Dentistry under sedation is a modern method that allows you to go through an unpleasant procedure with comfort. Parts of the brain responsible for increased levels of anxiety are temporarily blocked with anesthetic drugs. Under their influence, a person quickly calms down, falls into a shallow sleep, while remaining conscious. Ideal conditions are created for the doctor’s comfortable work, helping to significantly improve the quality and efficiency of procedures and perform a large volume in one appointment.
What is sedation in dentistry? How is it different from anesthesia or anesthesia?
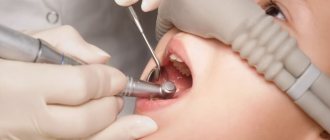
Anesthesia in dentistry – anesthesia of the treatment area (site). This is a mandatory manipulation - a traditional injection into the gum near the diseased tooth.
Sedation is a light medical sleep that relieves anxiety and fear. The patient in this state is asleep, but conscious, feels touch, hears the doctor. The main difference from anesthesia is that during sedation a person breathes completely independently. Sedation is accompanied by local anesthesia so that it is not scary or painful. Sedation allows the doctor to monitor the condition of a patient with concomitant diseases - kidney or heart problems, high blood pressure - so all procedures are comfortable and as safe as possible.
Anesthesia or general anesthesia is used during hospital treatment when a complex operation needs to be performed. In this case, the patient’s consciousness is completely turned off, local anesthesia - injections into the gums - is no longer needed, and breathing is controlled by equipment.
The use of sedation assumes the preservation of standard reflexes and the absence of depression of the nervous system. According to reviews from patients of different ages, during treatment they feel lightness and relaxation. On average, an hour after the end of the procedure, the person returns to his normal state and can go home with an escort. Our clinic has a small room where you can rest and sleep after treatment under sedation.
Which anesthesia option is better?
So, we went over the main properties of drugs for general anesthesia.
Now let's look at which options are better in each specific case. There are no identical children, they are all different. Some children will calmly accept the placement of a catheter at a very young age, while others will refuse a painless mask at the age of eight or nine. Therefore, we always carefully communicate with both the baby himself and his parents. This is necessary to establish trusting contact between the doctor and the little patient. Without this, it simply won’t be possible to work normally. At the same time, the most detailed information on the child’s health characteristics is collected so that the anesthesiologist can choose the most comfortable and safe option for general anesthesia. Interestingly, children very quickly begin to trust doctors if they see that everything was painless and the tooth no longer bothers them. As a rule, further treatment is much easier. We had a case when a girl fell from a swing in kindergarten, hit herself and lost an artificial crown, which almost three of her had to install. As a result, she returned to the clinic with her parents, brought the crown in her palm and asked to return it to its place.
Local anesthesia only
Suitable for
: brave children of all ages who trust the doctor.
This option is a little beyond the main topic of our post, but I also want to mention it. If a child initially comes with a bunch of damaged teeth, and for some reason intimidated by relatives, then such a scenario may be impossible. But it is necessary to treat. This is where the entire arsenal of general anesthesia tools will help us.
Local anesthesia and nitrous oxide
The child should have free nasal breathing. Nitrous oxide has a bunch of effects that we need. It relaxes, eliminates anxiety, and slightly improves your mood. The patient will be conscious during treatment. At the same time, in its pure form it will not be possible to numb the pain; preparing teeth will still be painful. Therefore, we usually let the child breathe through a special mask that covers only the nose. Many people really like this, plus we often tell stories about test pilots who also have special masks with a breathing mixture.
When the child relaxes, you can apply topical anesthesia with gel and then inject the main anesthetic. Unfortunately, under nitrous oxide it will not be possible to do a large amount of intervention at once. Children get tired of lying with their mouths open, and the mask begins to irritate them. Therefore, this method is better suited for small one-step interventions - one or two teeth. At the same time, we cannot increase the concentration above 50% for a child; we need to look for other, stronger, but safe drugs.
Local anesthesia and sevoflurane
Sevoflurane can be given to school-age children without any problems, but there are several nuances.
