The most common form of jaw injury is a bruise. No one is immune from this. For example, with a strong blow to the jaw, soft tissues, blood vessels, and capillaries are affected, resulting in the formation of hematomas and swelling. This is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after injury. The fact is that impaired jaw function entails a chain of negative consequences: difficulties while eating, deterioration in the quality of spoken speech, etc.
What causes bruises?
Jaw injury may result from:
- falls;
- blow;
- fights;
- children's games;
- accidents, etc.
The severity of the injury is determined taking into account the following factors:
- features of the surface or object that caused the injury;
- impact intensity;
- affected area of the face;
- condition of bone tissue before the incident.
The strength of the bruise and possible complications depend on the listed indicators. Regardless of the severity, it is important to see a doctor to evaluate the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment. This will avoid unforeseen consequences and quickly restore the damaged area.
Jaw displacement
One of the most common types of injuries is jaw displacement. The fact is that it is very easy to get such an injury, sometimes even unnoticed by yourself, for example, when actively chewing food or yawning. To avoid complications and surgery, it is better to treat a dislocated jaw immediately.
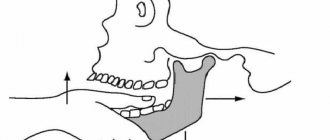
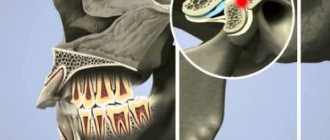
The lower jaw is connected to the temporal bone by two joints, the heads of which fit into the articular fossae. This gives us the ability to talk, chew and perform other movements. Signs of a dislocated jaw appear instantly, so the problem is easily diagnosed. When the heads pop out of the articular sockets, the jaw “jams” in the open position. This is accompanied by pain in the temporal bone area.
Causes of jaw dislocation
Displacement of the lower jaw occurs for the following reasons:
- sudden movement of the jaw in the process of chewing food, laughing, yawning, screaming;
- physical impact, for example, from a fall, impact;
- unprofessional reduction of the joint - if the person tried to solve the problem on his own;
- diseases of the skeletal system and joints, such as arthritis, arthrosis, rheumatism;
- displacement due to constant excessive load on the jaws;
- congenital anomalies of the temporomandibular joint;
- opening hard packages with teeth.
How to understand that a shift has occurred
Jaw displacement is difficult to miss. Dislocation can be anterior, posterior, unilateral or bilateral. The degree of complexity of a dislocation depends on the type of injury and is expressed by the following signs:
- with anterior displacement (when the jaw moves forward), the mouth freezes in an open position, pain appears in the parotid area, profuse salivation begins, and the proportions of the lower part of the face are disturbed;
- if the dislocation is posterior (the jaw goes back), then in addition to sharp pain, it becomes difficult for the person to breathe and swallow saliva, and it is almost impossible to open the mouth;
With complicated dislocations, bleeding from the ears, hematomas in the parotid area and swelling in the joint area are possible.
How to diagnose a dislocation
An experienced doctor can easily diagnose jaw displacement using a general examination and palpation. But in order to exclude the possibility of a fracture and make the most accurate diagnosis, an X-ray examination is prescribed, as well as a computed tomography or MRI of the joint.
How to treat jaw misalignment
In most cases, dislocation is treated by manual reduction. There are several methods of treating trauma: the Hippocratic method, the Blechman method, the Popescu method and a number of others. The exact method to treat a dislocation is determined only by the doctor, depending on the specific case. The jaw realignment procedure is carried out as follows:
- The patient takes a comfortable semi-lying position so that his face is at the level of the doctor’s forearm.
- The doctor places his thumbs on the teeth and clasps the jaw from below with the rest.
- By carefully applying pressure, the specialist returns the jaw to its original position.
- As a result, the head of the joint returns to the fossa. A characteristic click occurs and the patient reflexively closes the jaw. This indicates that the problem has been resolved.
Immediately after the jaw is realigned, it is fixed with a tight bandage, which must be worn for a week. For a complete recovery and to avoid relapse, it is necessary to abstain from rough food for a while and minimize stress on the joints. As a rule, the outcome of the procedure is favorable. But in case of old or complicated injuries, surgical intervention under local anesthesia is required.
Clinical picture
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the bruised area to identify hidden injuries that cannot be identified by a person without medical education. For example, symptoms of dislocations or fractures may not appear immediately. Professional consultation allows you to begin timely treatment, if required.
To recognize a jaw bruise, it is important to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the place where the blow fell, intensifying when pressed;
- visual signs (eg, swelling, redness, abrasions, bruises);
- limitation of jaw mobility when yawning, talking, chewing;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- general weakness.
Jaw bruises are less dangerous than more severe injuries, so recovery is usually quick.
The doctor may order an x-ray or computed tomography to establish an accurate diagnosis. These studies will assess the condition of the internal tissues of the affected area.
