31.10.2019
Many people are familiar with the procedure for removing the dental nerve (depulpation), which is used in case of inflammation in the pulp, acute pain and other indications. If you do not perform this manipulation, you can lose the entire tooth. But you need to understand that to save a tooth, removing the nerve alone is not enough. You need to carefully monitor your oral hygiene, prevent chips and cracks, and visit your dentist regularly. Read on for more details about the features of pulpless teeth. Let's consider how long a tooth lives without a nerve, and how to extend its “life” so that the tooth can last as long as possible without a removed nerve.
Nerve function and reasons for its removal
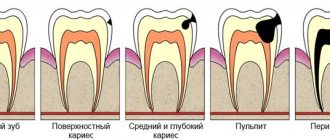
Dental nerve endings perform several functions: they respond to external stimuli (cold, hot, spicy, sour) and protect elements from pathogenic microorganisms. It is believed that teeth lacking pulp are more vulnerable to caries and other destructive processes.
Often, elements devoid of nerves may also differ in shade from healthy teeth, since they tend to darken. Because of this, the pulpless elements are called “dead” in another way. This process is due to the fact that the tooth is deprived of blood supply and does not receive the necessary minerals from the body.
It is worth considering in more detail the situations in which dentists recommend resorting to tearing out the tooth pulp and subsequently filling it with composite materials. In mild forms of caries, only the upper part of the tooth – enamel and dentin – is affected. In this case, doctors remove the damaged layers of the tooth without affecting its nerve endings. In advanced forms of the disease, the nerve endings of the tooth (pulp) may be damaged; in this case, dentists remove the tissue completely or only part of it.
The indication for depulpation is periodontitis. In this case, it is impossible to restore the health of the tooth without removing the nerve endings in it. Inflammation of the pulp is also possible if the dentist did not properly clean the dentinal tubules of the tooth or made mistakes when filling it. This type of problem in dentistry is called “drug-induced pulpitis.”
Other indications for depulpation include:
- extensive tooth destruction (more than 2/3 of the crown);
- prolonged aching pain in the element;
- the presence of stones in the root canals of the tooth;
- chipping or damage to the bone tissue of the elements as a result of consumption of hard foods or any trauma.
Nerve endings can also be removed in those elements that appear healthy. Pathological processes do not always begin in the visible part; in some cases, caries and inflammatory processes are localized in the deep layers, under the crown.
Why do you need to remove the pulp?
We talked about the main reasons why nerve inflammation occurs, but most often pulpitis becomes a consequence of advanced caries. Therefore, it is very important to visit a dentist, even if nothing bothers you. The decision to remove the pulp is made in the following situations:
- pulpitis has passed into the stage of periodontitis, when inflammation affects the whole complex of connective tissue in the tooth;
- large area of carious lesion;
- the infection spreads through the apex of the tooth root;
- the appearance of unbearable, prolonged pain;
- spread of infection under an artificial crown;
- consequences of improper treatment.
The nerve can be removed either completely or partially, it all depends on the degree of tissue damage. Depulpation will prevent the spread of the inflammatory process under the crown and preserve the natural tooth, which is a priority for endodontic therapy.
Characteristics of a pulpless tooth
The first problem that people encounter after depulpation is the fragility of the element. After the intervention, it is not recommended to chew hard and rough food on the problematic side, as this may cause breakage of the segment. After depulpation, many doctors advise patients to resort to restoring the problem unit using crowns or prosthetics. After restoration, it will be possible to preserve the integrity of the “dead” element for many years. With successful treatment and restoration, the tooth can last more than 10 years. Otherwise, the “dead” element will collapse within 1–2 years.
The service life of a pulpless unit largely depends on the quality of the dental canal filling by the dentist. Mistakes made by the doctor during the procedure can lead to various complications: dental cyst, fistula or gumboil. In this case, the unit cannot be saved. In order to minimize the risk of unpleasant consequences, the doctor must follow a clear algorithm for performing work to remove nerve endings. The patient, in turn, must regularly carry out hygiene measures (2 times a day) and visit the dentist at least once every 6 months.