With older children, it is easier to agree on local anesthesia while awake or the use of propofol with intravenous administration. There are several advantages to completely turning off consciousness, which does not happen with nitrous oxide. Firstly, the child does not experience extreme stress and does not develop dental phobia for the rest of his life. There is nothing worse than a stern nurse who kneels on you and holds a mouth opener while the doctor frantically tries to do something in the oral cavity.
Secondly, this allows for high-quality treatment when the doctor is confident that the patient will not twitch, start waving his tongue, or try to run away in the middle of an important stage.
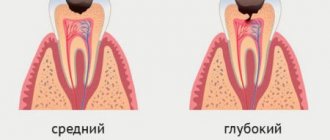
The anesthesiologist can vary the depth of anesthesia by changing the composition of the gas mixture. This makes it possible to accurately monitor the patient’s vital signs and ensure the desired level of relaxation and immobility. If you need to treat caries, then there is no point in injecting an additional anesthetic. The degree of CNS suppression is sufficient to make the patient comfortable. If you plan to treat pulpitis or periodontitis, or remove teeth, we additionally administer a local anesthetic. Otherwise, pain impulses will still reach the “sleeping” brain and cause a surge of adrenaline and involuntary movements. When consciousness is completely turned off, we can carry out any amount of intervention. Moreover, we are talking not only about some painful things like treating six carious teeth in one go, but also, for example, about taking accurate impressions for the subsequent production of orthopedic and orthodontic structures. Try convincing a sobbing four-year-old that he needs to sit still while the silicone in the impression tray hardens in his mouth.
Local anesthesia and propofol
This is prohibited for a child under three years of age to use. We have already discussed the features of propofol above. It does not have an analgesic effect, but only suppresses consciousness. This is why it must be supplemented with local anesthesia, as if the patient were awake. But its main advantage when working with teenagers is that they can follow simple commands. This makes the doctor's work easier. You can reduce the depth of anesthesia and ask to bite down on a template, model the structure based on the bite, or something similar. It is important for the dentist not just to depict fillings at the site of carious defects, but to carefully model the occlusal relationships of the jaws so that after treatment the biomechanics of chewing are ideal.
Types of sedation: superficial and deep
The following sedative methods of relaxing and calming patients are used in dentistry:
- Superficial is the best solution in a situation where the patient requires relaxation for a short period of treatment. Indicated for adults, as well as children from the age of three. A state of pleasant slumber is achieved by inhaling oxygen mixed with nitrous oxide. The nasal mask through which the gas passes is connected to the machine. The doctor can change the ratio of components and dosage based on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Deep - the medication is administered through an intravenous injection. This technique copes better with severe fear and anxiety. The technique is used for adults and children at least 15 years old. The relaxed state lasts longer than with a superficial state. The patient will need to stay in the clinic for some time and stop driving for 8 hours.
Anesthesiologists at the Refformat dental clinic in Moscow have been working with a wide variety of patients for a long time and their experience makes treatment safe. Any intervention, preparation and installation of prostheses will be comfortable and unnoticeable.
Coming out of a sedative state
At the end of treatment, the anesthesiologist turns off the nitrous oxide supply and increases the oxygen supply through the mask, which ensures faster removal of nitrous oxide from the patient's lungs. 5 minutes after the end of the treatment procedures, not even a trace of the sedative remains in the child’s body. Local anesthesia wears off after 1.5-2 hours. The child does not experience any consequences (such as dizziness or nausea, familiar to many from the effects of surgical anesthesia) after sedation. In rare cases, after sedation, a child may remain in an unusually calm state until the end of the day.
How is the sedation procedure performed?
The procedure consists of several stages. First, you need to get a consultation with a dentist - you meet the doctor and draw up a treatment plan.
For sedation, the patient will need to do a few simple tests:
- ECG.
- Donate blood for general analysis and biochemistry (detailed).
- Donate blood and get test results for hospitalization (for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis).
- If you have diseases, obtain permission from a specialized specialist.
