21.11.2019
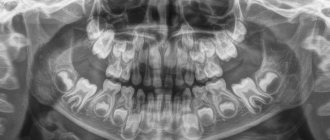
Children's baby teeth fall out and are replaced by permanent teeth. In rare cases, the first ones do not have time to fall out, but the second ones already grow nearby. This phenomenon received a specific name – “shark teeth”. Parents are always concerned about the question of what to do in such a situation.
Pathology mainly appears during the eruption of the lower central incisors. Less commonly, this happens with the growth of the upper incisors or molars.
Causes
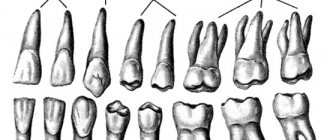
A child's first teeth erupt in a certain order, starting at about six months of age. There are deviations in one direction or another, which is due to a number of factors (climate, drinking water) and the individual characteristics of the baby. For some, they appear as early as 1.5 months, for others - closer to a year. They fall out in the same sequence and are replaced with permanent ones. Complete replacement of the dentition occurs on average at the age of 12-13 years.
But there are also situations when permanent teeth begin to grow right next to the second row of milk teeth. If they are located in parallel, then this is called “shark teeth”. The name was coined by analogy with the anatomical feature of sharks. These predators have teeth arranged in three rows.
Possible reasons:
- genetics;
- improper formation of tooth germs during intrauterine development;
- rickets;
- infectious diseases (sinusitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis).
Treatment
The appearance of a second set of teeth is a direct indication for visiting a pediatric dentist. However, you should not immediately tune in to a negative outcome. Correct treatment tactics completely eliminate this problem without developing any consequences. The main thing is early initiation of therapy and identification of the cause of the pathology. Further treatment tactics directly depend on the etiological factor:
- Extra milk tooth. Removal of the milk jug is the most common dental recommendation, after which correction of permanent teeth is not required. The indigenous “residents” are independently displaced into empty space. If this does not happen, the orthodontist corrects the position with a brace system, aligners or removable orthodontic structures. As a rule, baby teeth are removed in pairs, which affects the correct formation of the bite.
- Insufficient jaw development. The solution to this problem is artificial stimulation of development through removable or non-removable structures. The main difficulty of treatment is the young age of the young patient, which affects the care of prostheses. Invisalign, an elastic mouth guard that is simply put on and does not require special care, shows excellent therapeutic results.
- Hyperdontia. Treatment includes performing a maxillary X-ray, administering local anesthesia, removing the problematic tooth, and suturing the wound.
Why is it dangerous?
Despite the unattractive appearance of such a smile, there is no need to worry. Most often, dentists advise not to take any action. The root of the baby tooth softens, and the tooth falls out on its own after a certain period of time. The child facilitates this by loosening the tooth with his tongue or hands.
Despite the unattractive appearance of such a smile, there is no need to worry. Most often, dentists advise not to take any action. The root of the baby tooth softens, and the tooth falls out on its own after a certain period of time. The child facilitates this by loosening the tooth with his tongue or hands.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment tactics for “shark jaw” are always developed individually. The main thing for parents is to see the problem in time and not let it go.
If the second row does appear, experts recommend taking your time and waiting for a while. In 2-3 months, the roots of the milky elements can dissolve and they will fall out on their own.
Important: during this period it is necessary to carry out professional cleaning of the mouth, classical sanitation, rinsing with solutions and decoctions with an anti-inflammatory effect, monitor the hygienic condition of the mouth and remove sweets and excessively hard foods from the diet.
If the problem drags on for a long time, then doctors recommend extraction. This method is effective because the free space is quickly taken up by permanent elements. The same should be done if pain, change in enamel shade, swelling and inflammation appear in the area between the rows.
The process of teeth moving into the correct position after removal of excess units normally takes from 1 to 6 months. If after the specified period the situation does not change, orthodontic treatment is carried out using one of the types of structures:
- braces;
- aligners;
- kapp;
- retainers.
Important: modern diagnosis and a properly developed treatment plan allows you to avoid the development of a number of unfavorable situations and consequences.
The importance of proper breathing
Nasal breathing helps the jaws develop anatomically correctly. If you breathe through your mouth, there is a high risk of their underdevelopment. This fact can easily be explained by the fact that the tongue plays an important role in the formation of the jaws. In the first case, he takes the desired position. In the second case, the tongue is located at the bottom of the oral cavity and practically does not come into contact with the elements of the jaw arches. They do not develop properly and there is not enough space for permanent teeth.
The parents' job is to closely monitor their child's breathing. If nasal breathing is impaired during colds, a quick solution to the problem is required.
Concomitant pathologies
As already noted, the appearance of an anomaly is caused by a violation of embryogenesis and/or development of the child’s dental apparatus after birth.
The human body generates two types of teeth – primary and permanent. The first, 20 pieces, function from 2 to 6 years. Their replacement with permanent elements occurs in the period from 6 to 13-14 years.
By one year, the crowns of the “milk jugs” complete their formation and stop growing. The continued development of the jaws leads to the appearance of interdental spaces - diastemas and three.
