From this article you will learn:
- why does an abscess appear on the gum,
- what to do when the gums fester.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
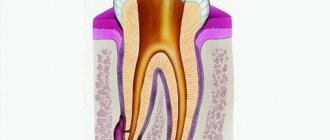
A prerequisite for the appearance of gum suppuration is the presence of a source of infection. Most often, this source is an infection in the root canals of the tooth, which develops there either due to poorly performed root canal filling, or due to the patient’s untimely treatment of dental caries or pulpitis. And in this case, the dentist will diagnose you: “Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis.”
The second main cause of gum suppuration is the formation of deep periodontal pockets during periodontitis. Such pockets contain a large amount of infection and can cause the formation of a purulent abscess in the gum. The choice of treatment method will depend on the cause of gum suppuration in your case. Therefore, you first need to determine why pus appeared in the gums, and only then begin treatment.
Content:
- Why does pus come out of the gums?
- Signs indicating a problem
- Causes of pus discharge from the gums
- How do dentists treat pus in gums?
- Additional procedures to help get rid of purulent gum disease
- Recovery after treatment
- Is it possible to cure an abscess at home?
The presence of purulent exudate in the gum tissue is a dangerous symptom that should never be ignored. If it appears, you should immediately consult your dentist. Otherwise, the inflammatory process will progress, which will lead to damage to neighboring structures and premature tooth loss.
Why does pus come out of the gums?
Suppuration is the result of infection penetrating into the deep tissues of the oral cavity. This is a kind of protective reaction of the body aimed at cleansing the affected area from a dangerous viral, bacterial or infectious agent.
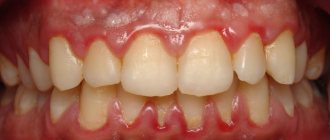
As soon as pathogenic microflora begins to spread inside the gums, blood circulation there increases. Due to this, immune cells are faster delivered to the dangerous focus. As a result, the tissues become red, swollen, and painful to the touch.
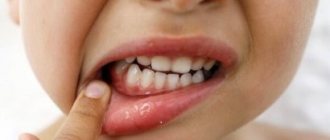
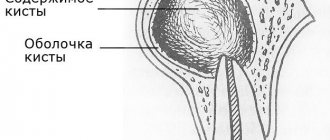
Pus in the gums is dead microbes and dead immune cells. As its volume increases, an abscess forms.
Signs indicating a problem
A purulent neoplasm is difficult to miss. A person complains about:
- discomfort in the affected area, which intensifies with palpation, pressure, chewing food, and talking;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth (caused by periodic discharge of blood and necrotic masses from the abscess);
- tissue swelling;
- swelling of the cheek (indicates that the inflammation has gone very far and emergency dental care is required).
If the patient continues to ignore the symptoms, his health will worsen. His body temperature will rise, headaches and weakness will appear.
A violent inflammatory process will disrupt the dentogingival apparatus. Then the unit will become mobile and can fall out at any moment.
Symptoms of gum abscess
Gingival abscess manifests itself in two types of symptoms: local and general clinical. Local symptoms are caused by reactive manifestations in the area of inflammation. The appearance of general symptoms is associated with intoxication of the body. The main symptomatic manifestations of the disease:
| Local inflammatory reaction | Symptoms of intoxication |
| pain when pressing on the affected unit; hyperemia of the gums over the area of inflammation; swelling of the tissue around the abscess; smell of rot from the mouth; violation of facial configuration; formation of a tubercle with purulent contents near the tooth; increased mobility of the diseased unit; darkening of tooth enamel; enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. | hyperthermia; dyspnea; cranialgia; violation of orientation in space; tachycardia; aching joints; lethargy; drowsiness; irritability. |
The leading symptom of an abscess is pain. It can be fixed only at the point of inflammation, but more often the discomfort radiates to the head, auricle, eye socket, neck, and neighboring segments. Soreness has different intensity, character (sharp, shooting, dull), occurs periodically in response to stress factors, or is constantly present.
Causes of pus discharge from the gums
The reasons for this phenomenon may be different. Let's name the most common ones:
- Periodontitis. The tip of the tooth root becomes inflamed. This is possible with advanced caries, poorly performed filling, or progressive pulpitis.
- Periodontitis. The dentogingival junction is damaged due to insufficient tissue nutrition, genetic predisposition, and reduced immunity. Food debris begins to accumulate in the resulting pockets, which leads to inflammation and suppuration.
- Gingivitis. Inflammatory gum disease. Bacteria begin to actively multiply due to poor hygiene and traumatic injuries. They penetrate the gums and cause suppuration.
- Periostitis. Chronic or acute inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw. It is the result of the spread of a dangerous infection through the bloodstream or through the lymph. It can also be a consequence of deep caries.
- Osteomyelitis. A purulent infectious-inflammatory process that covers various structures of the jaw and leads to necrosis of many tissues. Osteomyelitis can develop due to mechanical damage, spread of infection through the blood and lymph.
- Pericoronitis. Most often it has to do with a wisdom tooth that has not fully erupted. A voluminous hood of inflamed gums is formed over the unit, under which food accumulates. It serves as an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Therefore, in the absence of adequate treatment, very soon a person notices that he is secreting pus.
