Caries is the most common disease worldwide. Every person sooner or later experiences dental caries. The disease has several stages of development and at the initial stages of the pathological process it appears as a white spot. Treatment of caries in the stain stage can be treated therapeutically, that is, without preparing the tooth. There are several methods to stop the destruction of enamel and eliminate the lesion. In order to carry out treatment in a timely, painless and quick manner, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination by a specialist every 6 months.
Causes of caries in the spot stage
There are quite a lot of theories about the occurrence of caries and the factors that cause the pathological process. Nowadays, experts adhere to the modern theory of origin. Under unfavorable conditions in the oral cavity, an acid-base imbalance occurs on the surface of the teeth. Dental deposits in the form of plaque and stone contain pathological microorganisms and food debris. Microbes process simple carbohydrates and release acids that damage the enamel structure.
At the spot stage, the enamel loses trace elements in the subsurface layer and the lesion looks like a white spot. In the absence of treatment and good hygiene, further tissue destruction occurs and a cavity forms in the tooth. In a chronic course, pigmentation of the spot may occur, then a defect appears in the form of a brown spot.
Factors that contribute to the occurrence of caries:
- Poor or insufficient hygienic care of the oral cavity. The accumulation of plaque on the dental surface is a favorable environment for the growth and development of pathological microorganisms. The infection causes various diseases of the oral cavity, negatively affects the body, and can cause exacerbation of chronic pathologies or decreased immunity. Dentists recommend regularly and thoroughly cleaning your teeth and tongue from plaque.
- Genetic predisposition. Some hereditary factors contribute to the development of the carious process: malocclusion, thickness and composition of saliva, thickness of enamel, etc.
- Disturbances in the process of formation of tooth germs. If during pregnancy there was insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals into the body of the mother and baby, then there is a risk of disruption of the normal process of formation of dental tissues. As a result, after teething, the baby’s teeth have a weak structure and are quickly susceptible to carious lesions.
- Diseases of the body. Some pathologies of the body can disrupt the composition and thickness of saliva. Oral fluid not only mechanically washes the teeth, but also participates in the process of enamel mineralization and neutralizes the effect of acids. In people with viscous saliva, the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity is often unfavorable; multiple dental lesions occur.
- Diseases of the salivary glands. Pathologies are accompanied by disturbances in the production, composition and functions of oral fluid and can, in combination with other factors, cause caries.
- Poor nutrition. An elementary lack of vitamins, minerals, and microelements in the diet can be the cause of pathology.
Stains on an adult's teeth
Chalky stains on the teeth of an adult can signal dental caries. Tooth decay destroys teeth if they are not carefully cared for. Then dietary fiber remains in the interdental spaces, which is a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes. They begin to secrete organic acids, which contribute to the leaching of calcium from the teeth.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by mild symptoms. The patient is not bothered by pain. The lesion rarely causes discomfort, soreness or unpleasant sensations when eating too spicy, salty, sour, or sweet foods. In the acute course of the pathological process, the formation of a chalky spot occurs at the initial stage; in the chronic case, a brown, dark spot occurs.
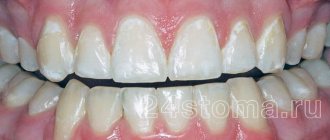
Caries in the spot stage often causes an aesthetic defect, especially if the lesion is located on the front teeth. A white spot can be localized in any part of the tooth, but is most often observed in the cervical area. Caries in the stain stage can be located under dental plaque, so it is detected during professional hygiene and preventive examination.
The mechanism of the problem
The health of dental units is ensured by a number of substances: these are vitamins A, C, E, D, group B, potassium, iron, iodine, magnesium, zinc and others. But the two main elements necessary to maintain the functionality of the jaw are calcium and fluoride.
Due to injury, work in a toxic industry, insufficient hygiene, or the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria on the surface of the enamel, it can lose useful compounds, which is why white spots, dots or stripes appear on the teeth (we will consider the result with a photo below).
Types of caries
Dental caries can be single or multiple depending on the number of teeth affected. There are different types of disease depending on the location of the lesion: cervical, approximal, fissure, contact. Depending on the course, the disease can be acute or chronic.