The phenomenon does not relate to pathology, and disappears during the period of completion of the formation of the permanent occlusion. If a child aged 2-6 years does not develop interdental gaps, this indicates an abnormality in the development of the jaws.
The change occurs as a result of a certain biochemical process - resorption. The resorbing system, consisting of lymphocytes, osteoclasts and connective tissue, takes part in the resorption of “milk jugs”. The main role is played by osteoclasts - destructive cells that dissolve bone tissue.
At the beginning, the partitions between the roots of milk teeth and the rudiments of permanent teeth dissolve. Then the destruction of their roots begins in the area of contact with the coronal part of the growing permanent units. As the roots reabsorb, baby teeth become increasingly mobile and eventually fall out.
If the permanent tooth germ is located not under the milk tooth, but with a displacement to the side, the resorption process is disrupted. The “milk jug” maintains a strong connection with the alveolar process, preventing the growth of permanent teeth. And he has no choice but to grow up in the wrong place for him, in the second row.
Thus, the late loss of "milk jugs" leads to the fact that the permanent units that should take their place can only erupt by moving to the side.
The small size of the jaw, due to its underdevelopment, also leads to the fact that there is not enough space for permanent teeth; they either crowd together or are located in the second row.
Overnumeration is a case when the number of teeth exceeds the required 32 units. This is a relatively rare abnormality, occurring in 2% of people. Men are susceptible to pathology more often than women.
Extra molars and canines are usually generated. Even with normal jaw parameters, there is no room for “extra” teeth, and they are forced to form a second row.
Prevention
There is no such prevention that guarantees 100% prevention of anomalies in children. But there are several rules to help reduce risks. Here is their list
- Establishing proper nutrition with sufficient amounts of all vitamins and microelements. There should be solid foods that train the dentofacial apparatus.
- Timely treatment of oral diseases. Carious processes often lead to disruption of the development of the dental system.
- Correct nasal breathing.
- Regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations and identification of possible problems.
If, when shark teeth appear in a child, the doctor advises removing a temporary tooth, do not be afraid of this. Modern dentists perform this procedure only when indicated and absolutely painlessly.
Possible consequences
The appearance of the second row leads to serious negative consequences for the oral cavity and dentofacial apparatus. Among them:
- violation of diction;
- poor chewing of food with subsequent indigestion;
- curvature of the roots of neighboring elements, their displacement from their “rightful” place;
- change in bite;
- formation of trema and diastemas.
What devices are used to prevent malocclusion in modern orthodontics.
In this publication, we will look at the main signs of Costen syndrome.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/vliyaet-li-soska-na-prikus.html we’ll figure out whether the pacifier affects the child’s bite.
Reviews
The appearance of an additional row of teeth is a rare occurrence in dentistry, and in most cases it is a harmless problem that can be easily corrected.
Parents need to be more attentive to the child during the process of changing teeth, to notice the first problems in a timely manner, so that they can then deal with them effortlessly and quickly.
If you have encountered this phenomenon and would like to share your opinion and experience regarding its elimination, please leave a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Types of hyperdontia
Pathology is divided into several types depending on the factors that caused it and the location of unnecessary elements.
| Name | Description |
| Typical hyperdontia | Extra elements are located in the dentition |
| Atypical hyperdontia | Eruption in different places, for example in the sky |
| True polyodontia | The appearance of extra buds |
| False polyodontia | The proximity of permanent and milk elements of the masticatory apparatus |
Main features
The disease has severe symptoms. However, signs may differ between children and adults. Polyodontia in adults is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Excess teeth appear on the palate and gums. Their structure and shape are distorted.
- Occlusion disorders.
- Problems with pronunciation.
- Turning the teeth from the main set to the side.
- Too close placement of dental elements to each other.
- Difficulty in chewing food and, as a result, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Inflammation of mucous structures due to injury to them by “extra” elements.
Children may develop additional baby teeth in infancy or from the first day of life. The symptoms are as follows:
- disruption of the eating process - the child constantly bites the mother, which makes breastfeeding impossible;
- disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system;
- swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- increased salivation;
- negative changes in body temperature;
- swelling of the tissues surrounding the erupting tooth.
Remember! The child most acutely perceives not speech problems that arise as a result of the disease, but ridicule from peers, which becomes a consequence of serious mental disorders.
Closedness and reluctance to behave openly in the presence of strangers can result in the child developing a sense of inferiority. For this reason, the anomaly requires immediate elimination using an individual approach.
Complications of polyodontia
If polyodontia is not treated, a complication of the disease is the worsening of the curvature of the dentition and, accordingly, the proportions of the face. Shark teeth grow out of place, which is clearly visible when smiling and laughing. Sometimes the pathology is noticeable even with closed lips, and the upper or lower lips may rise. Also, the jaw closes incorrectly, speech is impaired, and malfunctions of the mandibular joint appear.
Polyodontia disrupts the bite - teeth can shift and rotate in a row. Shark teeth cause crowding and hygiene in their area is difficult. This leads to the formation of caries and subsequent complications. The gums become inflamed and gingivitis and periodontitis develop.