quality of treatment. However, if they appear, you should consult your dentist. Also, after treatment, it is recommended to abstain for some time from physical activity, drinking alcohol, and eating hot and spicy foods.
To prevent pulpitis, carefully monitor your oral hygiene. Use only professional products. If during the day you do not have the opportunity to brush your teeth after eating, use Asepta Fresh mouthwash. It disinfects the oral cavity, effectively fights caries, and normalizes acidity.
Periodontitis treatment price
The cost of periodontitis treatment is always calculated individually, because it consists of a number of factors. The price of the service will depend on the set of diagnostic measures that are carried out not only at the beginning of treatment, but also at its intermediate stages. The price of the service will be influenced by the form of the disease, method of treatment, additional procedures, equipment and drugs that can be used during its course.
If you want to know the price of periodontitis treatment or make an appointment with Uni Dent dentists, just dial our contact phone number!