As practice shows, most often pus in the gums appears due to cuts, injuries, or wearing incorrectly selected dental prostheses. Chronic gum damage triggers an inflammatory process that is difficult to stop. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to your oral health. If an inflammatory focus appears, it must be sanitized immediately. This will avoid many complications.
Clinical trials
According to the results of clinical trials of the ASEPTA rinse after 3 weeks of use of the rinse, gum bleeding is reduced by 28.3%, inflammation is reduced by 32.3% and the hygienic condition of the oral cavity is improved by 33.5%.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Elena Ivanovna Fuchs, assistant at the department of therapeutic and pediatric dentistry. State budgetary educational institution of higher professional education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. Thermal Power Plant, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist A.A. DOMORAD, O.M. YAKOVLEV SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, Department of Microbiology
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, PhD, dentist. Department of Dentistry FKPV GOU VPO "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"
How do dentists treat pus in gums?
Typically therapy includes the following steps:
- Survey. The doctor finds out when the purulent neoplasm appeared, how quickly it grows in size, and how it manifests itself.
- Examination of the oral cavity. The doctor studies the location of the abscess, its color, shape. If necessary, gives a referral for an x-ray of the affected side of the jaw. X-rays are needed to understand the condition of the internal structures.
- Removing food debris, stone and soft plaque from teeth and gums. Sanitation of the oral cavity before treatment of an abscess.
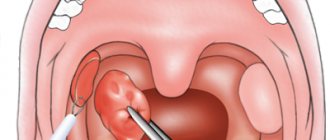
- Opening of a purulent neoplasm. Performed under local anesthesia. First, the patient is given an injection of anesthetic, and then the affected area is carefully dissected. As a result, purulent masses come out.
- Installation of drainage. To prevent exudate from beginning to accumulate in the gums again, a small drainage tube is installed into the incision. You need to walk with her for several days.
A mandatory stage of treatment is anti-inflammatory therapy. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and mouth rinses to prevent the recurrence of a purulent lesion.
It happens that pus is released when pressing on the tooth. In this case, there is no “bump” on the surface of the gum. In this case, the above scheme will be ineffective. The doctor removes the filling (if it was installed), cleans the dental canals and washes out all purulent accumulations. Places a special medicine and closes it with a temporary filling.
On the appointed day, the patient must come for a follow-up appointment. Then the doctor will assess whether the inflammation was removed. If yes, then he will replace the temporary filling with a permanent one; if not, he will re-place the anti-inflammatory composition in the canals and re-install the temporary filling material.
What to do if the tooth is not completely removed?
If a piece of a tooth or part of a root remains after removal, and the doctor did not notice it, then sooner or later the symptoms described above will appear. What to do if a tooth is pulled out and a fragment remains? First of all, there is no need to panic. A regular x-ray can detect the presence of foreign bodies, including remaining fragments. In most cases, tooth removal does not take much time and is performed using standard surgical techniques. If the case is complex, an incision of the mucosa may be required. Today there are advanced surgical treatment techniques, such as laser surgery. Thanks to this, in difficult cases it is possible to reduce the invasiveness of the intervention. Be that as it may, for a qualified dentist, coping with the complication will not pose any great difficulties. The main thing is to contact him in time.
Many people are interested in whether the tooth root can come out on its own. If after removal part of the root remains in the gum, then you definitely shouldn’t count on it. Sometimes a tooth fragment may come out on its own, but there is no need to hope for this either. Moreover, you should not try to remove a tooth fragment from the socket yourself. You will most likely hurt yourself even more. If you notice remains of a tooth in the hole, go to the doctor immediately.
Recovery after treatment
After opening and draining the cavity, the body has to mobilize all its resources to speed up the healing process. To help him, it is important:
- comply with all medical prescriptions;
- take medications prescribed by the dentist;
- Healthy food;
- avoid stressful situations;
- dress according to the weather;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- take a good vitamin and mineral complex;
- carefully monitor oral hygiene, include dental rinse, floss, and irrigator in your daily care.
Is it possible to cure an abscess at home?
Doctors do not allow you to open a flux tumor on your own. This may lead to the addition of a secondary infection. If you are unable to visit a dental clinic in the coming days, you can alleviate the uncomfortable symptoms with the help of:
- Therapeutic and prophylactic rinses. When performing them, you need to use water at room temperature, salt and soda, and pharmaceutical antiseptics.
- Apply cold compresses to the sore cheek.
Under no circumstances should you heat the inflamed area. This will lead to activation of purulent-necrotic processes and the spread of infection, which is very dangerous.
Other situations
Sometimes after tooth extraction a phenomenon called ecostosis occurs. After tooth extraction, the edge of the gum settles, causing part of the bone to protrude to the surface. Many patients may mistake a piece of bone for a tooth fragment. Ecostosis can be easily eliminated using the usual grinding procedure, so there is practically nothing to worry about in this case. Sometimes part of the bone material may come out of the hole, which is replanted with the patient before implantation if the height and volume of the native bone is not enough. Sometimes small pieces of bone material may come out through the sutures, but this is also not considered a serious complication.