White spot
Caries at the white spot stage is an acute pathological process of tissue destruction, which is characterized by primary damage to the enamel. It is characterized by the progressive loss of minerals by the tissue, the formation of a chalky spot. Upon examination, the enamel appears white, dull, and is easily destroyed by various irritants.
The lesion can have different sizes, round or oval shape. If left untreated, the disease enters a chronic stage or progresses and becomes acute initial caries. In this case, the enamel is destroyed and a defect is formed in the form of a cavity (hole). It is very important to identify the disease in a timely manner and eliminate it, since at the stain stage the enamel can be restored naturally without filling.
Dark spot stage
Initial caries in a chronic course looks like a brown or dark (black) spot. With prolonged flow, pigments and dyes enter the subsurface layer of enamel, which stain the tissue. It is also possible to spread infection, microbial decay products into porous enamel. This contributes to the progression of the disease and complicates treatment.
The occurrence of pathology during the gestational period
Pregnancy is stress for the body and a time during which a woman requires an increased concentration of nutrients in food. The fetus needs minerals and vitamins for the correct formation of all systems and organs, so the expectant mother may experience a deficiency of them. It happens that foci of demineralization occur as a result of toxicosis, when, due to constant nausea, an overly acidic environment is created in the mouth.
If a white spot appears on a pregnant woman’s tooth, this means that it is worth visiting not only a dentist, but also a gynecologist to rule out metabolic disorders and alleviate unpleasant symptoms.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics is an important stage of the examination, with the help of which the doctor will accurately diagnose and determine the treatment method for caries in the spot stage. The dentist conducts a clinical examination, probing, thermal diagnostics and various diagnostic tests.
When probing, a rough enamel surface is determined. Thermal tests are negative, that is, pain does not occur when exposed to cold or hot water. In some cases, radiography is performed to rule out periodontal disease.
Samples are necessary to differentiate caries in the spot stage from hypoplasia, fluorosis and other non-carious defects. Before using dyes, the tooth is cleaned and any dental deposits are removed. The enamel is dried and a special preparation is applied (methylene blue or red, tropeolin, carmine). The stage of caries development and the boundaries of its distribution are determined by the degree of staining of the defect. Non-carious defects are not stained with dyes, so the doctor excludes them.
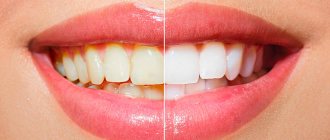
Treatment of chalky stains on teeth
Modern methods of treating white spots on enamel can stop the progression of the disease. The method of treatment depends on the factors that caused the disease.
1. If stains appear as a result of leaching of minerals, then tooth enamel is remineralized, which increases its resistance to various diseases. With this method of treatment, special pastes are applied to the teeth, which gradually build up a layer of minerals on the enamel and its destruction stops.
2. When fluorosis is diagnosed, teeth are treated with electrophoresis or application. Special dental trays are made for the patient, which are filled with medications and placed on the teeth.
How is caries treated in the spot stage?
Treatment of caries at the white spot stage is carried out using several methods:
- Remineralizing therapy. The most popular and effective treatment method, which is carried out at the stage of only the white spot. It involves saturating the affected tissues with microelements and minerals through the application of medicinal substances. Procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the course consists of 10-15 procedures.
- Fluoridation. Treatment consists of saturating the enamel with fluorides, as well as other microelements. Fluorapatites are more durable than hydroxyapatites, thus strengthening the enamel.
- Silvering. The method involves impregnation of carious lesions with a special preparation. During the procedure, silver ions are released, which settle in the enamel and stop the destructive carious process. Currently, the method is used extremely rarely, since it is not able to eliminate caries and stains the teeth in a dark color.
- The Icon technique is the most modern technology that has many advantages. It consists of layer-by-layer application of several drugs to the white spot. The products eliminate the porous layer, remove germs and seal the enamel. In this way, the cavity is filled without the use of boron. The treatment is very effective, painless and simple.
- Grinding. If other methods are ineffective, sanding the stain, usually brown, is used. The dentist, using a special bur or brush, carefully removes the affected tissue, followed by a course of fluoridation and remineralization.
