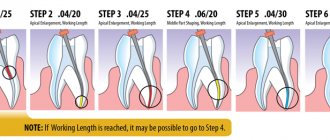
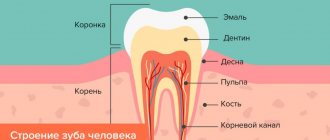
Cleaning of premises and high-quality processing of medical instruments is the most important link in the chain of measures to prevent nosocomial infections (nosocomial infections).
Sanitation must be carried out systematically. The rules of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 are legally established, which regulate the sequence and frequency of sanitary cleaning of premises and equipment in health care facilities.
Sanitation is a whole set of measures for cleaning surfaces from dust, visible dirt, blood, sputum, followed by disinfection with special means.
Manual disinfection cleaning
When carrying out mechanical (manual) washing of surgical instruments, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- All disinfection and treatment procedures are carried out by medical staff wearing gloves of sufficient thickness, gowns, masks, waterproof aprons, safety glasses, and sharp objects are handled with care.
- When preparing solutions, the manufacturer's instructions regarding concentration, temperature and exposure time should be followed.
- If powder products are used in the working solution, ensure that they are completely dissolved.
- Use soft, lint-free cloths, plastic brushes or cleaning guns. Do not use: metal brushes, coarse abrasives, excessive pressure.
- Place instruments carefully, avoiding overfilling trays.
- After manual disinfectant cleaning, surgical instruments are washed with running distilled water for 3 to 10 minutes (depending on the product used), removing remaining contaminants, and dried.
Types of sanitary cleaning in a medical facility
Wet cleaning of premises (floors, furniture, door handles, beds, medical equipment) is carried out twice a day, always using certified detergents and disinfectants.
General cleaning of health care facilities is carried out according to the established schedule:
- in operating rooms, delivery rooms, dental and dressing rooms at least once every 7 days;
- in the wards and corridors of infectious diseases departments - once every 10 days;
- in the wards and corridors of a regular department - once a month;
- in bathrooms, utility rooms - 2 times a month.
Walls, floors, furniture, and appliances are treated with rags soaked in a disinfectant solution. facilities. Disinfection of premises by irrigation from a hydraulic remote control is allowed (subject to compliance with personal protective measures). The equipment is wiped with rags and cleaned with brushes.
Machine cleaning and disinfection
Mechanized washing is carried out in specialized washing machines, where the standardization of cleaning and disinfection processes is ensured as much as possible. Before loading into the machine, instruments are pre-treated manually or in an ultrasonic bath and thoroughly washed to remove contaminating residues. During machine processing, thermal and chemical-thermal disinfection methods are used. Careful study of the operating instructions for washing machines and the recommendations of manufacturers of surgical instruments allows you to avoid poor-quality processing and damage to instruments.
Everything is documented.
Documentation is filled out daily to keep records of:
- Works of an ultraviolet bactericidal installation. The start, end, and duration of processing are recorded.
- Carrying out general cleaning.
- Autoclave operation. The name and number of instruments being sterilized, the time and mode of sterilization are recorded.
- Quality of pre-sterilization treatment. The name and number of instruments, the method of processing them, as well as the result of the test for occult blood (azopyram test) are recorded.
Ultrasonic cleaning
An effective mechanical method that complements manual cleaning of stainless steel and hard plastic CI is ultrasonic cleaning. Ultrasonic pre-sterilization cleaning (UPC) is performed in a special chamber filled with a cleaning solution, through which ultrasound is passed. Is used for:
- removal of stuck-on contaminants;
- accelerated disinfection and simultaneous intensive cleaning.
The rules that the surgical nurse should consider when ultrasonic cleaning of instruments are similar to the rules for manual cleaning and disinfection.
Disinfection and sterilization of medical instruments at the Dentville clinic
At the Dentville clinic, special attention is paid to organizing and carrying out disinfection and sterilization activities. One of the most important types of these activities is the processing of medical instruments, which takes place in several stages:
Stage 1 - disinfection of medical instruments.
Disinfection of a medical instrument is carried out with the aim of destroying pathogenic microorganisms on its surface - viruses, bacteria, fungi. It is carried out using disinfectants that have antibacterial and antiviral effects. Disinfectants used to disinfect medical instruments in our clinics are approved for use by the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Research Institute of Disinfectology” of Rospotrebnadzor.
Stage 2 – pre-sterilization cleaning of medical instruments.
The main purpose of pre-sterilization cleaning of medical instruments is to remove protein, fat, mechanical contaminants, as well as drug residues from products. This type of treatment is carried out using an ultrasonic bath, which provides high quality pre-sterilization cleaning. This is especially important when cleaning complex and small instruments.
Quality control of pre-sterilization cleaning of medical instruments is assessed by performing an azopyram test. The results of this control are recorded daily in a special journal.
Stage 3 – sterilization of medical instruments.
Sterilization of medical devices is the destruction of microorganisms of all types at all stages of development on a medical instrument using physical influences.
Sterilization of medical instruments is carried out using two methods:
1) steam method - sterilization in an autoclave. When using this method, the destruction of harmful microorganisms occurs when they are exposed to hot steam under pressure, at temperatures from 120 °C to 134 °C.