The finished results are sent to the clinic administrators. Be sure to write the surname, initials of the patient and the dentist. The documents are submitted for review to the anesthesiologist, who decides on admission to the operation under sedation and takes into account the possible consequences.
The administrator contacts the patient to clarify the date and time of arrival at the center. On the appointed day, it is recommended to arrive early for the appointment, but do not use personal transport. If necessary, administrators will help you call a taxi to get you back home.
Before the procedure begins, there is a conversation with the anesthesiologist. In the operating room, an individually selected dose of anesthetic will be administered through a nasal catheter and wire. Unlike anesthesia, the patient continues to breathe on his own, plunging into a pleasant half-sleep, without negative sensations. At the end of treatment, the patient is escorted to the rest room, where he has the opportunity to lie down and rest.
When will nitrous oxide treatment be effective?
1. Age over 3 years. Children are not psychologically ready for this type of manipulation and may be scared.
2. The child sits in the dental chair by himself - without panic fear or hysteria, but at the same time experiences slight discomfort. In this case, the oxygen mixture will help you relax and take your mind off unpleasant sensations.
3. Nasal breathing. The mask should remain on the face throughout the entire procedure, tightly covering the nose. This is due to the fact that the effect of the gas occurs gradually. First, the patient breathes pure oxygen, then the anesthesiologist gradually changes the gas ratio, increasing the nitrogen concentration. If you periodically remove or adjust the mask, the desired effect will not be achieved.
Methods of drug administration
Dentistry with sedation in Moscow is represented by various methods of administering medications: inhalation, oral and injection.
Inhalation method
Most often used in pediatric dentistry. The procedure uses nitrous oxide. “Laughing gas” evokes positive emotions in a child from visiting a doctor’s office and undergoing lengthy procedures. At the same time, the doctor’s work becomes significantly easier and more effective.
Oral route
Oral drug sedation is a method of calming in which a drug that eliminates agitation is taken an hour before the main treatment procedure begins. Using this sedation technique, an initial level of stress relief is provided, and the main stage, at which an anesthetic is administered intravenously or an oxygen mask is used, is facilitated.
Injection method
Intravenous sedation is recommended primarily during dental treatment in adults. The injection method involves administering drugs intravenously, directly into the hematopoietic bed. This method is good because it allows you to control the degree of both physical and emotional relaxation.
Indications for the use of pain relief
European and American dentists use sedation in dentistry when performing any manipulations. In Russia, such a procedure can not be performed in every clinic. Treatment and removal of teeth under sedation at Refformat dentistry allows patients to completely calm down and undergo all manipulations in complete relaxation.
Indications for use:
- Severe fear, fear of visiting the dentist, panic.
- Increased vomiting.
- The desire to receive a service with high comfort.
- Reduced pain threshold.
- The need for a long period of simultaneous treatment.
- Vascular or cardiac pathologies (additional consultation with a therapist is required).
- A symptom of cramped (enclosed) spaces.
- A sharp increase in blood pressure due to stress.
Benefits of using sedation in children
Therefore, we can say with confidence that the use of sedation has undeniable advantages. Among the advantages of the method are the following:
- The use of ZAX (nitrous oxide - oxygen sedation) makes dental treatment painless;
- The child does not experience psychological discomfort in the doctor’s office: in a state of sedative anesthesia, he does not smell unpleasant odors, does not hear the frightening sound of a drill, and does not distinguish between medical instruments;
- The use of ZAX removes tactile sensitivity, so the baby will not be frightened by vibrations, pressure, compression, etc., made by the doctor;
- The doctor is able to provide full treatment, because his access to the patient is no longer hampered. Now the dentist has enough time to apply the most effective modern treatment methods. He can also use any preparations, even those that harden for a long time;
- The risk of complications after dental treatment is reduced.
The use of sedation has ushered in a new era in pediatric dentistry. After all, doctors now have the opportunity to use modern composite materials for treatment. And they are more durable, hygienic and aesthetically pleasing compared to those previously used. Until recently, composite materials were not used for the reason that their placement requires careful drying of the tooth. The doctor must also wait a long time for the material and fixing glue to harden. Now he has the necessary time reserve.