- Classic filling. If treatment with other methods is impossible, filling is used. To do this, the doctor uses a small bur to remove the destroyed tissue, and then restores the tooth with filling materials.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. Physiotherapy procedures are used as complex therapy: electrophoresis and phonophoresis of calcium gluconate, phosphorus, sodium fluoride and other trace elements.
How is the treatment carried out?
Dental treatment consists of the following stages:
- Examination of the oral cavity, diseased tooth and collection of the patient’s medical history;
- Diagnostics, accurate diagnosis - clinical tests, x-ray diagnostics;
- Choosing the most appropriate treatment method;
- Professional teeth cleaning;
- Prescription of a course of applications, grinding or filling, depending on the method of treatment;
- Strengthening enamel and preventing hyperesthesia;
- Recommendations and advice to the patient after the procedure.
What does the pathology look like?
Initially, a very small speck is detected, which is difficult to notice with the naked eye. Over time, the focus of demineralization increases. The affected areas lose their natural shine because the crystalline structure of the substance covering the dentin is destroyed: it becomes porous, darkens and, due to a change in texture, turns into a reservoir for pathogenic microorganisms. At first, such microdestructions are painless, which indicates the need for visual control.
Most often, canines and incisors are affected, but sometimes pathology occurs on molars. It is important to notice it in time - the process is reversible with early diagnosis. If it is neglected, only radical methods of treatment will help (drilling, installing a large filling).
Treatment at home
Some procedures to eliminate the disease can be performed at home. To do this, you need to visit a specialist who will carry out professional hygiene and prescribe procedures. Treatment of enamel caries in the stain stage can be carried out using professional means: toothpastes, gels, applications. Very popular and quite effective are remineralizing gels (TOOTH MOUSSE, ROCS Medical Mineral and others), medicated toothpastes with a high content of fluoride and calcium (ROCS Medical, Elmex, Biorepair).
The products are used for cleaning teeth, and also in the form of applications - applied to the required surface for 5-10 minutes daily for 1-2 weeks. The active components of the products penetrate into the lesion, promote its remineralization - restoration of the structure with mineral substances.
Self-treatment of caries without consulting a specialist is most often ineffective; the carious process does not stop and affects the underlying tissues. The therapy procedure is quite serious and requires precise, correct implementation of the dentist’s prescriptions.
The use of traditional medicine, unfortunately, will not help eliminate carious defects. There are no herbs or remedies that can stop the disease. Some traditional medicine recipes have an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect, and therefore can only improve the general health of the oral cavity.
You may also be interested in
PARODONTAL
Mouthwash ACTIVE
Unique two-part mouth rinse reduces bleeding and inflammation
More about the product
PLUS
Professional toothpaste REMINERALIZATION
Restores tooth enamel, reduces hypersensitivity of teeth and gums and accelerates regeneration of the oral mucosa
Learn more about the product
Prevention of caries
The main method of preventing the disease is maintaining regular and high-quality hygienic care for the oral cavity. You should brush your teeth 2-3 times a day using selected and suitable hygiene products. Experts also recommend:
- Clean the interdental spaces daily with floss (dental floss);
- After each meal, rinse the mouth; if impossible, use chewing gum;
- If you have dentures or orthodontic structures, use an irrigator;
- Adhere to a proper healthy diet that will fully cover the daily dose of vitamins and minerals;
- Carry out professional cleaning and preventive examination 2 times a year;
- Treat chronic diseases of the body;
- Increase immunity.
We can conclude that treatment of caries in the spot stage is relatively simple, affordable and absolutely painless. It is important to diagnose and eliminate the pathological process in time, and for this it is necessary to examine the dentition yourself and visit the dentist every 6 months for preventive purposes.
Causes of problems in adults
White spots on tooth enamel can have different etiologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor examines and interviews the patient: he clarifies how oral care is carried out, whether there were injuries or other prerequisites for the appearance of foci of remineralization.