Contraindications
Before treatment, the doctor must collect medical history data, that is, all information about the patient’s health status. Contraindications to nerve removal may include:
- pregnancy (first and last trimesters);
- hepatitis, HIV infection;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa.
It is worth noting that in case of acute pain, some contraindications can be considered relative: the decision is made by the dentist.
Problems arising after depulpation
The first problem that patients encounter after removing the nerve from the problematic element is blackening of the enamel, which is a serious aesthetic defect. The reasons for crown darkening include the following factors:
- improperly performed dental work;
- insufficient intake of microelements;
- the use of dental instruments containing silver or resorcinol - formaldehyde during the intervention;
- damage to the blood vessels of the element and further disruption of blood supply.
A tooth that has turned black after depulpation.
Another problem after the intervention, which is often noted by patients in dental clinics, is pain in a tooth without a nerve. Discomfort may occur when pressing on the unit, tapping on it, or biting into food. The opinion that a “dead” tooth cannot hurt is considered erroneous. The cause of discomfort may be previous illiterate treatment, inflammation of periodontal tissue, etc. In such cases, the patient should immediately consult a doctor in order to identify the cause of the problem.
In a normal state, the “dead” element continues for another 7–10 days after depulpation. Sometimes the cause of discomfort is not the unit that has lost its nerve endings, but the healthy neighboring one. It will seem to a person that the cause of the problem is a previously treated tooth, since toothache is sometimes vague and difficult to determine its exact location. Sometimes pain is associated with damage to the gums during depulpation of elements that react to cold or hot food.
Pain immediately after dental procedures is normal. The main thing is that the intensity of the discomfort gradually decreases. Discomfort disappears, as a rule, 3 weeks after removal of the nerve endings from the tooth. An increase in pain symptoms is a sure sign of the development of infectious complications. In this case, the patient should contact a highly qualified dentist as soon as possible.
Why was the nerve removed, but the tooth hurts when pressed?
Why else can a filled tooth hurt? Some reasons for the problem include:
- Incomplete removal of nerve endings, and, as a result, preservation of their sensitivity;
- Poor quality canal filling. If the filling material is not placed tightly, pores remain in the tooth canals, in which pathogenic flora multiply over time. Bacteria destroy the tooth and the soft tissue located next to it. Which leads to pain.
- Doctor damage to the root. As a result of the error, inflammation often develops in the tissues located next to the element.
- Poor quality treatment of the tooth and its canals with antiseptic agents.
- Allergic reaction to components of composite materials.
- A cheap composite that will deteriorate over time.
- Foreign body in the tooth cavity. As a result of dental procedures, fragments or microscopic parts of instruments may remain in the dental tissues. Over time, this leads to severe pain in the jaw and the development of serious complications.
And also the “dead” unit is characterized by increased fragility. Cracks invisible to the naked eye may form on its surface. Because of them, a person feels discomfort while chewing food.
Procedure technology
The depulpation procedure can be carried out in three ways:
- vital extirpation – removal of the pulp occurs completely and is carried out under local anesthesia. The procedure involves removing the nerve in just one session, but requires careful examination;
- Devital amputation is the use of a special drug to mummify part of the nerve. It involves applying a special paste that leads to pulp necrosis. This technique is used extremely rarely, since it can cause a number of complications associated with necrotic processes in the nerves. Can only be found in low-budget dental offices;
- diathermy - necrosis of the nerve occurs by applying a current discharge, after which the dead nerve is removed. An electrode is inserted into the pulp area, passing a current through itself, which not only kills the nerve, but also cauterizes the wound.