Contraindications
Sedation is not anesthesia, which has an extensive list of prohibitions on its use. Its negative impact on the human body is minimal. However, this gentle method of sedation also has a certain number of contraindications:
- individual intolerance, allergies to medications;
- colds, flu, ARVI;
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, hepatitis);
- certain types of chronic diseases;
- myasthenia gravis;
- mental disorders;
- pregnancy;
- alcoholism, drug addiction.
Is sedation with ZAX safe?
Yes, it's safe. ZAX is completely harmless for children. Moreover, today it can be called the safest sedative. It is easy to use, is eliminated from the body without a trace, does not have a heavy or overly strong effect, and is not addictive. The child remains conscious, his breathing is not difficult, all reflexes are preserved. The use of ZACS ensures maximum safety, complete controllability and early activation of the patient.
You may have doubts about how well this technology has been tested. Despite the fact that it represents an innovation for Russia, ZAX sedation has long been used throughout the world (more than 30 years). The vast majority of pediatric dental clinics in the USA, Israel and the UK use ZAX as the main sedative. Thus, this technology can only be called new conditionally - it has long been tested and approved by professionals.
Pros and cons of sedation in dentistry
The main advantage of treatment, removal or prosthetics of teeth under sedation is that it is much easier and more convenient for the doctor to work with a patient who is in a relaxed state. The patient does not experience negative emotions and a persistent feeling of fear from visiting the doctor’s office. In the future, people will more often visit the dental clinic for preventive purposes.
The procedure also has disadvantages, although there are not many of them. The patient should spend an additional hour in the rest room. The cost remains quite high, which is fully explained by the high price of imported materials, high-quality equipment, as well as the duration of treatment. Initially, you will need to spend time and money on tests and consultation with specialists.
Is local anesthesia needed when using sedation?
Since nitrous oxide sedation only has a calming effect, then yes, local anesthesia is required, otherwise the child will experience pain (or other discomfort) during treatment. Sedation allows you to give a pain-relieving injection to your child unnoticed and prolongs the effect of the anesthetic.
Even routine treatment of dental caries in children under sedation requires local anesthesia. The purpose of sedation is to relieve psychological stress and calm down - otherwise the child simply will not allow him to do anything. And to eliminate pain is the task of local anesthetic drugs.
What drugs are used
Nitrous oxide or other drugs are used for inhalation anesthesia. The instructions for use of such drugs list as side effects: respiratory problems, cardiac depression (depending on the dose), nausea, vomiting. But worst of all, with a genetic predisposition, a dangerous disease can develop
[1] – hyperthermia. The chances of this happening are slim, but no one does genetic testing before dental treatment, so the possibility cannot be ruled out.
Other drugs are used intravenously and orally (in tablets), which also have side effects, although not as pronounced.
How it all happens
Treatment of children's teeth under anesthesia begins with an acquaintance and conversation with the doctor. Sometimes they play cartoons in the office, and some clinics offer toys. Then he is allowed to examine the mask, is asked to try it on, and they begin to supply pure oxygen, to which nitrogen is gradually added, increasing its concentration. After a couple of minutes the child falls asleep. After this, sensors for monitoring his condition are connected to him and treatment begins.
The duration of dental treatment in a dream varies depending on the defect, complexity of the process and other factors. At the end, they are given oxygen again. After the procedure is stopped, the child wakes up gradually. He is under the supervision of doctors for at least an hour in a specially designated room. That day it is better for him to stay at home and not visit the children's group.
When using tablets or intravenous drugs, the algorithm of action is the same, only without a mask and oxygen.
Types of anesthesia for children during dental treatment
Depression of consciousness can be deep, medium and superficial.
Medicines can be administered in different ways:
- Orally
. This is how we take regular pills. - Intravenously
. Oddly enough, some children are more comfortable with an injection than with a mask on their face. - Inhalation
. This is the most common way of administering drugs. Nitrous oxide is most often used.