A little anatomy
The jaw is the most protruding part of the head, so an attack on it acts like a long lever when turning, concussing the brain with maximum force due to its impact against the wall of the skull.
A blow to the jaw also causes a concussion. The main center responsible for coordinating the body – the brain stem and cerebellum – also suffers. We must not forget that the jaw at the place of its articulation closely interacts with the ear, which, in addition to the function of hearing, is also an organ of balance. An attack to the lower jaw affects the person's balance, and he immediately falls.
Primary treatment
A bruise can be diagnosed by external signs even before seeing a doctor. To eliminate pain and discomfort, it is recommended to perform the following measures:
- apply a tight bandage;
- Apply a cold compress to the bruised area.
For quick and painless treatment, the face must be at rest. It is better to avoid warming compresses, as they can lead to the development of inflammatory processes.
The consequences of bruises can be such conditions as fractures, fractures, dislocations of the hard tissues of the jaw and even a concussion. Treatment differs depending on each case, so you should not self-medicate. It is also worth noting that most injuries have similar symptoms, so they are easy to confuse. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. If you cannot go to the hospital yourself, it is recommended to call emergency medical help.
Medical care for jaw injuries
There is no specific treatment plan in such cases. But there is a list of general recommendations. Visits to the doctor are usually limited to one visit to evaluate the x-ray or CT scan.
If the patient escaped with an ordinary bruise, then treatment will be carried out at home. The patient will be given a bandage to hold the bones in the correct position. As mentioned above, you need to apply cold compresses. Ice, snow, and sterile gauze moistened with cold water are suitable for these purposes. Warming the affected area is contraindicated to avoid inflammation and worsening the clinical condition.
To eliminate pain, taking analgesics is allowed. Following simple rules will allow you to quickly get rid of the consequences of a bruise and return to your normal life.
Likely consequences
Any injury with negligence and non-compliance with medical recommendations can lead to all sorts of complications. If we talk about a bruise of the jaw, then it can develop into a post-traumatic form of periostitis, myositis or deformation of bone tissue. Any complications will require lengthy and likely expensive treatment. Injury to the masticatory muscles can cause limited mobility of the lower jaw, complicate chewing and swallowing, which directly affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract and metabolic functions of the body.
What happens to the brain after a blow to the jaw?
Since the anatomical structure of the jaw is such that certain actions can cause a concussion, it often becomes a target during a fight.
A jaw injury does not cause immediate pain, but the person often loses consciousness. This works on the principle of Archimedes' law - if you use a long lever, you can perform effective operations. The longer the lever, provided that the fulcrum is optimally present, the less force needs to be applied. Let's look at the law using the example of a blow to the jaw. At the top of the human skull is the brain. The upper jaw is its lower point. It is the same lever that, upon impact, can displace the brain. A fast and strong attack leads to such a state, and the injured person loses orientation in space and is knocked out.
The force of a blow that can knock a person out lies in this case in an impulse of energy. It starts from the legs, goes through the whole body and ends in a punch. Typically, the larger the fighter, the stronger his attack. With a half-ton impact on the skull, the brain begins to move sharply, then makes an abrupt stop, hitting the back of the head, and then the frontal lobe. Thus, the brain is injured on both sides at once, which leads to the release of hormones that usually ensure the transmission of information to neurons. This provokes a so-called electrical storm and leads to unconsciousness.
Diagnostic measures
If minor injuries to the maxillofacial area occur, they do not require contact with a dentist or surgeon, or urgent hospitalization. If there is severe and prolonged pain, the area of damage should be examined by a specialist.
The following are used as diagnostics:
- taking anamnesis;
- general examination by a surgeon, orthopedic dentist, traumatologist;
- special examination by an otolaryngologist, neurologist and other specialized specialists as necessary;
- X-ray examination of the maxillofacial area;
- CT scan;
- analysis of blood, urine, saliva.
Based on the data obtained, a general picture of the victim’s health is formed and a specific treatment is recommended.
The main therapeutic direction will be the following:
- taking painkillers;
- applying a pressure bandage;
- ensuring maximum peace for the victim;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures;
- local and general anesthesia;
- elimination of hematoma and infiltrate.
First aid
After a head impact, signs of TBI appear quickly. The main thing is to be careful. The most striking symptoms: vomiting, nausea, fainting. It is very important not to get lost, to act confidently and quickly:
- Call the doctors.
- Apply something cold to your head (ice, compress). This will help narrow the blood vessels, minimize the risk of hematomas, hemorrhages, lumps, and prevent or reduce swelling.
- Carefully examine the victim. Sharp pain in the neck may indicate damage to the vertebrae. It is important to fix the position and not change it until the ambulance arrives.
- In case of fainting, bring ammonia to your nose. Wipe with cool water. It is strictly forbidden to hit people on the cheeks. Such an action will increase the consequences of damage.
- Treat wounds. The use of chlorhexidine and hydrogen peroxide is allowed.