After the depulpation procedure, you may experience pain for several days that occurs when you squeeze your jaw or eat hot or cold food (drinks). This pain does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Lifespan of a tooth without a nerve
How long does a tooth live without a nerve? The duration of operation is influenced by several factors:
- Quality of oral care after the intervention. Typically, the dentist gives the patient a number of recommendations that he will need to adhere to for 1-2 weeks. All these recommendations are aimed at minimizing the negative consequences after pulp removal. Typically they include: avoiding solid and rough foods; temporary exclusion of coloring foods and drinks from the diet; thorough oral hygiene using brush paste and dental floss; limiting excessive physical activity.
- Food quality. Solid foods consumed immediately after the element is sealed may cause the seal to fall out. In addition, they often cause chips and cracks in the enamel of the problem unit. As mentioned earlier, the “dead” segment is more vulnerable to negative external factors.
- The effect of the treatment.
- Regularity of patient visits to dental clinics.
The patient can independently make the tooth last longer; to do this, you need to follow some rules:
- include in your diet more foods containing phosphorus, calcium and other microelements necessary for teeth;
- take vitamin complexes during the off-season;
- Avoid using whitening toothpastes;
- Avoid using hard bristle brushes.
If the sealed element is destroyed as a result of the inept actions of the doctor or the patient himself, then it will no longer be possible to restore it. The only way out of the situation in this case is to remove the “dead” tooth.
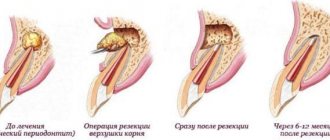
Stages of treatment
- Diagnostics . Before treatment, the doctor conducts an examination and takes an x-ray. It will show the structure of the root canals, their number, the depth of the carious cavity, and the condition of the tooth. Sometimes treatment is impossible and the tooth needs to be removed.
- Anesthesia . To numb the tooth and provide a comfortable treatment, local injection anesthesia (injection) is performed. In case of severe pain and severe inflammation, the gums are treated with an anesthetic gel or spray before the injection.
- Installation of insulation (cofferdam) . To isolate the canals from saliva and bacteria, a rubber dam is used - this is a latex scarf that is placed on the tooth being treated. Thanks to the rubber dam, sterile conditions are created for placing fillings and treating root canals.
- Treatment of hard dental tissues . All carious and destroyed tissues are removed, and access to the pulp chamber is created. A water-cooled drill is used to prevent surfaces from overheating. All fragile tooth walls are also removed in order to initially create good conditions for future restoration.
- Nerve removal . It is performed with small sterile instruments that look like needles. In some cases, a special apparatus is used: a tip with rotating instruments. This happens painlessly, since anesthesia was previously administered.
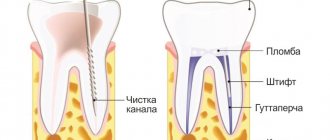
- Root canal treatment . The doctor cleans the canals, rinses them with antiseptic solutions, and measures their length. This is necessary in order to eliminate all infectious particles from the canals.
- Temporary filling . It is installed when it is impossible to fill the root canals immediately on the first visit. This also allows you to monitor the patient’s condition (after acute pain).
- Canal filling . Occurs on the first or next visit. A method for filling the canals is selected, then a permanent filling is placed in aesthetic dentistry.
- Control shot . After filling the canals, it is important to make sure that they are sealed tightly, to the top, and that there are no voids left. If the voids remain, re-inflammation will occur.
Methods for restoring the aesthetics of a pulpless unit
Darkening of tooth enamel is an aesthetic problem that not all patients can accept. Dentists offer a number of methods aimed at restoring the external characteristics of a “dead tooth.” What to do in this case? There are 3 main methods for restoring blackened enamel: endobleaching, installation of veneers and crowns. Let's consider each of the listed methods in more detail.
Endobleaching
The method involves introducing whitening agents into the upper layers of the tooth. Typically, dentists use sodium perborate for the procedure. Endo-whitening is possible not only to restore the aesthetics of a “dead” tooth, but also to lighten the enamel tone in healthy teeth.