Initial caries
Whitish matte formations may indicate that the pathological process has begun and will soon make itself felt. The main reason for its development is poor hygiene (a person brushes his or her teeth irregularly, not thoroughly enough, or does not floss). The disease can also be caused by an excess of carbohydrate foods in the diet, especially fast carbohydrates (white bread, sweets). The resulting plaque becomes a breeding ground for bacteria and a good “future reserve” for the formation of caries.
If you start therapy at this stage, you can get by with non-invasive procedures, but the neglected process will lead to the destruction of dentin and, as a consequence, to pulpitis (a diagram of pulp damage can be seen in the illustration).
Traumatic impact
It is not so easy to injure the jaw in everyday life, but there is an exception: often the cause of white spots and stains on the teeth is wearing braces and splints. After removal of the orthodontic structure, foci of demineralization are found on the enamel surface; their occurrence could be avoided by observing dietary restrictions and hygiene.
The root cause of lesions under braces is the accumulation of food debris (especially acidic and carbohydrate-rich foods). This is why doctors advise regularly using an irrigator after installing jaw retainers. The surface areas under the locks are poorly moistened with saliva, which aggravates the situation.
Patients who have not been treated by an orthodontist also have white spots on their teeth. They are associated with a constant load:
- frequent consumption of seeds, nuts and other solid foods;
- bruxism (involuntary clenching of the jaws both during sleep and while awake).
Athletes involved in contact martial arts are also at risk.
Industrial or occupational fluorosis
He can be:
- streaked or spotted (mild form);
- chalky-mottled (moderate severity);
- erosive and destructive (severe course of the disease).
It occurs due to excess fluoride in the patient’s body and also leads to the appearance of chalky or transparent spots, specks and stripes on the teeth. The disease manifests itself in people who have worked for a long time in industries with high fluoride concentrations:
- glass, ceramic, cement;
- woodworking;
- oil producing
Workers of hazardous enterprises are recommended to regularly visit the dentist to identify pathology in the early stages and undergo timely treatment.
Hypoplasia
Many dental diseases in an already born baby are a consequence of the incorrect lifestyle of the expectant mother, lack of vitamins, and poor ecology.
White spots on a child’s baby (less often permanent) teeth often occur due to underdevelopment of the enamel. The foundation for its formation in children is laid during the period of intrauterine development - at the 7th week of pregnancy. Permanent incisors and molars are formed from 5 months to 7–8 years.
The most popular prerequisites for the spread of pathology:
- hypovitaminosis D in the mother;
- toxicosis;
- transferred rubella;
- frequent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- birth injury.
The problem cannot be prevented with a 100% guarantee, but you can make every effort to reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
Methods of treating pathology for initial caries
Inflammation at the initial stage is treated without the use of a drill and anesthesia: this is a painless manipulation that prevents damage to dentin, and the enamel can be considered healthy after treatment. In some cases, only the doctor at the appointment sees white spots on the teeth, so it is better to carry out these procedures immediately after identifying the problem.
Remineralization
Remotherapy is the process of artificially saturating tissues with micro- and macroelements. It is also indicated after prolonged use of splints or braces.
Calcium gluconate is most commonly used by dentists. A swab soaked in the solution is applied to the previously cleaned and disinfected jaw and left for exposure for several minutes. Sometimes the procedure requires repetition.
To ensure long-lasting results:
- brush your teeth with a soft brush and low-abrasive toothpaste;
- exclude too cold and hot, spicy, sour foods for a day or two.
Fluoridation
There is significantly more calcium in bone tissue than fluoride. But the latter plays a decisive role in the process of absorption of calcium compounds. The best results are obtained by alternating saturation procedures.
The doctor performs the operation manually using gel, varnish or tampons containing the desired element. After manipulation, it is not recommended to use medicinal pastes for 2 months.
Electrophoresis, infiltration, ozonation
These are more complex, but nevertheless non-invasive or micro-invasive processes that allow you to restore enamel that is beginning to decompose without pain relief using:
- microcurrents delivering the necessary substances (electrophoresis with calcium or fluorine ions);
- ICON lamps, thanks to them the desired material penetrates the pores of the surface, restoring the enamel layer (infiltration);
- gas that disinfects the entire dentition, ridding it of pathogens, followed by the use of a material that prevents the development of caries (ozonation).