- If heavy bleeding begins in the temple area (spouts like a fountain), pinch the vessel with your fingers. After this, apply a bandage with furatsilin or miramistin. After attaching the bandage with a bandage, wrap your head with a bandage.
- If vomiting occurs, place the person on their side. This is necessary for the random flow of vomit so that the victim does not choke. It is advisable to place a clean cloth and change it periodically when it gets dirty.
Having done everything necessary, you need to wait for the doctors. If a person has not lost consciousness and feels more or less normal, you can not call an ambulance, but take him to the hospital yourself. The main thing to remember is that the consequences of TBI can be quite serious. Only a doctor can assess the condition, so a visit to the clinic should not be neglected.
Indications for hospitalization
A doctor may refer you for hospitalization if there are the following grounds:
- post-traumatic amnesia;
- prolonged loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- epileptic seizure;
- bleeding;
- disorientation;
- obvious disorders of the nervous system;
- the patient is pregnant (even if she feels normal).
During treatment for TBI, the patient's condition may fluctuate. Periodically, the symptoms intensify and subside. Predictions can only be made after a full course of therapy. Unfortunately, the mortality rate for TBI reaches 25%. The main cause of death is inadequate first aid and reluctance to go to the hospital.
First aid and treatment of bruises
Ice pack on problem area
Once the location of the damage has been identified, it is necessary to begin simple manipulations. Of course, they will depend on the nature of the damage. If there are open wounds, first of all they must be washed and treated with antiseptic.
Suitable products for this include hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Bepanten. Before applying the antiseptic, the wound can be washed with soapy water. The bleeding area must be covered with a clean cloth or, if available, a sterile bandage.
Then apply cold to the affected area through the cloth. This can be an ice pack or a regular towel soaked in cold water, which is applied through a waterproof film.
For severe pain, the following medications are recommended by mouth:
- Analgin;
- Ketorol;
- Nurofen;
- Sedalgin;
- Nise;
- Took;
- Tempalgin;
- Nemesis.
Diagnosis of TBI
Even if you provided first aid, know how to treat, and have previously encountered similar injuries, do not be arrogant. Examination of the victim by a qualified physician is mandatory. If you don’t want to call an ambulance, take him to the clinic yourself. Just before doing this, make sure that the spine is damaged and the skull bones are not cracked.
The most accurate conclusion can be made using magnetic resonance therapy and computed tomography of the head. The procedures are painless. With their help, you can thoroughly study the structure of the brain, look for the presence of hemorrhages, hematomas, etc.
If it is not possible to do MRI and CT (the clinic does not have machines), diagnostics should include:
- X-ray of the skull.
- Encephalography of the head.
- Examination by an ophthalmologist.
Encephalography will also help detect hemorrhage. In this case, hospitalization cannot be avoided.
If, after an injury, the patient has liquor leaking from the ears or bruises under the eyes in the form of glasses, you should consult a doctor immediately. Self-medication or lack of help, in this case, often leads to death.
You can undergo an MRI or CT scan in Moscow at any time of the day and regardless of the day of the week. You can find a clinic with 24-hour service, close to the patient, using the service: https://msk-mrt.ru/articles/. There are hundreds of medical centers operating in different modes here. Within a few minutes you can find a clinic and make an appointment by phone. Registration through the website allows you to get a discount on the examination.
The main symptoms of a jaw bruise
- pain in the bruised area, which becomes especially severe with pressure and movement;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- difficulties in speaking;
- it becomes painful for a person to chew;
- there is a loss of strength;
- a lump may form on the jaw;
- temperature rises;
- the jaw goes numb;
- swelling, redness, swelling, and hematomas are noticeable in the area of contact with an object or hard surface.
Unlike the symptoms of fractures, with bruises the jaw connects to the skull. Violation of the connection, as a rule, occurs in fractures (open and closed), dislocation, fracture, etc.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine shows high effectiveness in relieving the unpleasant symptoms of jaw injuries. If a specialist has diagnosed a jaw injury, but a fracture or dislocation is completely excluded, then you can use one of the popular folk recipes (see also: jaw fracture: symptoms and treatment methods). The following methods will help cope with the consequences of injury:
- "Fat ointment." Grind sea salt in a coffee grinder, grate (or very finely chop) the onion. Mix the ingredients with any animal fat and apply regularly to the injured area.
- Tinctures. Thoroughly chop birch buds, blue cornflower flowers, knotweed, bearberry leaves, corn silk or horsetail with a ceramic knife (you can use a metal tool, but this will negatively affect the quality of the finished product). Pour the crushed plant with vodka or alcohol diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. Insist for three days. Strain. Use for compresses.
- Pour bodyagi powder into warm boiled water and mix thoroughly. Apply the resulting diluted bodyaga to the site of the jaw injury.
- Attach a plantain leaf. It can be replaced with chopped wormwood or finely chopped crushed onions.