2) air method - sterilization in a dry-heat oven. When using this method, the destruction of harmful microorganisms occurs under the influence of dry hot air at a temperature of 180 °C.
To control the quality of sterilization of medical instruments, our clinics use special chemical indicators. The results of this control are recorded daily in special journals.
In addition, at Interdentos clinics, specialists from the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Moscow Region periodically monitor the efficiency of steam and air sterilizers.
The combination of the above measures allows our clinics to ensure maximum patient safety during manipulations at a dental appointment.
Features of processing individual groups of tools
Some groups of surgical instruments require special processing rules.
| Tool groups | Manual | Machine | Ultrasonic |
| Microsurgical | Manual Requires very careful handling | Machine Carefully secure using special holders | Ultrasonic Fix in special holders |
| Dental | Manual Pre-clean from dried residues, check compatibility with detergents | Machine Carefully secure using special holders, drills, cutters and grinding heads, additionally processed with ultrasound | Use ultrasonic chemicals in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations |
| Mechanical devices | Manual Do not immerse in a washing bath, do not allow water to penetrate into couplings and parts | Machine Only removable parts are processed with the manufacturer's permission | Ultrasonic processing is not subject to |
| Endoscopes and minimally invasive | Manual Rinse cavities and channels with special brushes along the entire length | Machine Pre-disassemble, remove seals, open or remove taps, secure | UltrasonicOnly those recommended by the manufacturer are processed |
| Flexible endoscopes | Manual: Before processing, remove valves and caps; after processing, rinse for a longer time and dry with slightly warm air. | Machine Only in special machines | Ultrasonic processing is not subject to |
Shadowless lamps improve visualization when doctors are working. And we have dark glasses for patients.
A dentist needs not just lighting, but super lighting. This improves the quality of diagnosis and further treatment. However, this may cause discomfort to the patient. Therefore, the VID clinic may offer you dark glasses. Of course, they are disinfected after each patient.
Any patient has the opportunity to familiarize himself with the clinic’s equipment, documentation and receive any other information
by phone:
8
(chief nurse Marina Nikolaevna Bezhevets).
Final disinfection
After cleaning, disinfecting and drying the instruments, sterilization is carried out to neutralize the remaining microorganisms. The main method of sterilization is autoclaving. It is mainly applied to stainless steel surgical instruments. Instruments that cannot be subjected to routine sterilization or that do not require sterilization are subject to final disinfection. The manual method uses a chemical method, the machine method uses chemical and chemical-thermal methods with intermediate cleaning. After the procedure, instruments should be thoroughly washed with demineralized sterile water and dried. As a rule, the following are subject to final disinfection: flexible endoscopes, elastic instruments made of plastic, rubber, latex.
What to pay attention to
How do you know if a dental clinic is sterile? Here are brief recommendations from Rospotrebnadzor:
- choose an institution with a license. Having a license means that the clinic has been checked by authorities for compliance with standards;
- enter into an agreement - it specifies your rights and obligations of the clinic;
- Please note: the doctor and assistants must wear masks and gloves;
- after your predecessor, all surfaces must be disinfected, that is, you must be invited into a thoroughly cleaned office;
- a personal chest napkin and rinse glass must be used;
- the instruments must be sterile - according to the rules, they are taken out from a sterile table or UV chamber in front of you.
Make an appointment
Most importantly, don’t hesitate to ask questions and voice your doubts! After all, the purpose of your visit is health, and sterility in the clinic is one of its main components.
Step 1: Disinfection of rotary dental instruments
Purpose: to destroy pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms that contaminated products during medical procedures.
Disinfection of rotary dental instruments should be carried out immediately after their use, without allowing contaminants to dry on them, by completely immersing them in a disinfectant solution. The thickness of the mortar layer above the products should be at least 1 cm.
Working solutions for disinfecting instruments are prepared in advance. To do this, the required amount of concentrated disinfectant is mixed with water in the proportions specified in the instructions for use of the disinfectant.
For your information
To accurately dose the concentrate, you can use a graduated measuring cup or a disposable injection syringe.
All containers with working solutions of disinfectants must be equipped with tight-fitting lids, have clear inscriptions or labels indicating the product used, its concentration, purpose, preparation date, and expiration date of the solution.
To process dental instruments, special small-volume containers are used, which can significantly reduce the consumption of disinfectants.
Note!
To disinfect medical devices used in dentistry, it is necessary to use disinfectants that have a wide range of antimicrobial activity, including bactericidal, virucidal, and fungicidal properties.
The choice of modes is carried out between viruses or fungi of the genus Candida.
In tuberculosis medical organizations, regimens should be used in which disinfectant solutions are active against mycobacterium tuberculosis.
It is not recommended to use preparations containing aldehydes, since they are capable of fixing organic contaminants on the surface of instruments.
When processing steel and carbide burs, you should avoid using products containing hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide - they can significantly deteriorate the properties of the tools.
Prolonged exposure of carbide and steel burs in the same container with a disinfectant solution can lead to their surface corrosion.