The attending physician will offer the patient several options to choose from, and the final decision on what to do if white spots appear on the teeth is made jointly.
Sealing and silvering of enamel in children
Fissures are depressions and grooves on the chewing surfaces, thanks to which the jaws can grind food efficiently. Despite their usefulness, with insufficient care they become a source of inflammation and proliferation of microbes, especially in children who, due to their age, do not yet fully observe hygiene. Considering the fragility of the tissues of a child’s body, this leads to almost instantaneous development of caries. Sealing (filling) is done with a material similar to a filling material.
After manipulation, dentists recommend a coating - for example, with silver nitrate, a bactericide, which prevents further destruction of the units and keeps the oral cavity sanitized.
CLINICAL CASE
The spots are located almost symmetrically on the four upper incisors, as well as the upper first molars. The enamel in the area of the stains is smooth, the surface is without defects, the stains are not stained with low molecular weight dye, and their presence does not cause pain. The presumptive diagnosis is mild (spotty) systemic hypoplasia.
A detailed analysis of the surface of the teeth reveals a pronounced microrelief, deep atypical perikymatia, enamel ridges and pronounced lines of Retzius in the cervical and middle third. Optically, a fairly high level of transparency of the incisal edge with a distinct mamelon pattern is determined, despite the fact that the visual assessment is hampered by opaque white spots. A characteristic feature of this clinical case is the pronounced susceptibility of the teeth to intense dehydration.
Rice. 1. Initial situation.
Rice. 2. Initial situation.
Rice. 3. View of teeth after isolation.
Even after a short external examination, the hard tissues of the teeth began to noticeably change in color. It is reasonable to assume that the pathogenic factors that led to the occurrence of local changes in the form of white spots could also affect the structure of the tissues as a whole, making them less dense and, as a result, more hygroscopic.
The method of direct composite restoration with preliminary minimally invasive excision of altered tissues with a diamond bur under microscope control was chosen as treatment. Professional dental hygiene had to be carried out in a separate visit: during the cleaning process, changes associated with tissue dehydration turned out to be too pronounced, which made it difficult to select the shade of the composite. Treatment was continued only the next day. Despite the difficult conditions for analyzing the optical properties and color, the shade was still determined - sample A2 on the Vita scale.
However, due to the fact that the intervention was limited to working in the surface layer of transparent enamel, to reproduce the excised tissue, it was sufficient to use one opalescent shade of YE material Esthet-XHD. The depth of occurrence of white spots in the dental tissues turned out to be very uneven - from 0.1-0.2 mm on the surface to 0.6-0.8 mm in the deepest areas, however, in all teeth the spots were located within the enamel. All work from start to finish was carried out under a microscope with magnification of 10 and 16 times. The preparation was carried out with diamond burs with red and yellow stripes under intense water cooling.
After isolation and before applying the conditioner, the enamel was air-abrasively prepared with aluminum oxide sand (25 microns). This stage allows you to increase the specific surface area of the enamel and improve its wettability, which leads to an increase in adhesion strength.
Rice. 4. View after excision of white spots with a bur.
Rice. 5. View after excision of white spots with a bur.
Rice. 6. View after excision of white spots with a bur.
Rice. 7. View of teeth after sandblasting and etching. The teeth are separated from each other by Mylar matrices to prevent the adhesive from reaching the contact point.
To prevent rapid hardening of the composite material, an orange filter was installed under the light of the microscope.
The duration of the work was approximately 3 hours. During finishing, a coarse diamond bur with a green stripe was used to imitate the natural microrelief of the patient's teeth. By taking it with your fingers and making careful horizontal movements, you can successfully imitate deep perikymatia and other non-standard enamel formations.
Rice. 8. View after applying the restoration material.
Rice. 9. Contouring, grinding and polishing of the restorations was carried out directly under the rubber dam.
Rice. 10. View of the finished restorations immediately after polishing.
Rice. 11. View of the restorations the day after completion of treatment. Thanks to painstaking surface treatment and reproduction of all the nuances of the enamel surface, the boundaries of the composite are practically indistinguishable.