A healthy element loses its original external characteristics due to a number of factors:
- pulp damage followed by hemorrhage;
- installation of a composite, which began to color the crown of the tooth in a pinkish tint;
- darkening of the crown as a result of silvering of the tooth.
Endobleaching is performed according to the appropriate algorithm:
- Performing professional cleaning to remove hard and soft dental plaque.
- Removing old fillings.
- Injection of a bleaching agent into the cavity of the problematic element.
- Installation of a temporary filling.
The procedure is performed every week until the tooth becomes similar in shade to the rest of the row. The minimum number of visits to the dentist is 4–5 times. The permanent composite material is installed 10 days after the last gel injection procedure.
The results of endobleaching last for an average of 2–3 years. After this time, the procedure is repeated again in cycles. Patients are not recommended to undergo more than 3 courses of whitening due to the risk of crown breakage.
This method has a number of disadvantages:
- Impossibility of predicting the result of restoration.
- The impossibility of completely restoring the enamel due to its dullness.
- There are a number of contraindications to the procedure: allergic reactions to the injected bleaching agents; pregnancy; cracks in the enamel; pathologies of the endocrine system.
Veneers
The structures are thin linings made from several types of materials - ceramics and composites. Ceramic plates are often made from zirconium dioxide or porcelain. Porcelain veneers are identical to the enamel color of healthy units. This is achieved due to the transparency of the composites used.
Composite veneers are more affordable, but their service life does not exceed 5 years. This is due to the fragility of the products and their rapid loss of their original appearance.
Installation of veneers is also carried out in stages:
- Selection of the optimal shade of the plates.
- Grinding of the top layer of enamel for better attachment of the product to the tooth. During the procedure, about 0.5–1.5 mm of enamel is ground off.
- Manufacturing of crowns on special machines using 3D technologies. Products are produced in dental laboratories using impressions previously taken from the patient’s dentition.
- Fixation of finished structures using a special adhesive.
There are contraindications for installing veneers:
- bite pathologies;
- enamel abrasion;
- high risks of dental injury;
- bruxism;
- element wobble.
The most significant disadvantage of veneers is the need to wear them throughout your life. This is due to the fact that the teeth on which the onlays are installed are subjected to preliminary grinding and can no longer be restored.
Crowns
Dentists consider this method of restoring the appearance of a “dead” tooth to be preferable. This is due to several reasons:
- Increasing the strength of a problem unit by 30–60%.
- Possibility of preserving the root during the procedure.
- Possibility of ensuring uniform load on all areas of the jaw.
- Protection of tooth tissues from external negative influences.
- The disadvantage of the procedure is the need to grind the top layer of the tooth.
All methods of restoring a “dead” tooth have a negative impact on its health. In order not to resort to the restoration procedure, it is necessary to follow a number of preventive rules. These include: timely visits to the dentist; competent choice of dental care products; daily hygiene measures; flossing after meals; high-quality cleaning of the surface of the tongue; timely change of toothbrush (once every 3 months).
What causes complications?
After root canal filling, complications sometimes arise such as:
- the canals are sealed loosely, not completely (voids remain): re-treatment of the canals is required;
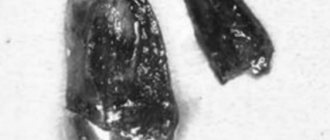
- broken instrument: during operation, the instrument may break off and remain in the canal (for example, in curved and curved canals);
- root perforation: when the tooth root is injured during work;
- removal of filling material beyond the root;
- repeated inflammation, when not the entire nerve was removed and the infection remained;
- bleeding from root canals.
Our Otradnoe Dental Center provides highly qualified dental care, including nerve removal, which is absolutely painless. Our doctors always conduct a thorough diagnosis and select appropriate treatment. Thanks to the extensive experience of our doctors, advanced equipment, and modern antiseptic solutions, treatment is carried out efficiently and without complications.